Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Dec 26, 2020; 12(12): 1474-1491
Published online Dec 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1474
Published online Dec 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1474
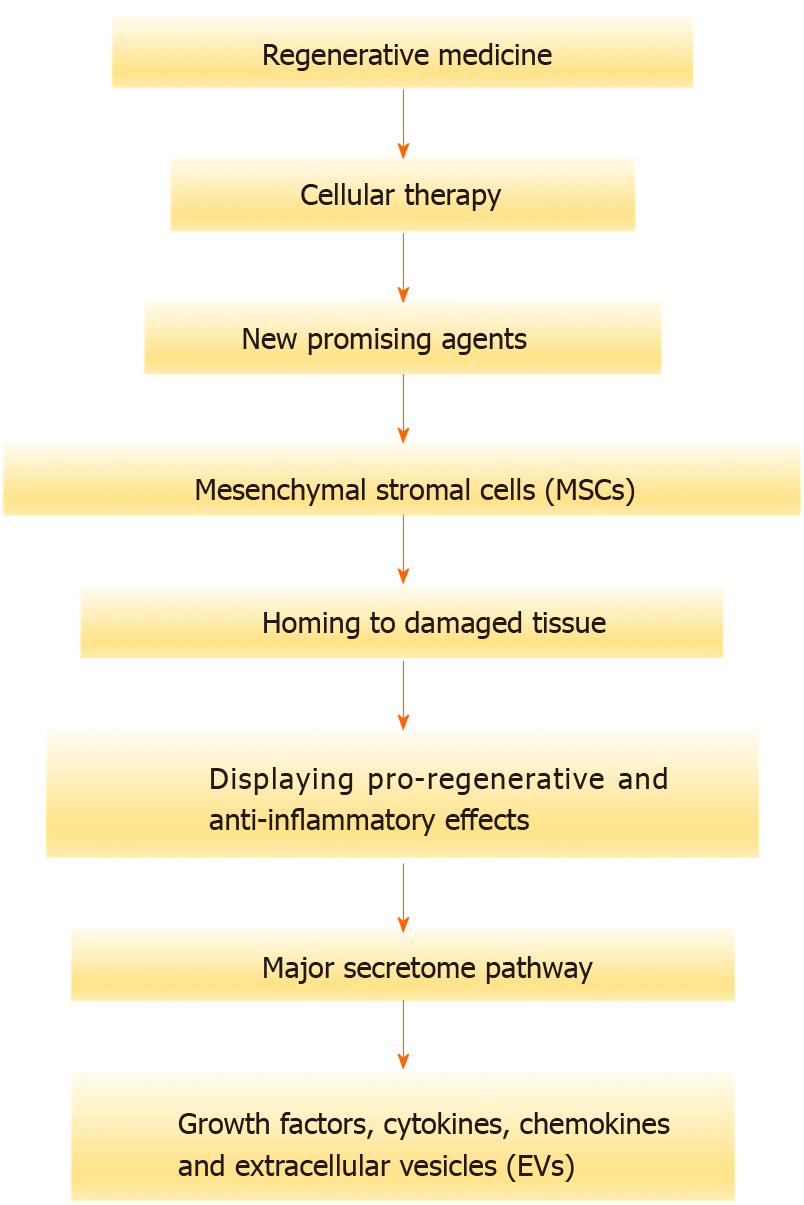
Figure 1 A flow chart showing the use of the cell-free approach to enhance the safety of mesenchymal stromal cell-based therapy.
MSC: Mesenchymal stromal cell; EVs: Extracellular vesicles.
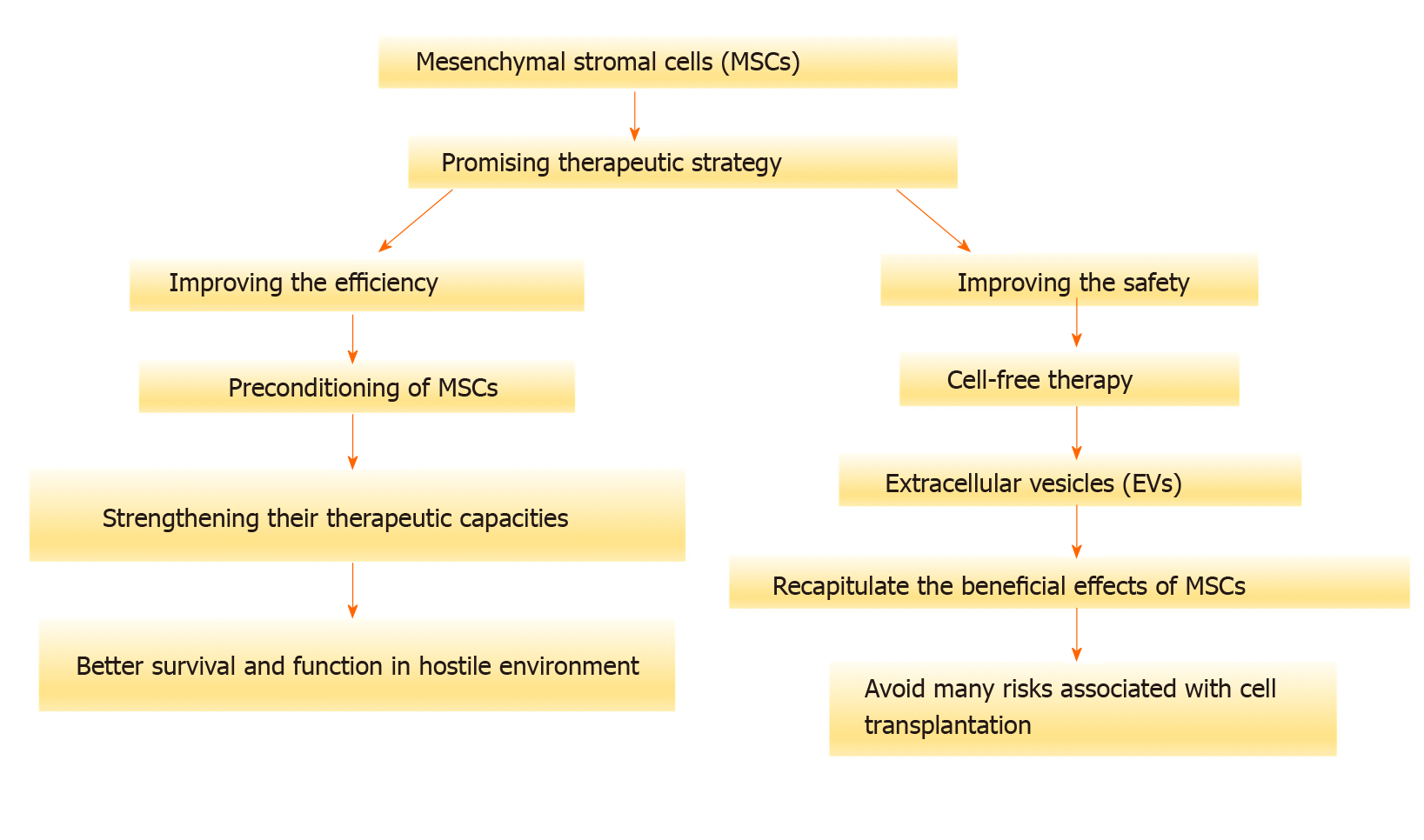
Figure 2 Mesenchymal stromal cells as a promising therapeutic strategy with improved efficiency and safety.
MSC: Mesenchymal stromal cell; EVs: Extracellular vesicles.
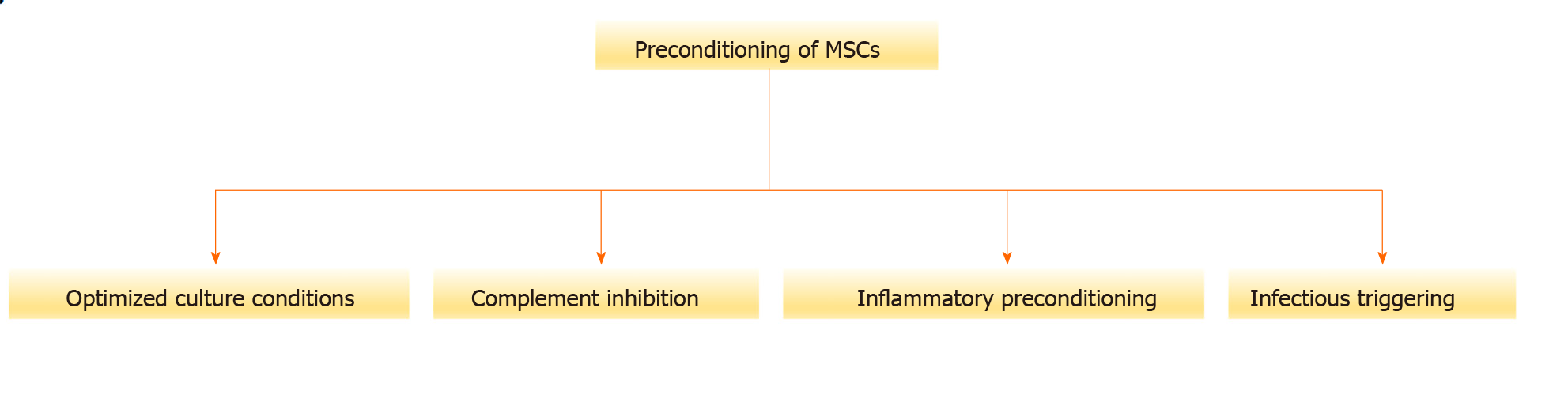
Figure 3 Strategies applied in the preconditioning of mesenchymal stromal cells.
MSCs: Mesenchymal stromal cells.
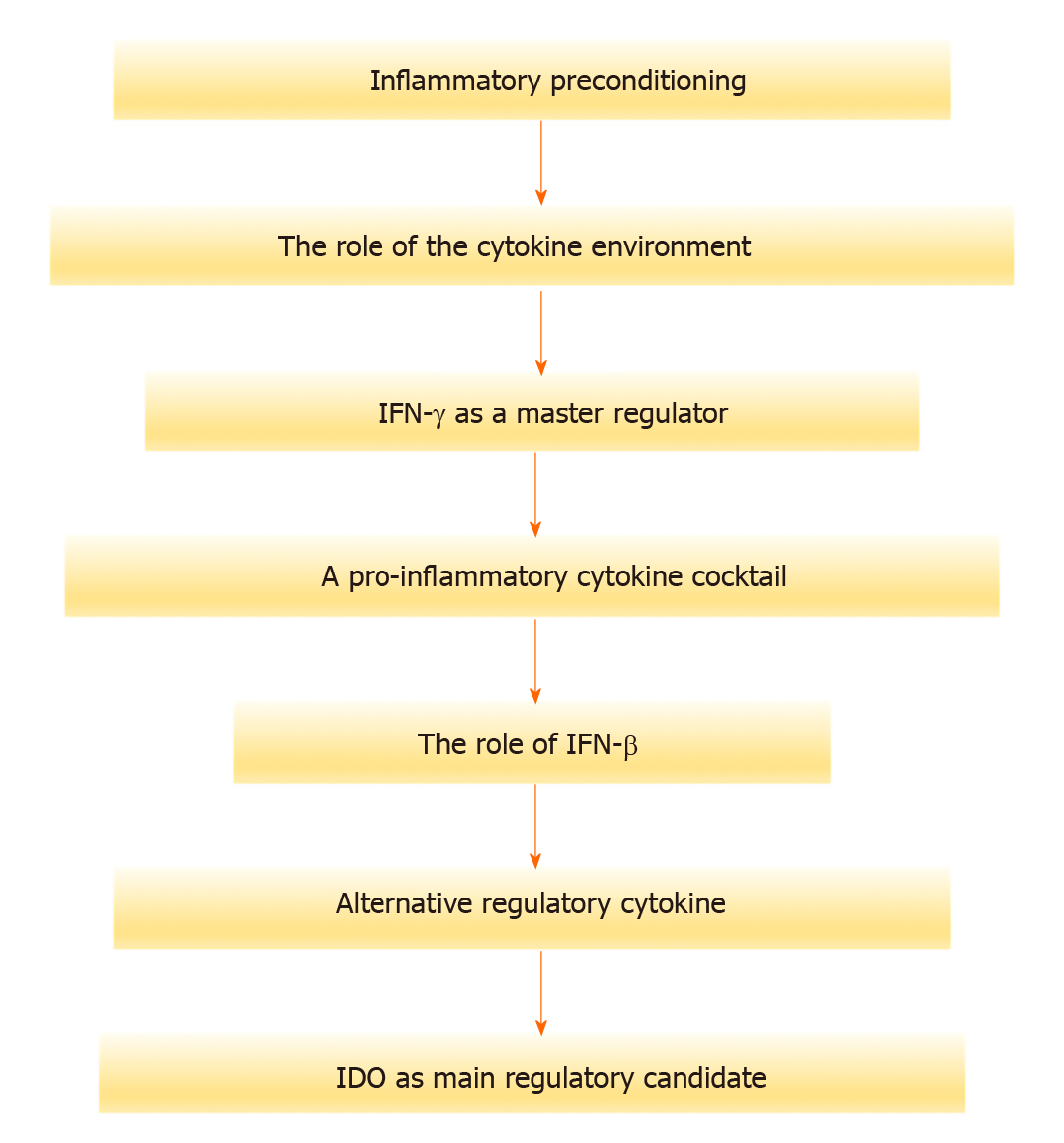
Figure 4 The inflammatory specific cytokine environment is pivotal in determining the fate and behaviors of mesenchymal stromal cells.
IFN-γ: Interferon-γ; IFN-β: Interferon-β; IDO: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.
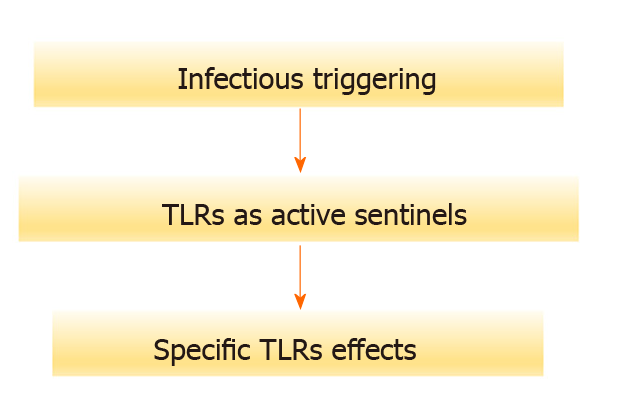
Figure 5 The infectious environment may modulate mesenchymal stromal cells through different pattern and function of toll-like receptors.
TLRs: Toll-like receptors.
- Citation: Najar M, Martel-Pelletier J, Pelletier JP, Fahmi H. Novel insights for improving the therapeutic safety and efficiency of mesenchymal stromal cells. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(12): 1474-1491
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i12/1474.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1474