Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2020; 12(4): 251-265
Published online Apr 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i4.251
Published online Apr 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i4.251
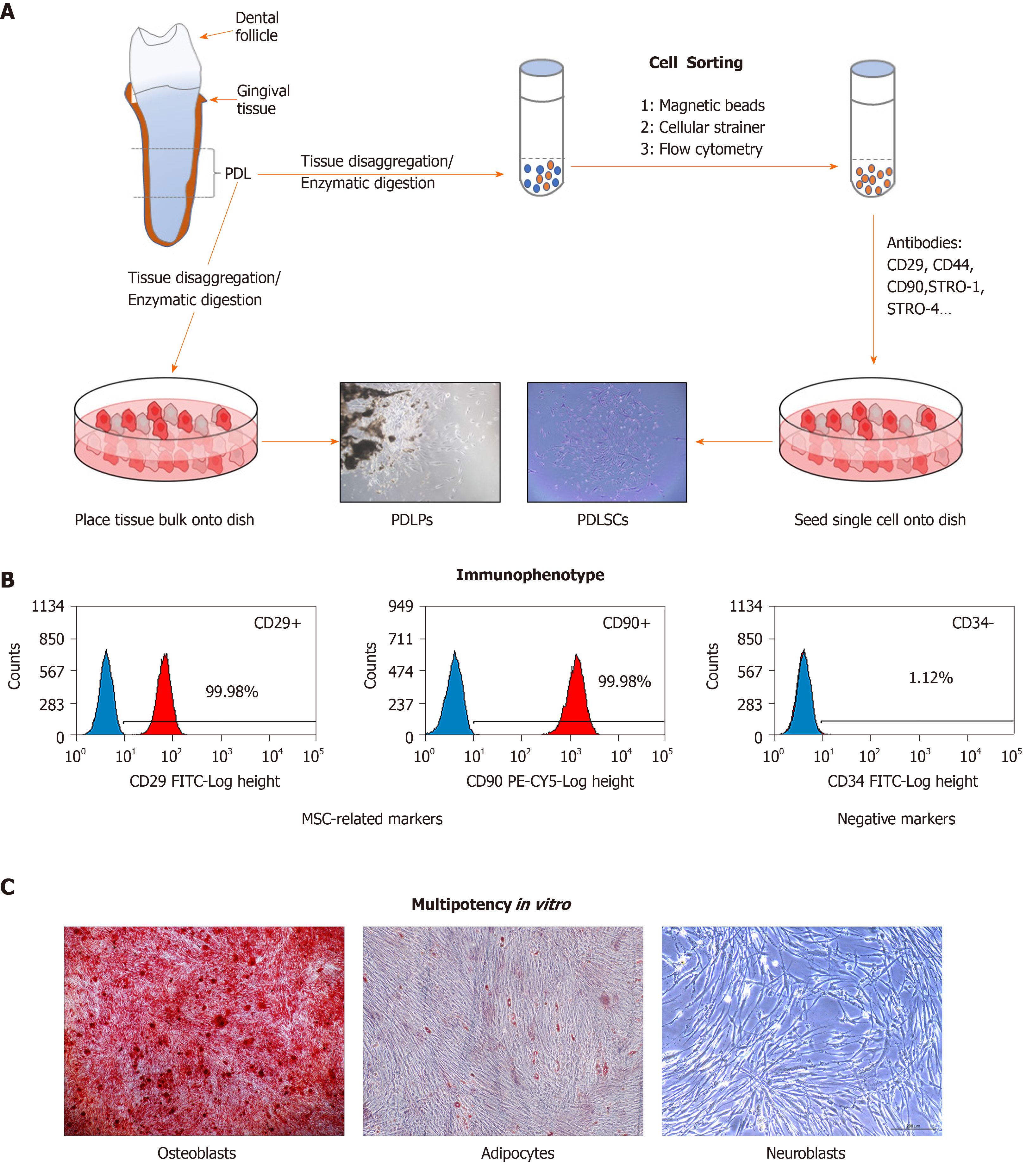
Figure 1 Isolation and characterization of periodontal ligament stem cells.
A: Diagram of the isolation of periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLPs) and PDLSCs from human PDL tissue; B: Flow cytometric analysis to assess the immunophenotype of PDLSCs. Markers of mesenchymal stem cells (CD29, CD90) and non-mesenchymal stem cells (CD34); C: Assessment of the differentiation potential of PDLSCs in vitro. PDL: Periodontal ligament; PDLPs: Periodontal ligament progenitor; PDLSCs: Periodontal ligament stem cells.
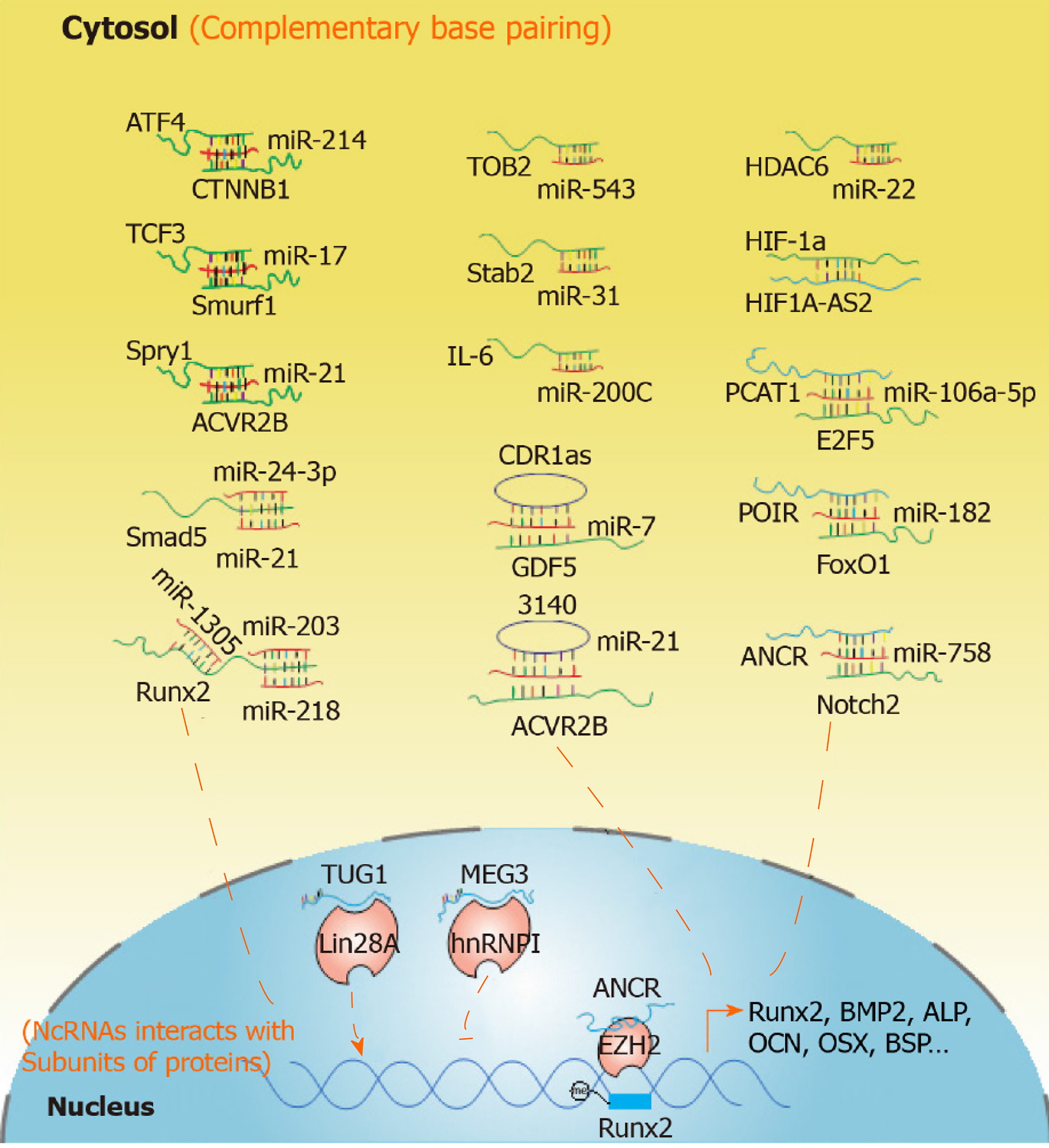
Figure 2 Regulatory mechanisms of noncoding RNAs associated with the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells.
Red indicates miRNAs, green indicates mRNAs, blue indicates long noncoding RNAs and purple indicates circular RNAs. Collectively, the regulatory mechanism of miRNAs is to directly bind to the 3’-UTR of target genes and inhibit the mRNA levels or protein expression. Long noncoding RNAs regulate the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells at the transcriptional, posttranscriptional or epigenetic level. And the demonstrated mechanism of circular RNAs is to act as miRNA sponges to inhibit the mRNA levels of target genes. ATF4: Activated transcription factor 4; CTNNB1: Catenin beta 1; TCF3: Transcriptional factor 3; Smurf1: Smad ubiquitin regulatory factor 1; Spry1: Palmitate phosphoprotein Sprouty1; ACVR2B: Activin A receptor type 2B; Smad5: SMAD family member 5; Runx2: Runt-related transcription factor 2; TOB2: Transducer of ERBB2; Satb2: Special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 2; IL-6: Interleukin-6; CDR1as: Antisense to the cerebellar degeneration-related protein 1 transcript; GDF5: Growth differentiation factor 5; HDAC6: Histone deacetylase 6; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; HIF1A‑AS1/2: HIF1A antisense RNA 1/2; PCAT1: Prostate cancer-associated ncRNA transcript-1; E2F5: E2F transcription factor 5; POIR: Osteogenesis impairment-related long noncoding RNA of periodontal ligament stem cells; FoxO1: Forkhead box O1; ANCR: Anti-differentiation noncoding RNA; Notch2: Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 2; TUG1: Taurine upregulated gene 1; Lin28A: Lin-28 homolog A; MEG3: Maternally expressed gene 3; hnRNP I: Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein I; EZH2: Enhancer of zeste homolog 2; BMP2: Bone morphogenetic protein-2; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase, OCN: Osteocalcin; OSX: Osterix; BSP: Bone sialoprotein; miR: MicroRNA; ncRNAs: Non-coding RNAs.
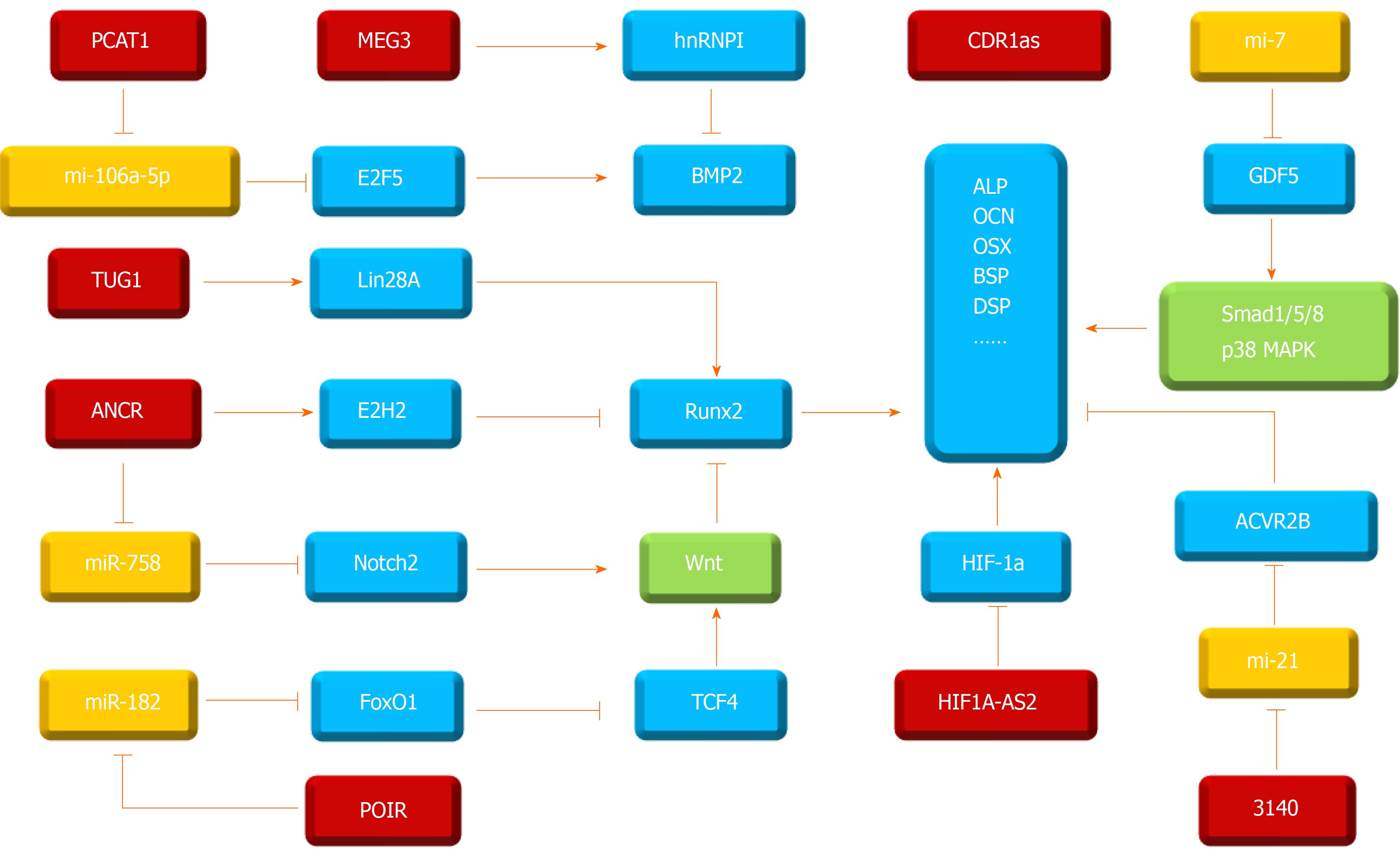
Figure 3 Overview of the role of long noncoding RNAs and circular RNAs during osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells.
Red frame indicates long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) or circular RNAs (circRNAs), yellow frame indicates miRNAs interacted by lncRNAs and circRNAs, blue frame indicates target mRNAs or osteogenesis-related biomarkers, green frame indicates signaling pathways associated with osteogenic differentiation. These lncRNAs and circRNAs affect downstream factors to trigger related biomarkers or signaling pathways and then regulate the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells. PCAT1: Prostate cancer-associated ncRNA transcript-1; E2F5: E2F transcription factor 5; MEG3: Maternally expressed gene 3; hnRNP I: Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein I; BMP2: Bone morphogenetic protein-2; TUG1: Taurine upregulated gene 1; Lin28A: Lin-28 homolog A; Runx2: Runt-related transcription factor 2; ANCR: Anti-differentiation noncoding RNA; EZH2: Enhancer of zeste homolog 2; Notch2: Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 2; FoxO1: Forkhead box O1; POIR: Osteogenesis impairment-related lncRNA of periodontal ligament stem cells; TCF4: Transcription factor 4; CDR1as: Antisense to the cerebellar degeneration-related protein 1 transcript; GDF5: Growth differentiation factor 5; Smad1/5/8: SMAD family member 1/5/8; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; HIF1A‑AS1/2: HIF1A antisense RNA 1/2; ACVR2B: Activin A receptor type 2B; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase, OCN: Osteocalcin; OSX: Osterix; BSP: Bone Sialoprotein; DSP: Desmoplakin; miR: MicroRNA.
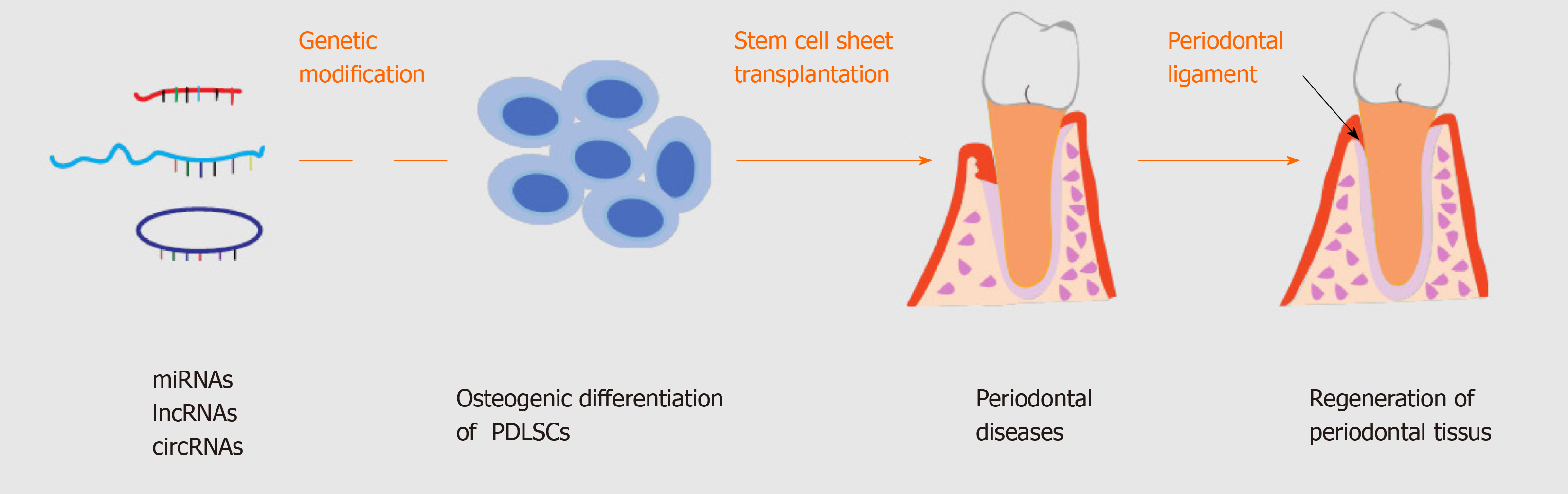
Figure 4 Schematic diagram of noncoding RNAs genetic modification-based periodontal ligament stem cells transplantation therapy applications for periodontium regeneration of periodontal disease.
Genetic modification of noncoding RNAs in periodontal ligament stem cells can regulate the capability of osteogenic differentiation. periodontal ligament stem cells sheet with powerful osteogenic differentiation capability be injected or transplanted into the location of bone defects to regenerate the periodontium in periodontal diseases. miRNAs: MicroRNAs; lncRNAs: Long non-coding RNAs; circRNAs: Circular RNAs; PDLSCs: Periodontal ligament stem cells.
- Citation: Qiu W, Wu BL, Fang FC. Overview of noncoding RNAs involved in the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(4): 251-265
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i4/251.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i4.251