Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2025; 17(7): 107212
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.107212
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.107212
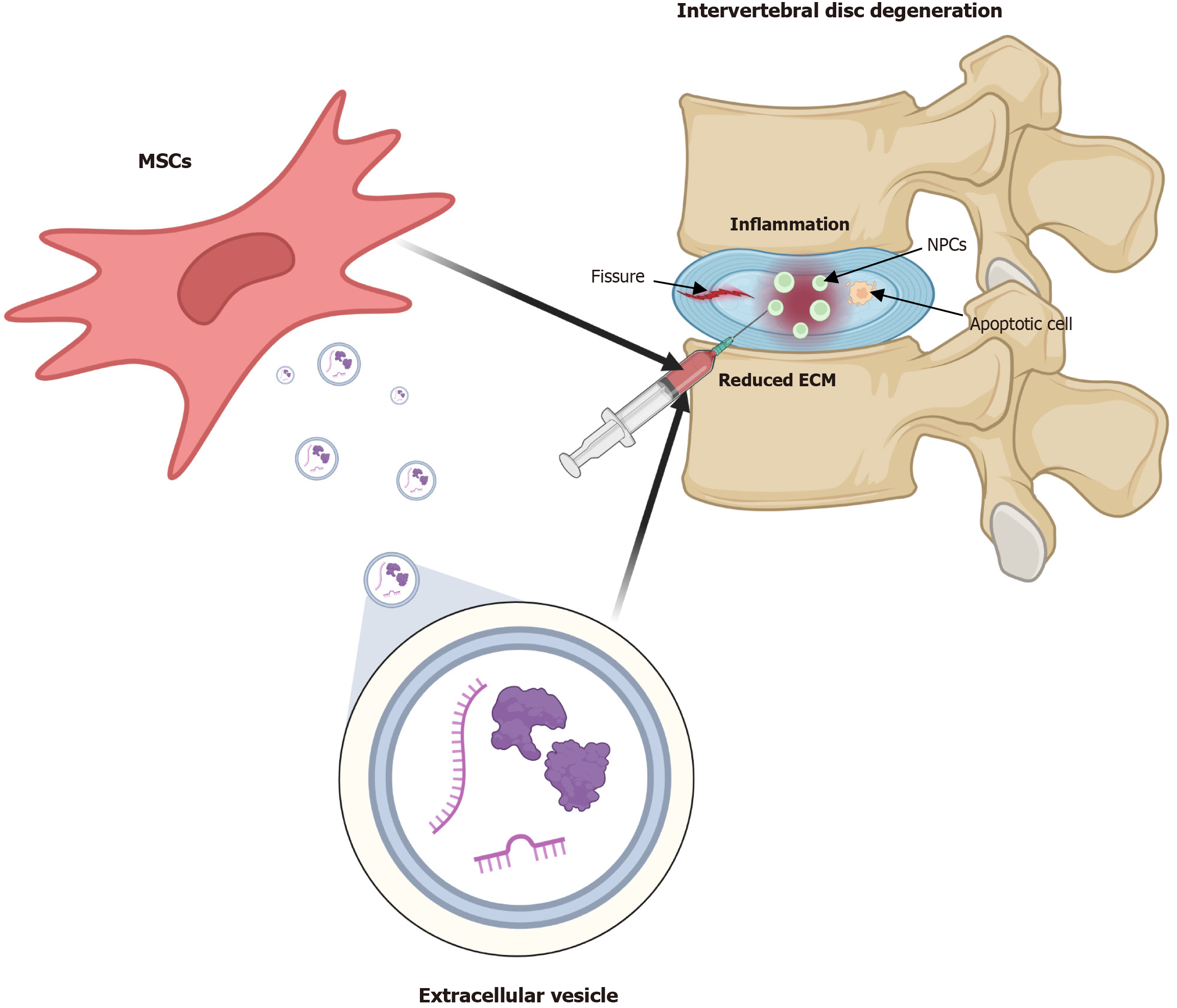
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the effects of mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular vesicles on disc degeneration.
Mesenchymal stem cells are initially isolated and cultured from tissue samples, and during culture, extracellular vesicles are generated in the medium, collected, isolated and purified. Resuspended extracellular vesicles are delivered to degenerating discs via intradiscal injection. MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell; NPC: Nucleus pulposus cell; ECM: Extracellular matrix.
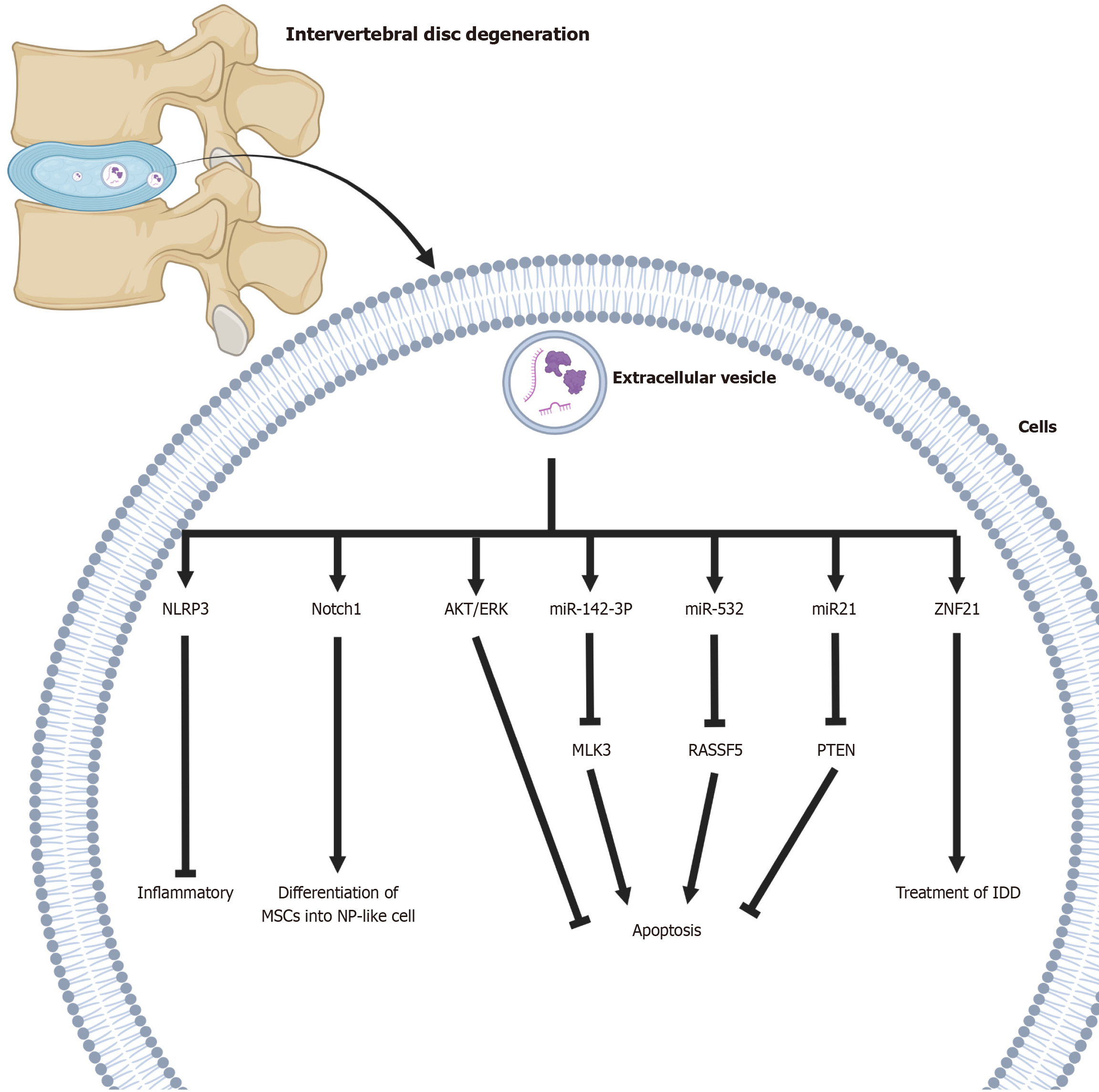
Figure 2 Mechanism of extracellular vesicle to treat intervertebral disc degeneration.
Extracellular vesicle inhibits apoptosis of nucleus pulposus and induces differentiation into nucleus pulposus cells for the treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration through microRNA and specific mechanisms. NLRP3: Nod-like receptor protein 3; AKT: Protein kinase B; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; MLK3: Mixed-lineage kinase 3; RASSF5: Ras association domain family member 5; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog; NP: Nucleus pulposus; IDD: Intervertebral disc degeneration.
- Citation: Lim YJ, Seo MS, Park S, Lee GW. Therapeutic strategies for intervertebral disc degeneration: Extracellular vesicles and microRNAs derived from mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(7): 107212
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i7/107212.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.107212