Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2024; 16(3): 344-352
Published online Mar 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i3.344
Published online Mar 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i3.344
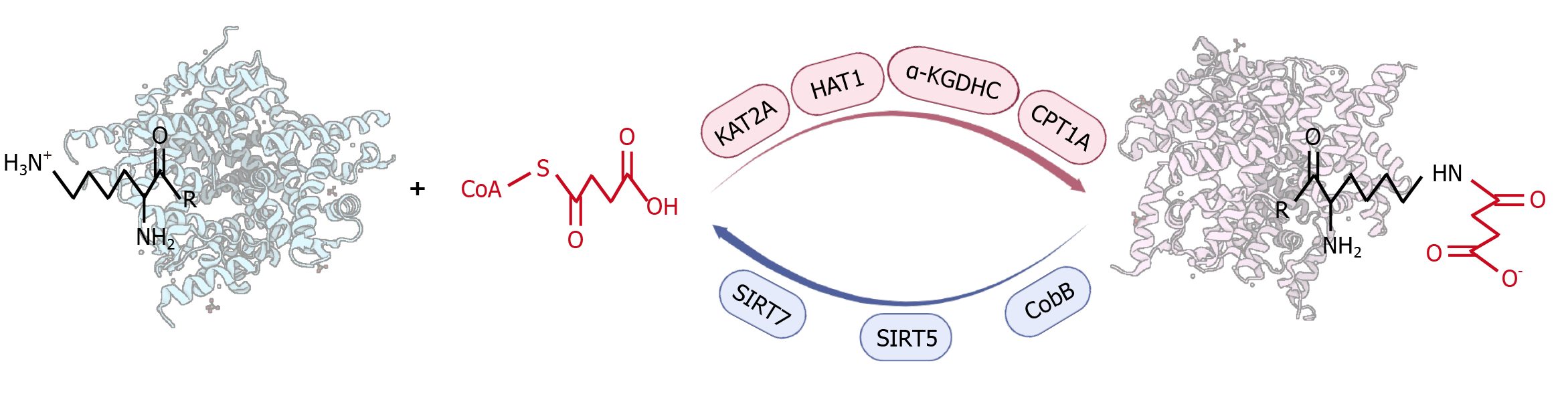
Figure 1 Mechanisms for succinylation.
Succinylation is the process of transferring negatively charged four-carbon succinyl groups to amines of lysine residues through enzymatic and non-enzymatic manners using succinyl-CoA as a direct substrate. The succinylation degree can be promoted by succinyltransferases, such as lysine acetyltransferase 2A, histone acetyltransferase 1, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, and carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A. Meanwhile, desuccinylases, including CobB, sirtuin 5, and sirtuin 7 negatively regulate the extent of protein succinylation. KAT2A: Lysine acetyltransferase 2A; HAT1: Histone acetyltransferase 1; α-KGDHC: α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex; SIRT5: Sirtuin 5; SIRT7: Sirtuin 7; CPT1A: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A.
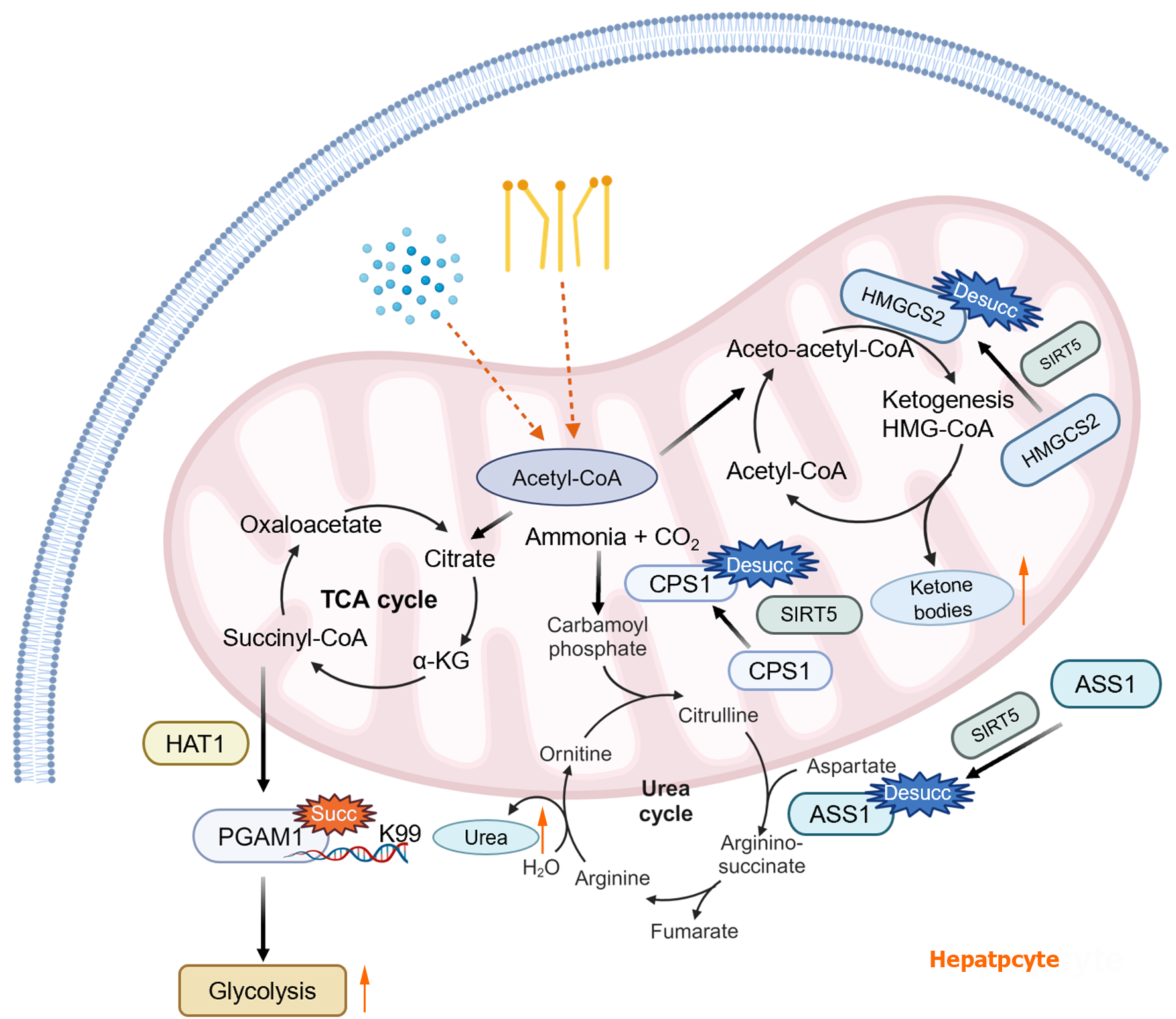
Figure 2 Effect of succinylation on hepatic metabolic pathways.
The influence of succinylation on hepatic glucose metabolism occurs in the following ways: (1) Under the stimulation of succinyl-CoA. Histone acetyltransferase 1 causes the K99 site of phosphoglycerate mutase 1 to be succinylated and promotes its enzyme activity, thus promoting glycolysis; (2) the influence of succinylation on hepatic amino acid metabolism. Sirtuin 5 promotes urea production by regulating the desuccinylation of arginine succinate synthetase 1 and carbamoyl phosphate synthase 1; and (3) the influence of succinylation on hepatic lipid metabolism. Sirtuin 5 induces desuccinylation of mitochondrial 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthetase 2 and promotes ketone body formation. HAT1: Histone acetyltransferase 1; SIRT5: Sirtuin 5; TCA: Tricarboxylic acid; HMGCS2: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthetase 2; PGAM1: Phosphoglycerate mutase 1; ASS1: Arginine succinate synthetase 1.
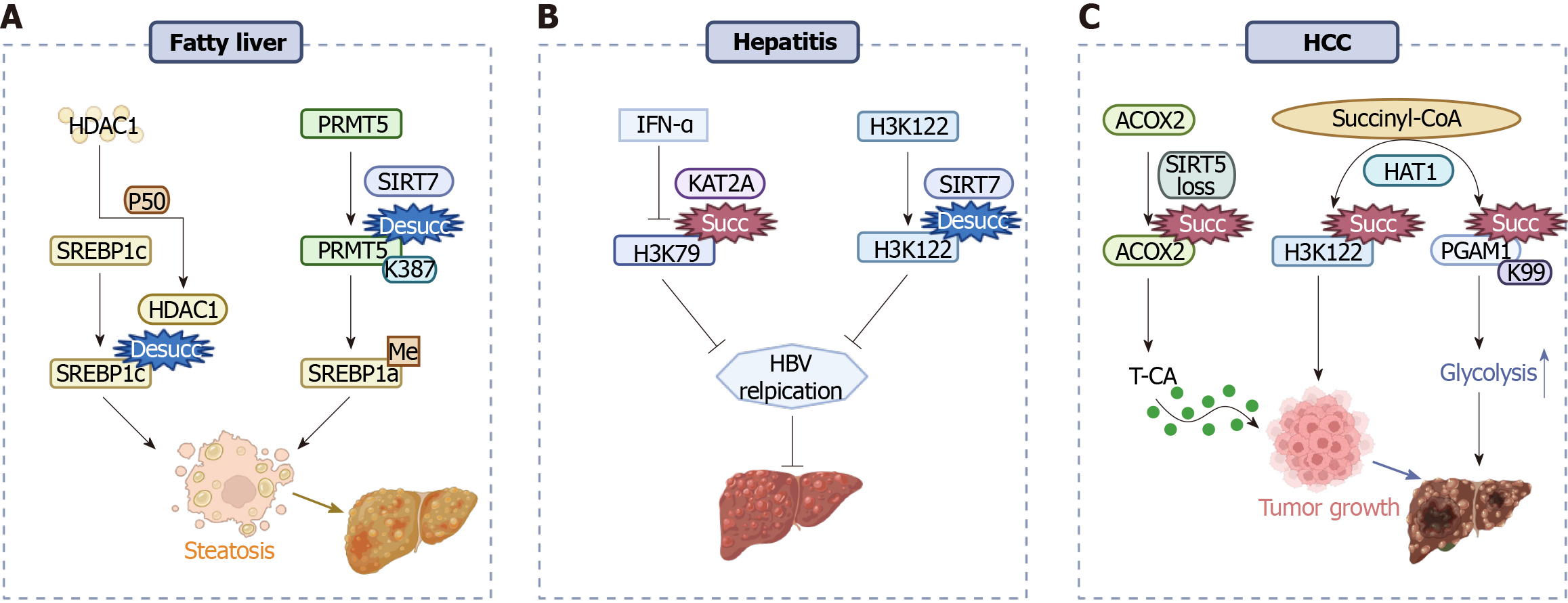
Figure 3 Succinylation affects the progression of fatty liver, hepatitis, and hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: P50 stabilizes histone deacetylase 1 protein to keep desuccinylation of sterol-regulatory element binding protein 1c, thereby promoting fatty liver. Sirtuin 7 (SIRT7)-mediated desuccinylation of SIRT7 mediates the desuccinylation of arginine methyltransferase 5 at K387 promotes fatty liver by inducing arginine methylation of SREBP1a; B: IFN-α inhibits lysine acetyltransferase 2A-mediated succinylation of histone H3K79 and SIRT7 promotes desuccinylation of histone H3K122, which restrains viral replication and hepatitis; C: Sirtuin 5 deficiency activates acyl-CoA oxidase 2 succinylation, leading to elevated bile acid levels and promoting hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Histone acetyltransferase 1 not only promotes hepatocellular carcinogenesis by activating H3K122 succinylation but also promotes the glycolytic pathway by promoting succinylation of phosphoglycerate mutase 1 at K99, thereby promoting HCC. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; PRMT5: SIRT7 mediates the desuccinylation of arginine methyltransferase 5; SREBP: Sterol-regulatory element binding protein; ACOX2: Acyl-CoA oxidase 2; HAT1: Histone acetyltransferase 1; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; PGAM1: Phosphoglycerate mutase 1.
- Citation: Liu S, Li R, Sun YW, Lin H, Li HF. Protein succinylation, hepatic metabolism, and liver diseases. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(3): 344-352
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i3/344.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i3.344