Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2021; 13(7): 670-684
Published online Jul 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i7.670
Published online Jul 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i7.670
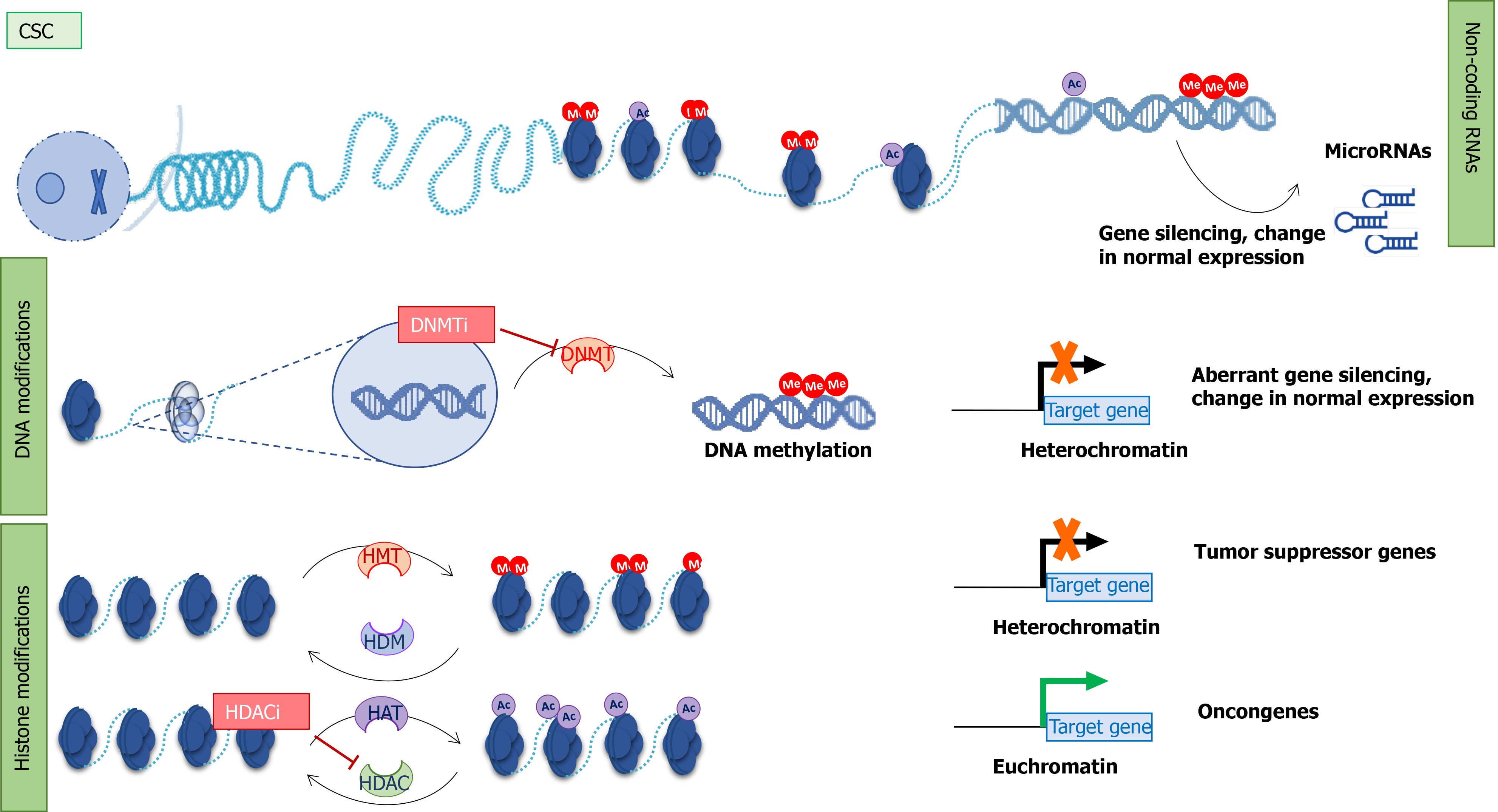
Figure 1 Epigenetic mechanism in cancer stem cells and therapeutical approaches.
Epigenetic modifiers: Non-coding RNA, DNA methylation, and histone modifications. Non-coding RNAs (microRNAs) regulate gene expression. microRNA expression can be regulated by other epigenetic modifiers. DNA methyltransferases add a methyl group to cytosine in the DNA sequence. This results in aberrant gene silencing and changes in normal gene expression. Posttranslational modifications of histone proteins (acetylation in purple and methylation in red) can affect chromatin structure. Histone enzymes add/remove acetyl or methyl groups. Histone deacetylases and DNMTs are the main targets of epigenetic inhibitors. CSC: Cancer stem cell; Me: Methyl group; Ac: Acetyl group; DNMT: DNA methyltransferases; HDAC: Histone deacetylases; HAT: Histone acetyltransferases; HMT: Histone methyltransferases; HDM: Histone demethylases; DNMTi: DNA methyltransferases inhibitors; HDACi: Histone deacetylases inhibitors.
- Citation: Abballe L, Miele E. Epigenetic modulators for brain cancer stem cells: Implications for anticancer treatment. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(7): 670-684
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i7/670.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i7.670