Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2024; 16(2): 70-88
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.70
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.70
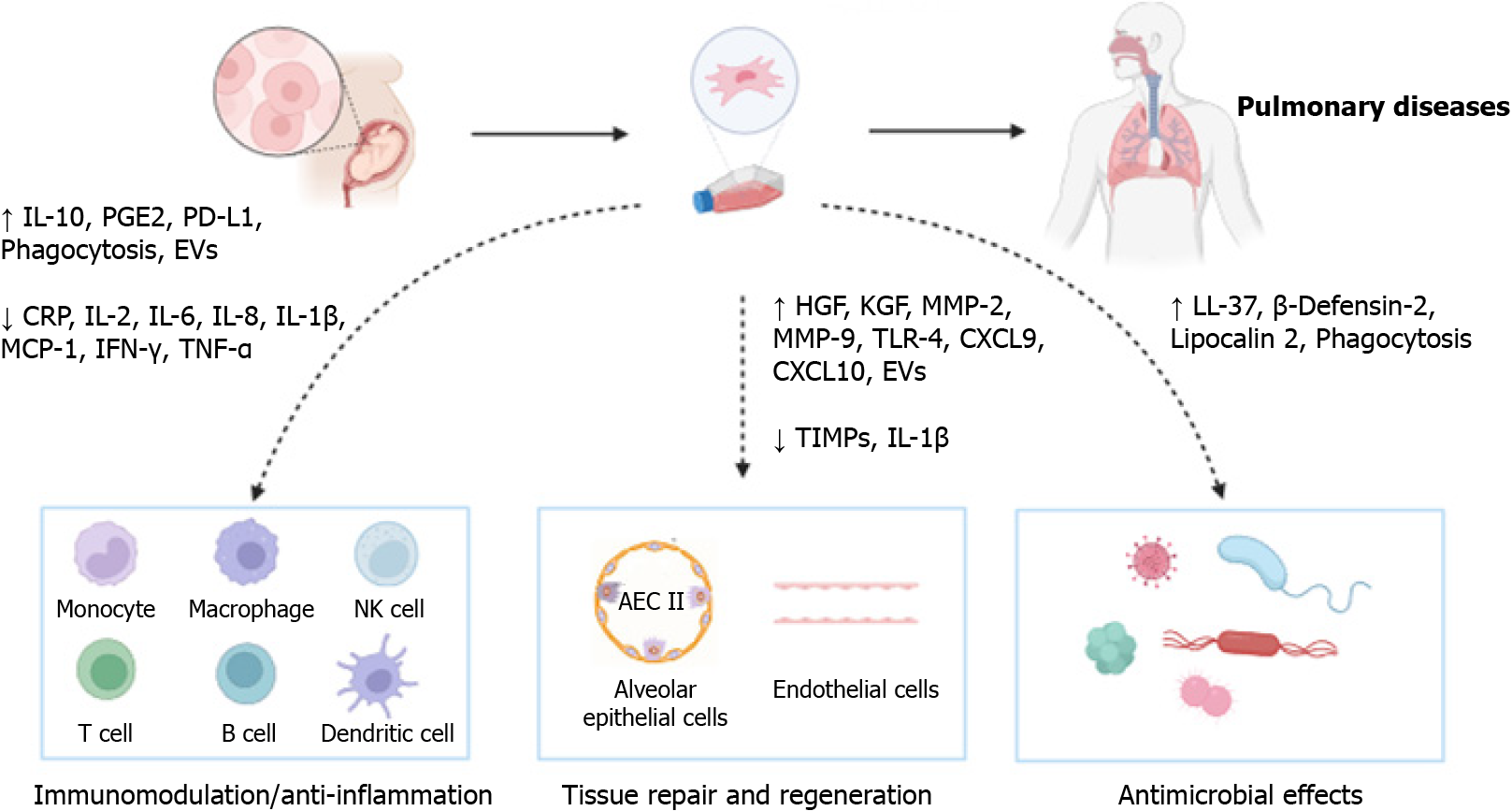
Figure 1 Potential mechanisms of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells therapy in pulmonary diseases.
The therapeutic effects of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in treating pulmonary diseases involve multiple mechanisms, such as the immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory functions, the regenerative and differentiation properties, and the antimicrobial effects. IL: Interleukin; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; PD-L1: Programmed cell death protein ligand 1; EVs: Extracellular vesicles; CRP: C-reactive protein; MCP: Monocyte chemoattractant protein; IFN: Interferon; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; KGF: Keratinocyte growth factor; MMP: Matrix metalloprotease; TLR: Toll-like receptor; CXCL: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand; TIMP: Tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase; NK: Natural killer; AEC: Alveolar epithelial cell.
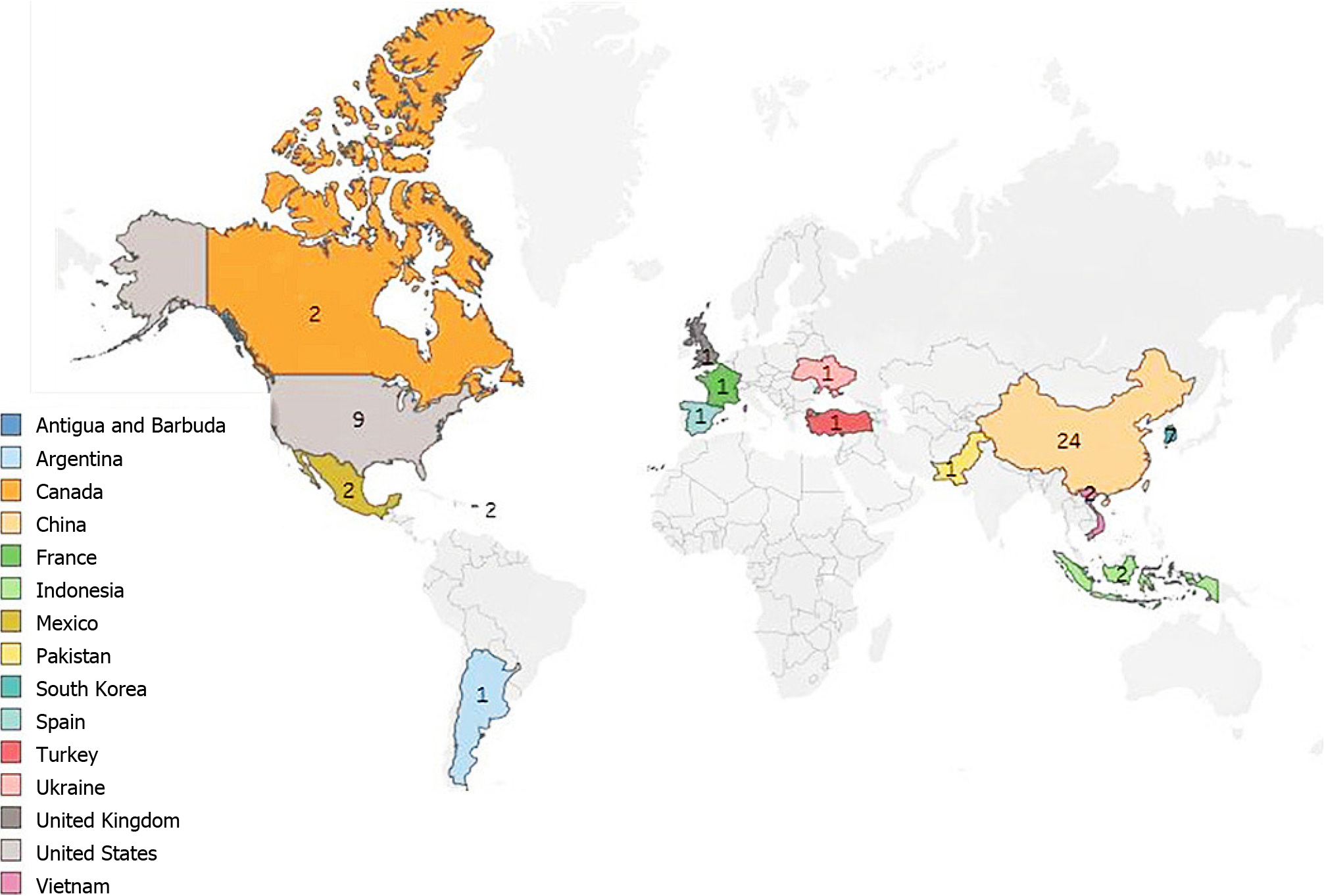
Figure 2 The geographical location and distribution of the clinical trials in pulmonary diseases.
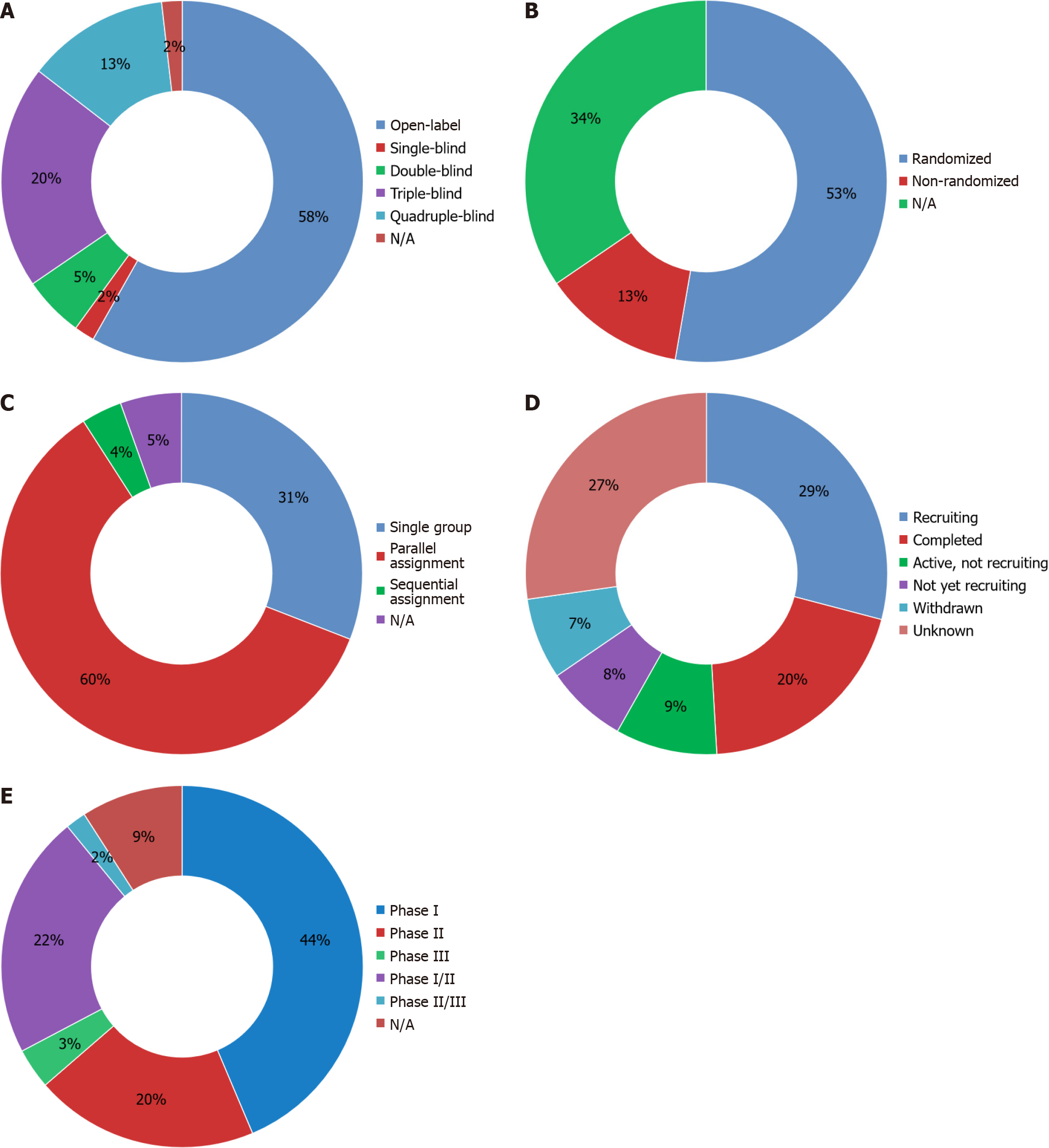
Figure 3 Characteristics of clinical trials involving umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells therapy for pulmonary diseases.
A: Masking of clinical trials; B: Allocation of clinical trials; C: Intervention model of clinical trials; D: Status of clinical trials; E: Phase of clinical trials. N/A: Not available.
- Citation: Meng M, Zhang WW, Chen SF, Wang DR, Zhou CH. Therapeutic utility of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells-based approaches in pulmonary diseases: Recent advancements and prospects. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(2): 70-88
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i2/70.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.70