Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2021; 13(10): 1513-1529
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1513
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1513
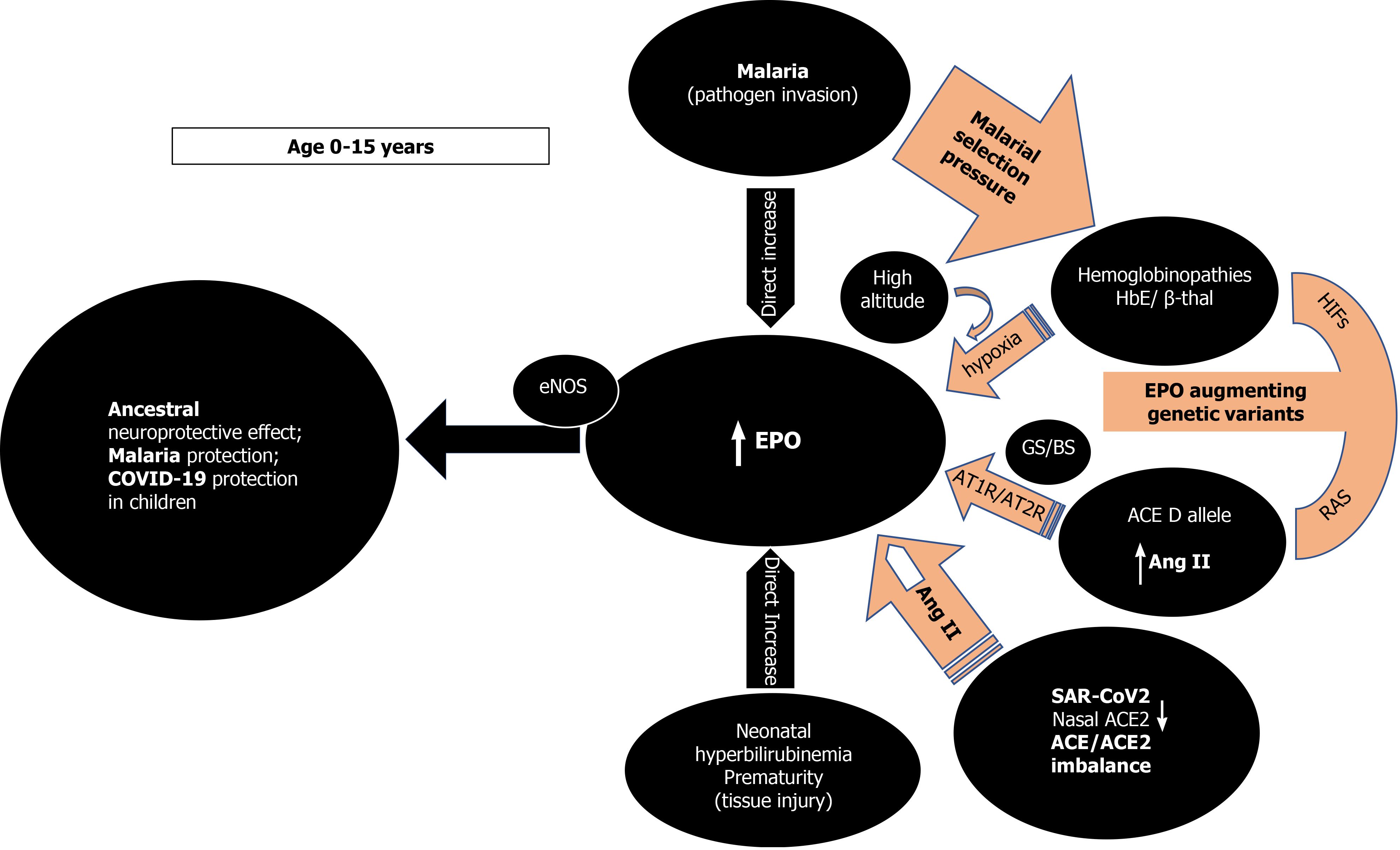
Figure 1 Age dependent erythropoietin secretion and effect of erythropoietin augmenting genetic determinants inducing ancestral neuroprotection, malaria protection, and possibly coronavirus disease 2019 protection in children.
ACE: Angiotensin converting enzyme; ACE2: Angiotensin converting enzyme 2; EPO: Erythropoietin; Ang II: Angiotensin II; β-thal: Beta thalassemia; GS/BS: Gitelman syndrome/ Bartter Syndrome; HIFs: hypoxia inducible factors; SARS-COV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2; COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019; RAS: Renin angiotensin system; AT1R: Ang II type 1 receptor; AT2R: Ang II type 2 receptor; eNOS: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase.
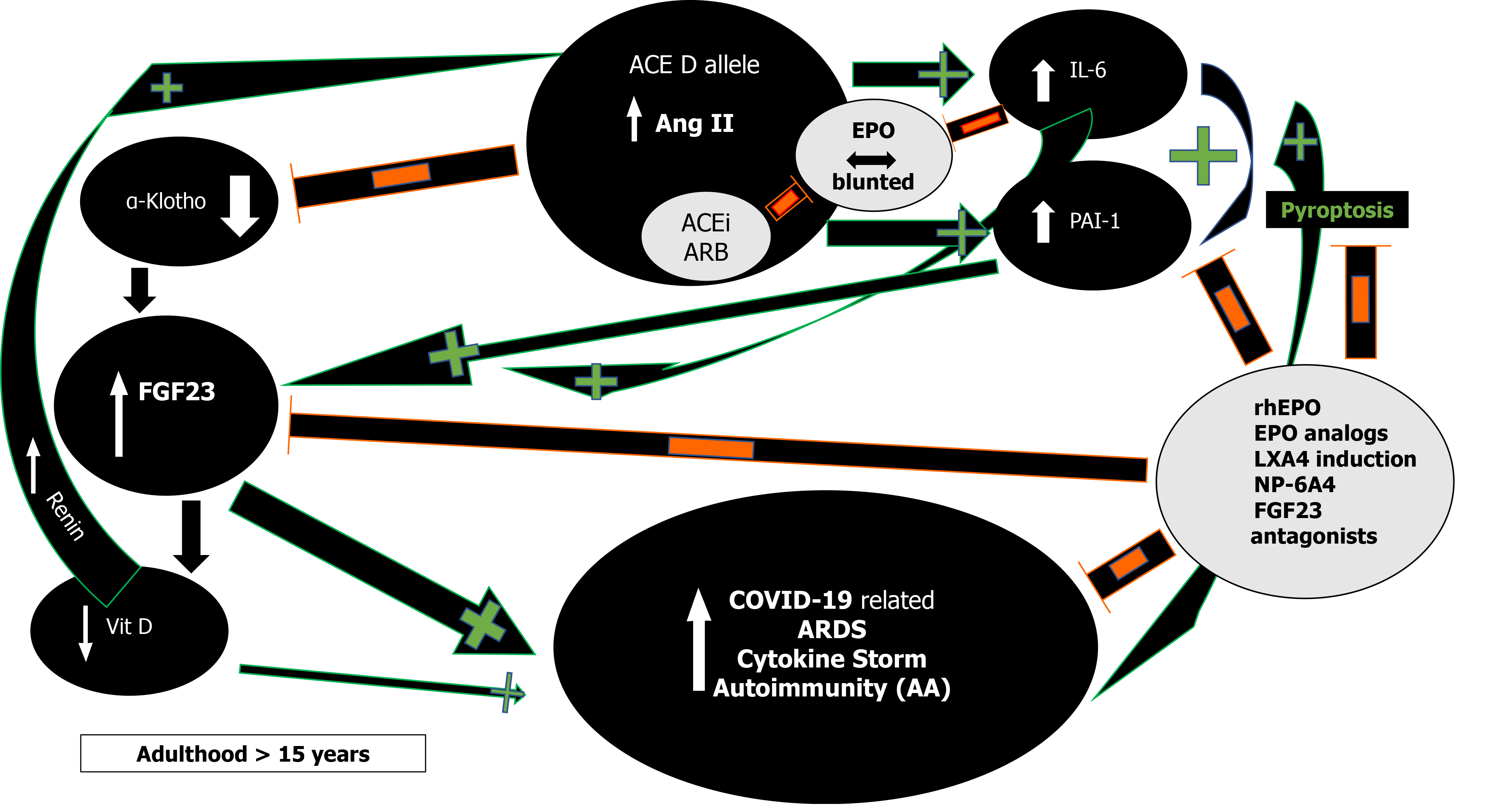
Figure 2 Proinflammatory effects of angiotensin converting enzyme D allele induced Angiotensin II via plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and interleukin 6 induction and their effects on the α-Klotho/fibroblast growth factor 23 axis; inhibitory action of recombinant human erythropoietin/erythropoietin analogs/Lipoxin A4/fibroblast growth factor 23 antagonists.
Orange minus sign denotes inhibition. Green plus sign denotes stimulation. ACE: Angiotensin converting enzyme; FGF23: Fibroblast growth factor 23; PAI-1: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; IL-6: Interleukin 6; rhEPO: Recombinant human erythropoietin; Vit D: Vitamin D; ARDS: Acute respiratory distress syndrome; AA: Autoantibodies; LXA4: Lipoxin A4; ACEi: Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors; ARB: Angiotensin receptor blockers; NP-6A4: AT2R peptide agonist.
- Citation: Papadopoulos KI, Sutheesophon W, Manipalviratn S, Aw TC. Age and genotype dependent erythropoietin protection in COVID-19. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(10): 1513-1529
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i10/1513.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1513