Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Dec 26, 2020; 12(12): 1603-1622
Published online Dec 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1603
Published online Dec 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1603
Figure 1 Chemical structure of 6-gingerol (C17H26O4).
Figure 2 Identification of nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
A: Primary cultured nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells (NPMSCs) showed a rod-shape; B: NPMSCs presented a spindle-shape after passage; C: NPMSCs showed highly expression of CD73, CD90, and CD105 and low expression of hematopoietic stem cell markers CD34, CD45, and HLA-DR; D-F: Multipotential differentiation of NPMSCs.
Figure 3 6-Gingerol alleviates hydrogen peroxide-induced decrease of nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cell viability and intracellular reactive oxygen species level.
A: The viability of nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells (NPMSCs) treated with different concentrations of 6-gingerol (6-GIN) was detected by cholecystokinin-8 (CCK-8); B: CCK-8 results of NPMSCs treated with different concentrations of hydrogen peroxide; C: Effect of 6-GIN on the NPMSC viability induced by hydrogen peroxide; D: Statistical analysis of the production of intracellular reactive oxygen species [NPMSCs treated with cell culture medium (CON group), 80 μmol/L hydrogen peroxide alone (HYD group), hydrogen peroxide and 30 μmol/L 6-GIN (6-GIN group), or hydrogen peroxide and 6-GIN combined with 10 mmol/L 3-methyladenine (3-MA group)]. All data are the mean ± SE of at least three independent experiments. aP < 0.05 vs 0 μmol/L 6-GIN group; bP < 0.05 vs 0 μmol/L H2O2 group; cP < 0.05 vs 0 μmol/L blank control; dP < 0.05 vs 80 μmol/L H2O2 group; eP < 0.05 vs CON group; fP < 0.05 vs HYD group; gP < 0.05 vs 6-GIN group. 6-GIN: 6-gingerol; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; H2O2: Hydrogen peroxide; 3-MA: 3-Methyladenine.
Figure 4 6-Gingerol decreases hydrogen peroxide-induced nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cell apoptosis.
Nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells (NPMSCs) were treated with cell culture medium (CON group), 80 μmol/L hydrogen peroxide alone (HYD group), hydrogen peroxide and 30 μmol/L 6-gingerol (6-GIN group), or hydrogen peroxide and 6-GIN combined with 10 mmol/L 3-methyladenine (3-MA group). A: 6-GIN partially blocks hydrogen peroxide-induced matrix metalloproteinase loss. The data are expressed as the ratio of red over green fluorescence intensity assessed by flow cytometry; B-C: Representative pictures and statistical analysis of NPMSC apoptosis rate by Annexin-V/PI dual staining in different groups; D: TUNEL assay results of NPMSCs in different groups (bar = 200 μm); E: Quantitative analysis of fluorescence results; F-I: Western blot results and quantitative analysis of apoptosis related proteins (cleaved caspase-3, Bax, and Bcl-2) in different groups; J: Bcl-2/Bax ratio. All data are the mean ± SE of at least three independent experiments. eP < 0.05 vs CON group; fP < 0.05 vs HYD group; gP < 0.05 vs 6-GIN group. 6-GIN: 6-gingerol; H2O2: Hydrogen peroxide; 3-MA: 3-methyladenine.
Figure 5 6-gingerol regulates the expression of extracellular matrix proteins.
Nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells (NPMSCs) were treated with cell culture medium (CON group), 80 μmol/L hydrogen peroxide alone (HYD group), hydrogen peroxide and 30 μmol/L 6-gingerol (6-GIN group), or hydrogen peroxide and 6-GIN combined with 10 mmol/L 3-methyladenine (3-MA group), bar = 100 μm. A-C: The mRNA expression of aggrecan, collagen II, and matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP-13); D-G: Representative immunofluorescence photomicrographs and quantitative analysis of fluorescence results of collagen II and MMP-13. All data are the mean ± SE of at least three independent experiments. eP < 0.05 vs CON group; fP < 0.05 vs HYD group; gP < 0.05 vs 6-GIN group. 6-GIN: 6-gingerol; H2O2: Hydrogen peroxide; 3-MA: 3-methyladenine.
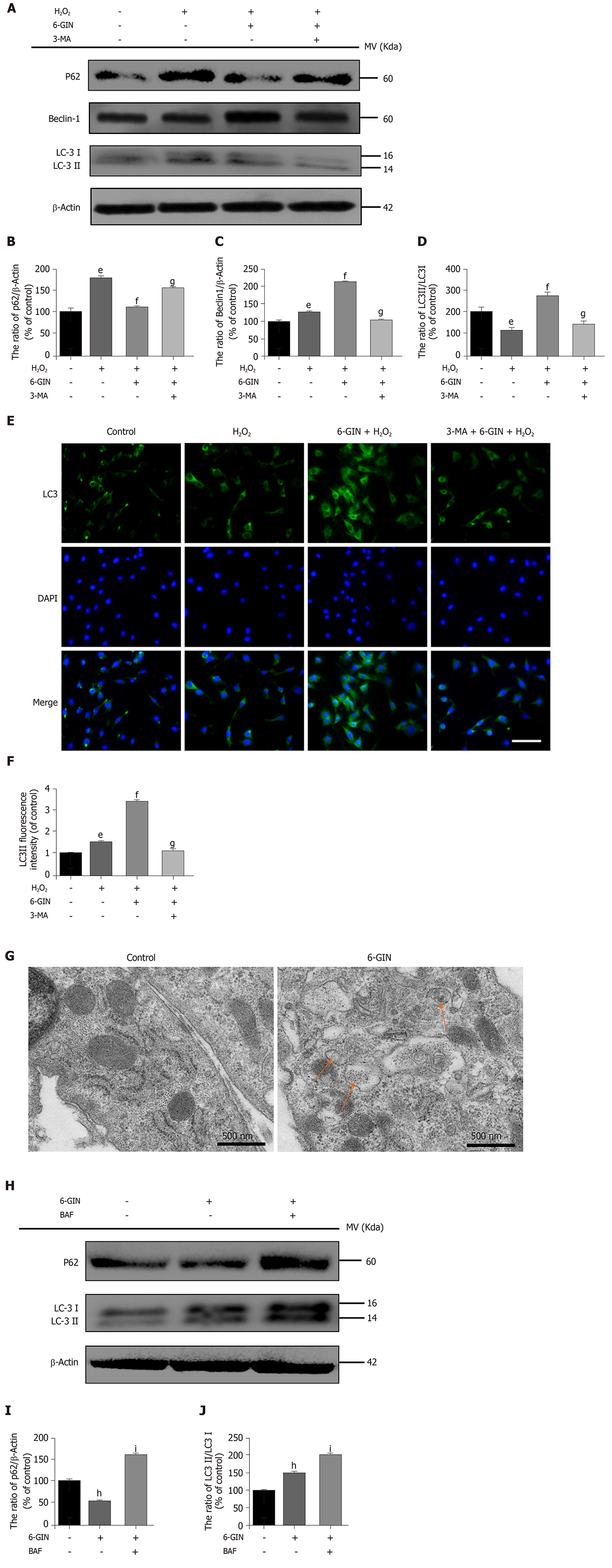
Figure 6 Role of autophagy in the protective effect of 6-gingerol.
Nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells (NPMSCs) were treated with cell culture medium (CON group), 80 μmol/L hydrogen peroxide alone (HYD group), hydrogen peroxide and 30 μmol/L 6-gingerol (6-GIN group), or hydrogen peroxide and 6-GIN combined with 10 mmol/L 3-methyladenine (3-MA group). A-D: Western blot results and quantitative analysis of the expression of the autophagy-related proteins P62, Beclin1, and LC3II/I; E-F: Immunofluorescence results and quantitative analysis of LC-3 expression (bar = 100 μm); G: Autophagosomes detected by transmission electron microscopy in NPMSCs. (Orange arrows: autophagosomes); H-J: Western blot results and quantitative analysis of the autophagy-related proteins P62 and LC3II/I in NPMSCs treated with 6-GIN (6-GIN group) or 6-GIN and 100 nM BAF (BAF group). All data are the mean ± SE of at least three independent experiments. hP < 0.05 vs blank control; iP < 0.05 vs 6-GIN only group. 6-GIN: 6-gingerol; H2O2: Hydrogen peroxide; 3-MA: 3-methyladenine.
Figure 7 Activity of PI3K/Akt pathway in the 6-gingerol related protective effect.
A-B: Western blot results and quantitative analysis of the expression of the PI3K/Akt pathway-related proteins p-Akt and Akt. Nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells were treated with cell culture medium (CON group), 80 μmol/L hydrogen peroxide alone (HYD group), hydrogen peroxide and 30 μmol/L 6-gingerol (6-GIN group), or hydrogen peroxide and 6-GIN combined with 10 mmol/L 3-methyladenine (3-MA group). All data are the mean ± SE of at least three independent experiments. eP < 0.05 vs CON group; fP < 0.05 vs HYD group; gP < 0.05 vs 6-GIN group. H2O2: Hydrogen peroxide; 6-GIN: 6-gingerol; 3-MA: 3-methyladenine.
Figure 8 Schematic of protective effects of 6-gingerol.
6-gingerol (6-GIN) inhibits nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cell apoptosis and extracellular matrix degeneration by promoting autophagy via the PI3K/Akt pathway under oxidative damage induced by hydrogen peroxide alone (H2O2 group). NP: Nucleus pulposus; 6-GIN: 6-gingerol; NPMSCs: Nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells; H2O2: Hydrogen peroxide; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
- Citation: Nan LP, Wang F, Liu Y, Wu Z, Feng XM, Liu JJ, Zhang L. 6-gingerol protects nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells from oxidative injury by activating autophagy. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(12): 1603-1622
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i12/1603.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1603