Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2021; 13(7): 795-824
Published online Jul 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i7.795
Published online Jul 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i7.795
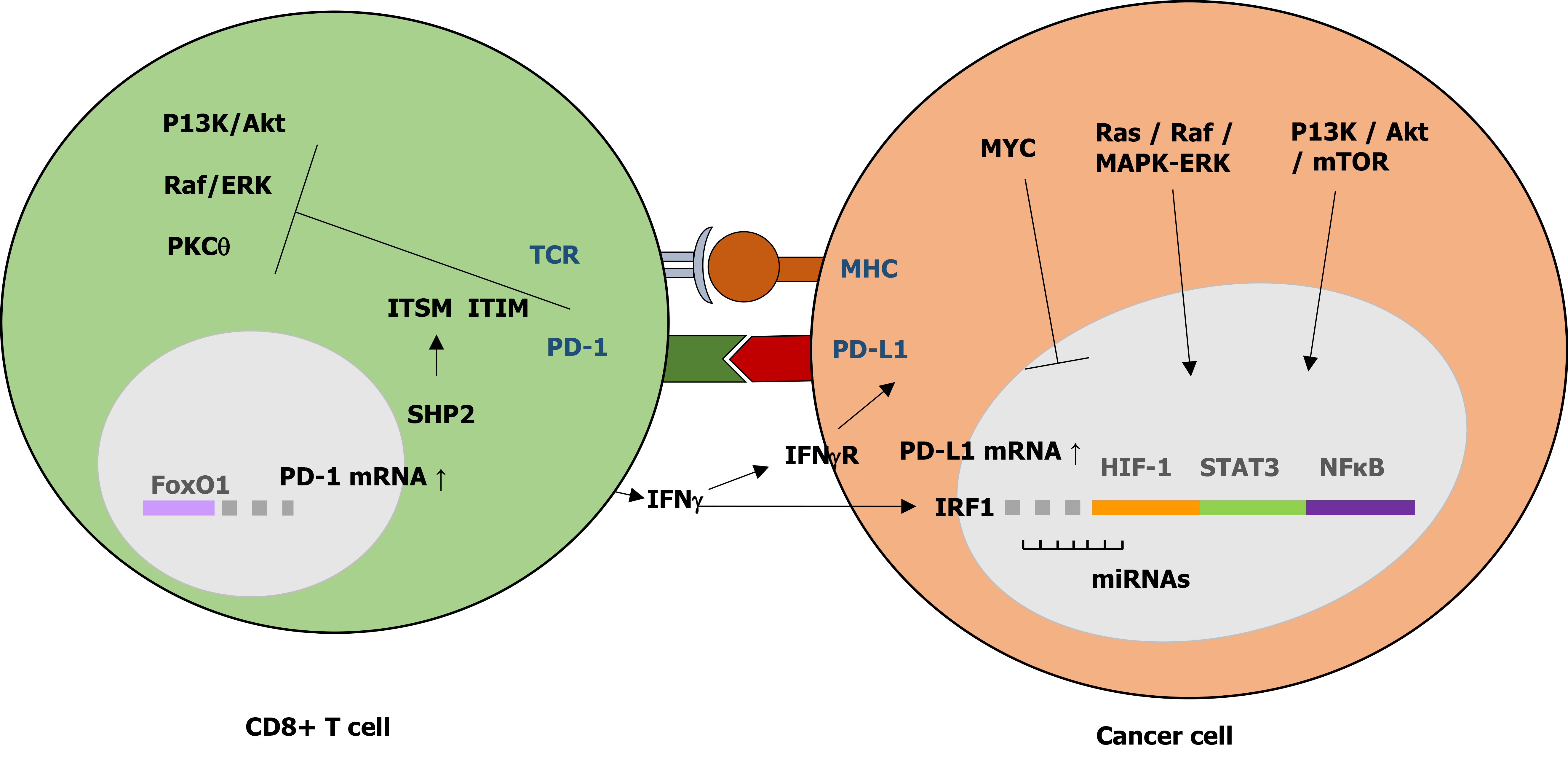
Figure 1 Regulatory mechanism of programmed death-1/programmed death ligand 1 signaling in cancer.
The interaction between programmed death-1 and programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) leads to the inhibition of T cell functional activation. PD-L1 expression in cancer cells is regulated by aberrant oncogenic pathways. PD-1: Programmed death-1; PD-L1: Programmed death ligand 1; TCR: T cell receptor; ITSM: Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif; ITIM: Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif; IRF: Interferon regulatory factor.
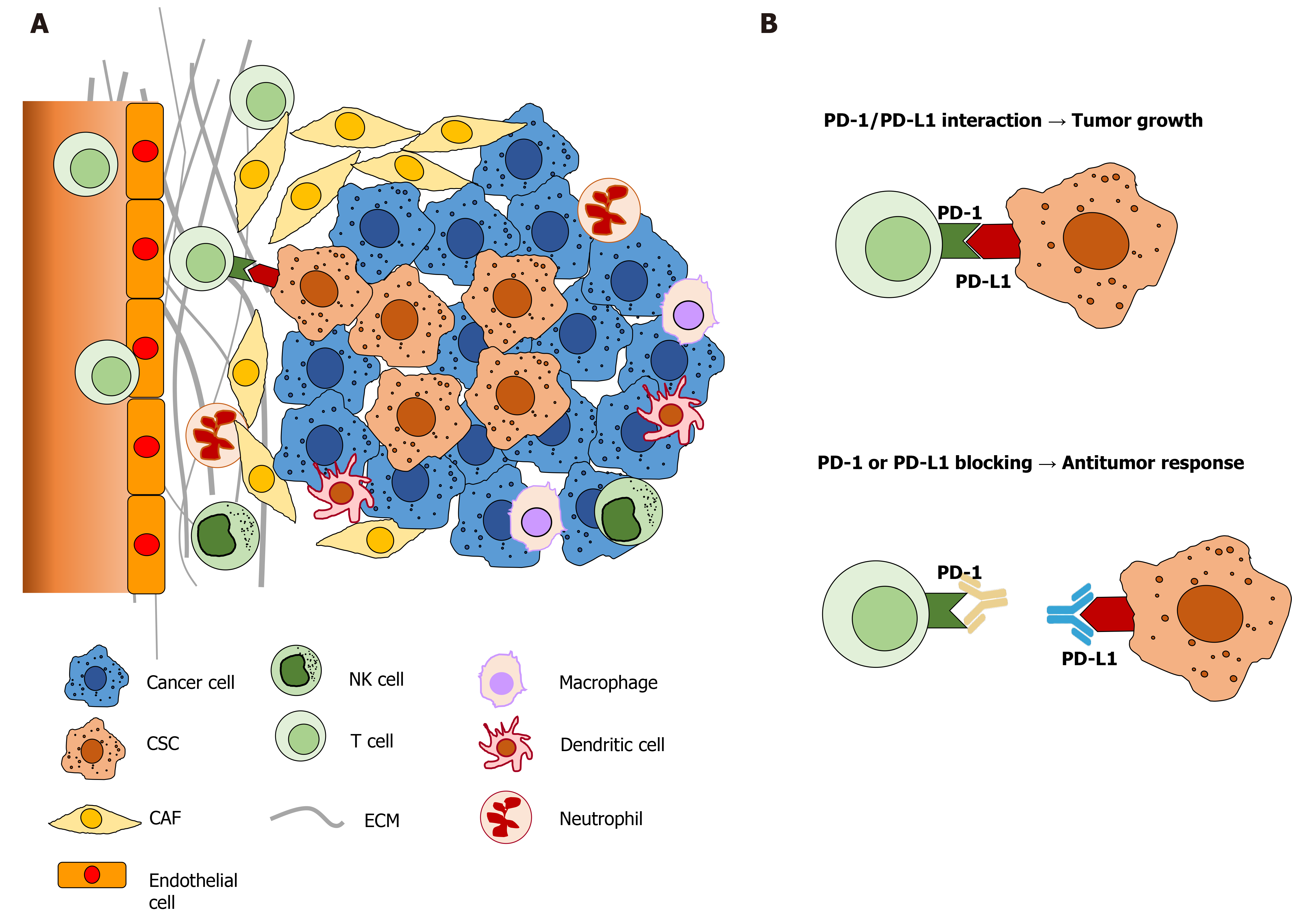
Figure 2 The complexity of hepatocellular carcinoma and its microenvironment.
A: Hepatocellular carcinoma and its tumor microenvironment are composed of various cell populations, including differentiated cancer cells, cancer stem cells, cancer associated fibroblasts, immune and endothelial cells; B: Programmed death-1 and programmed death ligand 1 interaction and inhibition by neutralizing antibodies in tumor growth. PD-1: Programmed death-1; PD-L1: Programmed death ligand 1; CSC: Cancer stem cells; CAF: Cancer associated fibroblast; ECM: Extracellular matrix; NK: Natural killer.
- Citation: Sukowati CHC, El-Khobar KE, Tiribelli C. Immunotherapy against programmed death-1/programmed death ligand 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma: Importance of molecular variations, cellular heterogeneity, and cancer stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(7): 795-824
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i7/795.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i7.795