Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2021; 13(5): 342-365
Published online May 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i5.342
Published online May 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i5.342
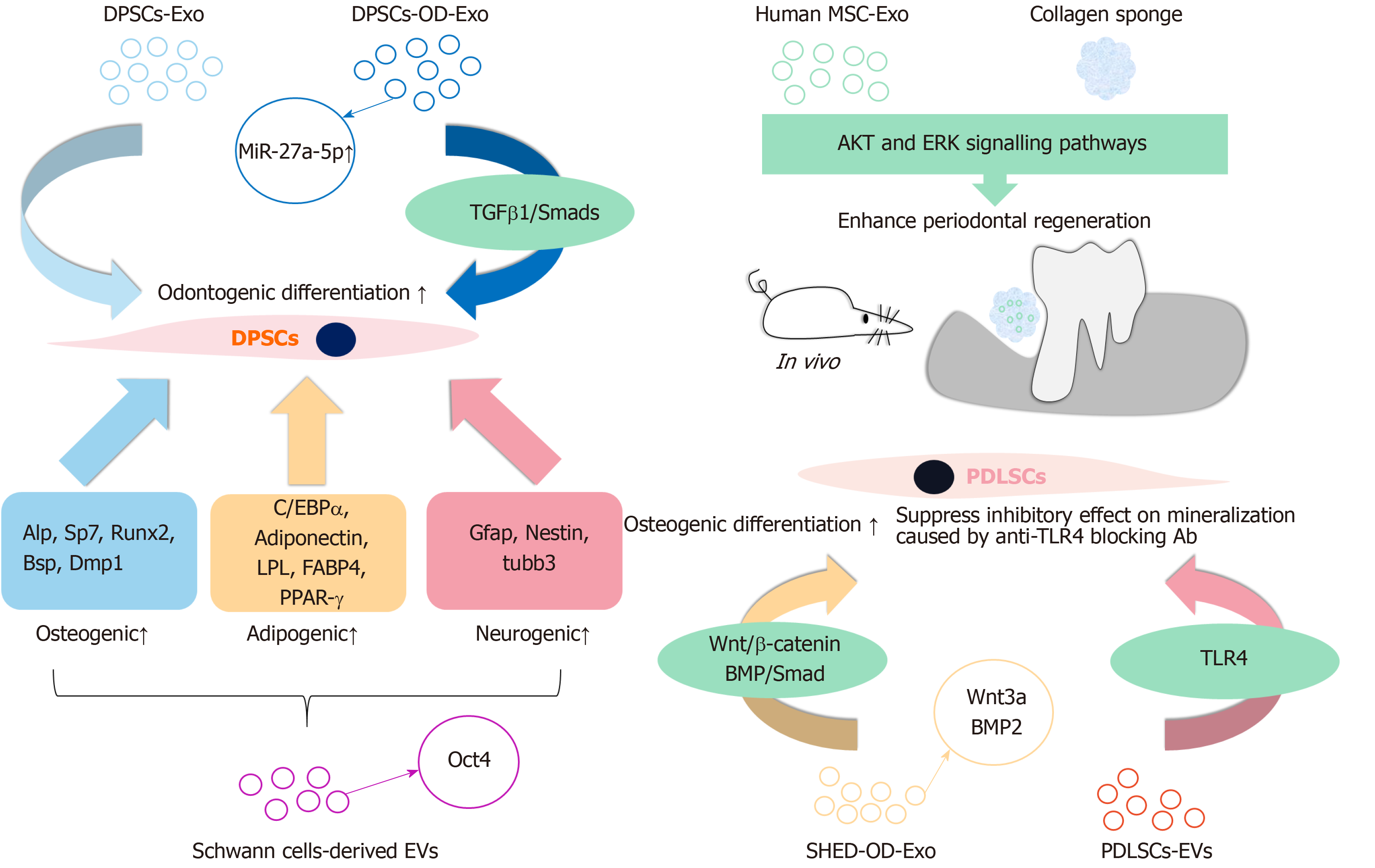
Figure 2 Reported extracellular vesicles that mainly contributed to the odontogenic/osteogenic differentiation process of dental mesenchymal stem cells.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) from a variety of cell sources can influence the osteogenic, adipogenic and neurogenic differentiation process of dental mesenchymal stem cells. Exo: Exosomes; DFSCs: Dental follicle stem cells; LPL: Lipoprotein lipase; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cells; PDLSCs: Periodontal ligament stem cells; PPAR-γ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ; SHED: Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth; TGFβ1: Transforming growth factor β1.
- Citation: Yin JY, Luo XH, Feng WQ, Miao SH, Ning TT, Lei Q, Jiang T, Ma DD. Multidifferentiation potential of dental-derived stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(5): 342-365
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i5/342.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i5.342