Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2020; 12(11): 1276-1294
Published online Nov 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i11.1276
Published online Nov 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i11.1276
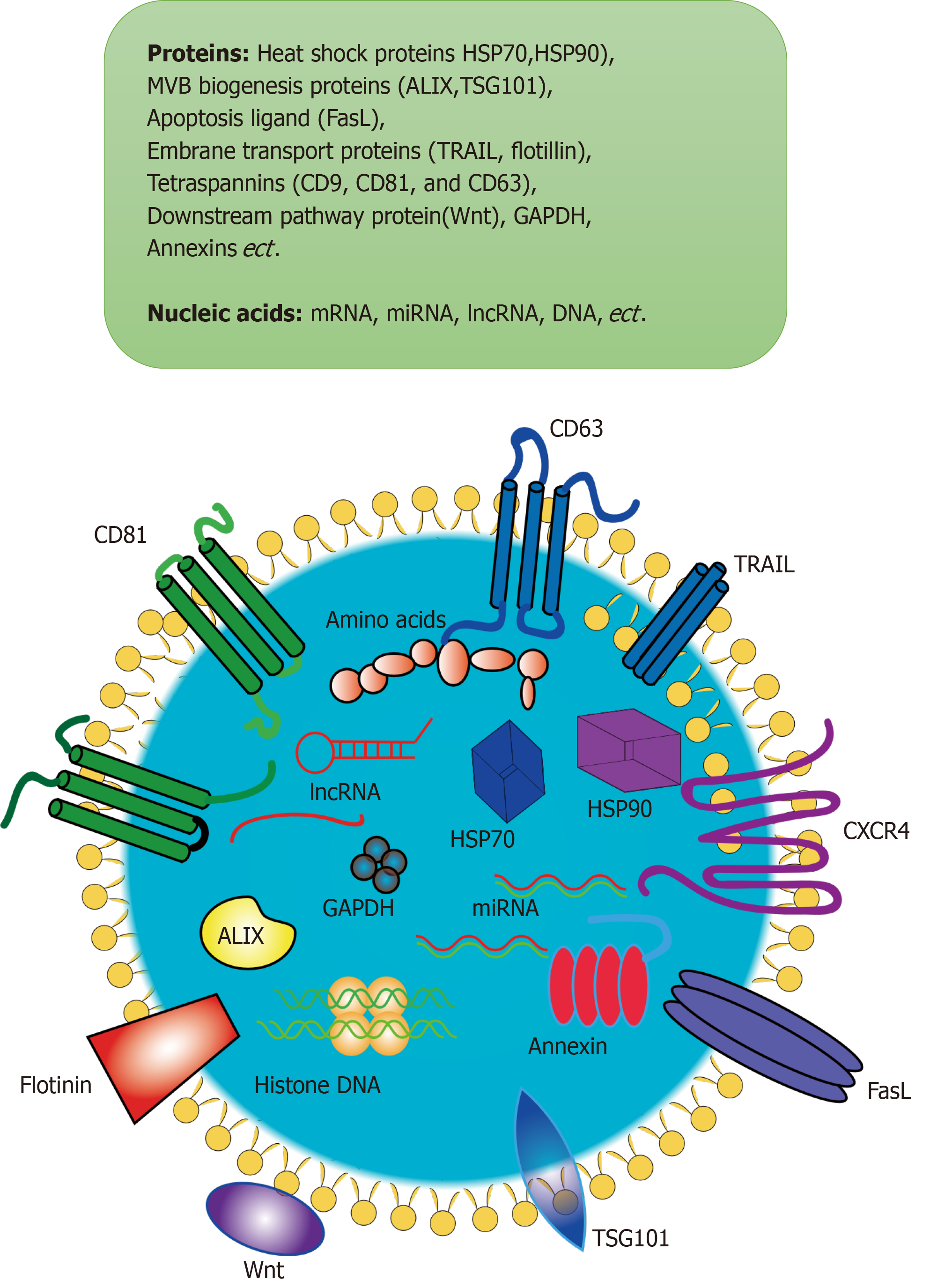
Figure 1 Exosomes are small vesicles that are secreted by cells and wrapped in membranes made up of lipid bilayer molecules.
Exosomes contain proteins, nucleic acids, and other substances. Their proteins include heat shock proteins, MVB biogenesis proteins, cytoskeleton proteins, apoptosis, ligand, embrane transport proteins and so on. Their nucleic acids include mRNA, miRNA, lncRNA, DNA, and so on. ALIX: ALG-2 interacting protein X; CXCR4: CXC-chemokine receptor 4; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; HSP70: Heat shock 70 kDa protein; TSG101: Tumor susceptibility gene 101 protein.
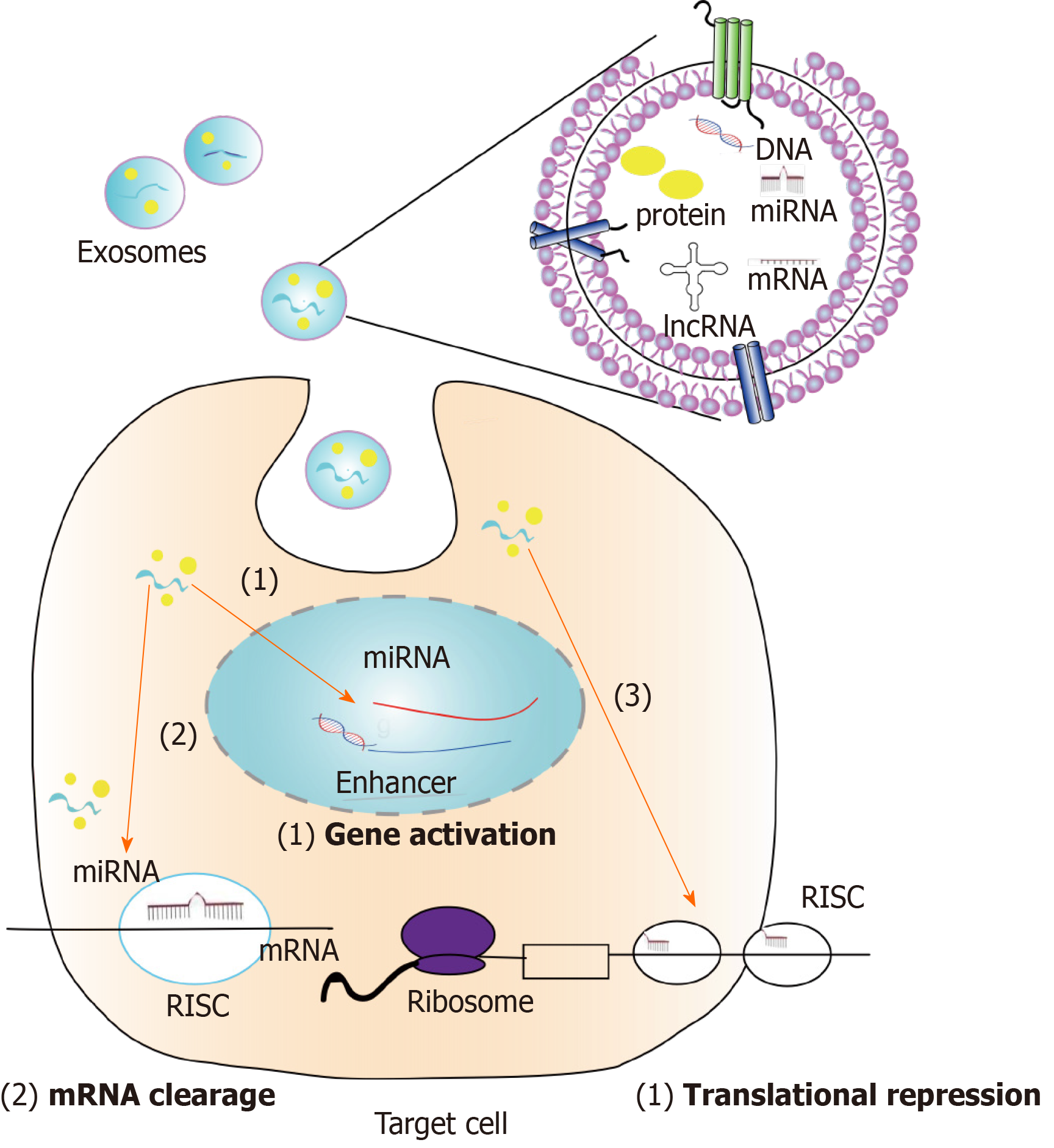
Figure 2 Exosomes were first isolated from the cultured supernatant of stem cells and injected intravenously into the model.
The exosomes then reach the damaged site, are absorbed by the cells, and enter the cell: (1) Exosome-derived microRNA binds to enhancers in the nucleus to promote gene expression; (2) miRNA in exosomes bind to the 3’-UTR of the mRNA for mRNA degradation; and (3) exosomes inhibit mRNA translation. The second and third ways have been studied, and the first way is based on the assumption of existing studies. RISC: RNA-induced silencing complex.
- Citation: Xu HK, Chen LJ, Zhou SN, Li YF, Xiang C. Multifunctional role of microRNAs in mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in treatment of diseases. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(11): 1276-1294
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i11/1276.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i11.1276