Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2014; 6(4): 380-390
Published online Sep 26, 2014. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i4.380
Published online Sep 26, 2014. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i4.380
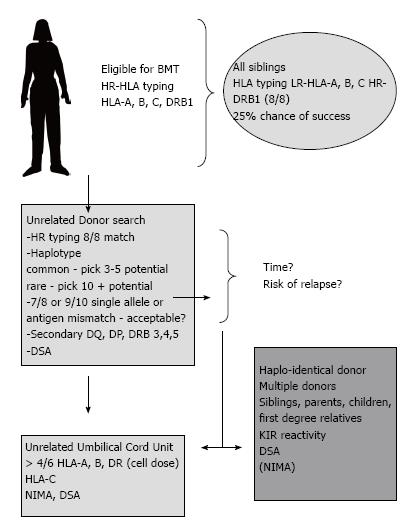
Figure 1 Example of a potential donor search algorithm that aims to expedite finding a suitable stem cell donor.
A blend of high and low resolution approaches are employed. In certain situations the likelihood of finding an un-related donor match is low due to rare alleles and haplotypes. Consideration of a haplo-identical BMT may be considered at an earlier stage. Abbreviations: HR: High resolution (allele level); LR: Low resolution (antigen level); NIMA: Non-inherited maternal antigen; KIR: Killer cell Ig-like receptors; DSA: Donor-specific antibodies; BMT: Bone marrow transplant.
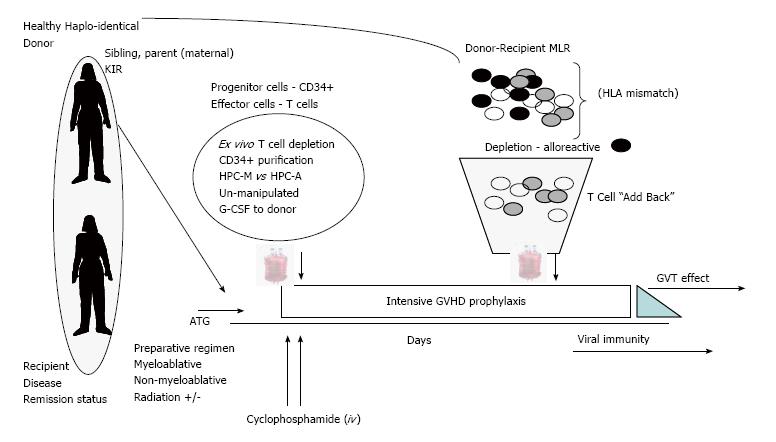
Figure 2 Current approaches to Haplo-identical bone marrow transplant.
Recent novel strategies include issues of donor selection, ex vivo complete or partial T cell depletion of HPC-M or HPC-A grafts and the use of anti-thymocyte globulin. Additional strategies include in vivo administration of “high dose” cyclophosphamide and intensive multi-agent GVHD prophylaxis. Finally, in an effort to overcome severe prolonged immune suppression the addition of donor T lymphocytes that have been purged of alloreactive T cells may be of benefit. Abbreviations: DSA: Donor-specific antibodies; MLR: Mixed lymphocyte reaction; HLA: Human leukocyte antigen; GVT: Graft-versus tumor; KIR: Killer cell Ig-like receptors; GVHD: Graft-vs-host disease; ATG: Anti-thymocyte globulin.
- Citation: Ricci MJ, Medin JA, Foley RS. Advances in haplo-identical stem cell transplantation in adults with high-risk hematological malignancies. World J Stem Cells 2014; 6(4): 380-390
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v6/i4/380.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v6.i4.380