Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2023; 15(10): 979-988
Published online Oct 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i10.979
Published online Oct 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i10.979
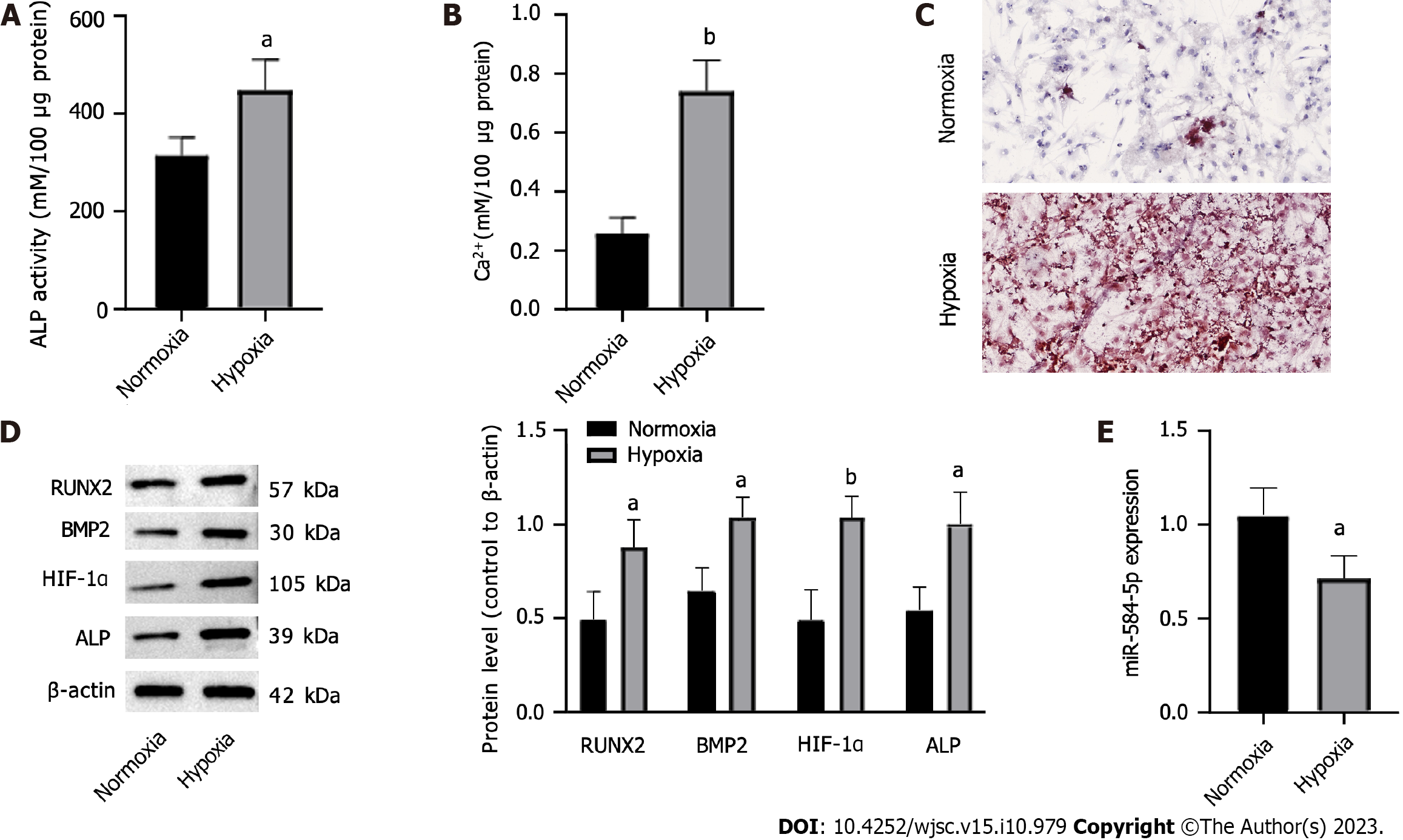
Figure 1 Hypoxia stimulation promotes the osteogenic differentiation of periosteal stem cells.
A: Alkaline phosphatase activity; B: Intracellular calcium ion level; C: Alizarin red S staining chelated Ca2+ form an orange-red complex; D: Osteogenic differentiation-related protein levels; E: MiRNA-584-5p expression in periosteal stem cells. One-way ANOVA and t tests were used to demonstrate differences between the hypoxia-induced and normal control groups. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; RUNX2: RUNX family transcription factor 2; BMP2: Bone morphogenetic protein 2; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1; miRNA: MicroRNA.
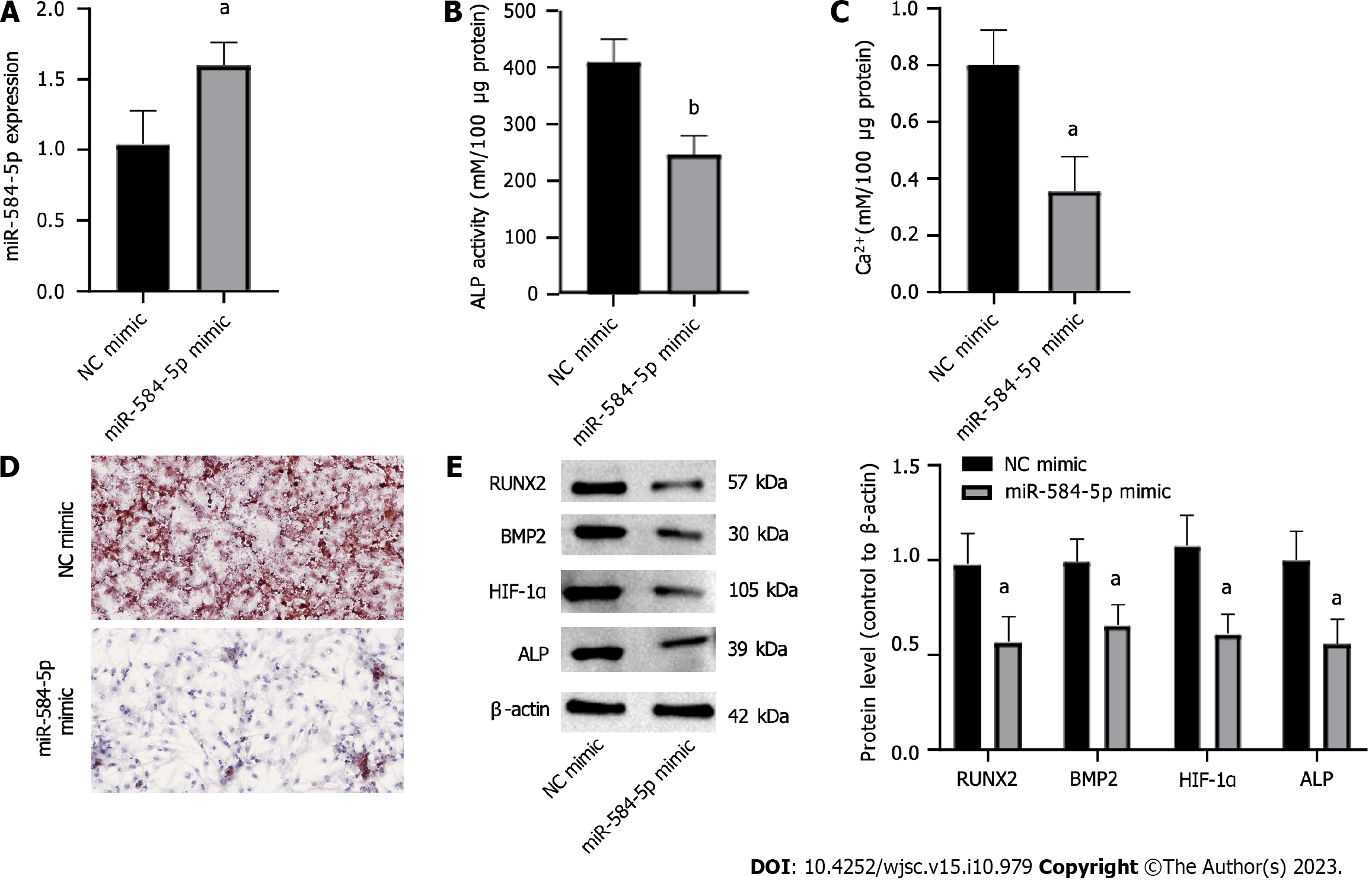
Figure 2 Upregulation of miRNA-584-5P inhibits the osteogenic differentiation of periosteal stem cells induced by hypoxia.
A: MiRNA-584-5p (miR584-5p) expression in stem cells; B: Alkaline phosphatase activity; C: Intracellular calcium ion level; D: Alizarin red S staining chelated Ca2+ form an orange-red complex; E: Osteogenic differentiation-related protein expression. One-way ANOVA and t tests were used to demonstrate differences between the miR584-5p mimic and negative control groups. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; RUNX2: RUNX family transcription factor 2; BMP2: Bone morphogenetic protein 2; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1; miRNA: MicroRNA; NC: Negative control.
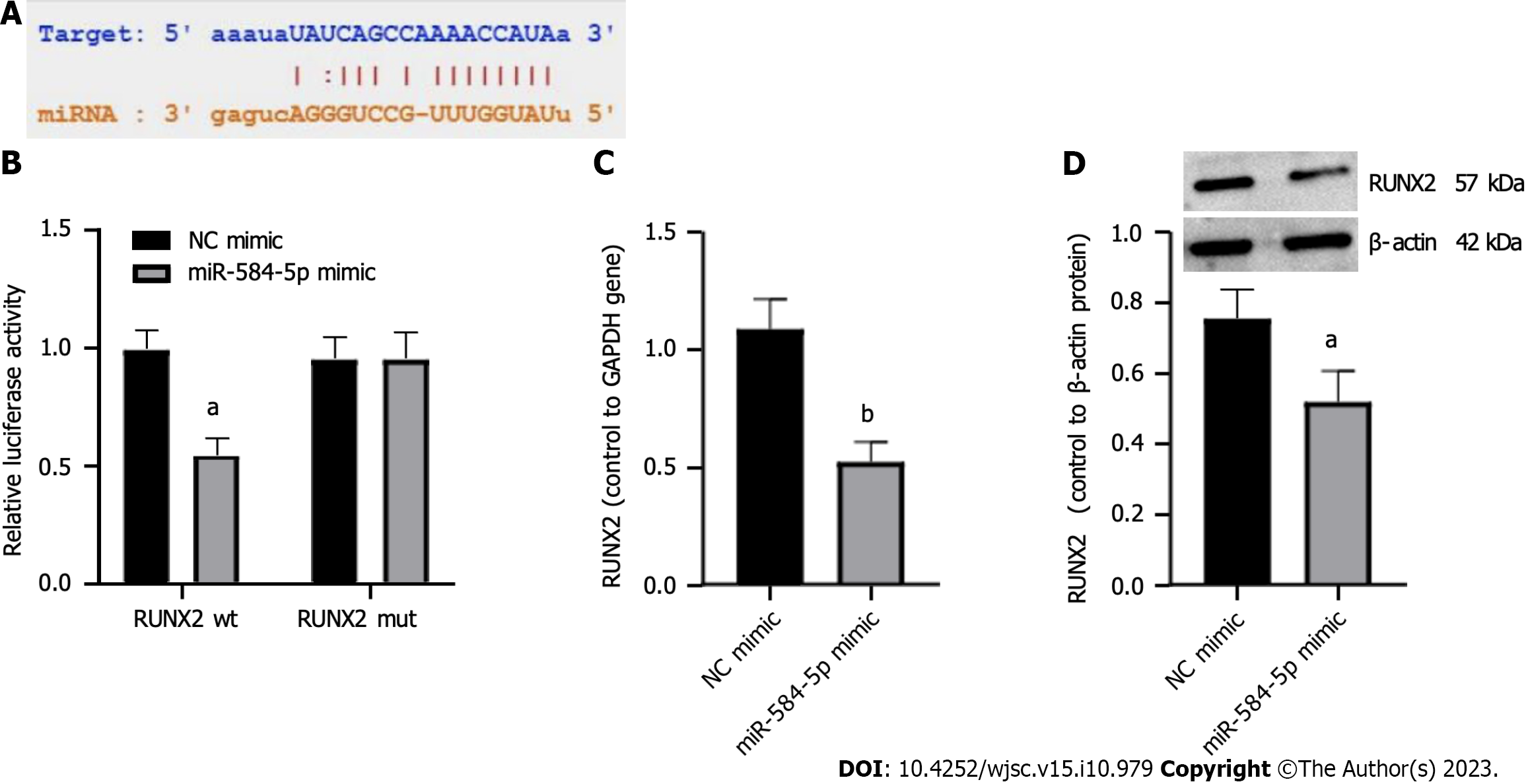
Figure 3 Prediction of the miRNA-584-5p target.
A: Potential binding sites of miRNA-584-5p and the 3’-untranslated region of RUNX family transcription factor 2 (RUNX2); B: Dual luciferase reporter gene assay; C: Quantitative polymerase chain reaction determination of RUNX2 expression; D: Western blot determination of RUNX2 protein expression. One-way ANOVA and t tests were used to demonstrate differences in RUNX2 responses between the miR584-5p mimic and negative control groups. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. RUNX2: RUNX family transcription factor 2; NC: Negative control; wt: Wild type; mut: Mutant; miRNA: MicroRNA.
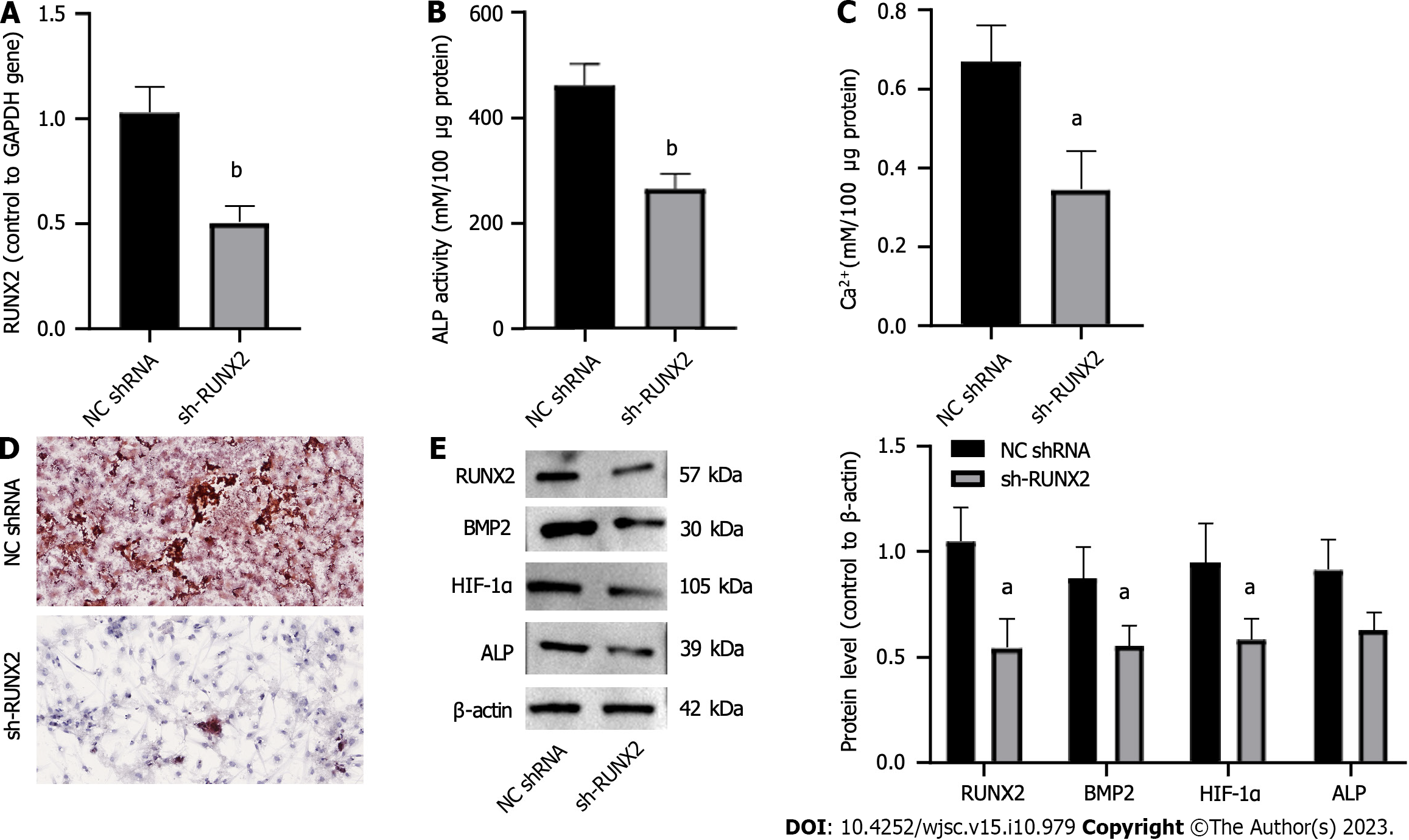
Figure 4 Downregulation of RUNX family transcription factor 2 inhibits the osteogenic differentiation of periosteal stem cells induced by hypoxia.
A: RUNX family transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) expression; B: Alkaline phosphatase activity; C: Intracellular calcium ion level; D: Alizarin red S staining chelated Ca2+ form an orange-red complex; E: Osteogenic differentiation-related protein expression. One-way ANOVA and t tests were used to demonstrate differences between the sh-RUNX2 and normal control shRNA groups. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; RUNX2: RUNX family transcription factor 2; BMP2: Bone morphogenetic protein 2; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1; shRNA: Small hairpin RNA.
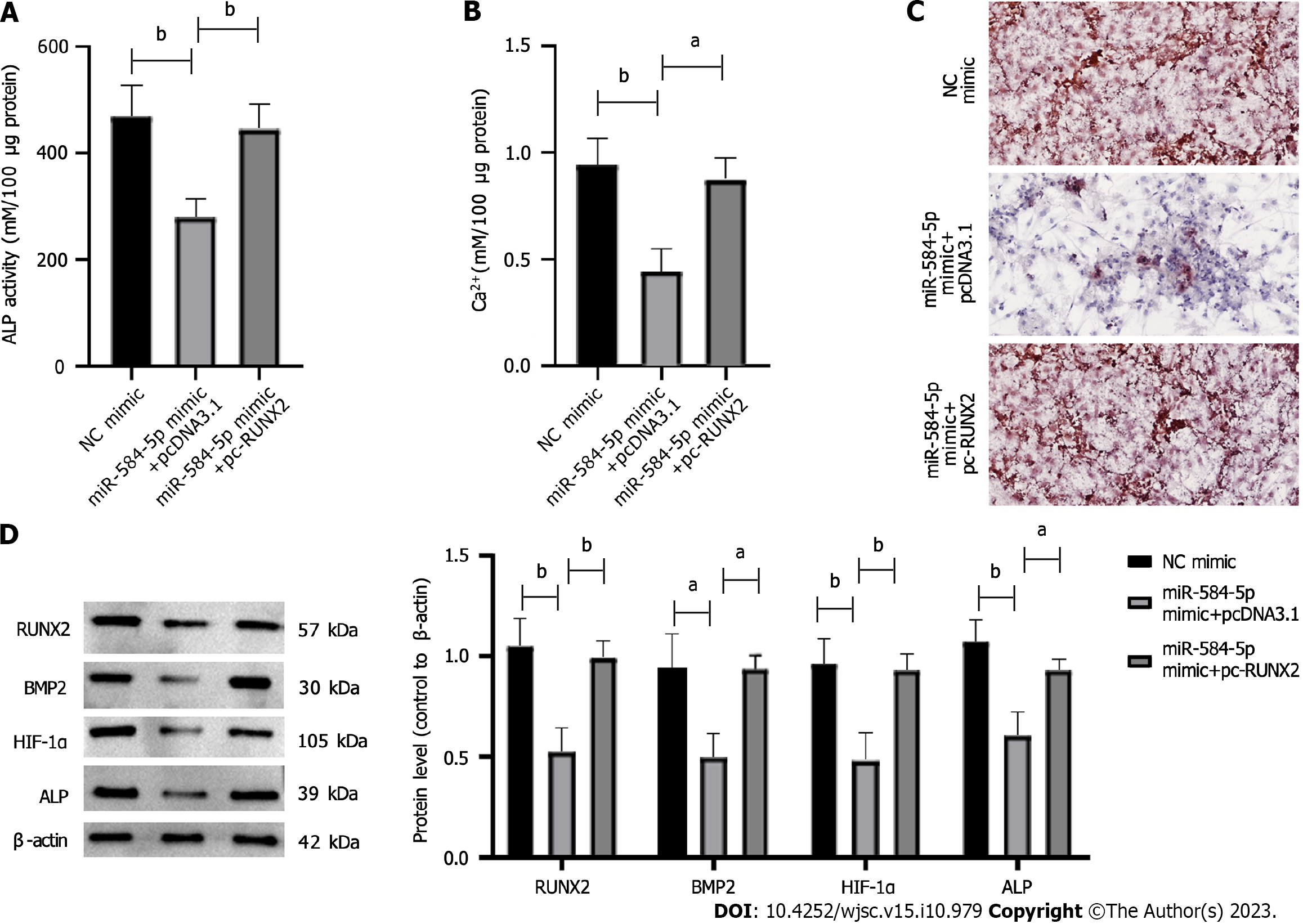
Figure 5 MiRNA-584-5p regulates hypoxia-induced osteogenic differentiation of periosteal stem cells by targeting RUNX family transcription factor 2.
A: Alkaline phosphatase activity; B: Intracellular calcium ion level; C: Alizarin red S staining chelated Ca2+ form an orange-red complex; D: Osteogenic differentiation-related protein expression. One-way ANOVA and t tests were used to demonstrate differences between the miR-581-5p mimic + pcDNA3.1-, NC mimic-, and miR-584-59 mimic + pc-RUNX family transcription factor 2-expressing constructs. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; RUNX2: RUNX family transcription factor 2; BMP2: Bone morphogenetic protein 2; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1; miR: MicroRNA; NC: Negative control.
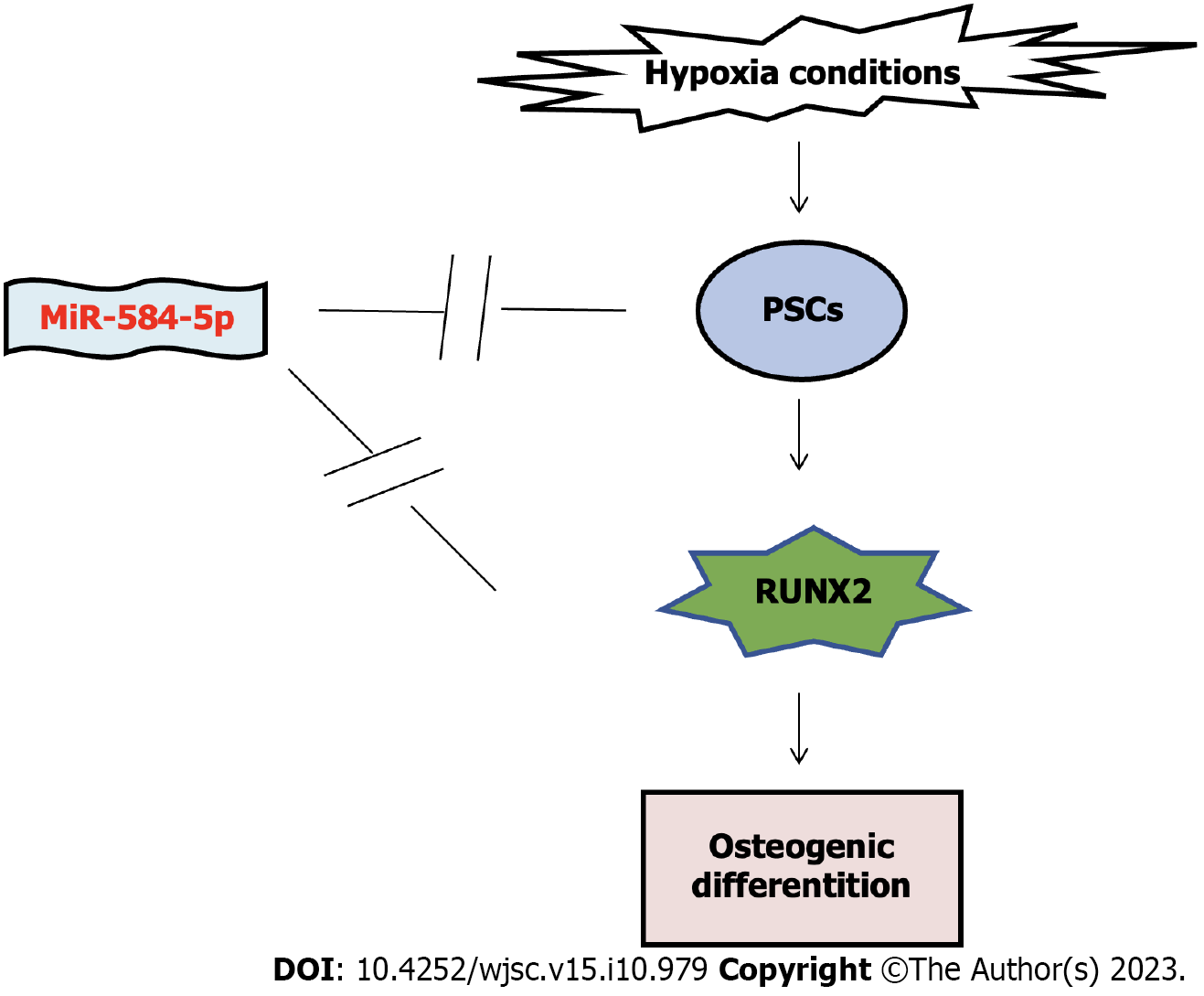
Figure 6 The interregulation of microRNA-584-5p/RUNX family transcription factor 2 on hypoxia-induced periosteal stem cell osteogenic differentiation.
The hypoxic environment induces periosteal stem cells to undergo osteogenic differentiation by activating the RUNX family transcription factor 2 (RUNX2)-related pathway; however, miR-584-5p overexpression can inhibit osteogenic differentiation by downregulating RUNX2 expression. PSC: Periosteal stem cell.
- Citation: Lu JJ, Shi XJ, Fu Q, Li YC, Zhu L, Lu N. MicroRNA-584-5p/RUNX family transcription factor 2 axis mediates hypoxia-induced osteogenic differentiation of periosteal stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(10): 979-988
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i10/979.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i10.979