Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Stem Cells. Jan 26, 2012; 4(1): 1-8
Published online Jan 26, 2012. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v4.i1.1
Published online Jan 26, 2012. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v4.i1.1
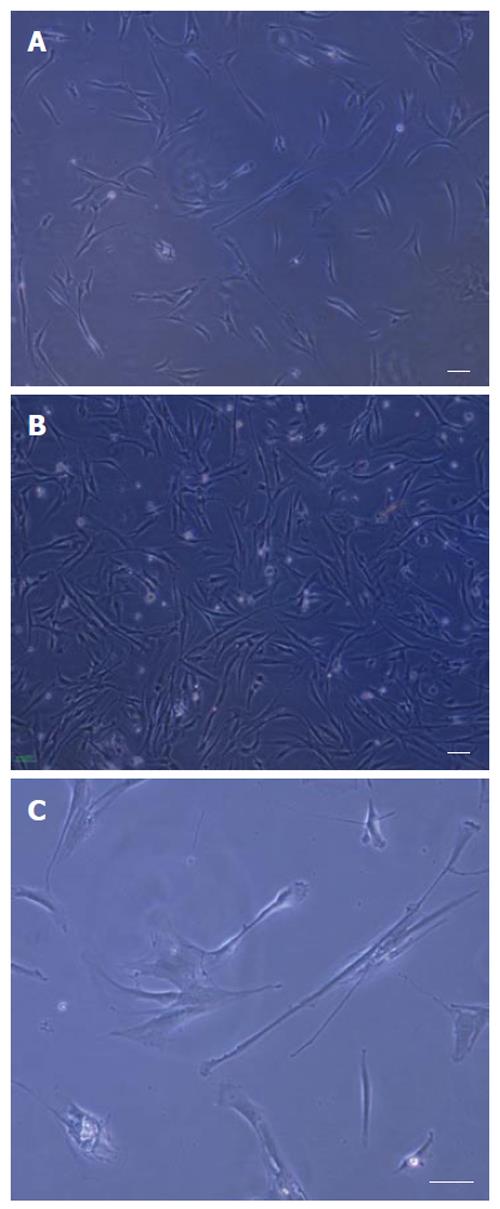
Figure 1 Isolation and culture of rat bone marrow derived MSCs.
A: An adherent monolayer was achieved in the following 6-7 d; B: A relatively homogenous culture was obtained in the following 9-10 d; C: As the culture proceeded, the cells had both small spindle and wide-shaped morphology. Scale bar for figures A-C: 100 μm.
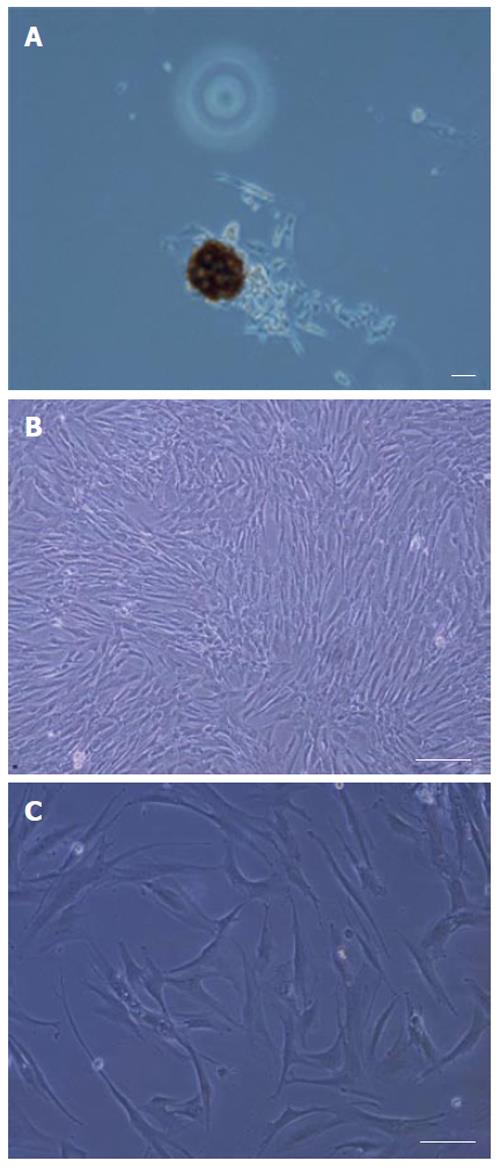
Figure 2 Isolation and culture of human bone marrow derived MSCs.
A: Appearance of a single cell-derived colony composed of a few fibroblast-like cells; B: Appearance of a relatively homogeneous culture; C: Appearance of the flat type and the polygonal morphology in human derived MSC culture. Scale bar for figures A-C: 100 μm.
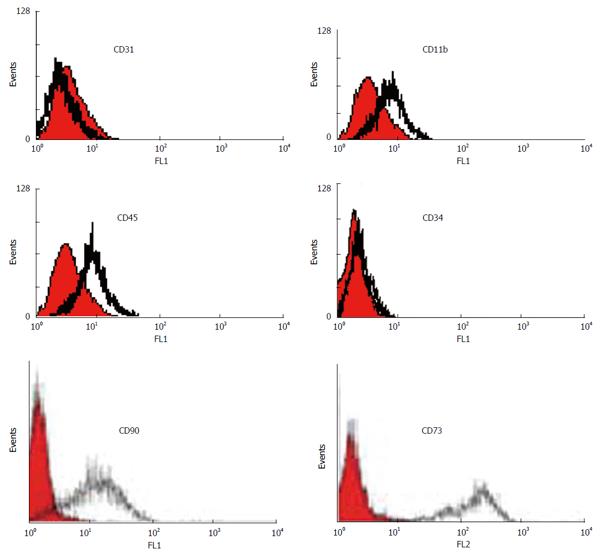
Figure 3 Immunophenotyping of human bone marrow derived MSCs using flow cytometry.
The shaded area shows the profile of the negative control. Mesenchymal stem cells were negative for CD 11b, CD45, CD34 and CD31. The cells were positive for CD90 and CD73.
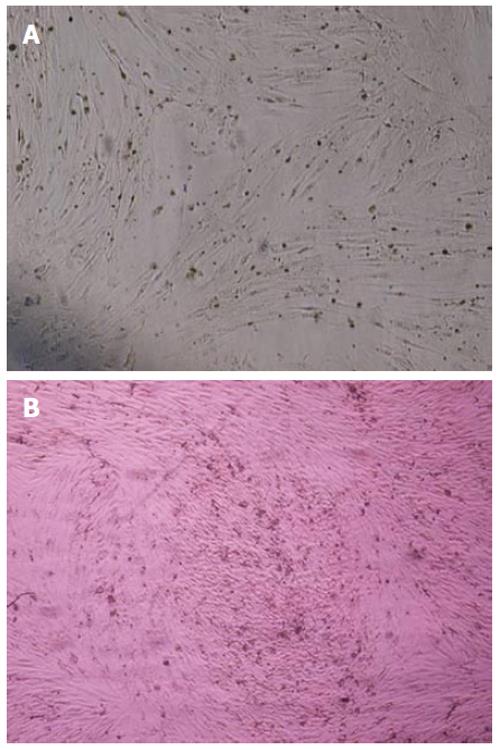
Figure 4 Differentiation of human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells into adipocytes and osteoblasts.
A: The adipose droplet in differentiated cells after staining with oil red; B: Osteogenic differentiation was positive for alizarin red staining. Original magnification: X 100.
- Citation: Ayatollahi M, Salmani MK, Geramizadeh B, Tabei SZ, Soleimani M, Sanati MH. Conditions to improve expansion of human mesenchymal stem cells based on rat samples. World J Stem Cells 2012; 4(1): 1-8
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v4/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v4.i1.1