Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Nov 27, 2021; 13(11): 1568-1583
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1568
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1568
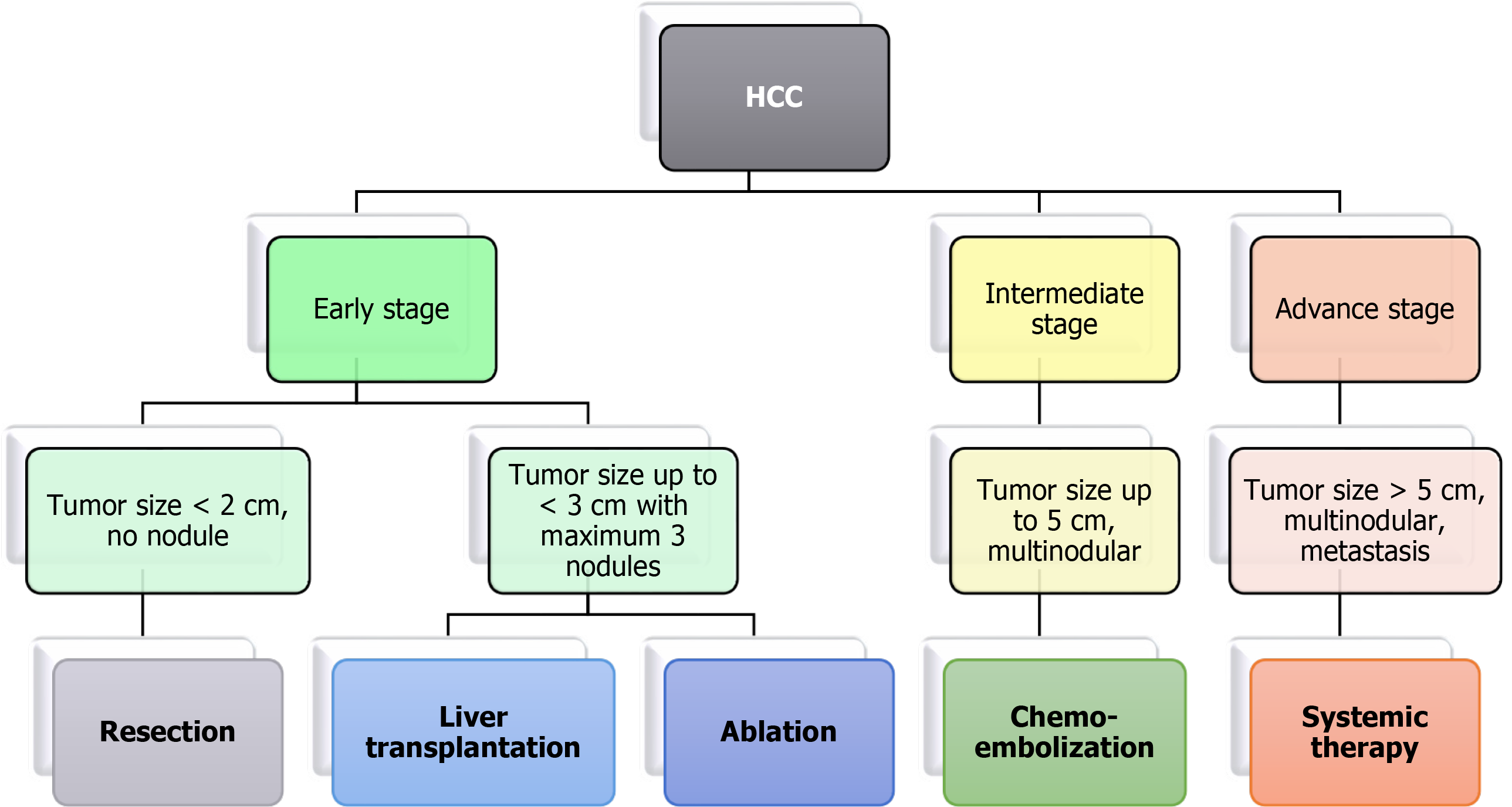
Figure 1 Treatment modalities for hepatocellular carcinoma based on tumor-node-metastasis staging.
HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
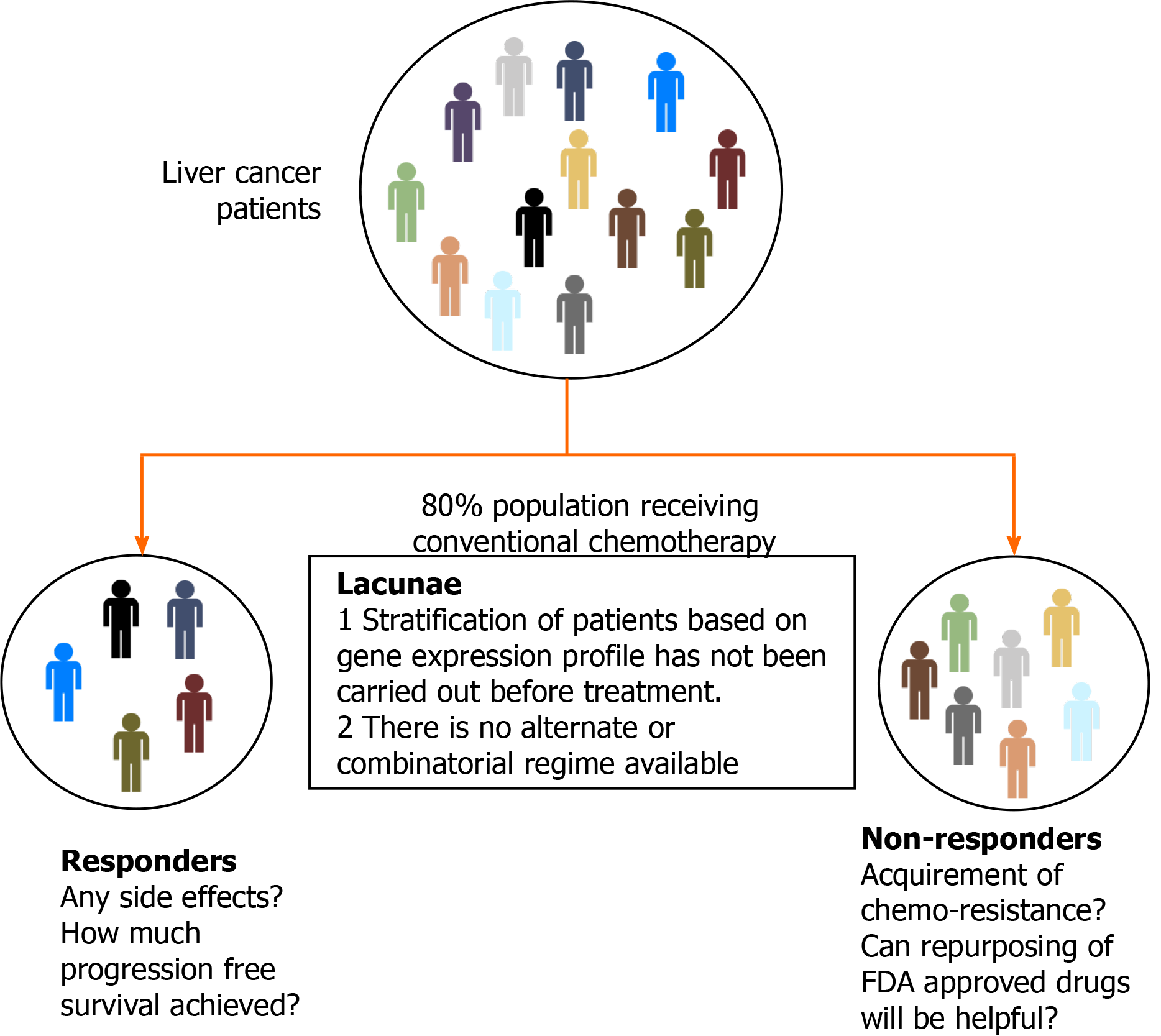
Figure 2 Challenges in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
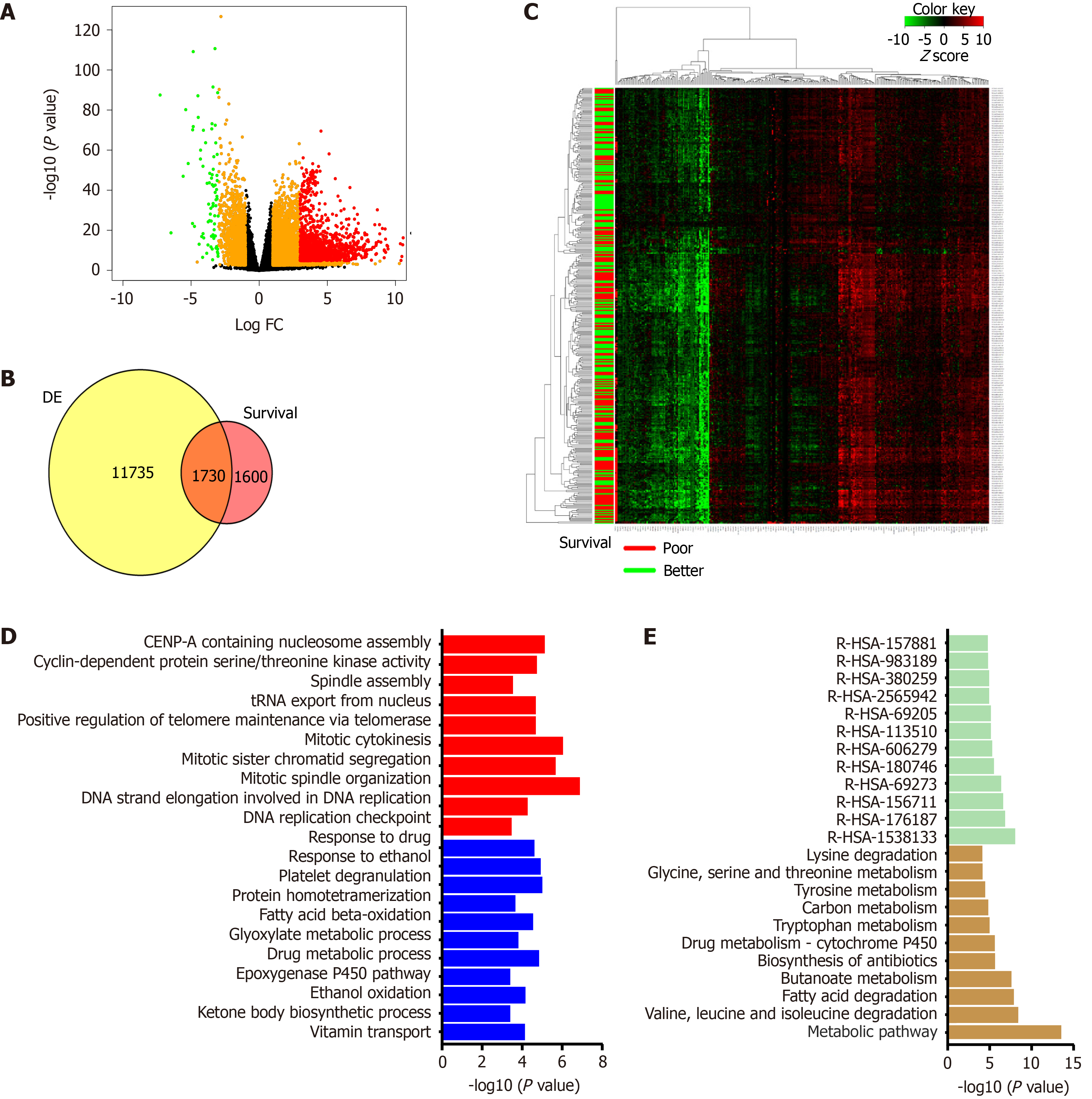
Figure 3 The cancer genome atlas liver hepatocellular carcinoma data analysis.
A: Volcano plot representing differential gene expression between 373 tumor samples and 50 normal samples. Genes colored with red or green are most significantly altered; B: Venn diagram showing overlap between differentially expressed gene list and genes affecting survival of patients upon alteration (survival); C: Normalized expression of top 300 genes associated with overall survival represented using heatmap. Patients with overall survival below the median are marked with a red bar while those above the median are marked with a green bar; D: Altered biological process from overlap gene. Upregulated processes highlighted with red and downregulated processes are depicted as blue; E: Pathways analysis for overlap genes. Deregulated KEGG pathways shown by yellow bars and reactome pathways displayed using green bars. DE: Differentially expressed gene list.
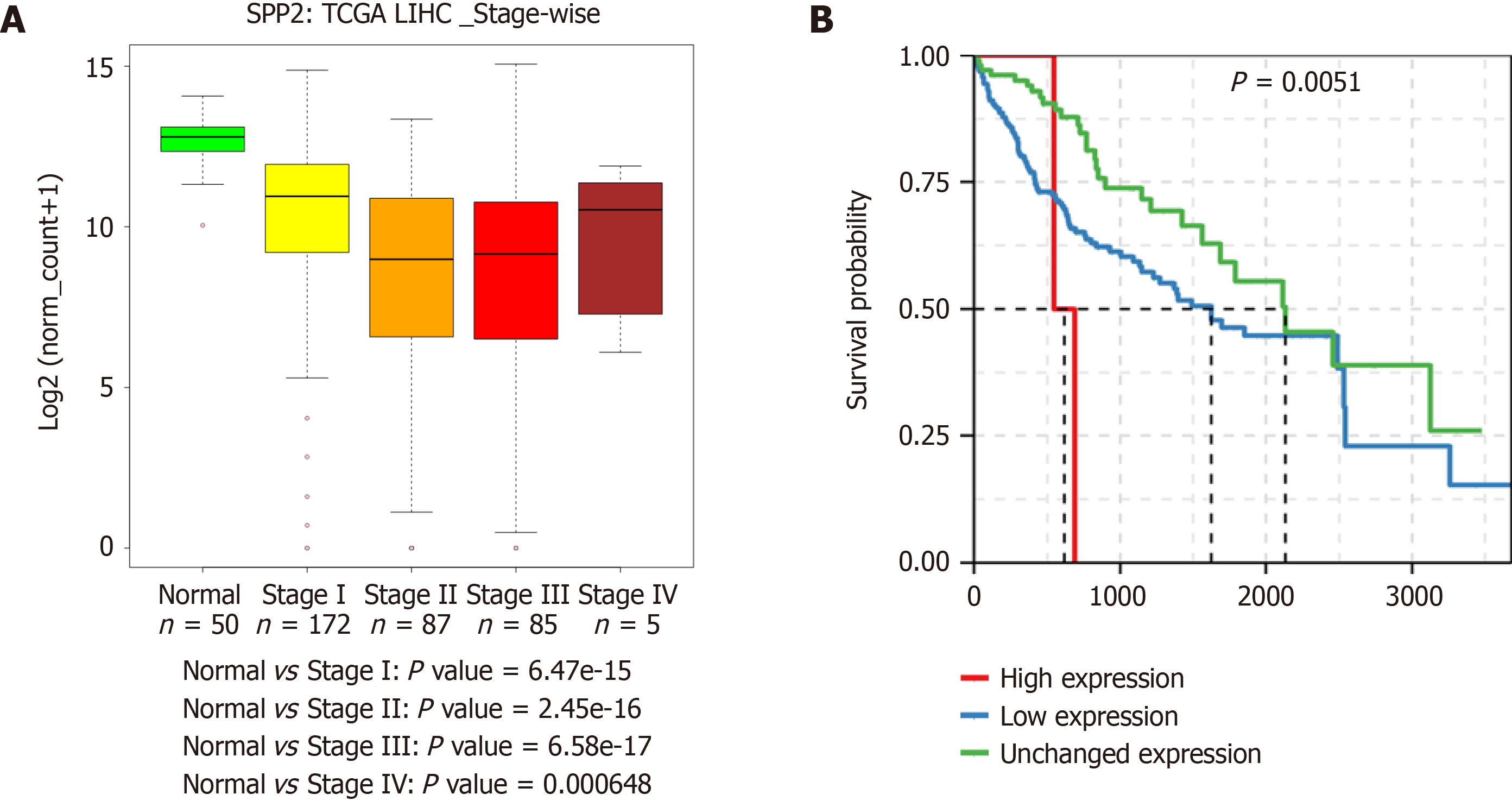
Figure 4 Expression of SPP2 in the cancer genome atlas liver cancer cohort.
A: Stage-wise expression of SPP2; B: Patient survival associated with SPP2 expression. TCGA: The cancer genome atlas; LIHC: Liver hepatocellular carcinoma.
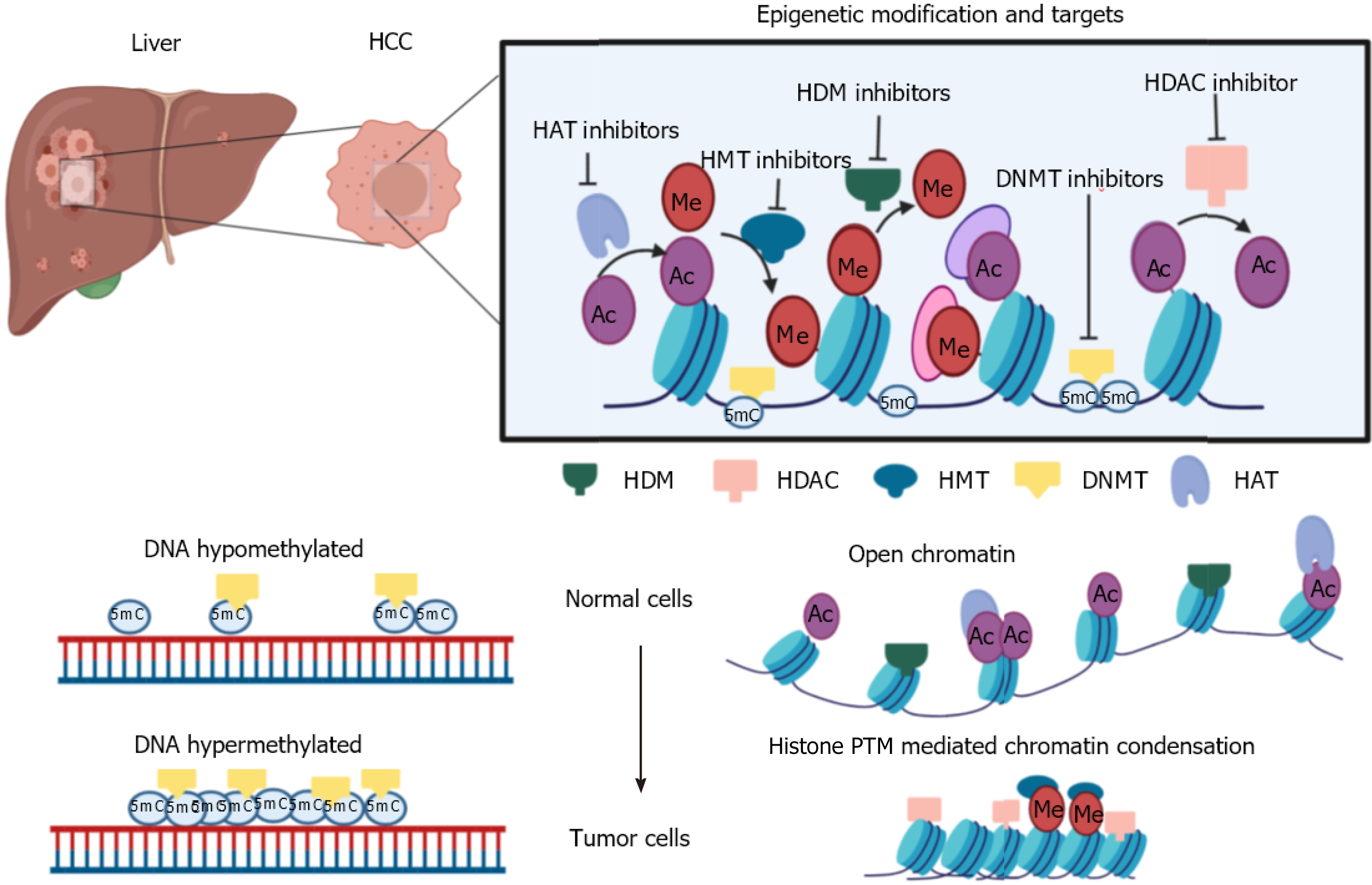
Figure 5 Schematic illustration of epigenetic modifications observed in hepatocellular carcinoma and chromatin modifiers targeted by epi-drugs.
The figure represents general epigenetic alterations observed in hepatocellular carcinoma and different epigenetic modifiers that can be targeted via small molecule inhibitors. Moreover, DNA and chromatin mediated alterations observed in tumors are highlighted. Changes in DNA methylation and histone post-translational modifications levels inside normal cells lead to tumor formation. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; HDM: Histone demethylase; HDAC: Histone deacetylase; HMT: Histone methyltransferase; DNMT: DNA methyltransferase; HAT: Histone acetyltransferase.
- Citation: Natu A, Singh A, Gupta S. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Understanding molecular mechanisms for defining potential clinical modalities. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(11): 1568-1583
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i11/1568.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1568