Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2024; 16(2): 151-162
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.151
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.151
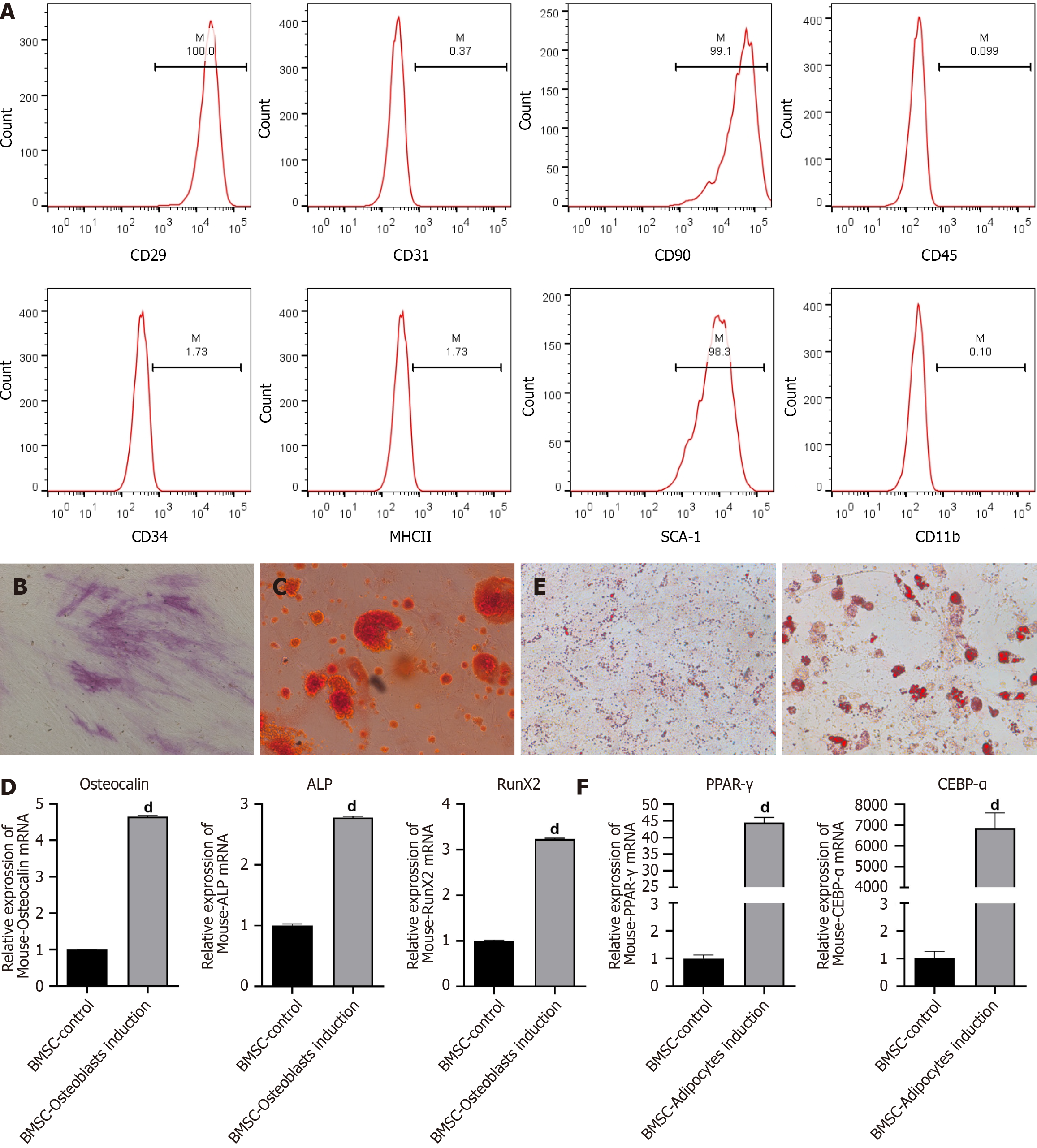
Figure 1 Osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells.
A: Bone mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) were isolated from mice bone marrow tissues. Flow cytometry was used to detect the expressions of CD29, CD31, CD90, CD45, CD34, MHCII, SCA-1 and CD11b; B-D: BMSCs were induced towards osteogenic differentiation. ALP staining was used to evaluate alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity (B); calcium deposits were visualized by Alizarin red staining (C); the mRNA levels of osteogenic genes, including Osteocalin, Runt-related transcription factor 2 and ALP, were detected by reverse transcription coupled to the quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) (D); E and F: BMSCs were induced towards adipogenic differentiation. Representative images of Oil red O staining (E), the mRNA levels of adipogenic genes, such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and CCAAT enhancer-binding protein alpha, were measured by RT-PCR (F). All values are shown as mean ± SD. dP < 0.0001. n = 3. BMSC: Bone mesenchymal stem cell; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; RunX2: Runt-related transcription factor 2; CEBPα: CCAAT enhancer-binding protein alpha; PPARγ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma.
Figure 2 Jumonji domain-containing 1C was upregulated while nuclear factor-κB activation were not affected during bone mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation.
A: Jumonji domain-containing 1C (JMJD1C) mRNA level in bone mesenchymal stem cells after osteoblast induction was measured by reverse transcription coupled to the quantitative polymerase chain reaction; B-D: The protein expressions of JMJD1C and p-nuclear factor-κB were determined by western blot; E-G: The levels of inflammatory cytokines [interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha] were detected using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. All values are shown as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, dP < 0.0001, NS: No significance. n = 3. JMJD1C: Jumonji domain-containing 1C; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL: Interleukin; NF-κB: nuclear factor-κB.
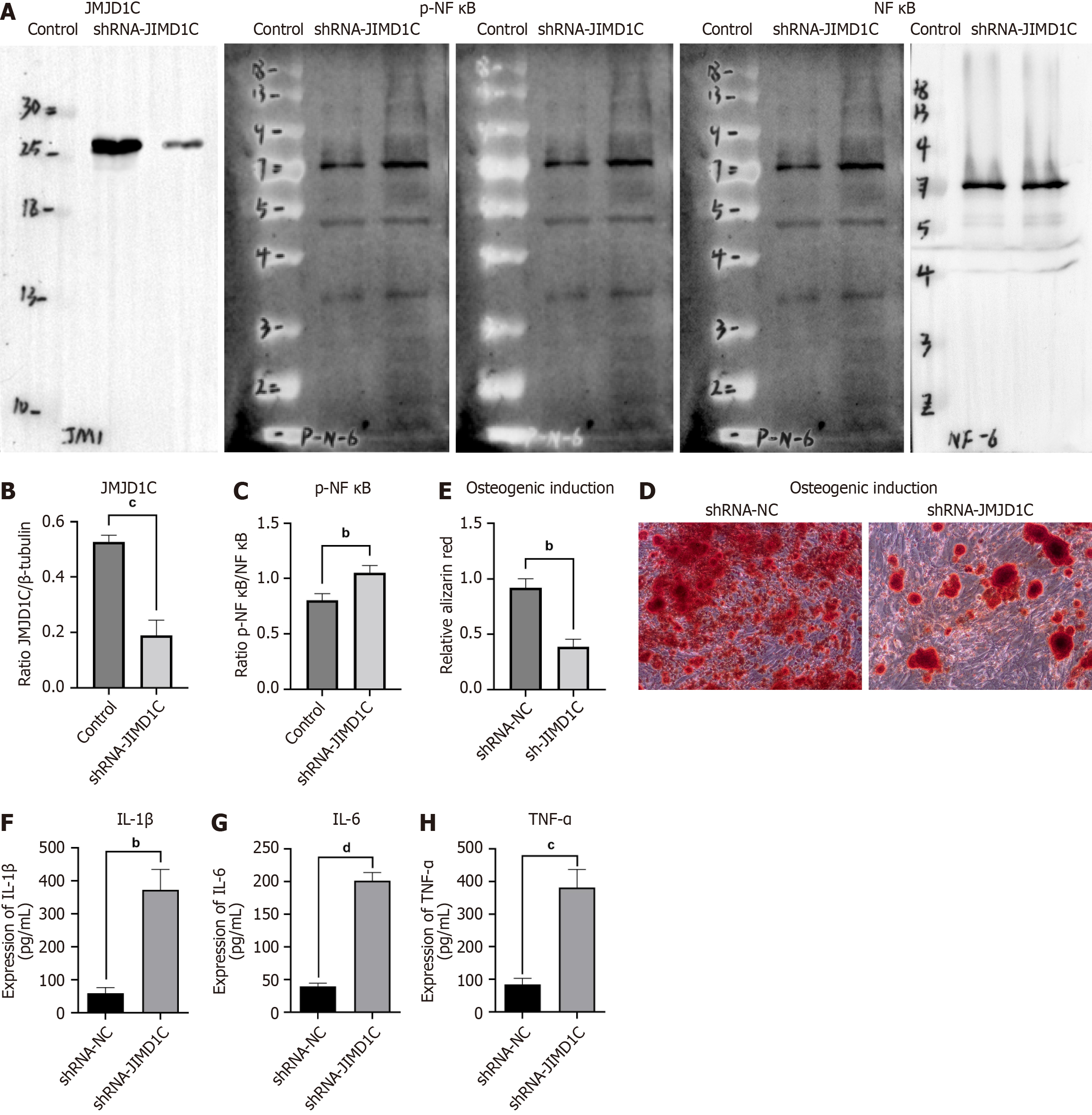
Figure 3 Jumonji domain-containing 1C knockdown inhibited osteogenic differentiation and upregulated p-nuclear factor-κB expression in bone mesenchymal stem cells.
Bone mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) were transfected with sh-NC or short hairpin RNA against Jumonji domain-containing 1C (sh-JMJD1C). A-C: Western blot was adopted to measure JMJD1C and p-nuclear factor-κB protein levels; D and E: Detection of osteogenic differentiation ability of BMSCs using alizarin red staining; F-H: Cytokines secretion level of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. All values are shown as mean ± SD. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001, n = 3. JMJD1C: Jumonji domain-containing 1C; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL: Interleukin; NF-κB: nuclear factor-κB.
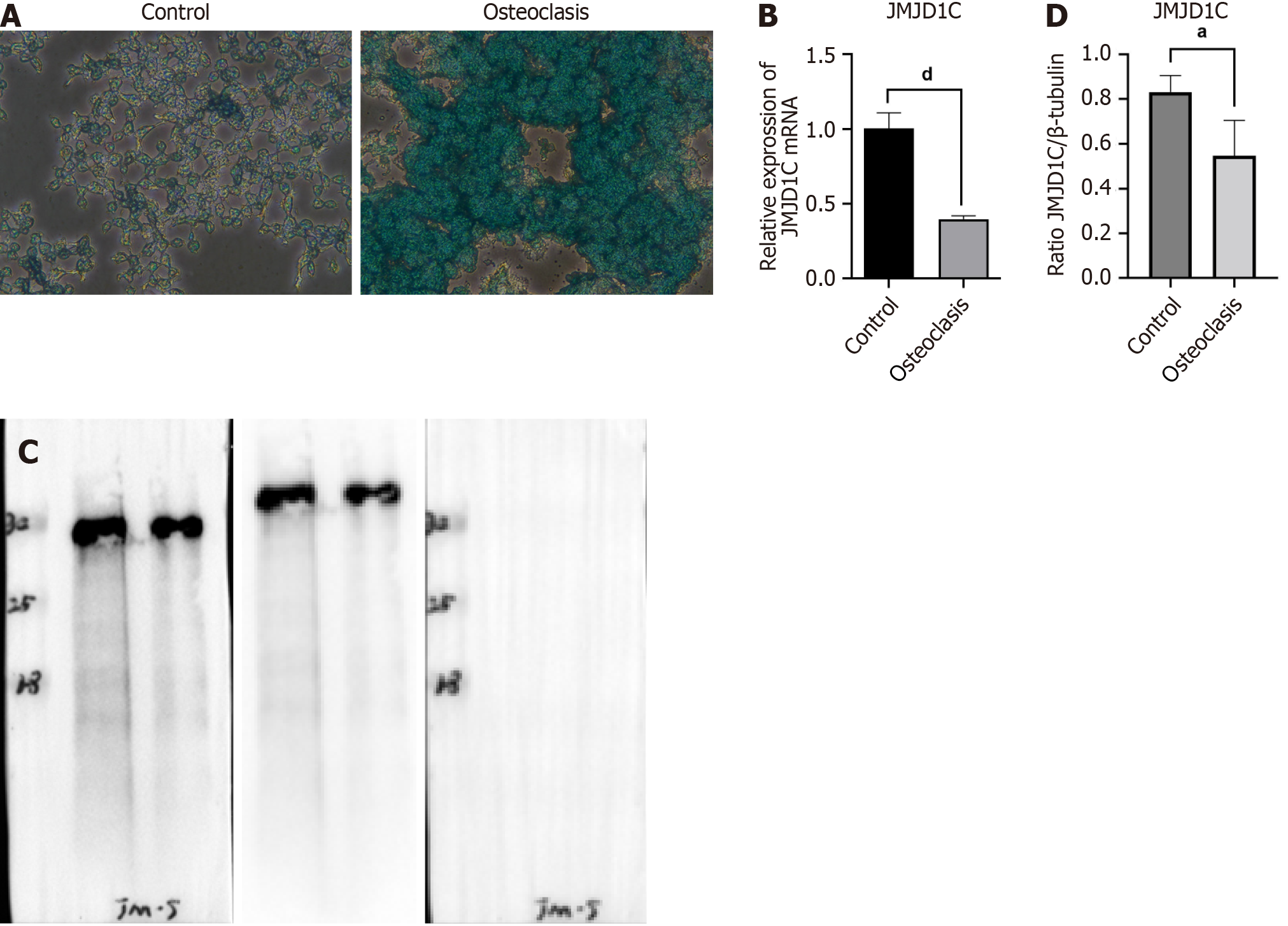
Figure 4 Jumonji domain-containing 1C was downregulated after bone marrow-derived macrophages osteoclast differentiation.
Bone marrow-derived macrophages were incubated with RANKL for osteoclast differentiation. A: Representative images of tissue-resistant acid phosphatase staining were presented; B-D: Jumonji domain-containing 1C mRNA and protein levels in MMCs after osteoclast induction were measured by reverse transcription coupled to the quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blot. All values are shown as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, dP < 0.0001, n = 3. JMJD1C: Jumonji domain-containing 1C.
- Citation: Li JY, Wang TT, Ma L, Zhang Y, Zhu D. Silencing of Jumonji domain-containing 1C inhibits the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via nuclear factor-κB signaling. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(2): 151-162
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i2/151.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i2.151