Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2021; 13(7): 776-794
Published online Jul 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i7.776
Published online Jul 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i7.776
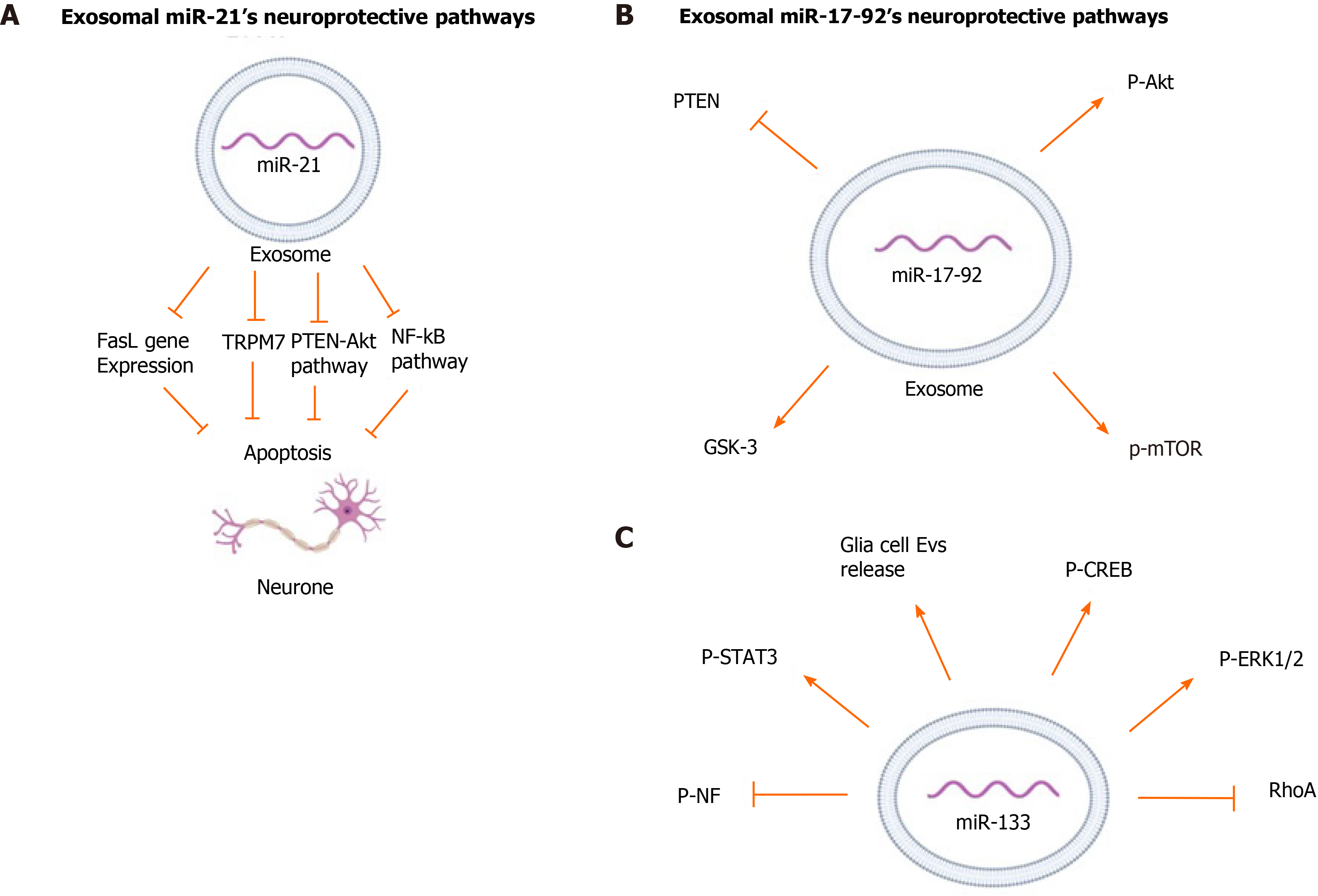
Figure 1 Neuroprotective pathways regulated by mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived exosomes.
A: Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived exosomal miR-21; B: Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived exosomal miR-17-92; C: Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived exosomal miR-133.
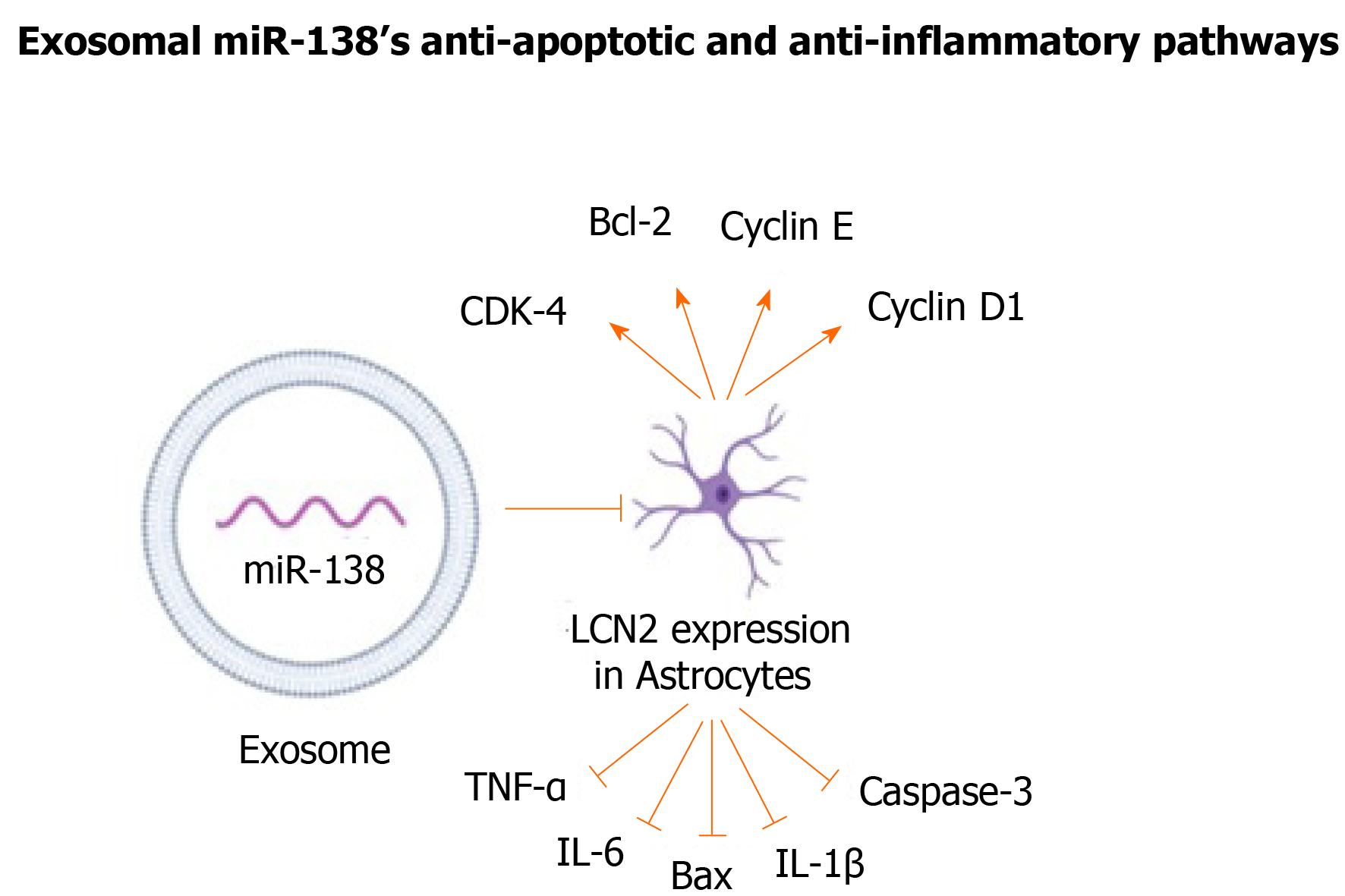
Figure 2 Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived exosomes overexpressing miR-138 repressed inflammatory and pro-apoptotic factors, and increased anti-apoptotic and cell cycle markers.
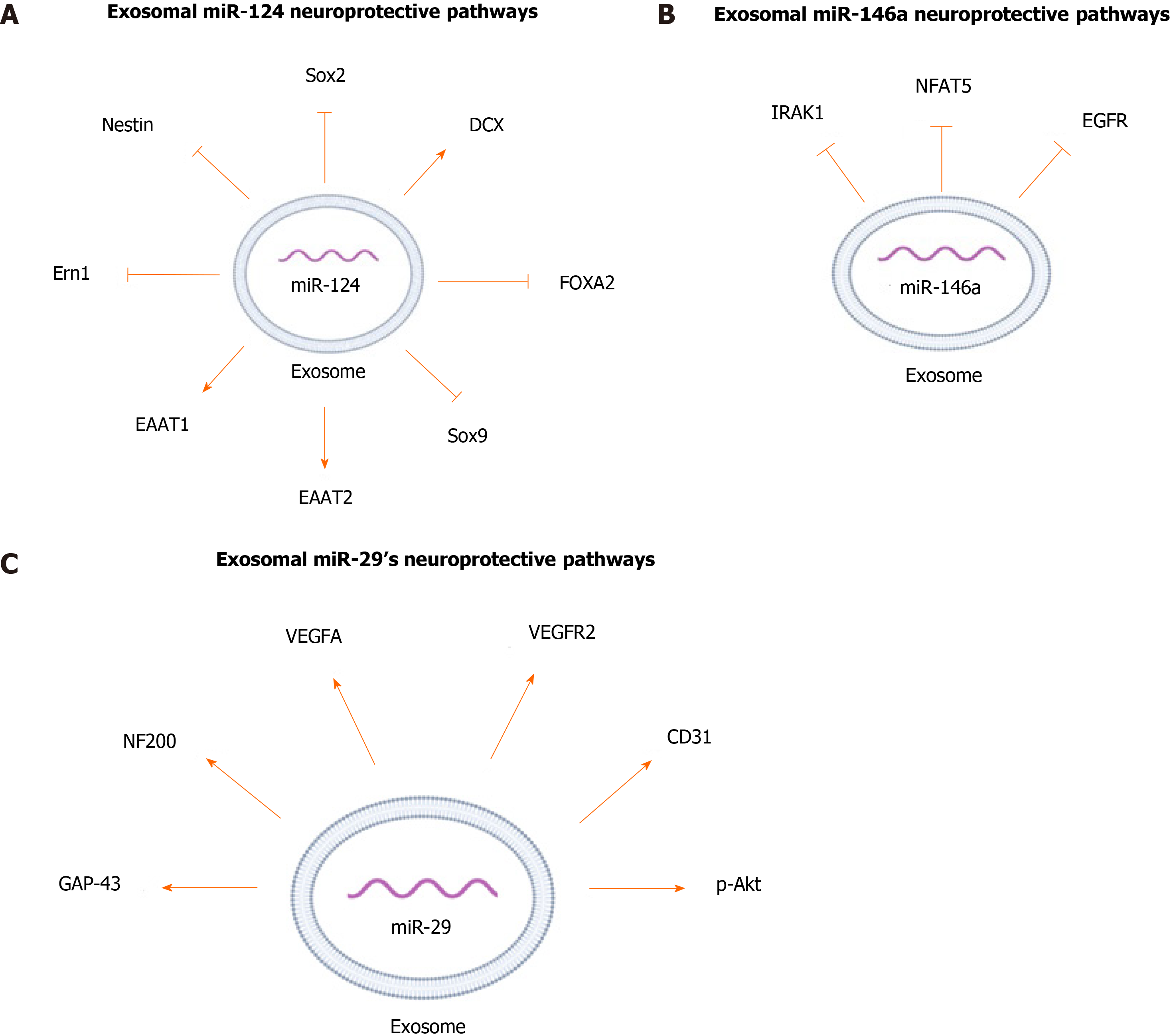
Figure 3 Neuroprotective pathways regulated by exosomal microRNAs.
A: Exosomal miR-124; B: Exosomal miR-146a; C: Exosomal miR-29.
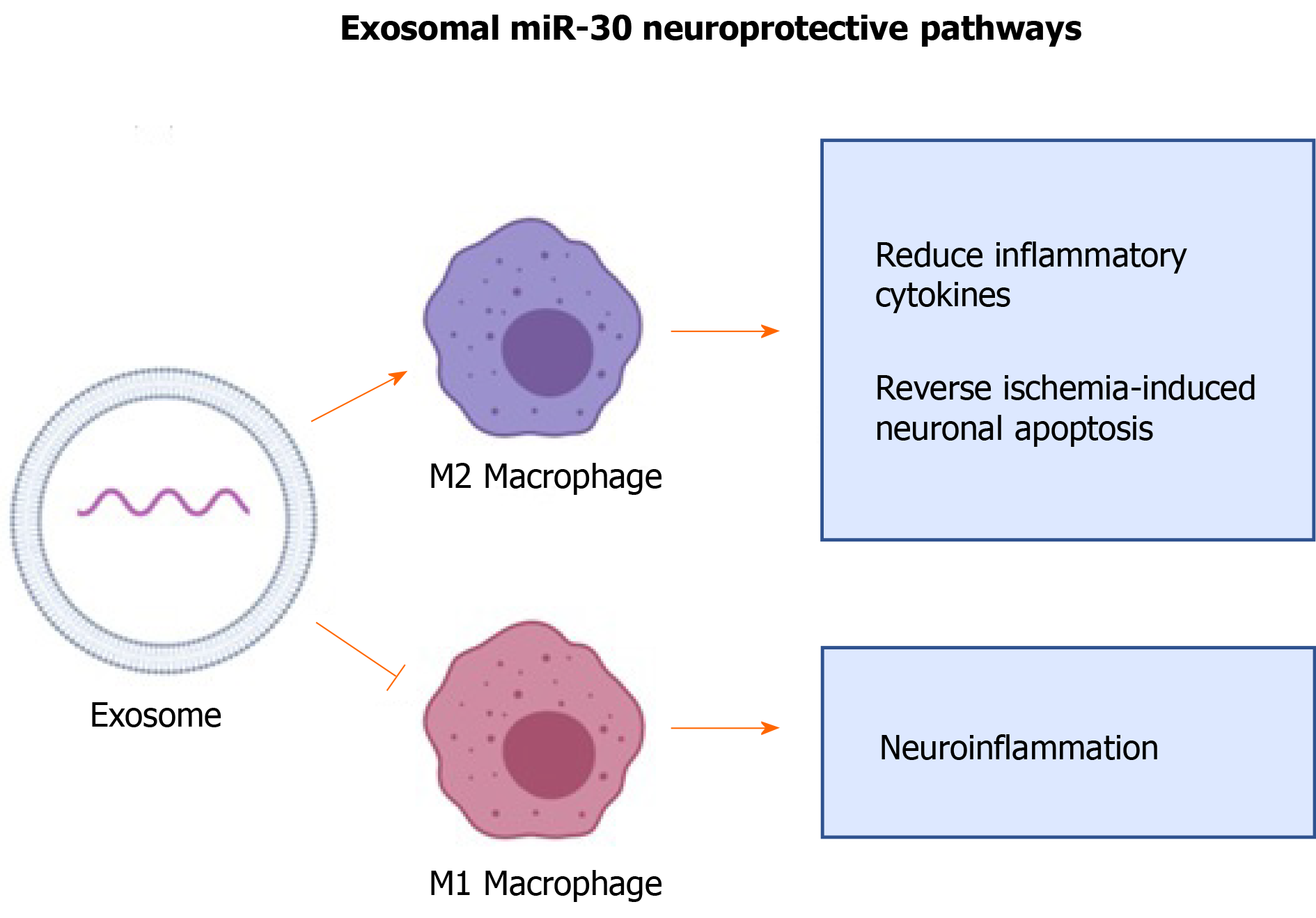
Figure 4 Exosomal miR-30 regulated autophagy-mediated brain injury by promoting anti-inflammatory (M2) macrophage polarization and suppressing pro-inflammatory macrophages (M1) polarization.
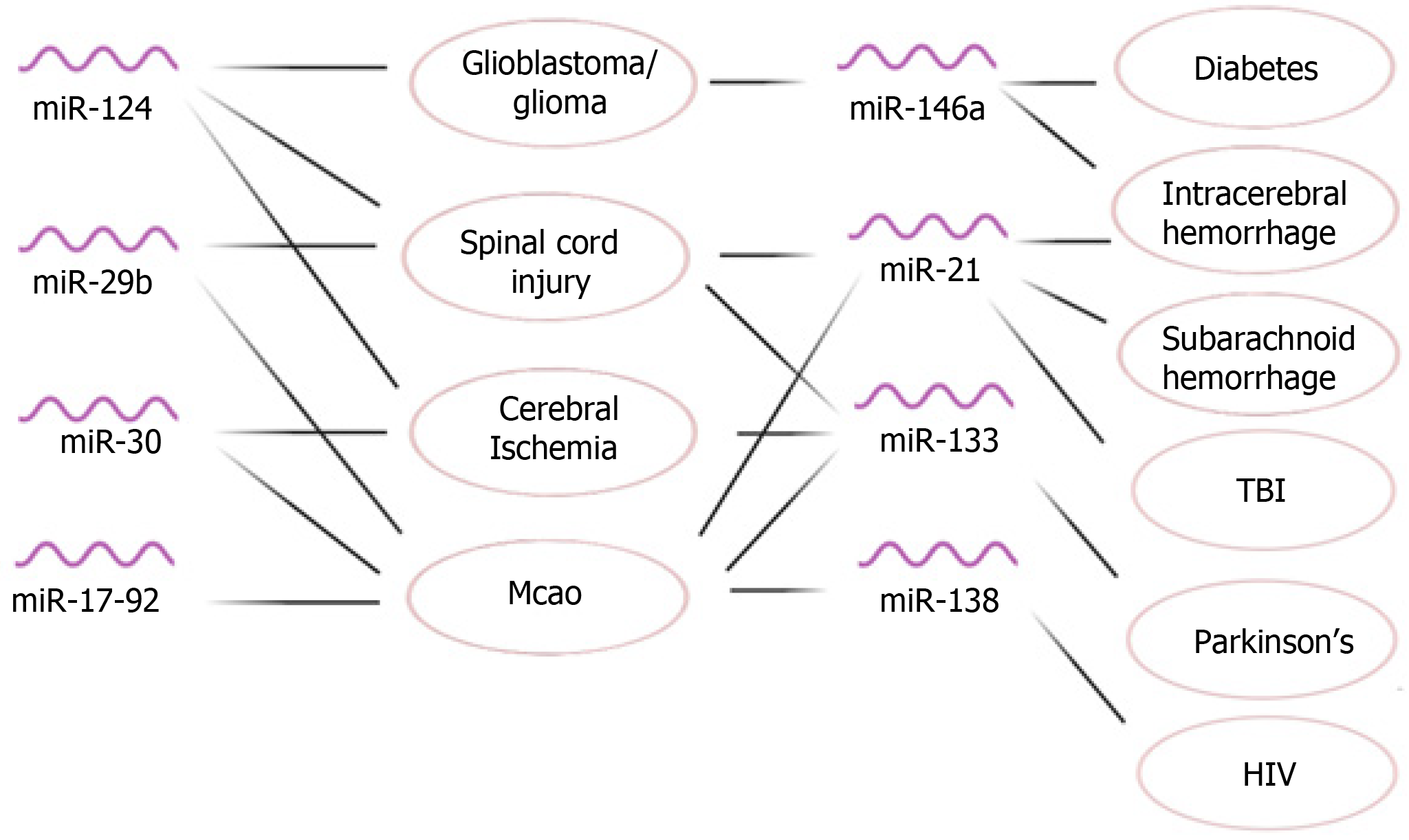
Figure 5 Neuroprotective effects and therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived exosomal miRNAs for neurological disorder disease models.
- Citation: Nasirishargh A, Kumar P, Ramasubramanian L, Clark K, Hao D, Lazar SV, Wang A. Exosomal microRNAs from mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: Biology and applications in neuroprotection. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(7): 776-794
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i7/776.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i7.776