Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2025; 17(4): 102421
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.102421
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.102421
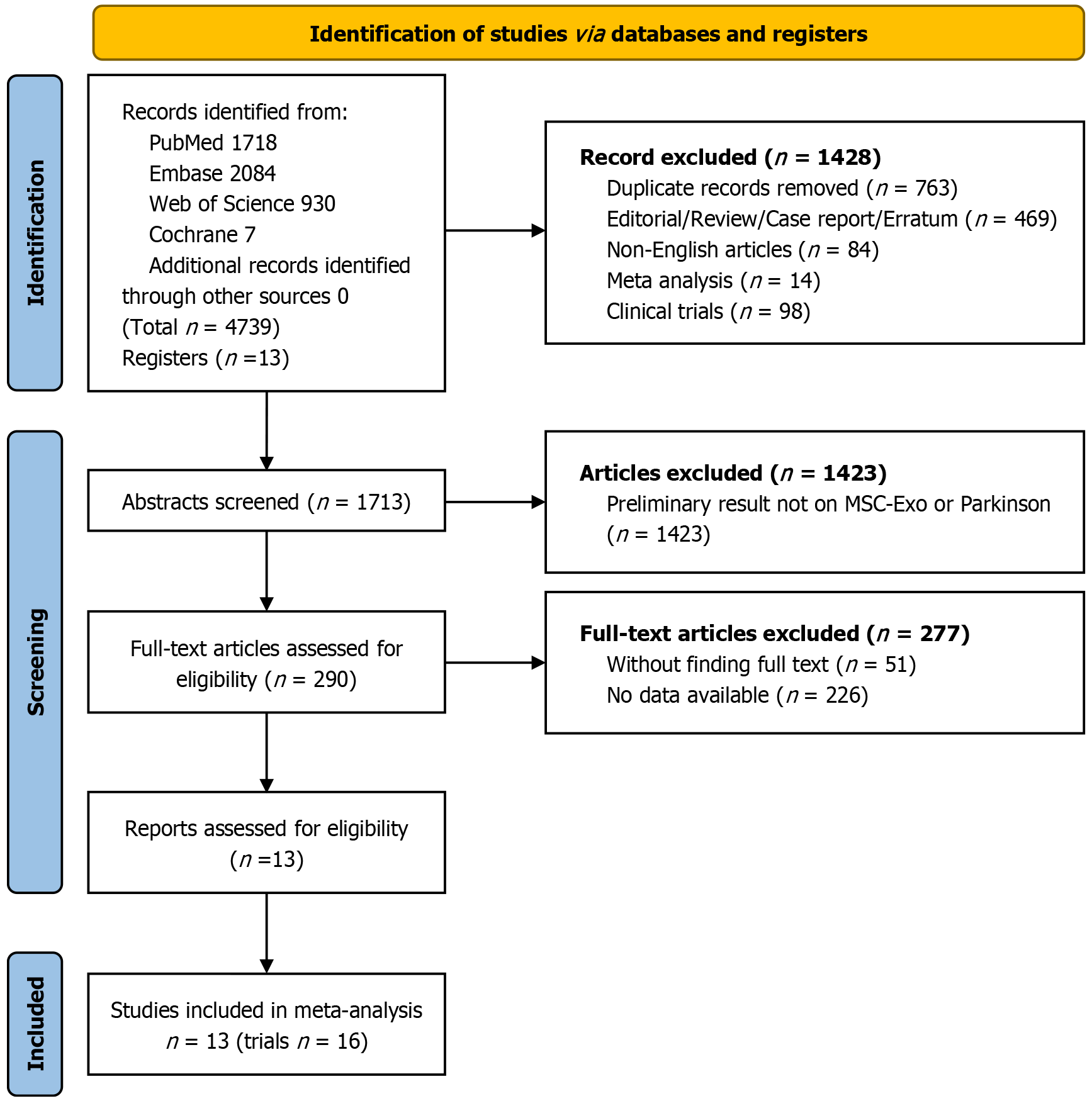
Figure 1 Flow diagram of the literature search and selection process for meta-analysis.
MSC-Exo: Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome.
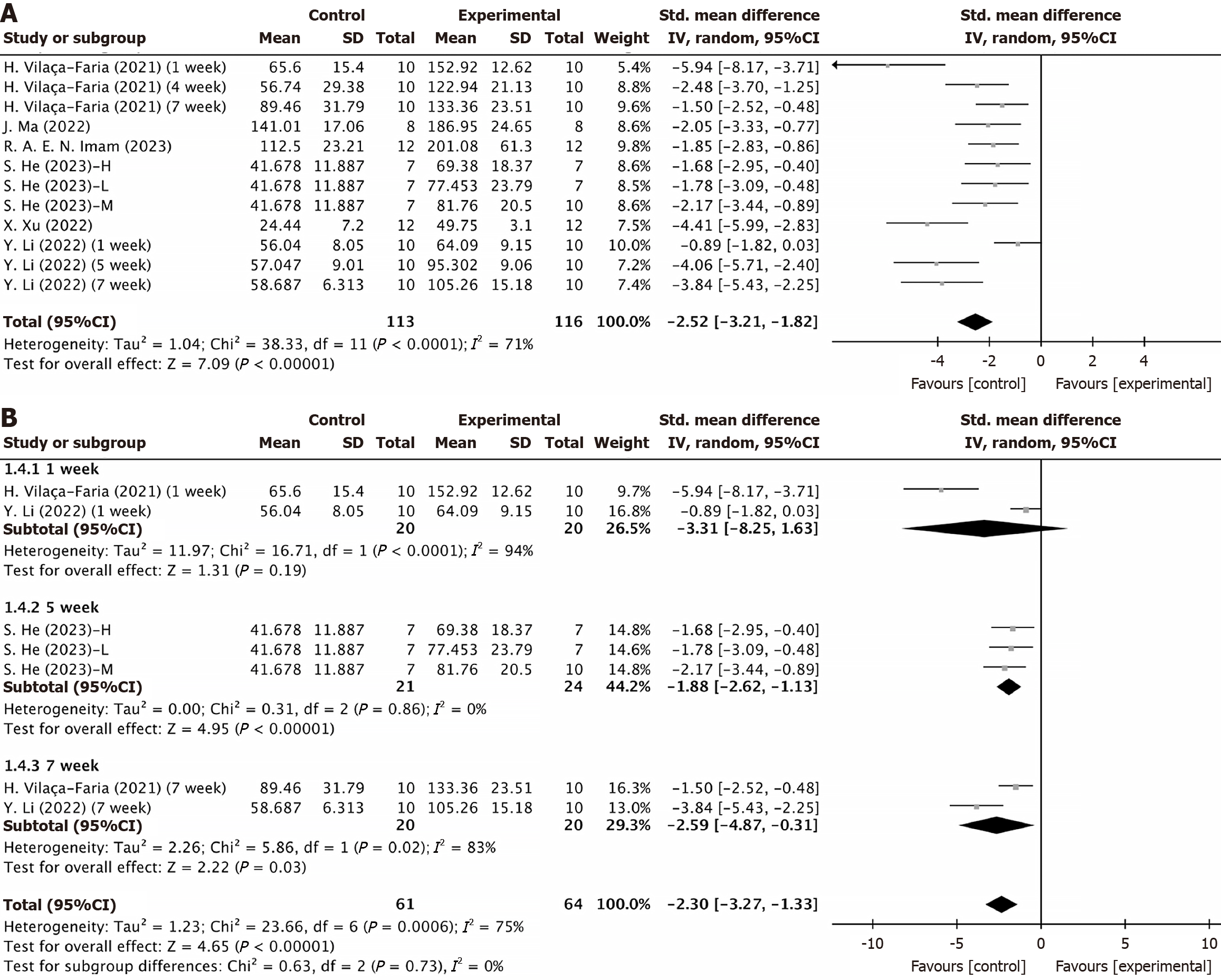
Figure 2 Forest plot.
A: Rotarod test; B: Subgroup analyses by mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicle intervention period. CI: Confidence interval; SD: Standard deviation.
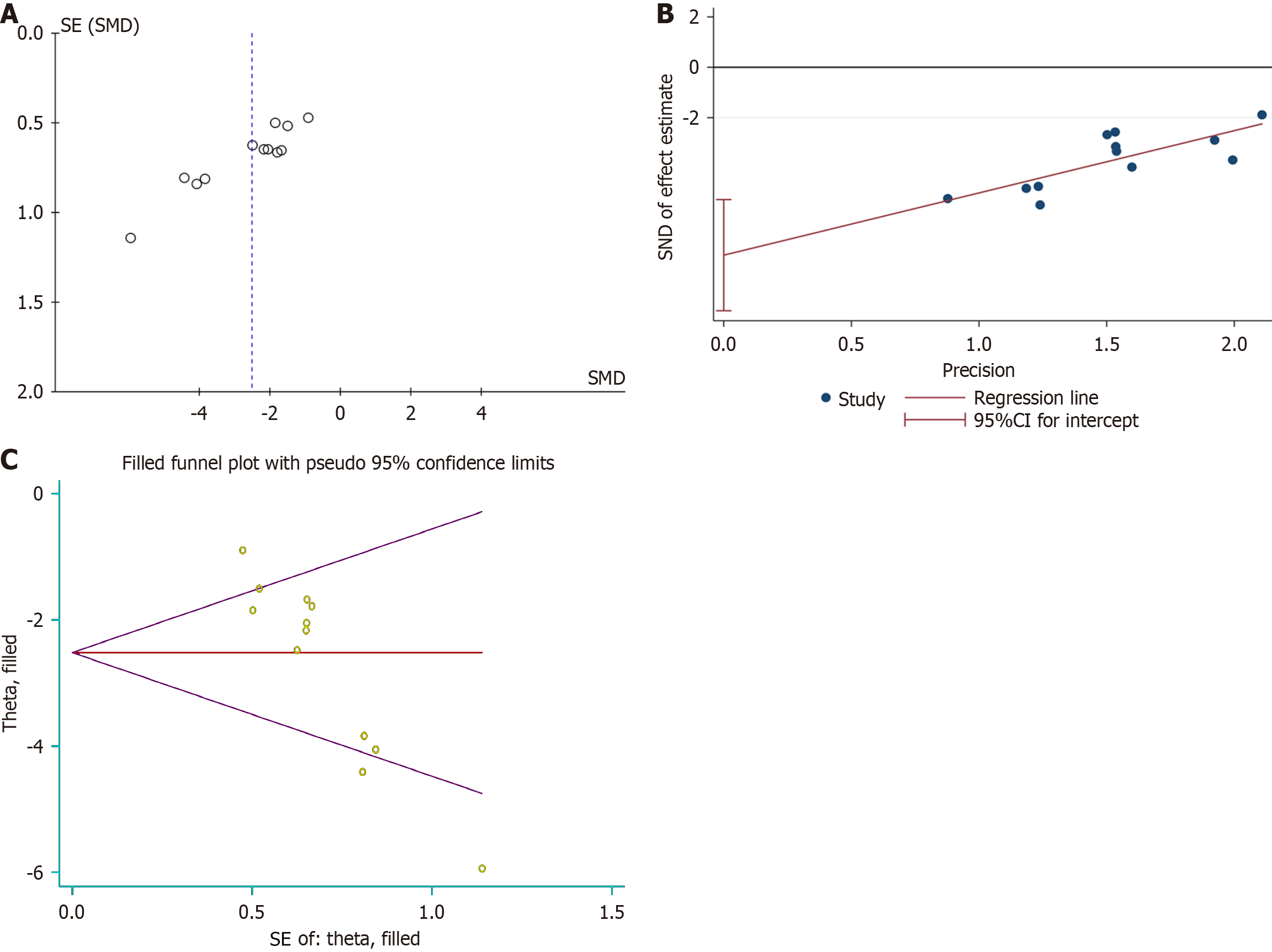
Figure 3 Rotarod test plots.
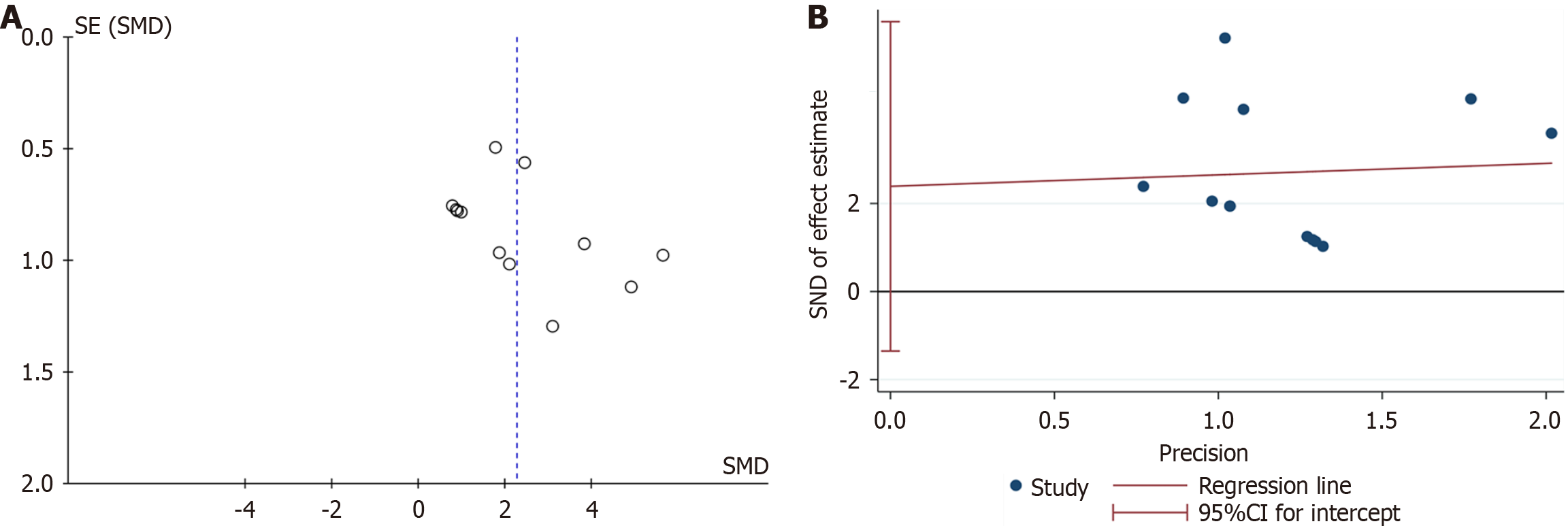
A: Funnel plot with pseudo-95% confidence limits; B: Egger’s publication bias plot; C: Filled funnel plot with pseudo-95% confidence limits. CI: Confidence interval; SMD: Standardized mean difference.
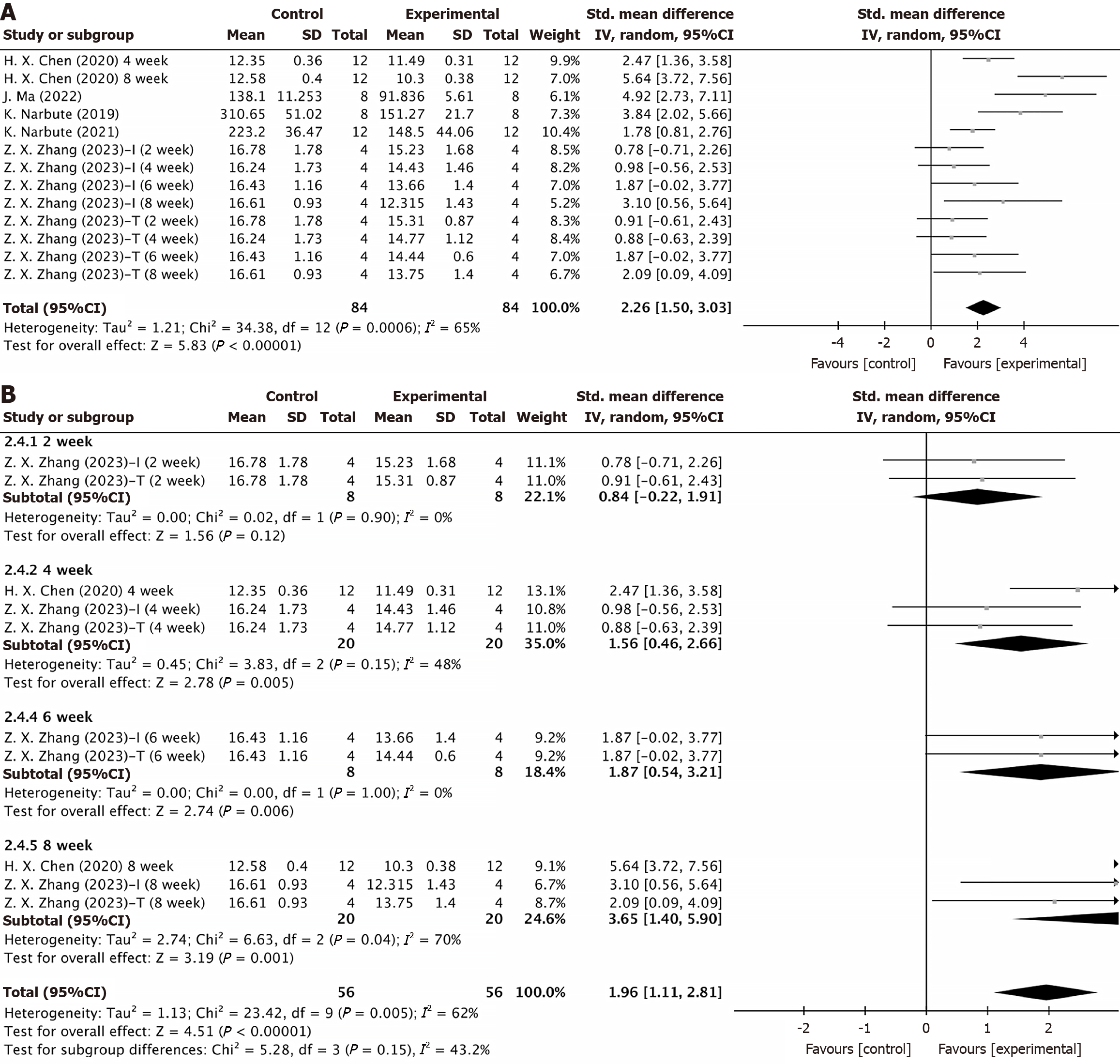
Figure 4 Forest plot.
A: Apomorphine turning behavior test; B: Subgroup analyses by mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles intervention period. CI: Confidence interval; SD: Standard deviation.
Figure 5 Apomorphine turning behavior test plots.
A: Funnel plot with pseudo-95% confidence limits; B: Egger’s publication bias plot. CI: Confidence interval; SMD: Standardized mean difference; CI: Confidence interval.
Figure 6 Forest plot.
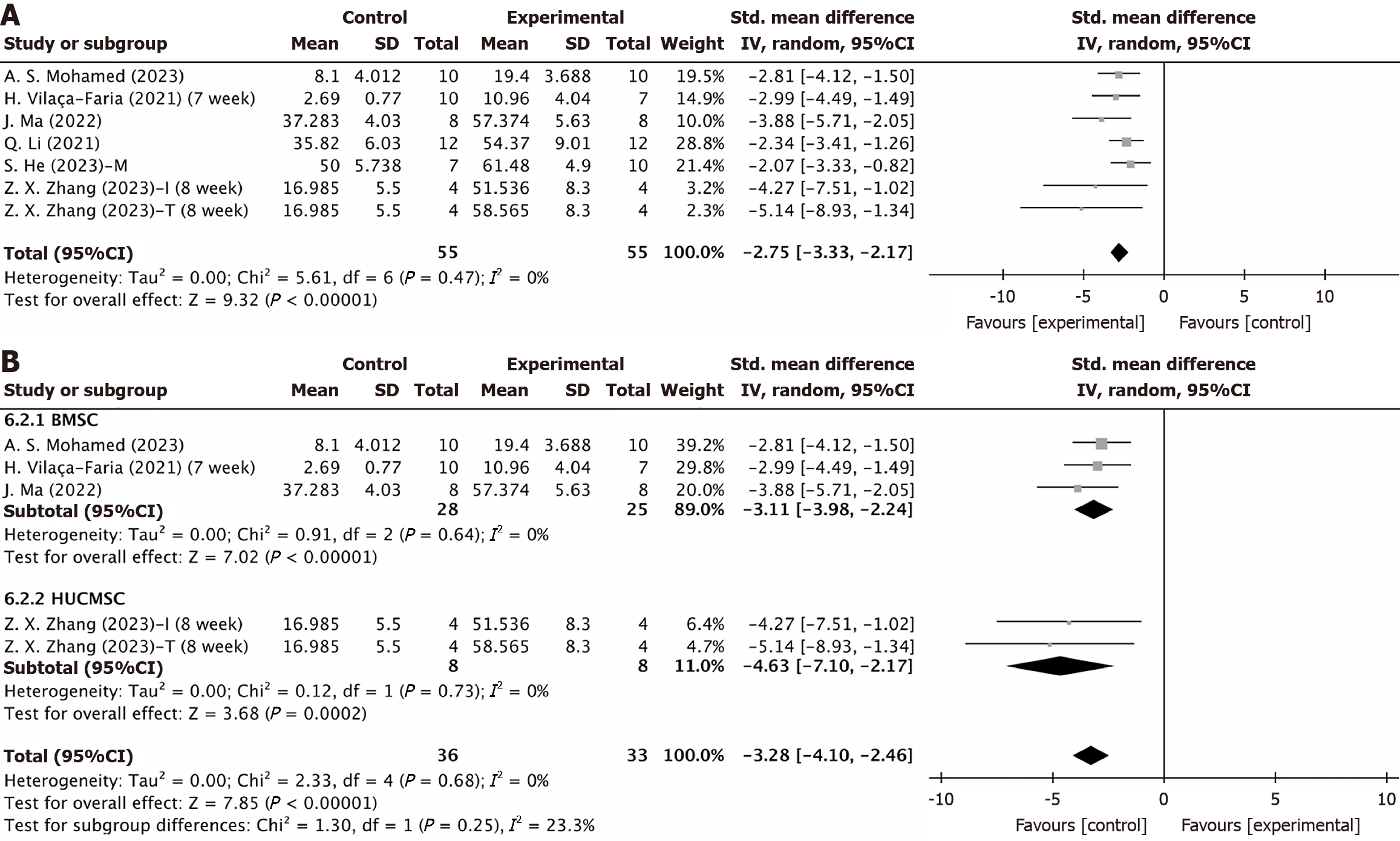
A: Number of tyrosine hydroxylase-positive cells in the substantia nigra; B: Mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles source subgroup for tyrosine hydroxylase-positive cells in the substantia nigra. CI: Confidence interval; BMSC: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell; HUCMSC: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell.
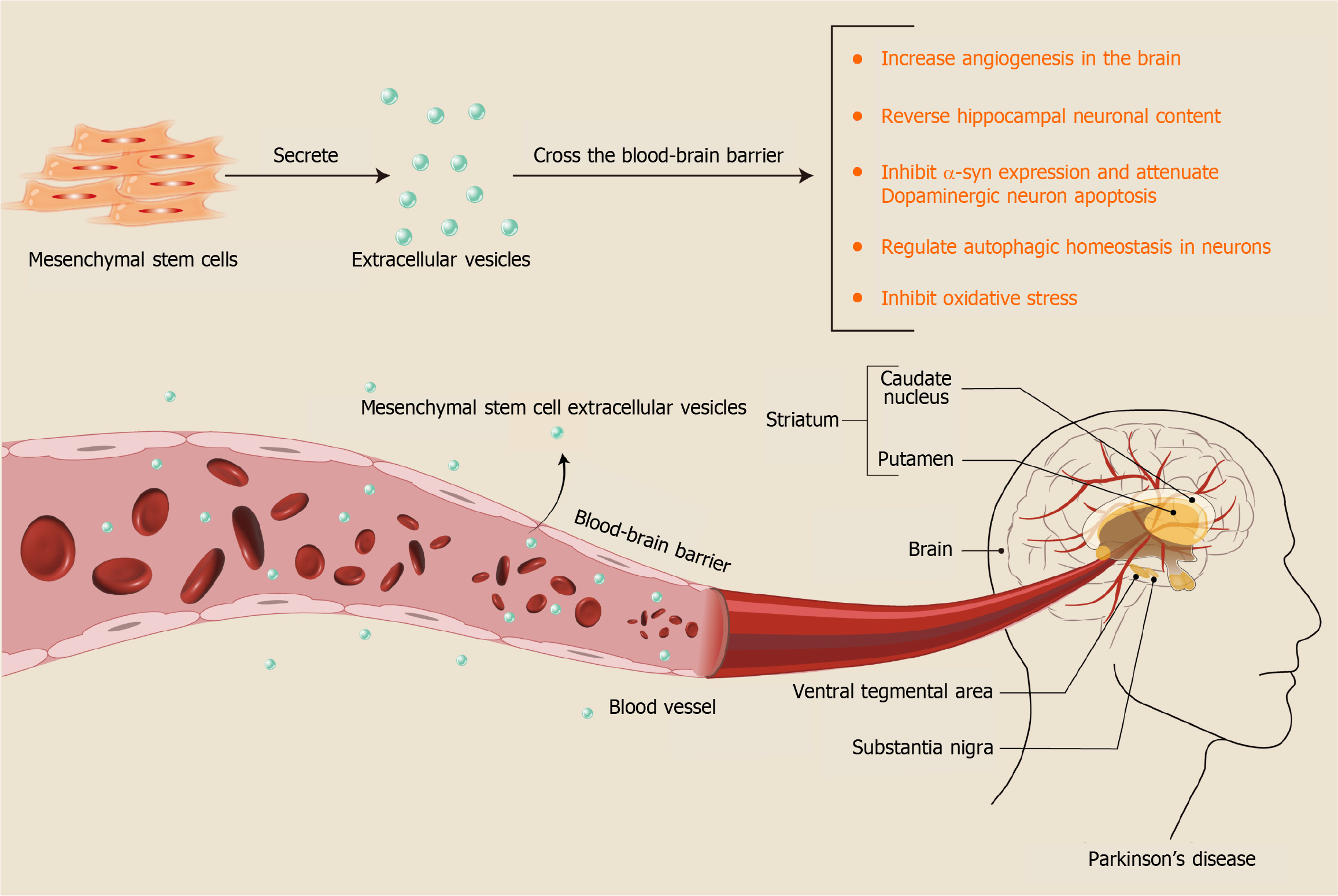
Figure 7 Mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in treating Parkinson’s disease.
α-syn: α-synuclein.
- Citation: Wang XS, Wang Y, Xu Y, Zhang SR, Zhang Y, Peng LL, Wu N, Ye JS. Effectiveness of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles therapy for Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review of preclinical studies. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(4): 102421
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i4/102421.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.102421