Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2021; 13(10): 1564-1579
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1564
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1564
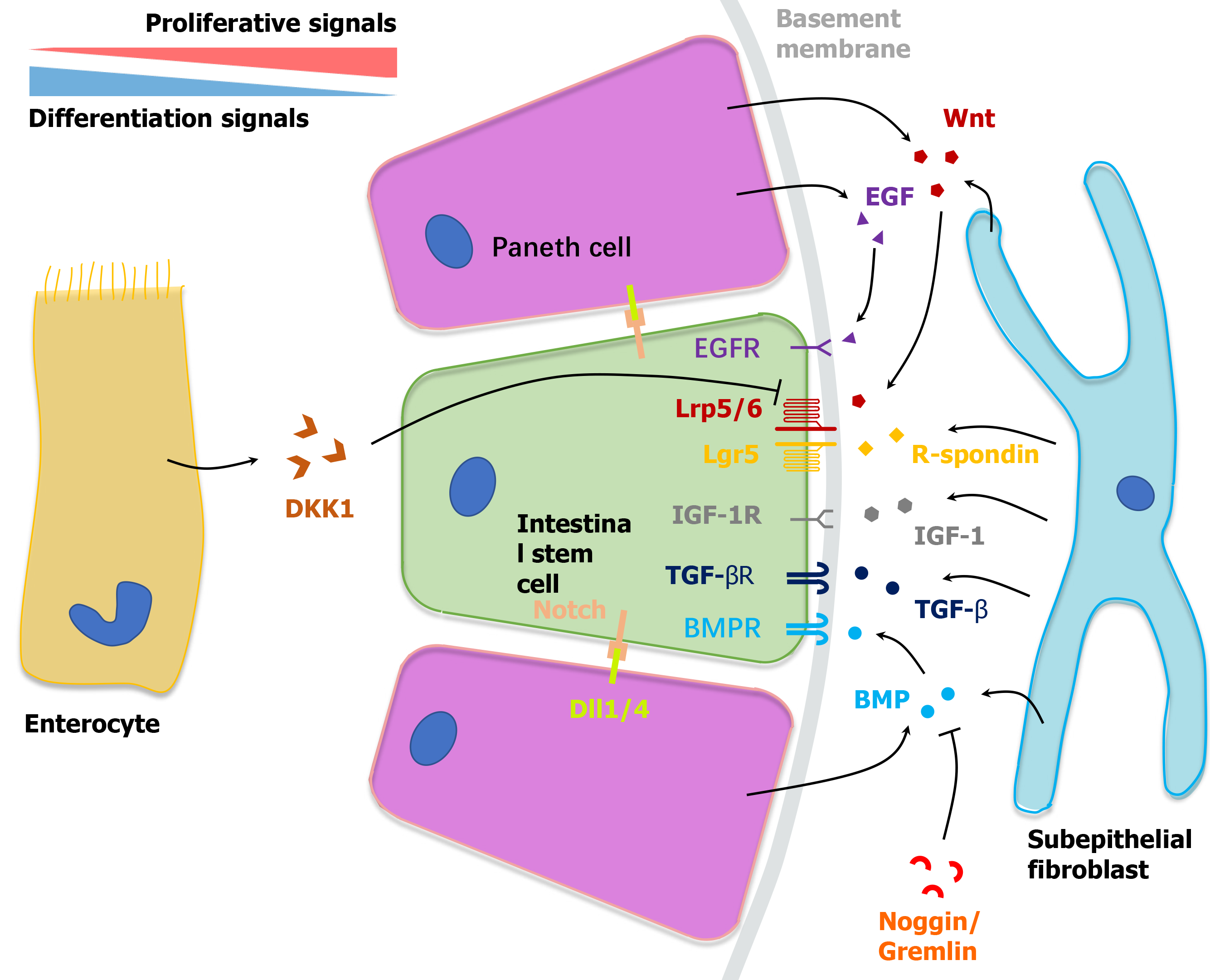
Figure 1 Niche microenvironment of intestinal stem cells at the crypt bottom.
Bidirectional gradients of biochemical signals established by neighboring cells including Paneth cells, subepithelial cells and enterocytes regulate the self-renewal and differentiation of intestinal stem cells synergistically. TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; TGF-α: transforming growth factor-α; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; IGF: insulin-like growth factor; BMPR: Bone morphogenetic protein receptor; BMP: Bone morphogenetic protein; DKK1: Dickkkopf-1; Dll1/4: Delta-like 1/4.
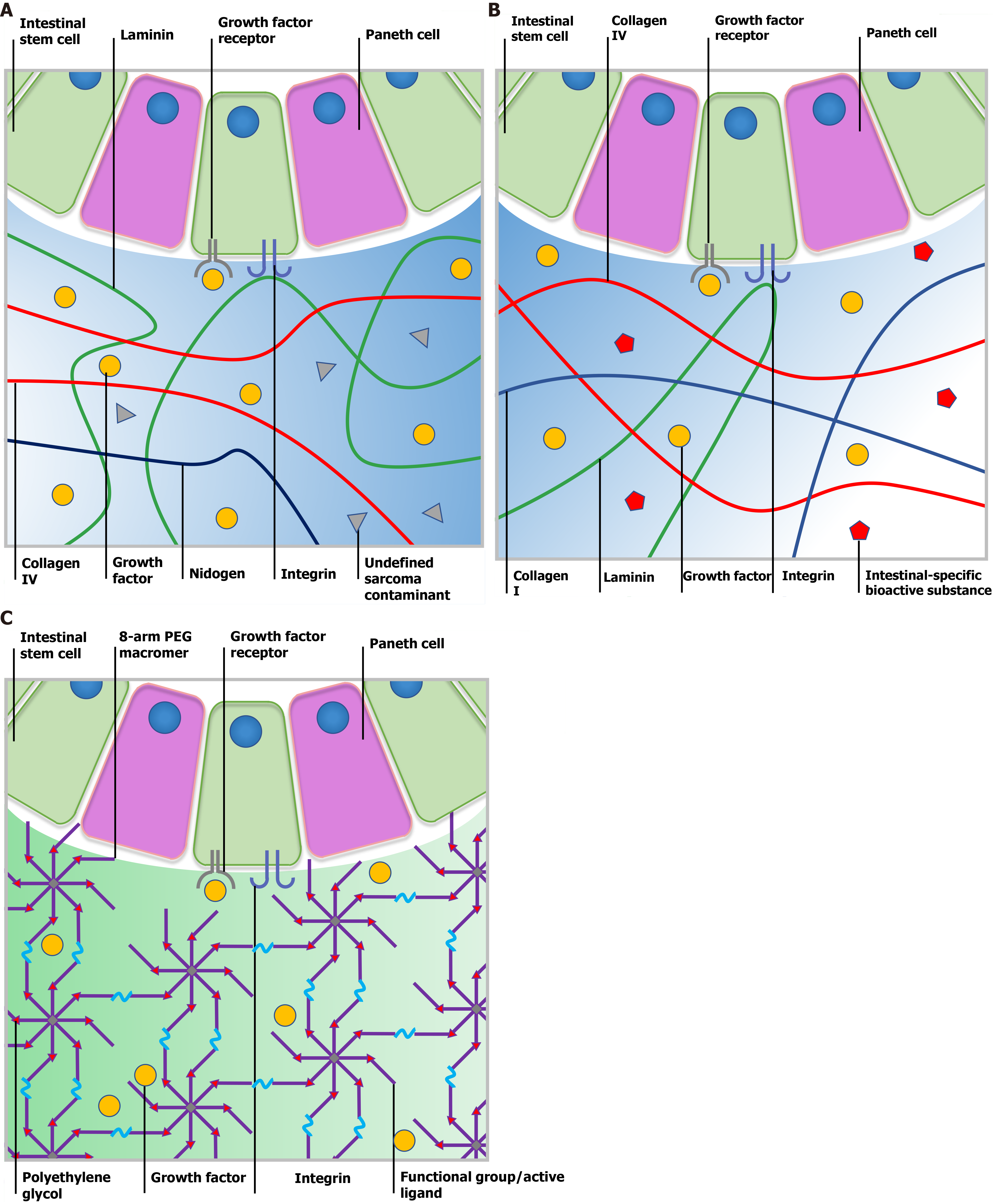
Figure 2 Comparison of Matrigel, decellularized extracellular matrix and a synthetic matrix.
A: Ill-defined Matrigel is variable in composition. Although certain bioactive factors exist, Matrigel still contains undefined contamination from the tumor microenvironment, which leads to low reproducibility and biosecurity; B: Submucosa-derived decellularized extracellular matrix (dECM) provides intestinal stem cells (ISCs) with a natural microenvironment closest to native tissue and the crypt niche. Tissue-specific bioactive substances could help maintain the physical phenotype of cultured ISCs. However, the composition of dECM may vary from batch to batch and be affected by the age, gender and health status of source animals; C: Polyethylene glycol is one of the most frequently used synthetic material for cell culture as it is bioinert and tunable. Following modification with diverse functional groups or active ligands, researchers can manipulate the physical and chemical parameters to further support organoid formation. PEG: Polyethylene glycol.
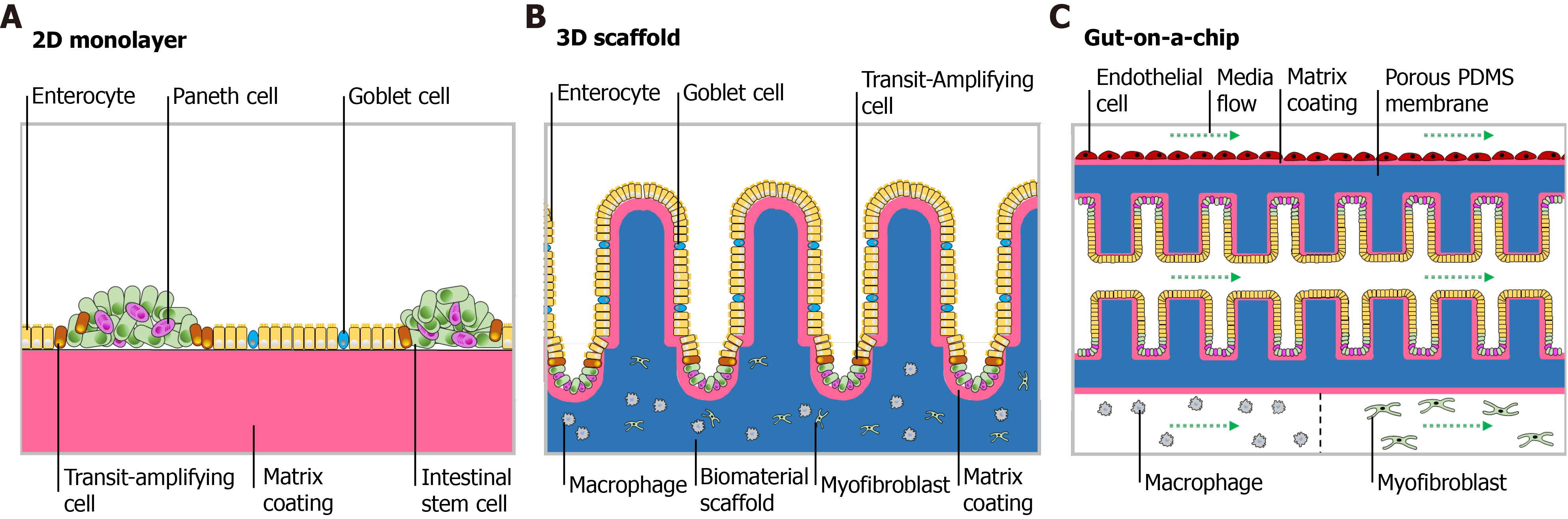
Figure 3 Multiform reconstitution of the intestinal stem cell niche.
A: On matrix coating with relatively high substrate stiffness, intestinal stem cells (ISCs) generate an epithelial monolayer that recapitulates polarized cell distribution and barrier function; B: Micropatterned scaffold with suitable extracellular matrix coating enables ISC self-renewal, differentiation and epithelial cell migration and resembles distinct crypt-villus or multilayer architecture; C: Gut-on-a-chip allows incorporation of vasculature and lymph-vessels into the organoid technique and provides an effective platform for high-throughput drug screening.
- Citation: Xu ZY, Huang JJ, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Wu XW, Ren JA. Current knowledge on the multiform reconstitution of intestinal stem cell niche. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(10): 1564-1579
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i10/1564.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1564