Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Mar 26, 2025; 17(3): 102088
Published online Mar 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i3.102088
Published online Mar 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i3.102088
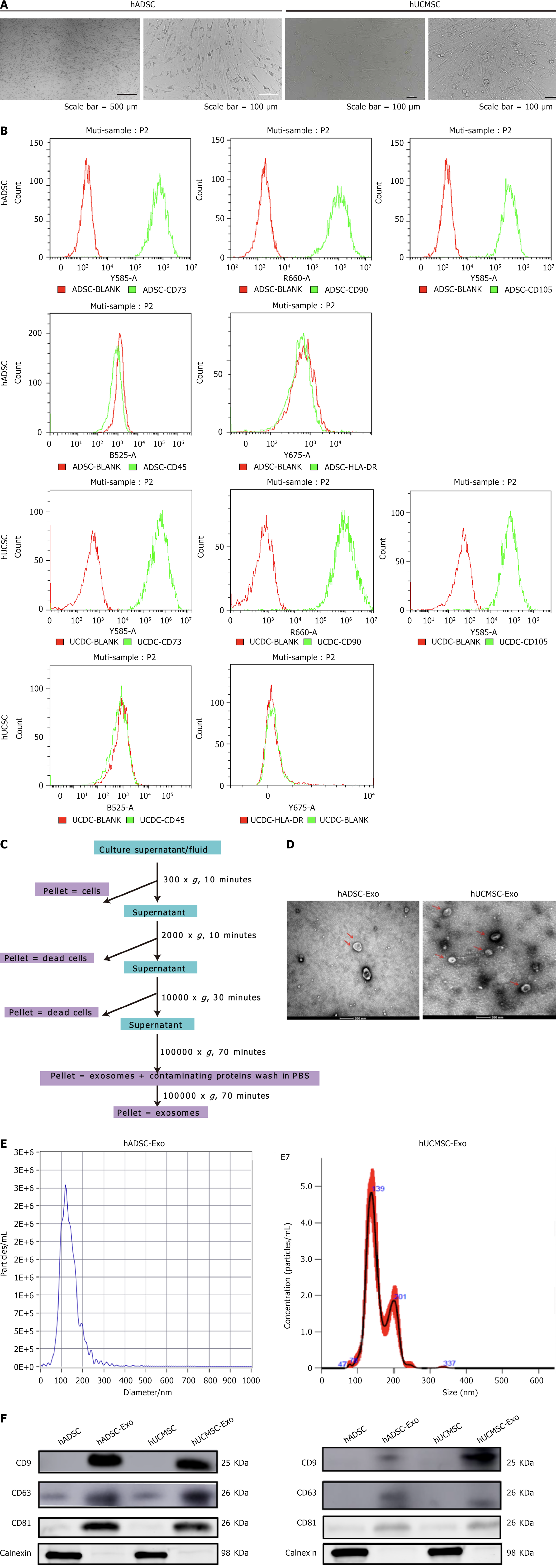
Figure 1 Identification of exosome from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell and human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell.
A: Morphology of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell (hADSC) and human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell (hUCMSC); B: Analysis of surface markers on hADSCs and hUCMSCs showed high CD105, CD90, and CD73 expression, but negative HLA-DR and CD45 expression; C: Schematic presentation of exosome isolated from hADSC and hUCMSC by differential ultracentrifugation; D: By TEM, purified hADSC exosome (hADSC-Exo) and hUCMSC exosome (hUCMSC-Exo) exhibit cup-like morphologies; E: Nanoparticle analysis of hADSC-Exo and hUCMSC-Exo; F: hADSC-Exo and hUCMSC-Exo express CD63, CD9, CD81 and calnexin is not expressed. hADSC: Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell; hUCMSC: Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell; hADSC-Exo: Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome; hUCMSC-Exo: Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome.
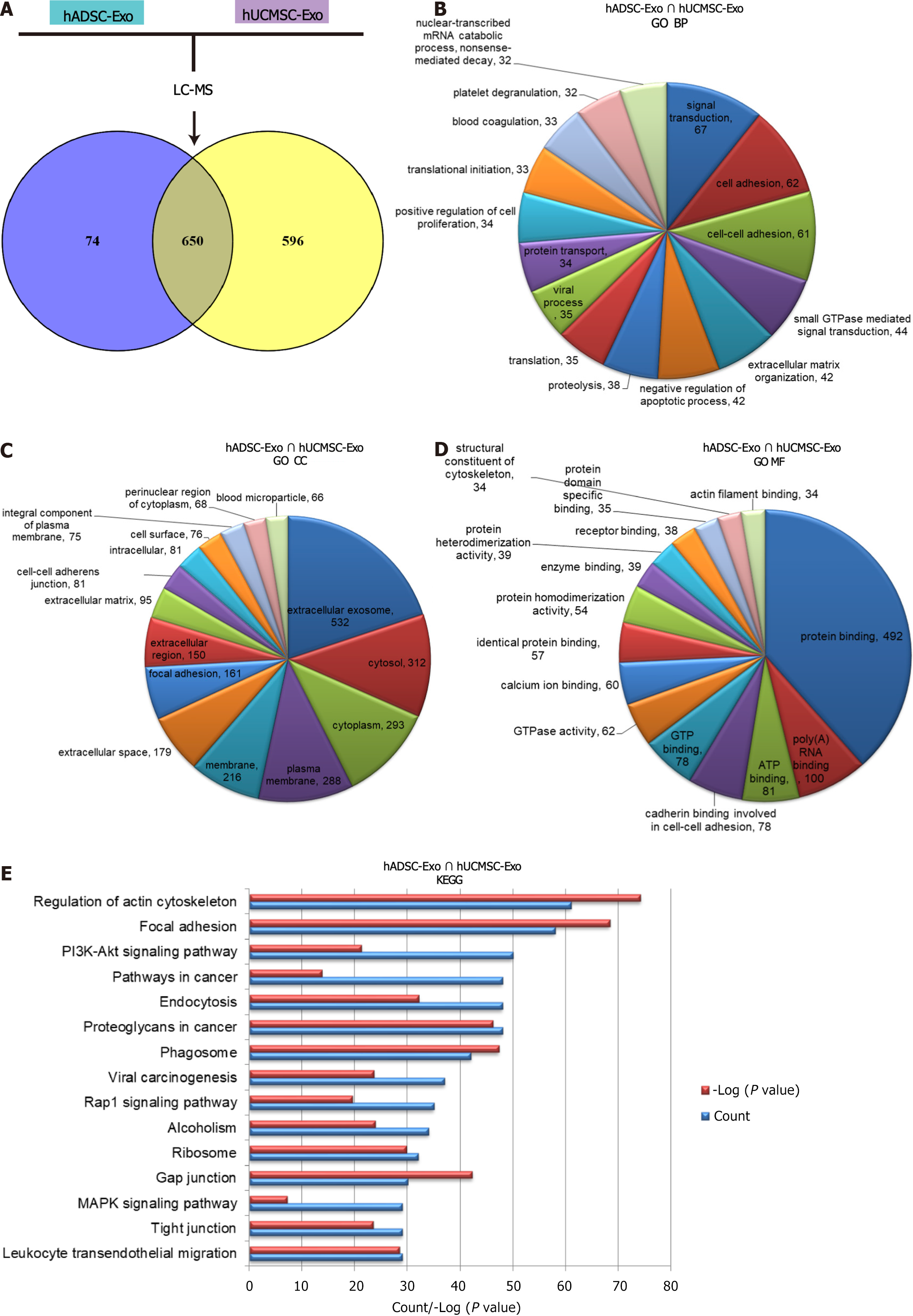
Figure 2 Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analysis based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry proteome analysis data of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome and human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome.
A: Venn map showing the intersection proteins of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome (hADSC-Exo) and human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome (hUCMSC-Exo); B-D: Gene Ontology analysis of hADSC-Exo and hUCMSC-Exo liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry common proteins. A chart indicates biological process (B), cellular components (C) and molecular function (D); E: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway of hADSC-Exo and hUCMSC-Exo common proteins. hADSC-Exo: Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome; hUCMSC-Exo: Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome; LC-MS: Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry; GO: Gene Ontology; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; BP: Biological process; CC: Cellular component; MF: Molecular function.
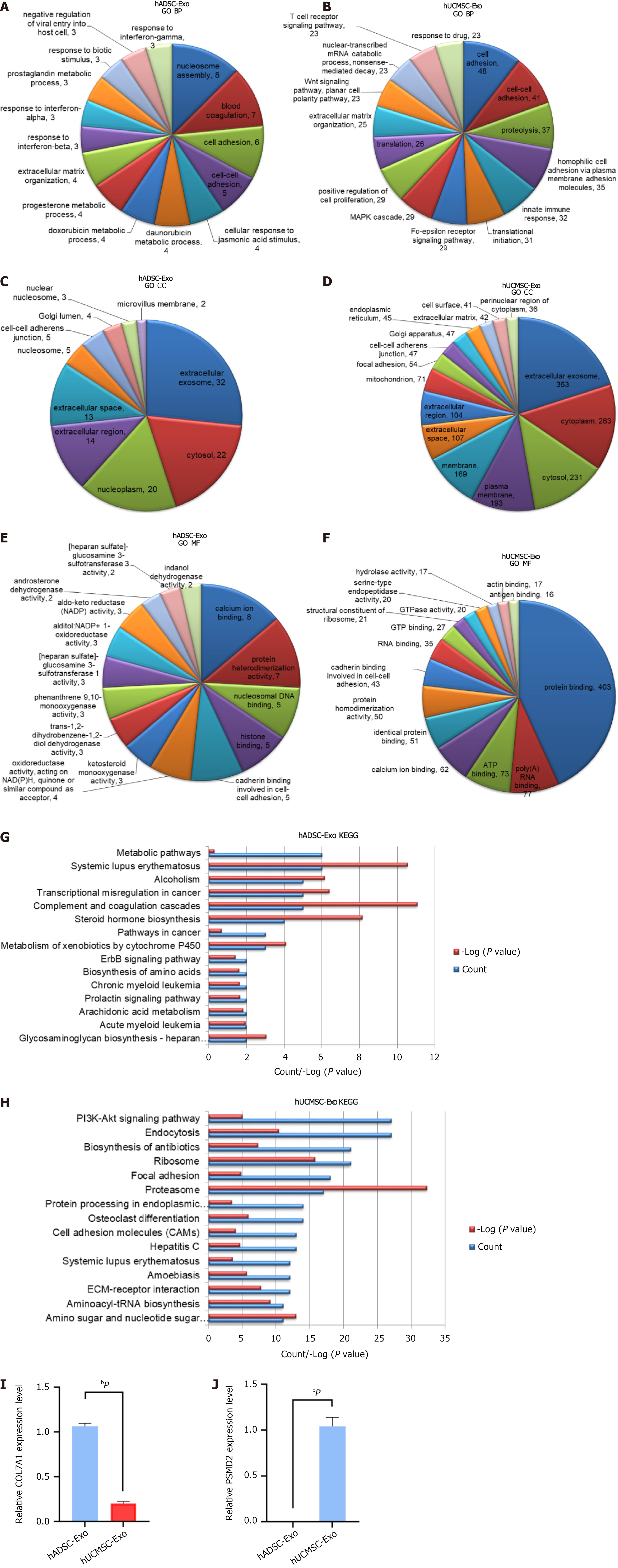
Figure 3 Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analysis based on heterogeneous characteristics of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes and human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome.
A and B: Heterogeneous characteristics of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome (hADSC-Exo) (A) and human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome (hUCMSC-Exo) (B) function analyzed by biological process analysis; C and D: Heterogeneous characteristics of hADSC-Exo (C) and hUCMSC-Exo (D) function analyzed by cellular components analysis; E and F: Heterogeneous characteristics of hADSC-Exo (E) and hUCMSC-Exo (F) function analyzed by molecular function analysis; G and H: Heterogeneous characteristics of hADSC-Exo (G) and hUCMSC-Exo (H) function analyzed by Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis; I and J: The mRNA expression of COL7A1 (hADSC-Exo, I) and PSMD2 (hUCMSC-Exo, J) was detected by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (data were presented as mean ± SD. bP < 0.01, n = 6, unpaired t-test. hADSC-Exo: Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome; hUCMSC-Exo: Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome; GO: Gene Ontology; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; BP: Biological process; CC: Cellular component; MF: Molecular function.
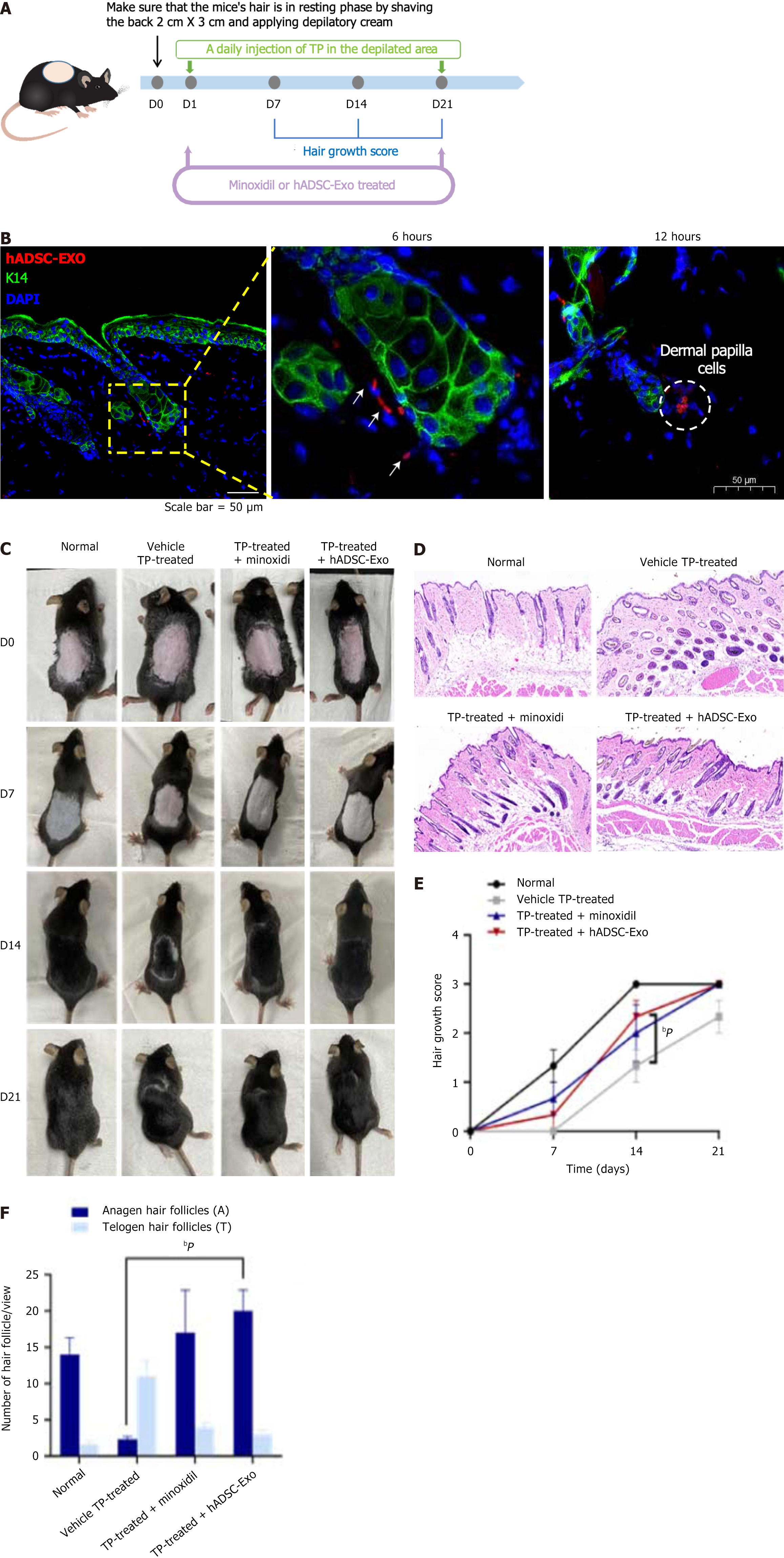
Figure 4 Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes improve the hair regeneration in androgenetic alopecia mice model.
A: Schematic flowchart of the experiment of testosterone propionate-treated and shaved in androgenetic alopecia mouse model; B: PKH26-labeled human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome (red) retention in the site of hair follicle; C: Hair growth of C57BL/6 mice in each group; D: hematoxylin and eosin staining of mouse skin histopathological sections in each group; E: Hair growth score in each group; F: The number of follicles in each group. Differences among four groups were assessed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test and one-way ANOVA; error bars represent SEM. bP < 0.01, compared with testosterone propionate-treated group. Six mice were randomly selected from each group for histological examination. TP: Testosterone propionate; hADSC-Exo: Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome.
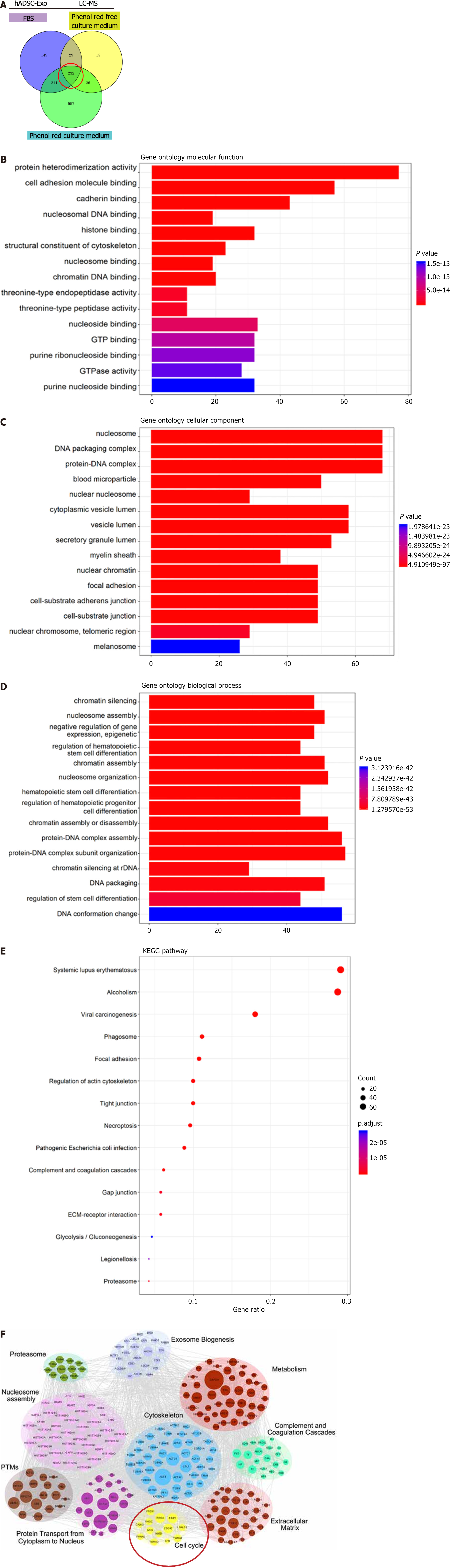
Figure 5 Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analysis based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry proteome analysis data of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes in different culture medium.
A: Venn map showing the intersection of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes (hADSC-Exo) proteins in different culture systems: Control medium (fetal bovine serum), phenol red free culture medium (Gibco, NY, United States), and phenol red culture medium (Takara, Japan); B-D: Gene Ontology analysis of hADSC-Exo liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry proteome analysis data. A chart indicates molecular function (B), cellular components (C) and biological process (D); E: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway of hADSC-Exo proteins; F: STRING network analysis of the intersection of hADSC-Exo proteins. hADSC-Exo: Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome; LC-MS: Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry; FBS: Fetal bovine serum.
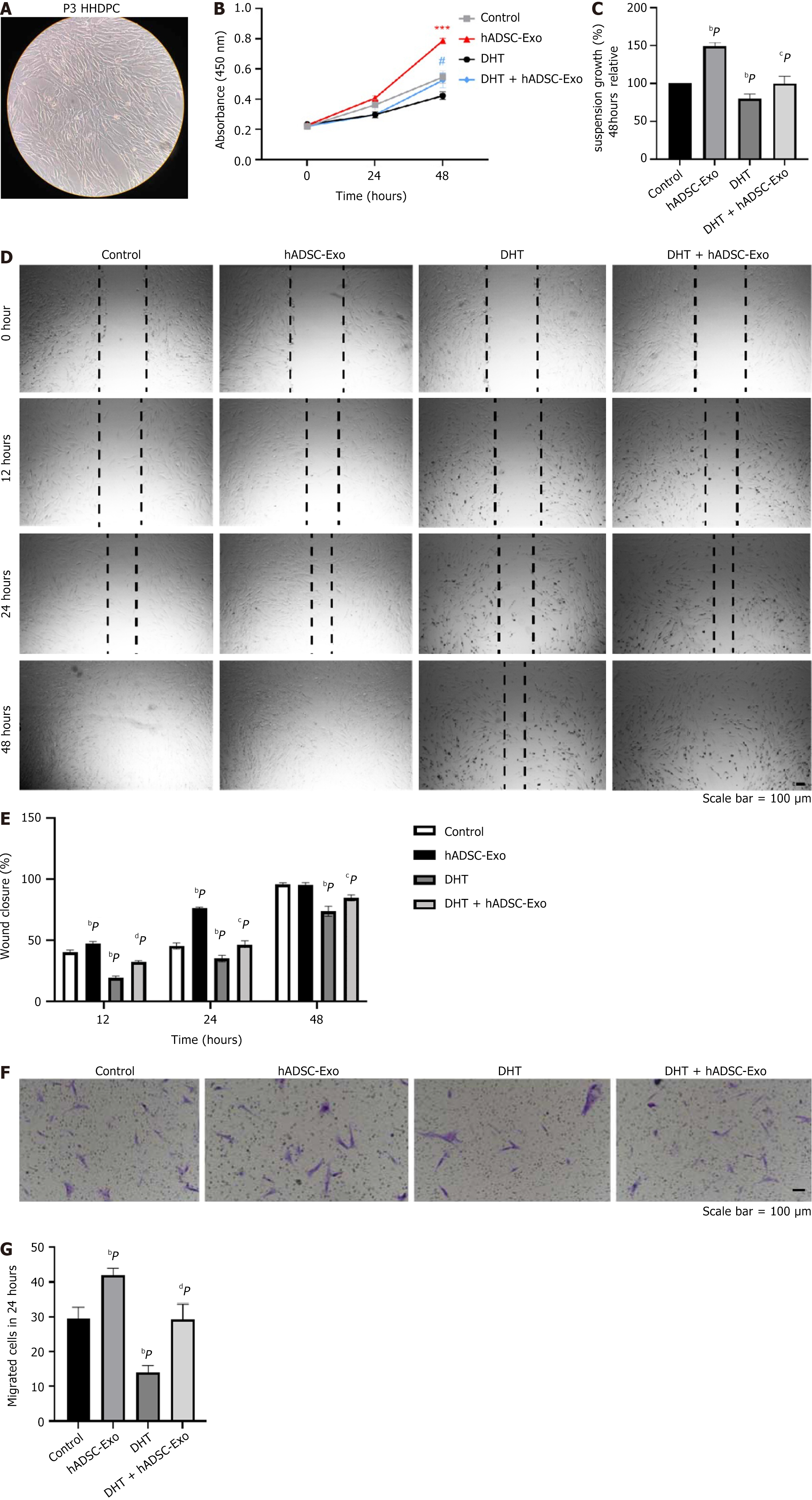
Figure 6 Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome improves the hair regeneration in androgenetic alopecia cell model.
A: Human hair dermal papillary cells were used in subsequent analyses from passage 3 (P3); B and C: Cell counting kit-8 (CCK8) assay. CCK8 assay was carried out to measure the cell growth in 48 hours (B). Cell survival was determined by the CCK8 assay at 48 hours (C); D and E: The wound healing assay was used to assess migration in cells (D). Statistical analysis of the results of wound healing assay in each group (E); F and G: The migratory properties of human hair dermal papillary cells were analyzed using the Transwell migration assay with Transwell filter chambers (F). Statistical analysis of the results of Transwell migration assay in each group (G). bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001. HHDPC: Human hair dermal papillary cell; DHT: Dihydrotestosterone; hADSC-Exo: Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome.
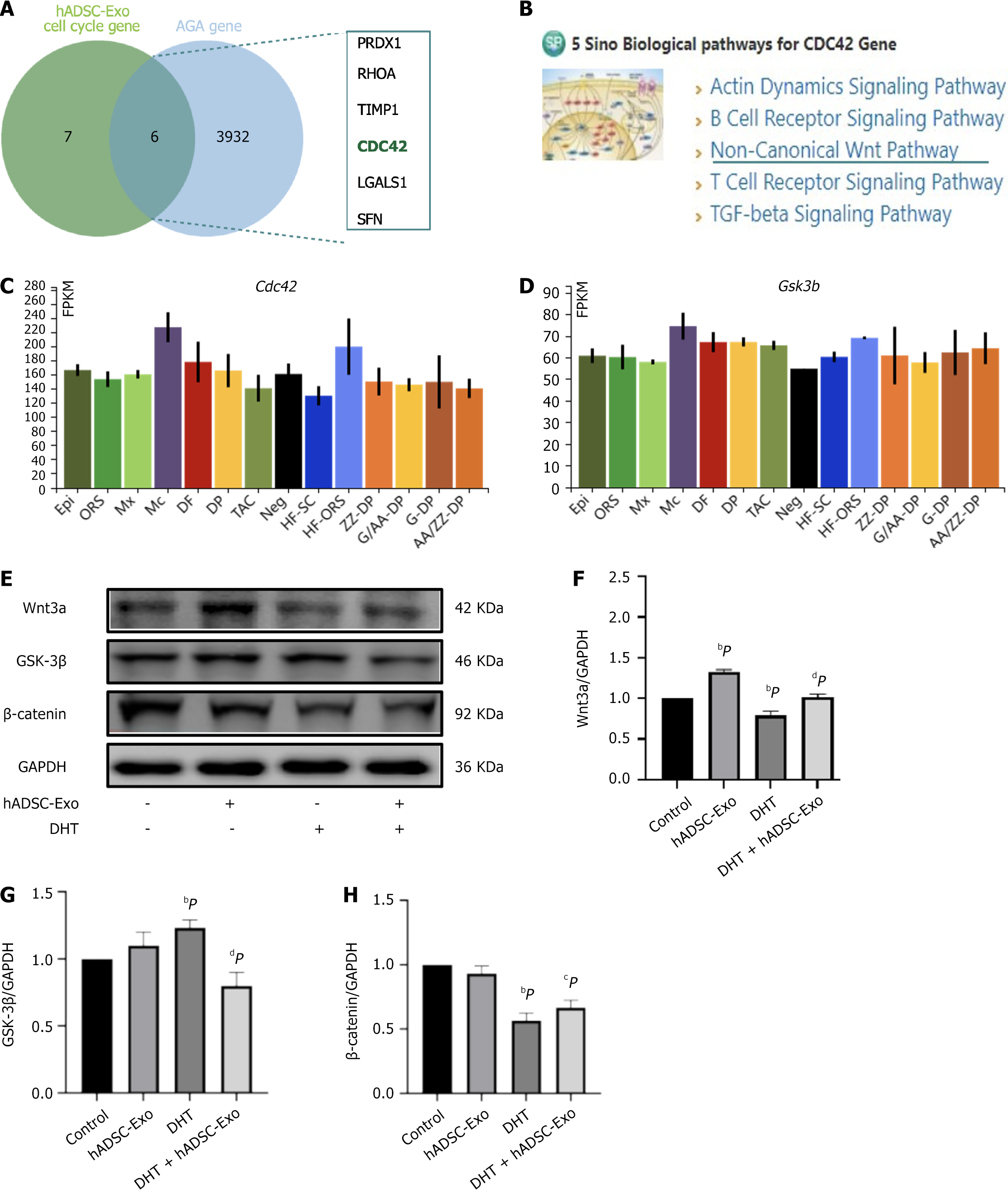
Figure 7 Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes regulate dermal papillary cell proliferation via cell division cycle protein 42/Wnt/β-catenin pathway in androgenetic alopecia.
A: Venn diagram demonstrating the intersections of genes from the androgenetic alopecia gene set and human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes cell cycle gene; B: Five-sino biological pathway enrichment diagram; C: Using single-cell mRNA-sequencing data from the Hair-GEL database, cell types expressing cell division cycle protein 42 (http://hair-gel.net/) were identified; D: Using single-cell mRNA-sequencing data from the Hair-GEL database, cell types expressing glycogen synthase kinase-3β (Gsk3β) (http://hair-gel.net/) were found; E: Representative western blotting image of GSK-3β after human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes was overexpressed in human hair dermal papillary cells; F-H: Statistical analysis of the western blotting in each group. Wnt3a (F), GSK-3β (G) and β-catenin (H). Differences among five groups were assessed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test and one-way ANOVA, and error bars represent SEM. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001, Compared with control group. hADSC-Exo: Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome; AGA: Androgenetic alopecia; Cdc42: Cell division cycle protein 42; Gsk3b: Glycogen synthase kinase-3β; DHT: Dihydrotestosterone.
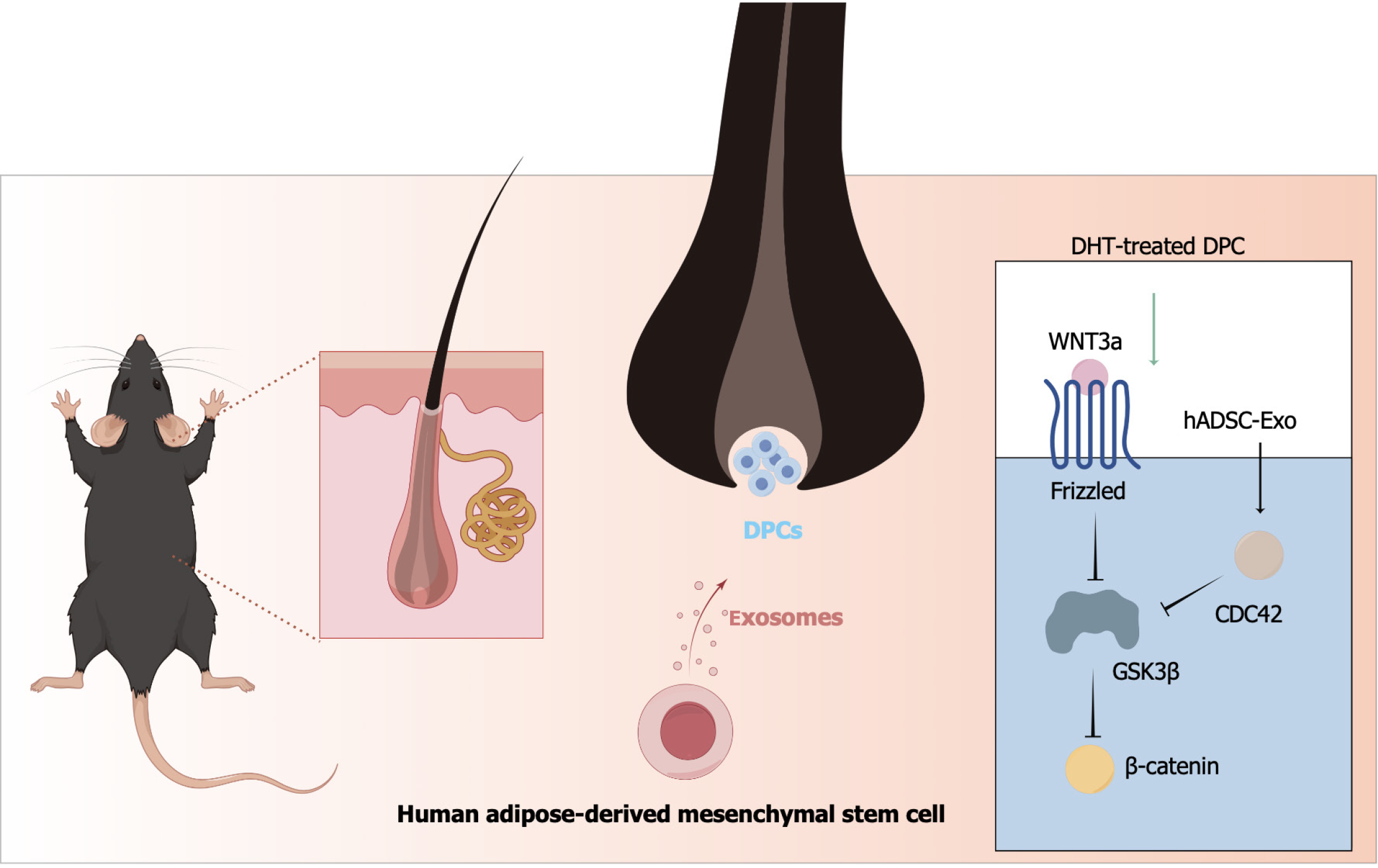
Figure 8 Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome regulate dermal papillary cells proliferation via Wnt/β-cate
- Citation: Fu Y, Han YT, Xie JL, Liu RQ, Zhao B, Zhang XL, Zhang J, Zhang J. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes enhance the development of hair follicle to ameliorate androgenetic alopecia. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(3): 102088
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i3/102088.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i3.102088