Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Oct 27, 2021; 13(10): 1208-1214
Published online Oct 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i10.1208
Published online Oct 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i10.1208
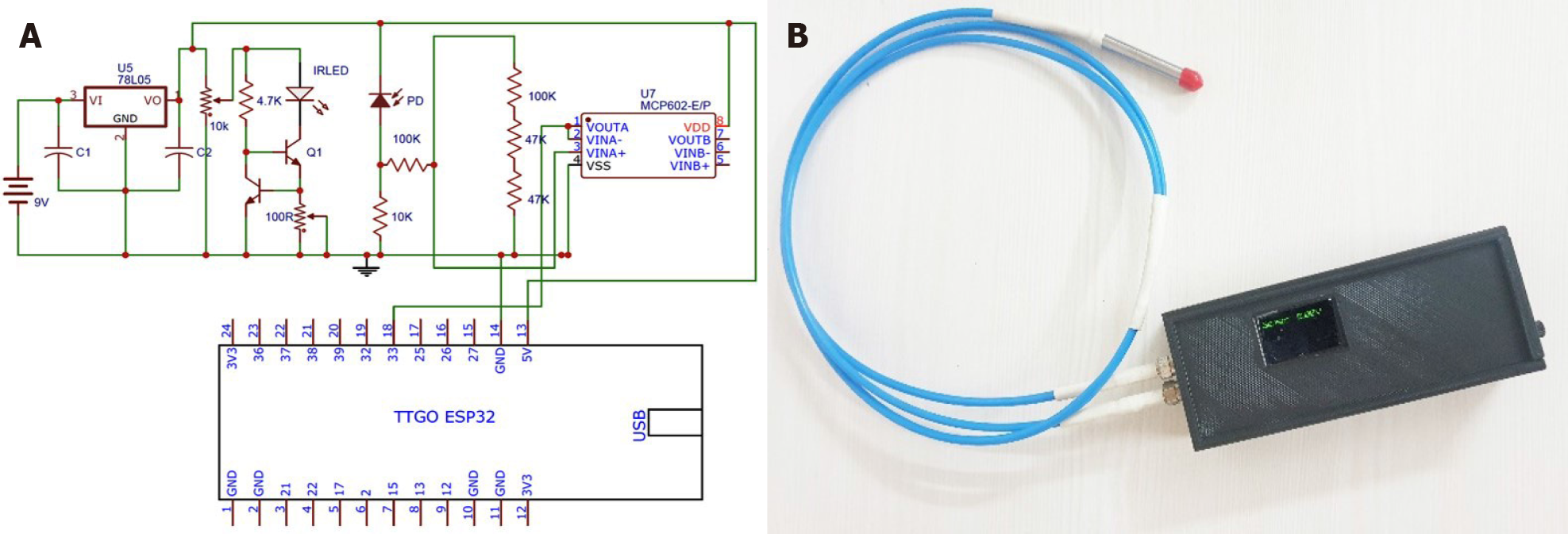
Figure 1 Principle and set-up of the hand-held real time device to measure macrovesicular steatosis.
A: Optoelectronics circuit, B: Handheld point of care device.
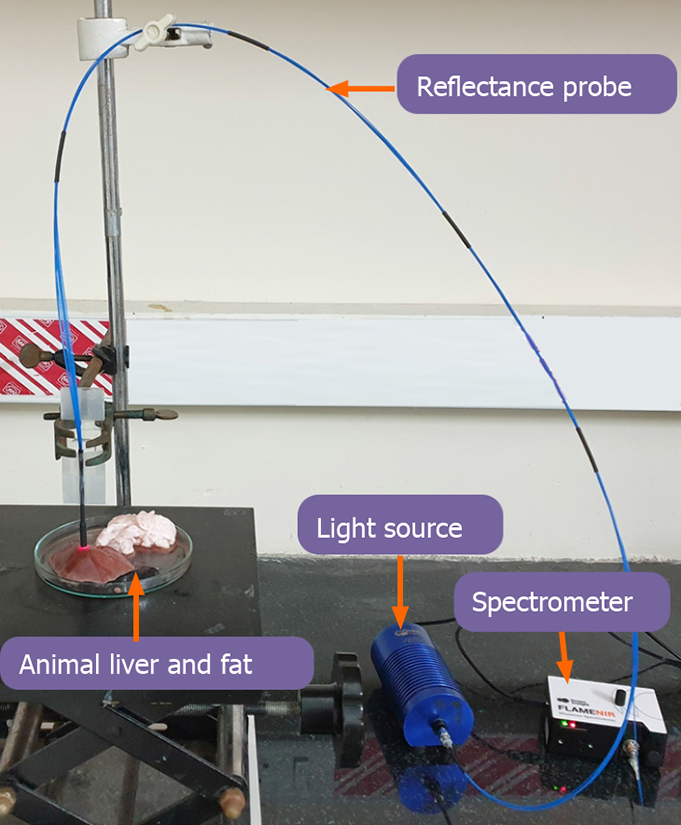
Figure 2
Proof-of-concept study using the prototype model of the device.
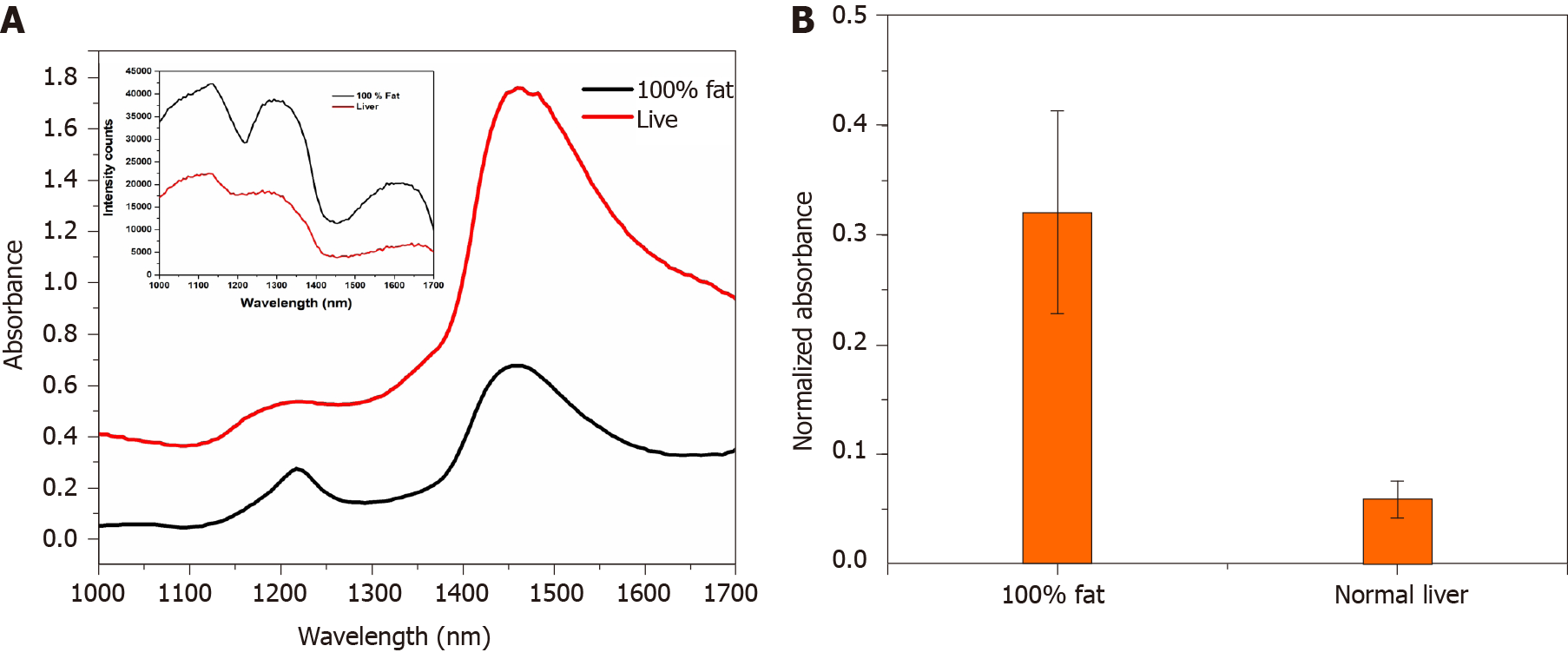
Figure 3 Comparison between large animal liver retrieved from abattoir and 100% fat.
A: Absorbance spectrum of abattoir retrieved large animal liver and 100% fat (inset: intensity spectrums of liver and 100% fat); B: Calculated absorbance response of abattoir retrieved large animal liver and 100% fat.
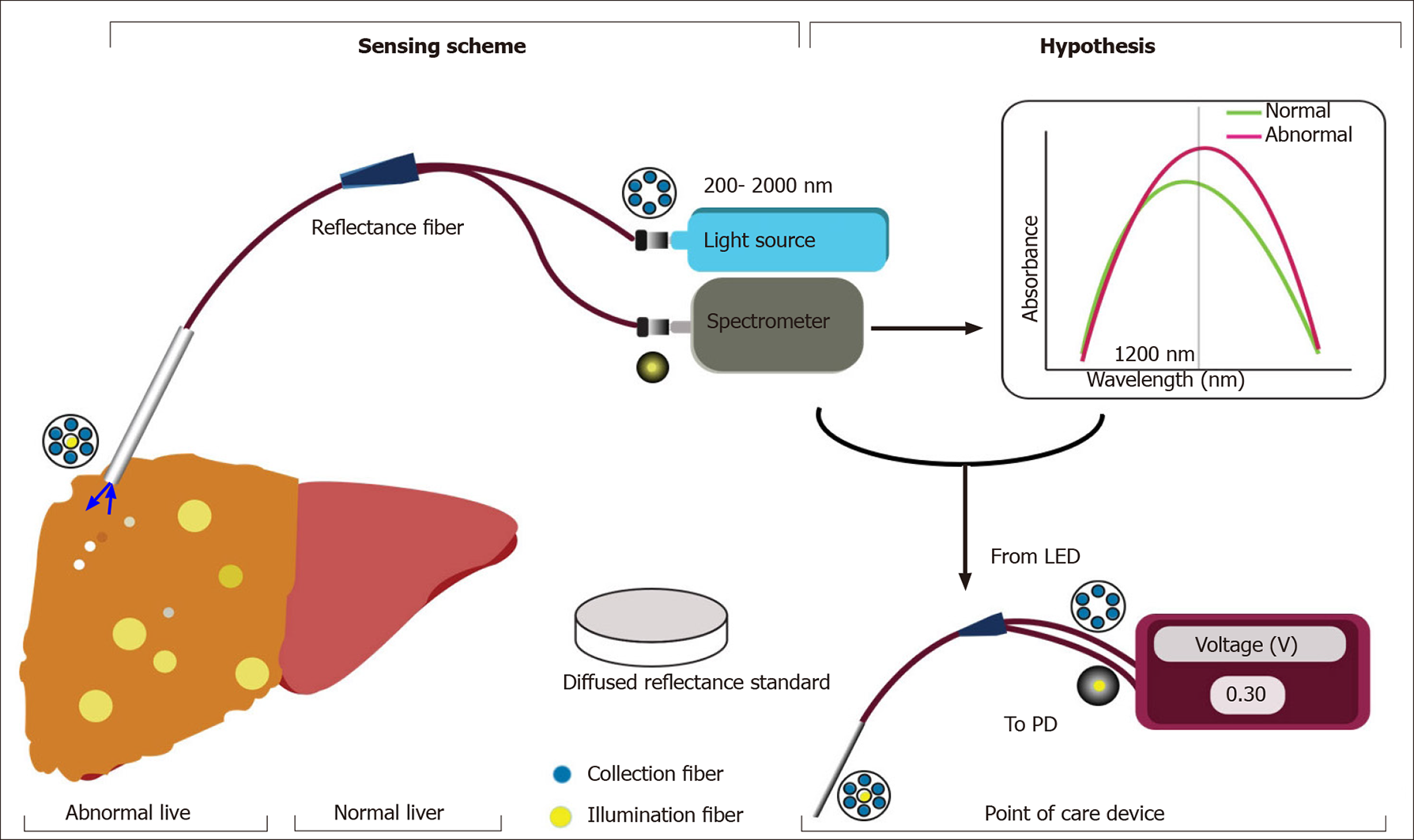
Figure 4 Schematic representation of the proposed study design, experimental setup, and hypothesis towards the development of handheld device.
It consists of reflectance probe bundle with home-made plastic block to house light emitting diode, photodetector, optoelectronic circuitry, and display. PD: Photodetector.
- Citation: Rajamani AS, Rammohan A, Sai VR, Rela M. Non-invasive real-time assessment of hepatic macrovesicular steatosis in liver donors: Hypothesis, design and proof-of-concept study. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(10): 1208-1214
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i10/1208.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i10.1208