Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2025; 17(7): 107688
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.107688
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.107688
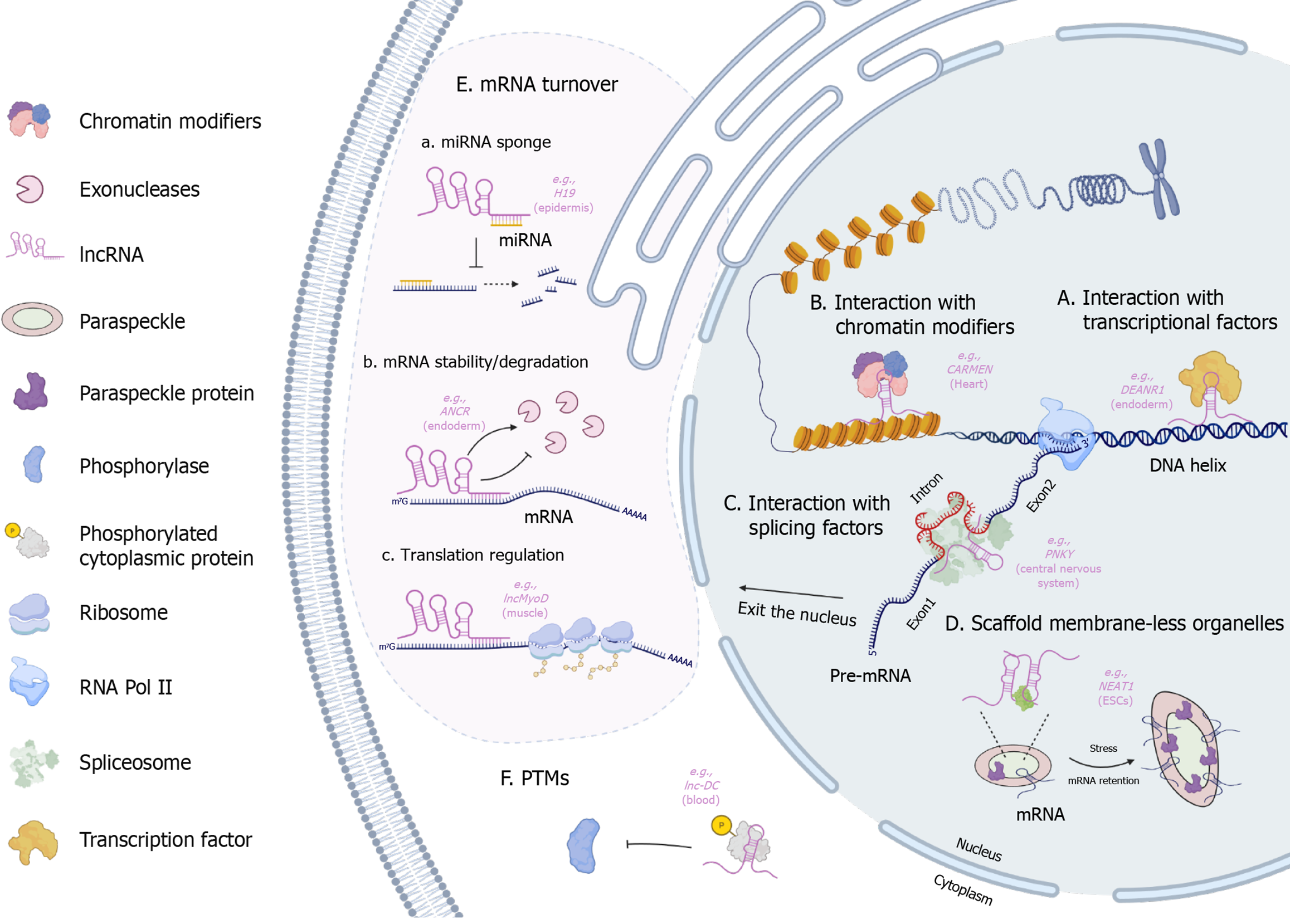
Figure 1 Functions of long non-coding RNAs in different cellular compartments.
Long non-coding RNAs participate in diverse cellular processes and play specific functions in different cellular compartments. Long non-coding RNAs (LncRNAs) A: interact with transcription factors to affect gene activation and transcription. For example, during endoderm differentiation, definitive endoderm-associated lncRNA1 promotes forkhead box transcription factor A2 expression and guides polycomb repressive complexes 2 to specific chromatin sites through cis-regulation and mediates transcriptional silencing by catalyzing H3K27me3; B: Collaborate with chromatin modification factors to alter chromatin status; C: Participate in the regulation of alternative splicing by interacting with splicing factors. For instance, in central nervous system differentiation, Pnky cooperates with polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 to control alternative splicing events; D: Serve as structural scaffolds that recruit proteins to assemble membrane-less organelles. A notable example is nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1, which facilitates the formation of paraspeckles by recruiting paraspeckle-associated proteins, resulting in the assembly of shell-like nuclear bodies; E: Are involved in mRNA turnover: They may function as molecular sponges, modulating microRNA (miRNA) stability to influence the repression of miRNA target mRNAs (a); they can also directly affect mRNA stability and degradation. For example, H19 acts as a competitive endogenous RNA by binding miR-130b-3p to regulate keratinocyte differentiation and interacts with polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 to stabilize sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c mRNA (b); lncRNAs regulate mRNA translation (e.g., LncMyoD participates in the translation control of myogenesis via the MyoD-LncMyoD-insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein axis) (c); F: LncRNAs can function as scaffolds for the regulation of post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation. For example, during blood differentiation, lncRNA in dendritic cells binds cytoplasmic signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, preventing its interaction with the tyrosine phosphatase Src homology region 2 domain containing phosphatase-1 and thereby inhibiting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 dephosphorylation. Created in BioRender. Available from: https://BioRender.com/5f0vac6. DEANR1: Definitive endoderm-associated lncRNA1; CARMEN: (CAR)diac (M)esoderm (E)nhancer-associated (N)oncoding RNA; NEAT1: Nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1; ESCs: Embryonic stem cells; miRNA: MicroRNA; ANCR: Anti-differentiation noncoding RNA; PTMs: Post-translational modifications; Lnc-DC: Long non-coding RNA in dendritic cell; lncRNA: Long non-coding RNA.
- Citation: Li YH, Yao YN, Zhou SA, Wang Y. Regulation and intervention of stem cell differentiation by long non-coding RNAs: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(7): 107688
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i7/107688.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.107688