Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Jan 26, 2023; 15(1): 1-15
Published online Jan 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i1.1
Published online Jan 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i1.1
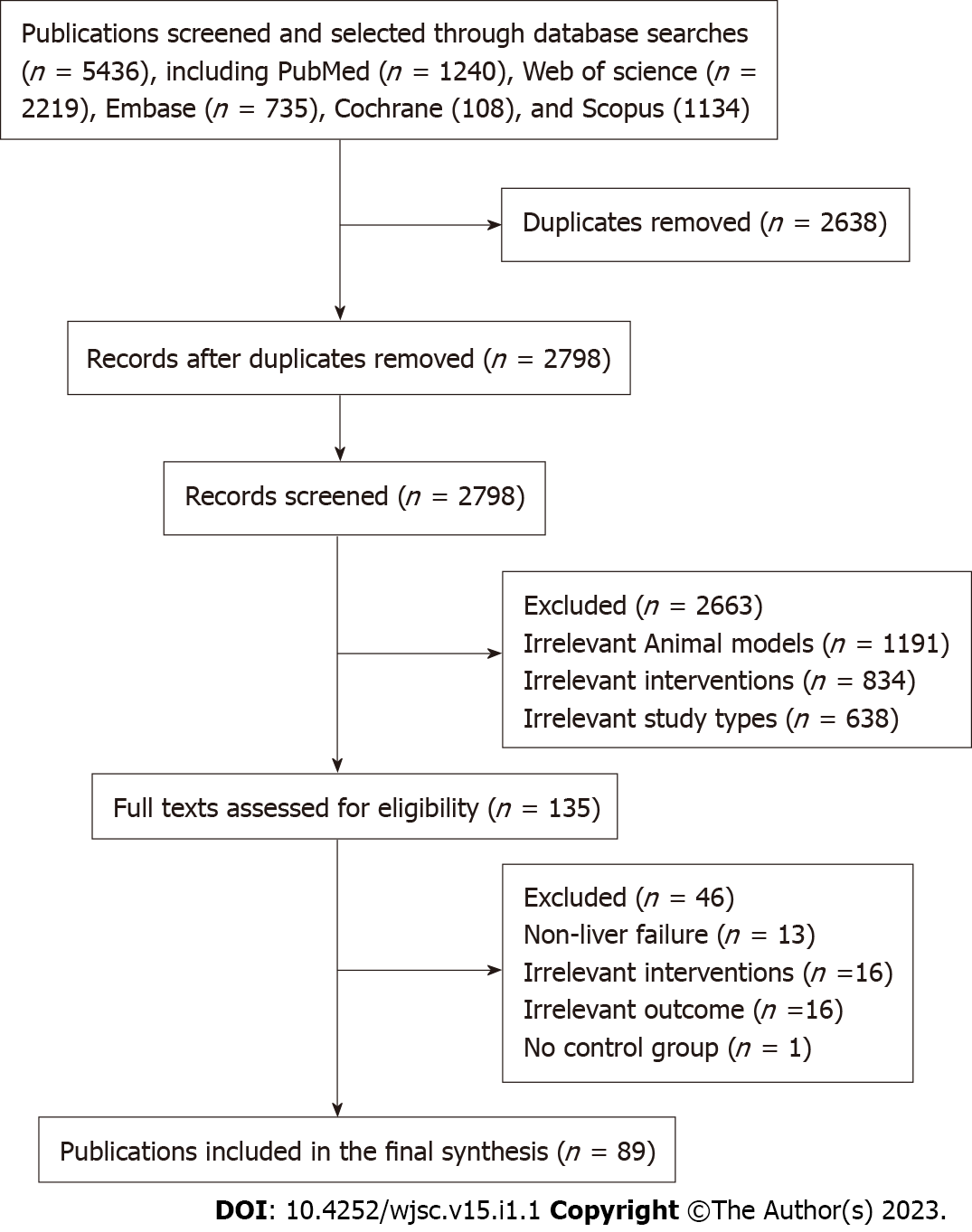
Figure 1 Flow diagram for study selection.
A total of 5436 articles were obtained from 5 databases. After removing repetitive articles and those that did not meet the inclusion criteria by reading the title, abstract, and full text, 89 articles were finally included.
Figure 2 Risk of bias assessment results.
10 items in 6 aspects including selection bias, performance bias, detection bias, attrition bias, reporting bias, and other biases were used to evaluate the quality of included studies. The risk of bias of all studies about a certain item is expressed as a percentage.
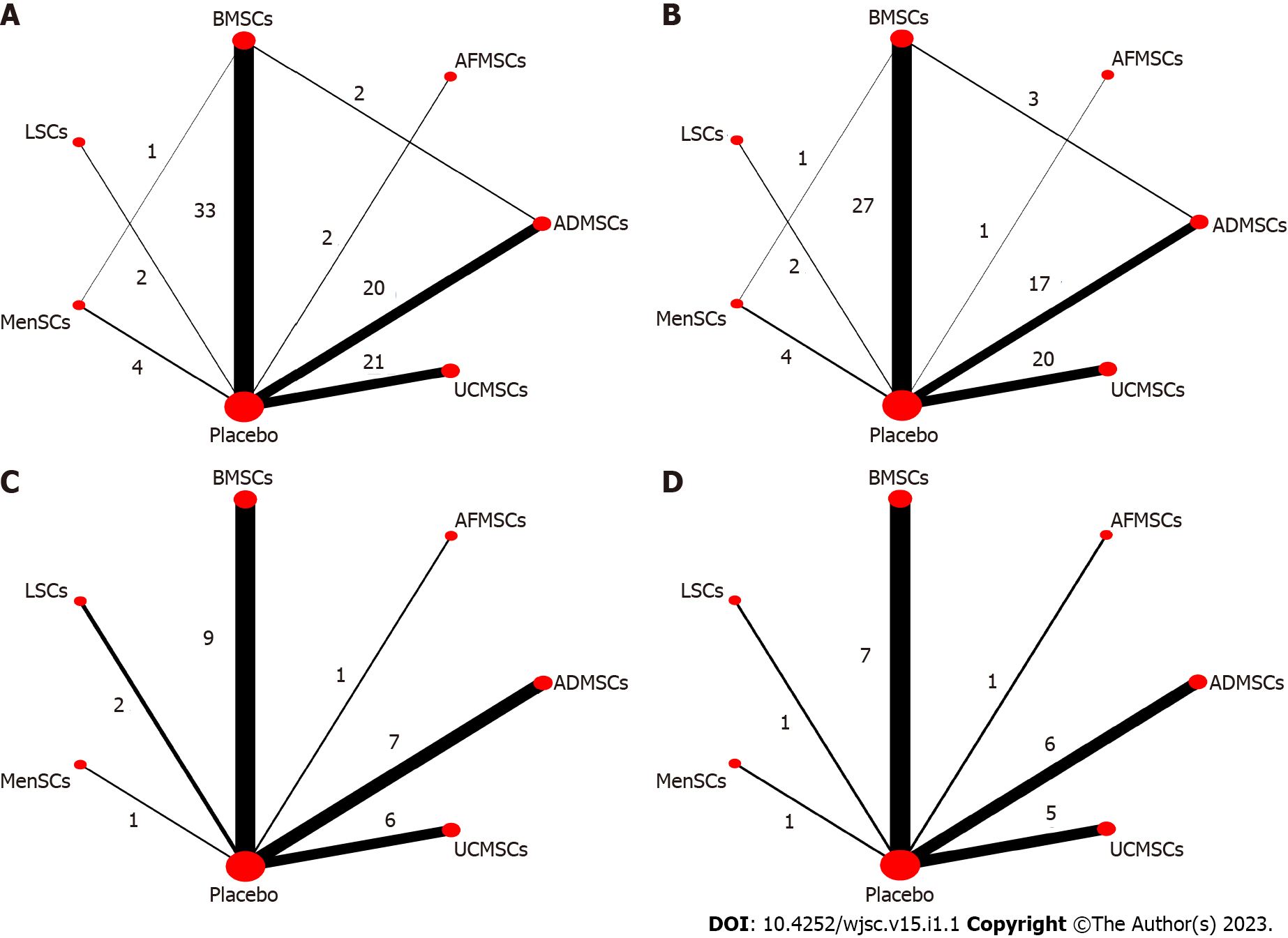
Figure 3 Evidence network diagram.
Circle size represents sample size involved, thickness of the line segment represents the number of studies involving both interventions. A: Alanine aminotransferase; B: Aspartate aminotransferase; C: Tumor necrosis factor-α; D: Interleukin-6. BMSCs: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; LSCs: Liver stem cells; MenSCs: Menstrual blood-derived stem cells; AFMSCs: Amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells; ADMSCs: Adipose mesenchymal stem cells; UCMSCs: Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.
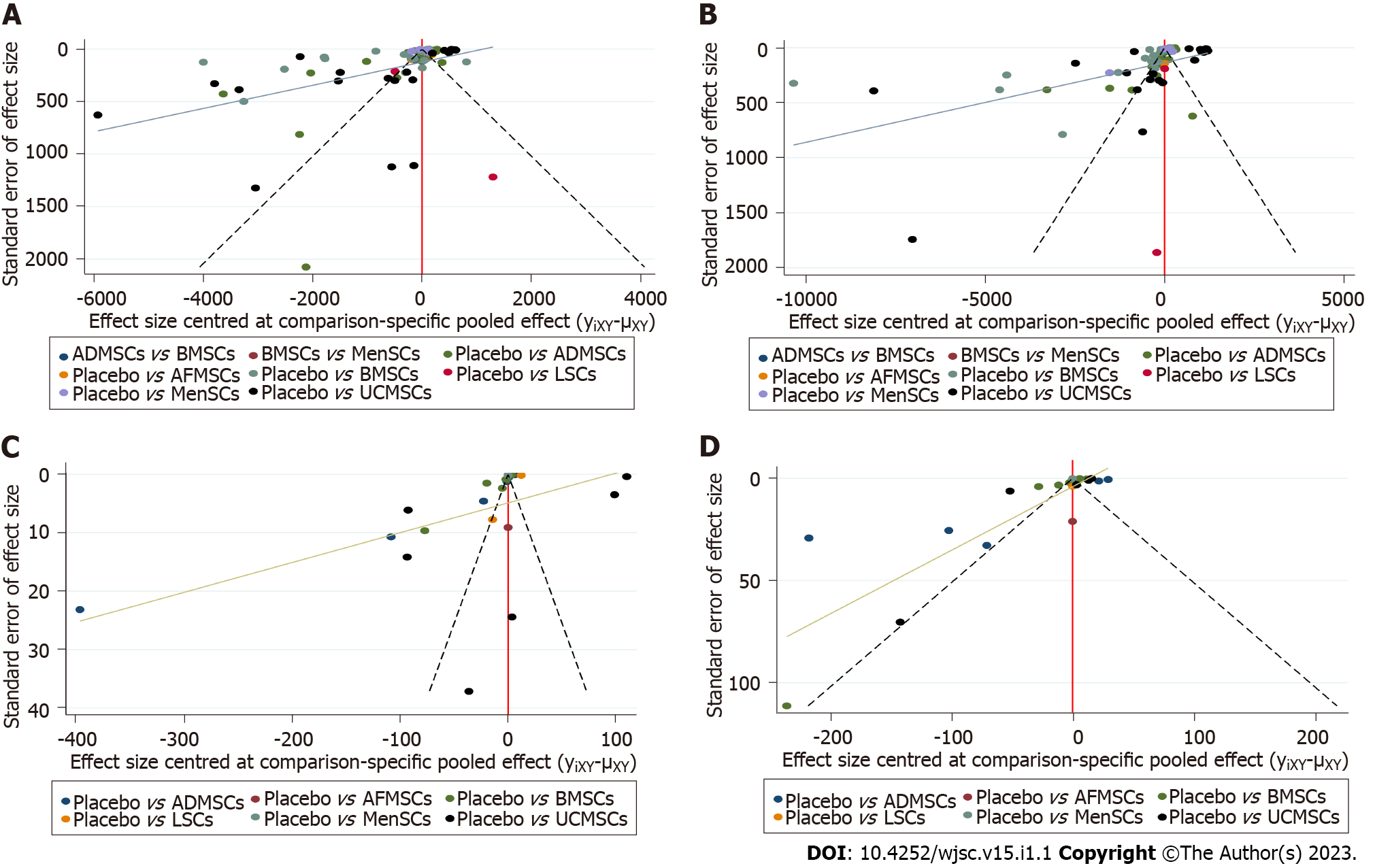
Figure 4 The comparison-correction funnel plot.
The dotted lines on both sides of the funnel plot represent 95% confidence intervals, and each point represents a study. If each point falls within the dotted line and is symmetrically distributed on both sides of the vertical line, there is no publication bias. On the contrary, it indicates the possibility of publication bias. A: Alanine aminotransferase; B: Aspartate aminotransferase; C: Tumor necrosis factor-α; D: Interleukin-6. BMSCs: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; LSCs: Liver stem cells; MenSCs: Menstrual blood-derived stem cells; AFMSCs: Amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells; ADMSCs: Adipose mesenchymal stem cells; UCMSCs: Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.
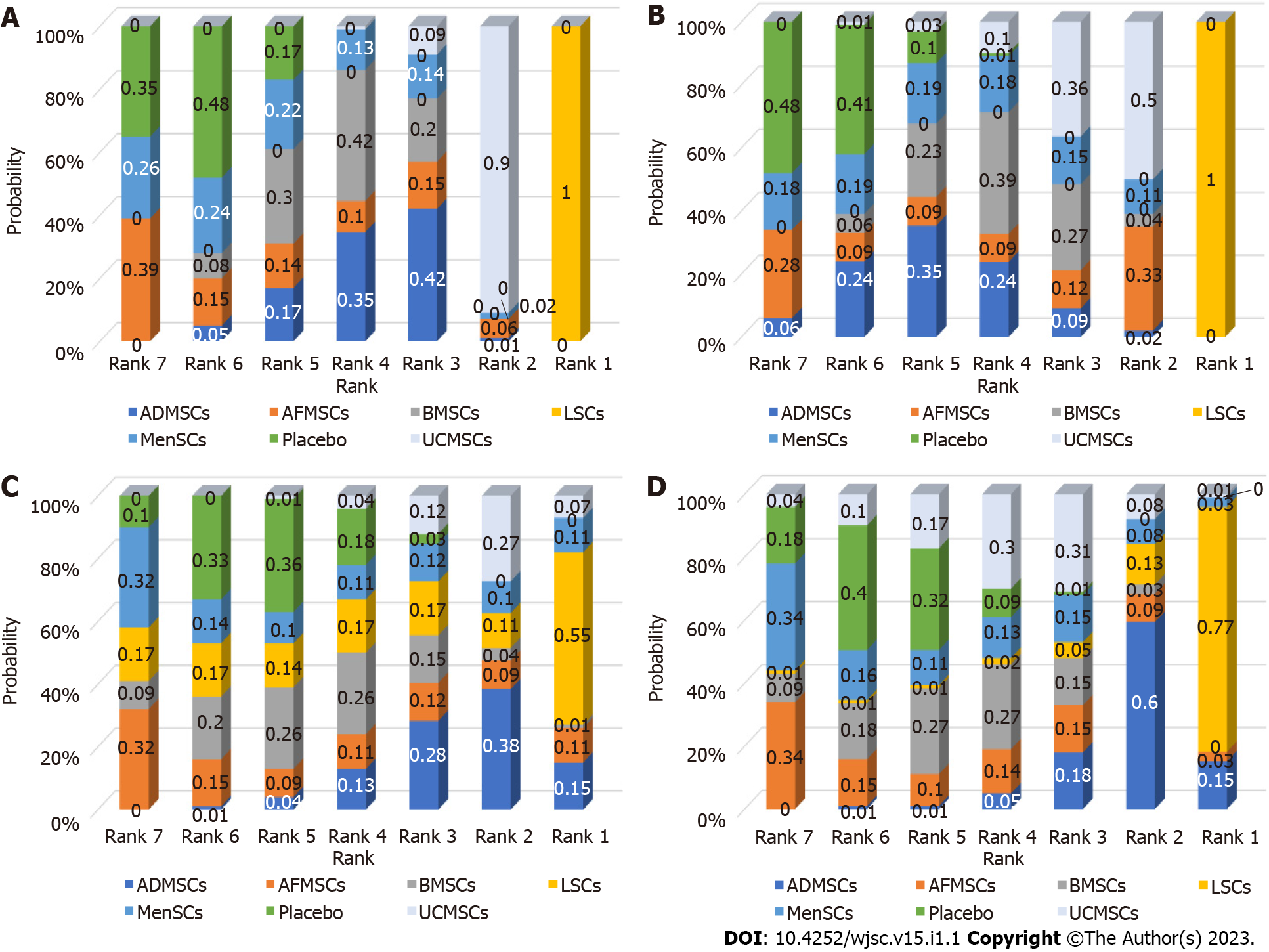
Figure 5 Ranking results.
The higher the probability of being ranked first, the better the treatment effect of that intervention. A: Alanine aminotransferase; B: Aspartate aminotransferase; C: Tumor necrosis factor-α; D: Interleukin-6. BMSCs: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; LSCs: Liver stem cells; MenSCs: Menstrual blood-derived stem cells; AFMSCs: Amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells; ADMSCs: Adipose mesenchymal stem cells; UCMSCs: Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.
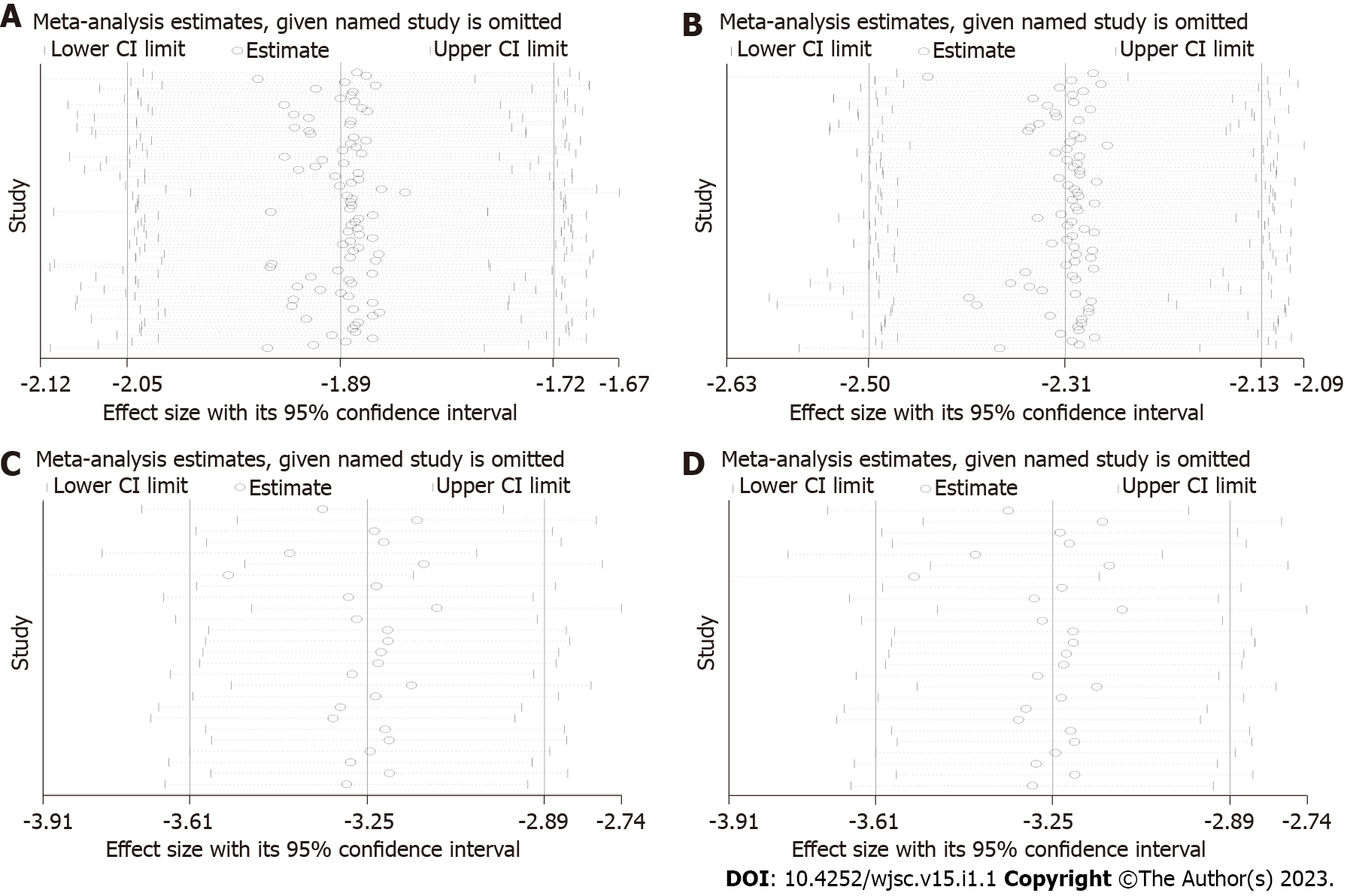
Figure 6 Results of sensitivity analysis.
After excluding a certain study, the remaining studies were combined for analysis to see if there were any changes in the effect sizes. If the results of the remaining studies were basically the same as the previous total combined results (the range of the confidence interval did not change significantly), the results of the meta-analysis were considered to be reliable. Conversely, the results of the meta-analysis were considered unreliable. A: Alanine aminotransferase; B: Aspartate aminotransferase; C: Tumor necrosis factor-α; D: Interleukin-6. CI: Confidence interval.
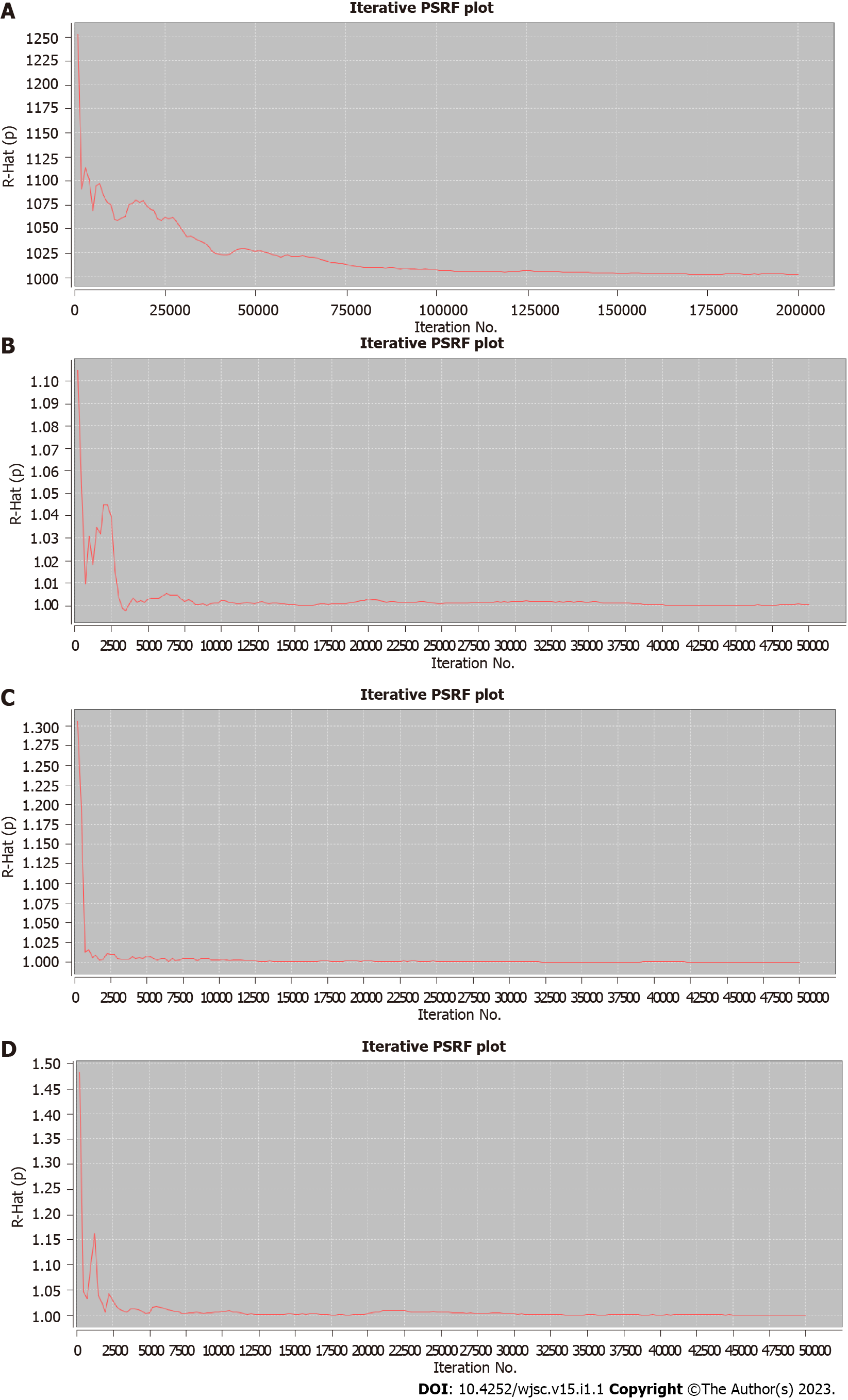
Figure 7 Results of potential false positive factor.
After a certain number of iterations, the curve finally approaches 1, which indicates that the results of the network meta-analysis have good robustness and reliability. A: Alanine aminotransferase; B: Aspartate aminotransferase; C: Tumor necrosis factor-α; D: Interleukin-6. PSRF: Potential false positive factor.
- Citation: Ma JF, Gao JP, Shao ZW. Acute liver failure: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of optimal type of stem cells in animal models. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(1): 1-15
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i1.1