Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Mar 26, 2025; 17(3): 103560
Published online Mar 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i3.103560
Published online Mar 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i3.103560
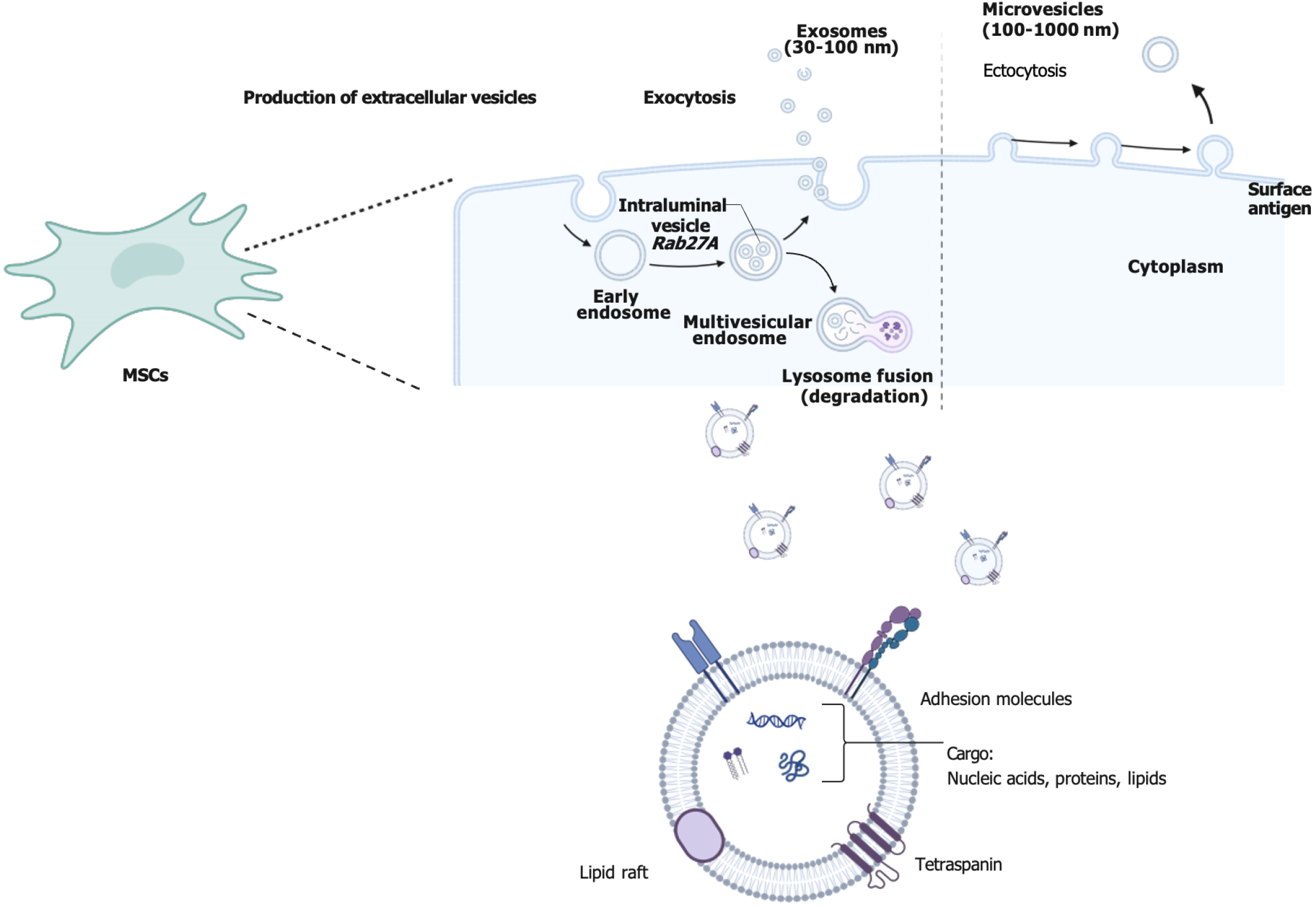
Figure 1 Exocytosis of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells.
The diagram illustrates the process of exosome biogenesis: From early endosomes to multivesicular bodies, and finally the secretion of exosomes containing various components such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, cell adhesion molecules, and transmembrane proteins. MSC: Mesenchymal stem cells.
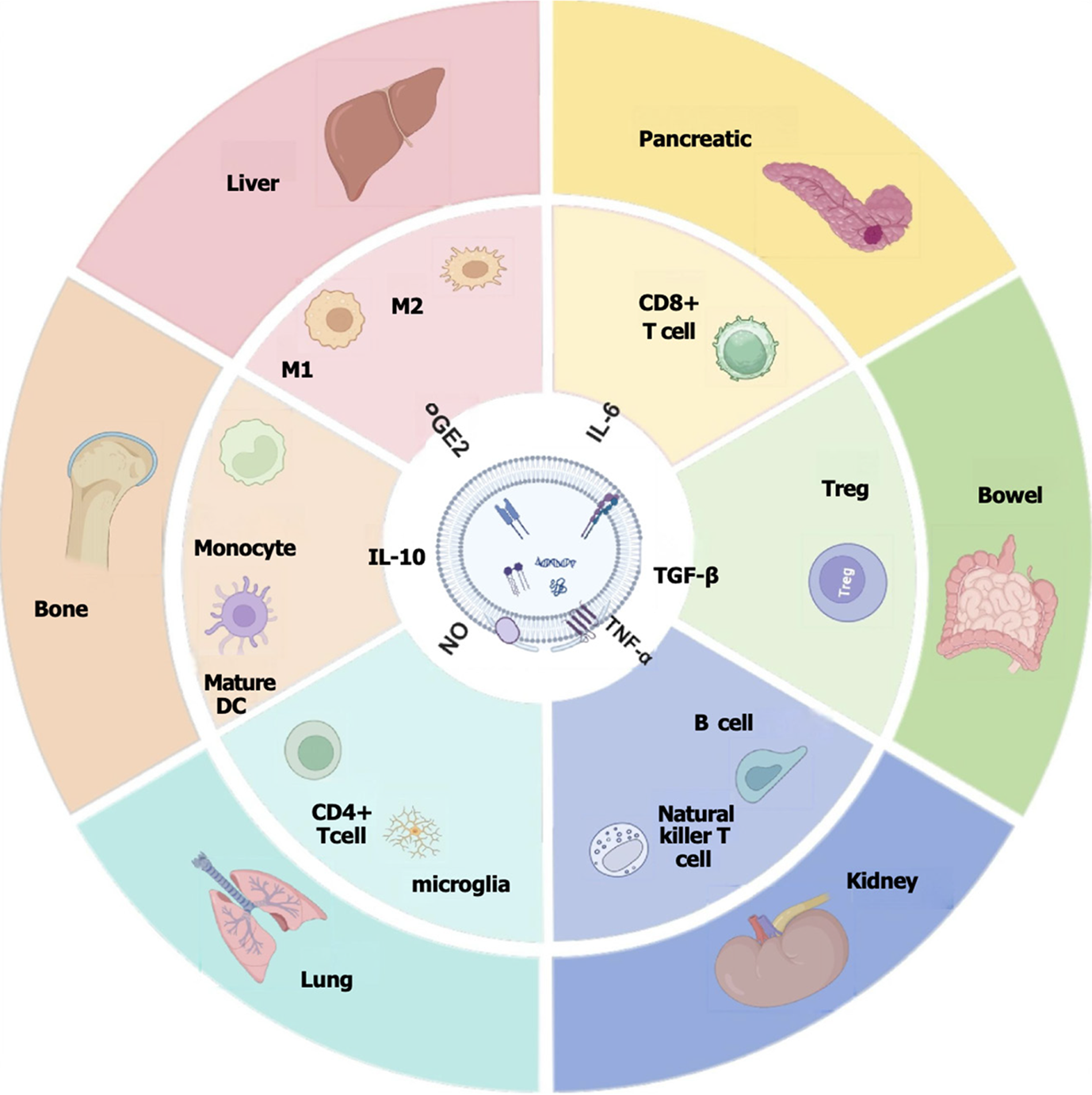
Figure 2 Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes regulate immune responses in diseases through different cytokines.
PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; IL-6: Interleukin 6; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-beta; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor-alpha; IL-10: Interleukin-10; NO: Nitric oxide; DC: Dendritic cell.
- Citation: Yi YF, Fan ZQ, Liu C, Ding YT, Chen Y, Wen J, Jian XH, Li YF. Immunomodulatory effects and clinical application of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(3): 103560
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i3/103560.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i3.103560