Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2020; 12(11): 1354-1365
Published online Nov 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i11.1354
Published online Nov 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i11.1354
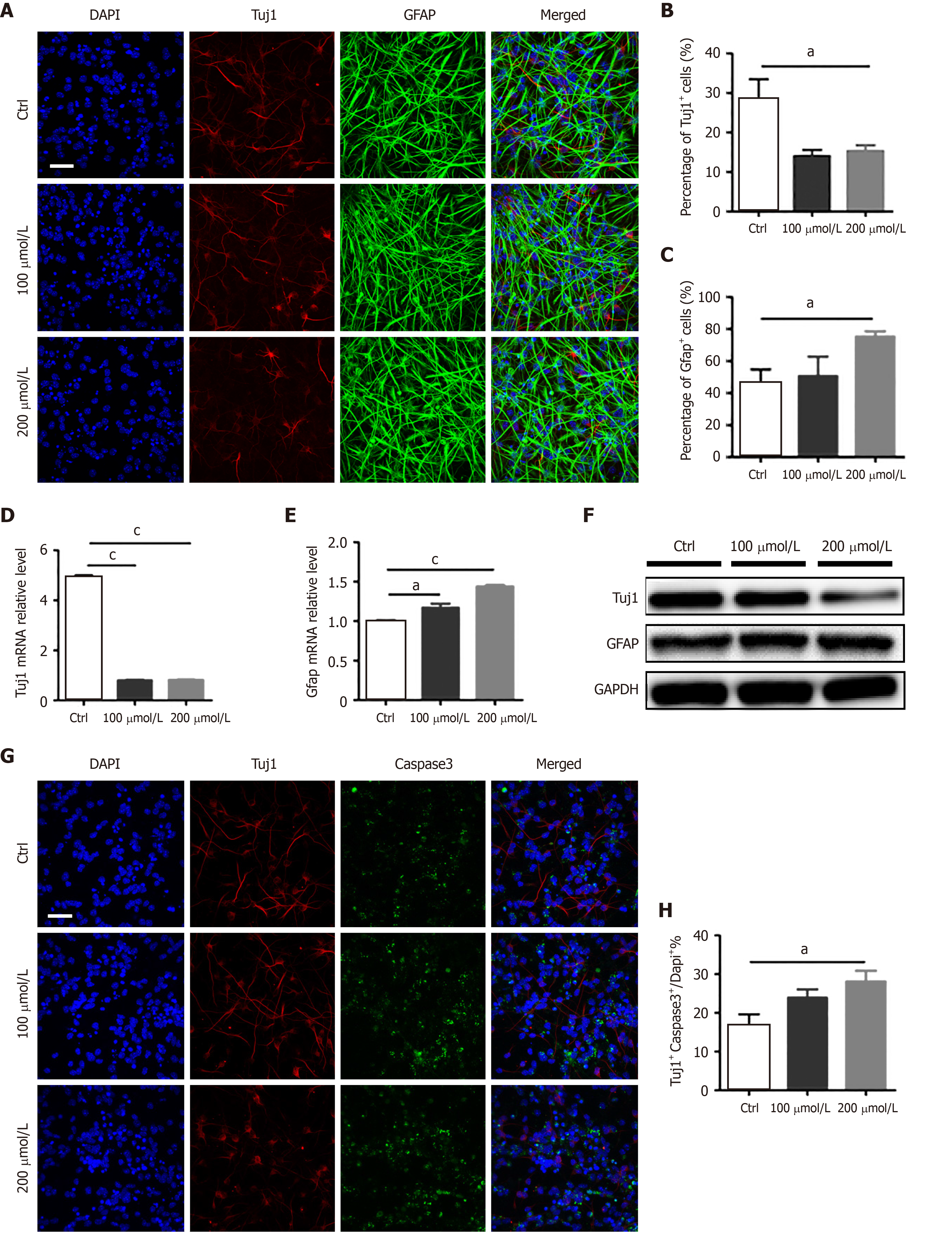
Figure 1 AlCl3 exposure affects adult neural stem cell differentiation and neuron survival invitro.
A: Immunostaining of adult neural stem cell differentiated in the presence of AlCl3 for β-III tubulin (Tuj1) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) expression (Scale bar: 100 μm); B and C: The number of Tuj1+ cells decreased while that of GFAP+ cells increased (n = 8); D and E: The relative mRNA level of Tuj1 significantly decreased, and that of GFAP increased (n = 3); F: Western blot assay showing that Tuj1 protein expression was significantly decreased by AlCl3 at 200 μmol/L, while GFAP protein expression was increased. GAPDH was used as a loading control; G: Representative images of apoptosis in newborn neurons (scale bar: 100 μm); H: The number of newborn neurons decreased after AlCl3 exposure (n = 8). Data are represented as the mean ± SE (n = 3). Statistically significant differences are indicated: aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. Tuj1: β-III tubulin; GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein.
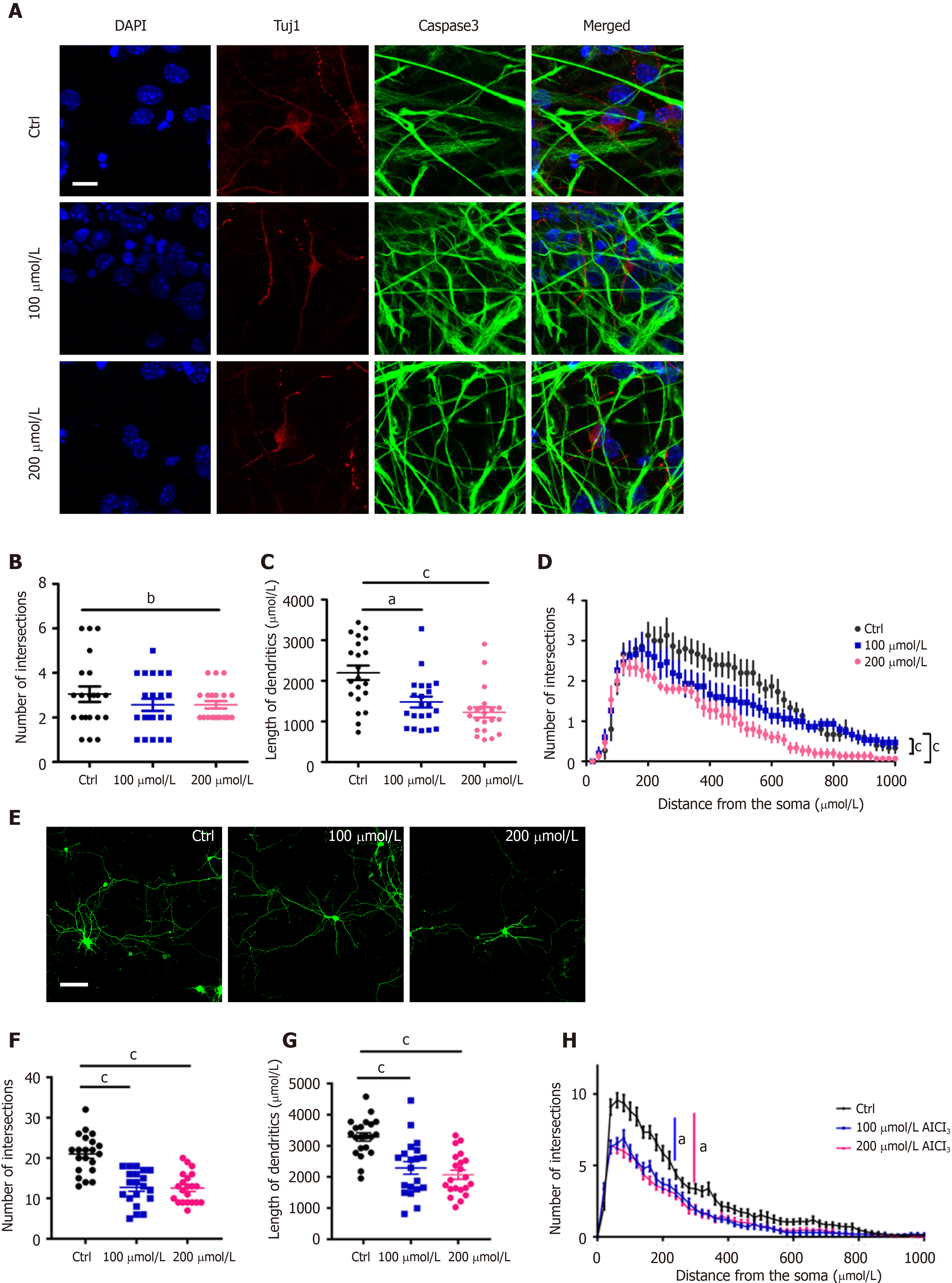
Figure 2 AlCl3 exposure inhibits neuronal development.
A: Representative images of adult neural stem cell differentiation (scale bar: 100 μm); B-D: Sholl analysis in newborn neuron indicated that the intersection number and length of dendrites both decreased after AlCl3 exposure (n = 21); E: Representative images of hippocampal neurons (scale bar: 100 μm); F-H: Sholl analysis indicated that the intersection number and length of dendrites both significantly decreased in hippocampal neurons after AlCl3 exposure (n = 21). Data are represented as the mean ± SE (n = 3). Statistically significant differences are indicated: aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. Tuj1: β-III tubulin; GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein.
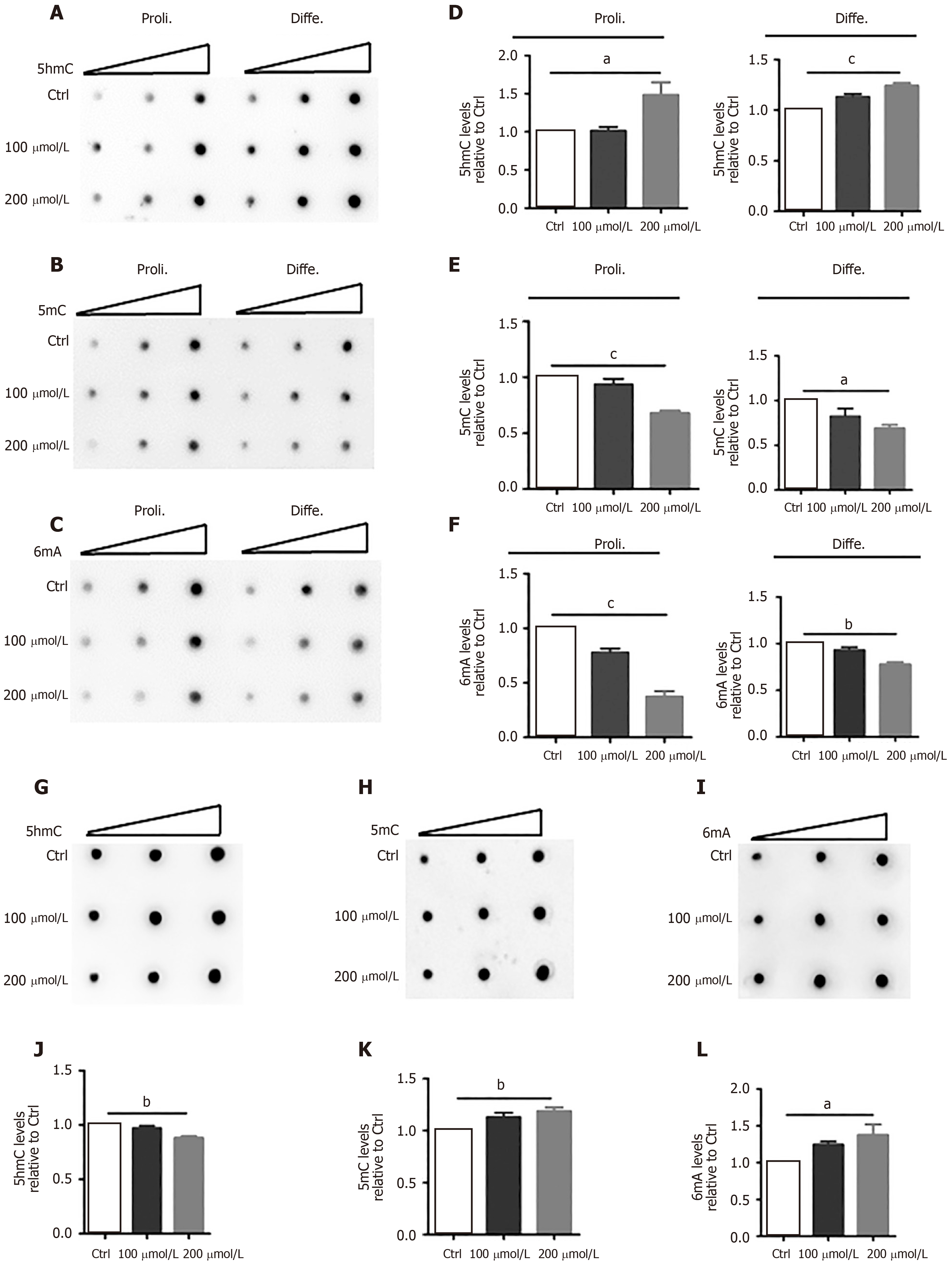
Figure 3 AlCl3 exposure alters the levels of DNA 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, 5-methylcytosine, and N6-methyladenine in adult neural stem cells and neurons.
A-C: Representative images of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), 5-methylcytosine (5mC), and N6-methyladenine (6mA) dot-blot assays in adult neural stem cell (aNSC) differentiation and proliferation; D-F: Quantification revealing that the relative levels of 5-mc and 6mA both decreased in aNSC proliferation and differentiation, but the level of 5hmc increased (n = 3); G-I: Representative images of 5hmC, 5mC, and 6mA dot-blot assays in neurons; J-L: Quantification revealing that the relative levels of 5hmC decreased but those of 5mC and 6mA increased in neurons (n = 3). Data are represented as the mean ± SE (n = 3). Statistically significant differences are indicated: aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP< 0.001. 5hmC: 5-hydroxymethylcytosine; 5mC: 5-methylcytosine; 6mA: N6-methyladenine.
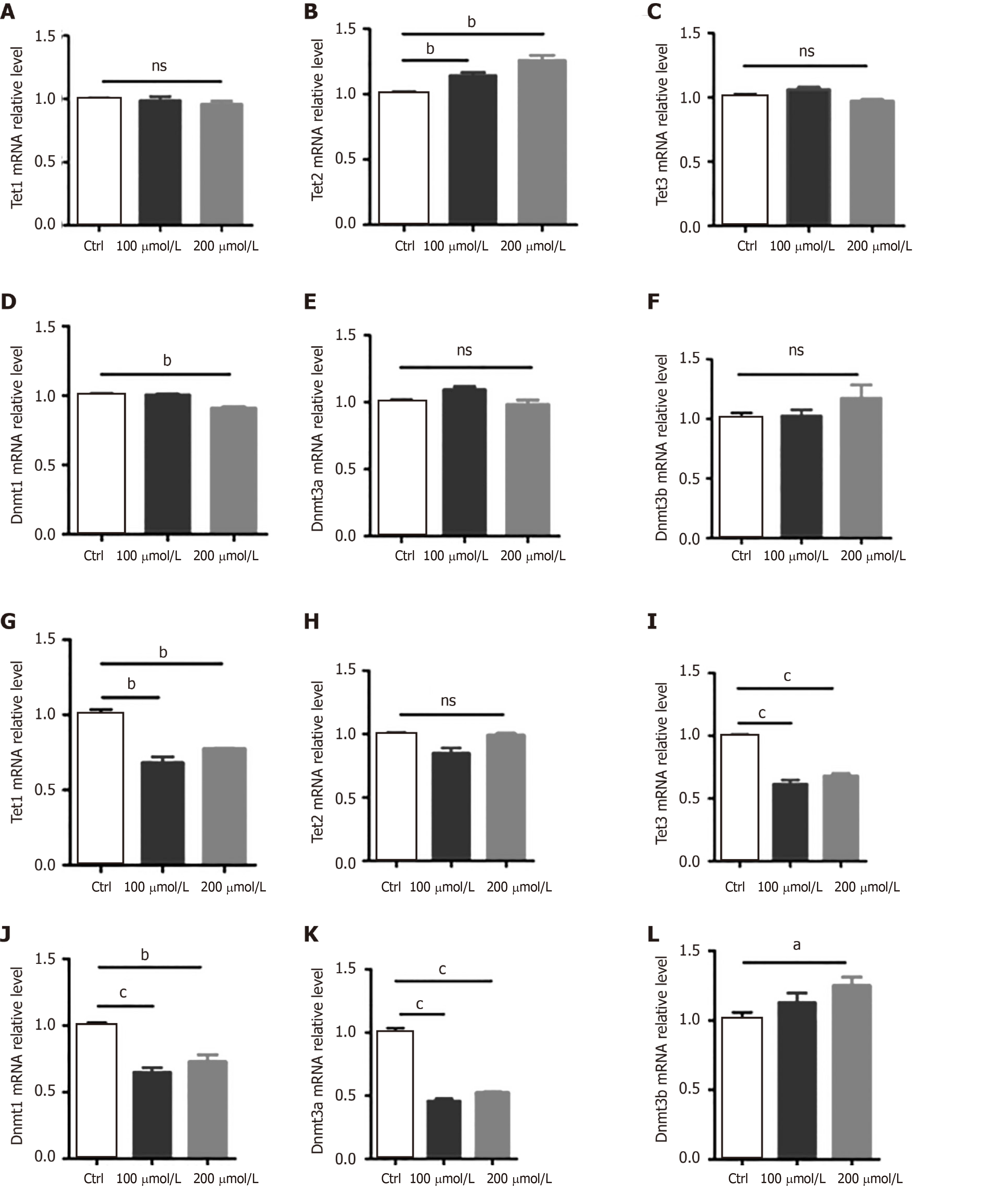
Figure 4 AlCl3 exposure regulates the expression of Tets and Dnmts at the transcriptional level in adult neural stem cells and neurons.
A-F: The relative mRNA levels of Tet1, Tet2, Tet3, Dnmt1, Dnmt3a, and Dnmt3b in aNSCs; G-L: The relative mRNA levels of Tet1, Tet2, Tet3, Dnmt1, Dnmt3a, and Dnmt3b in neurons. Data are represented as the mean ± SE (n = 3). Statistically significant differences are indicated: aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
- Citation: Cheng XJ, Guan FL, Li Q, Dai G, Li HF, Li XK. AlCl3 exposure regulates neuronal development by modulating DNA modification. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(11): 1354-1365
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i11/1354.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i11.1354