Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2020; 12(10): 1196-1213
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1196
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1196
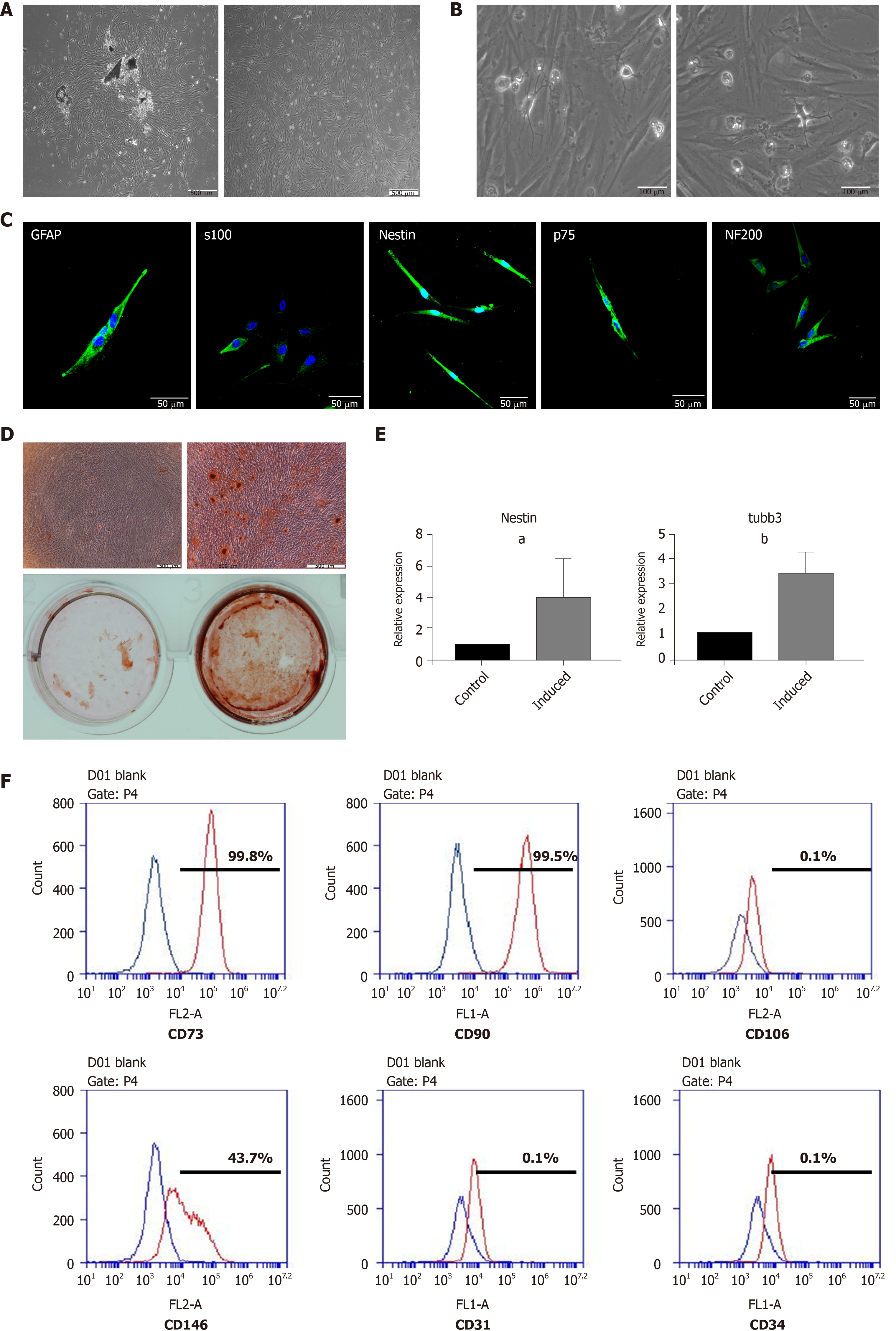
Figure 1 Isolation, culture, and multilineage differentiation of dental pulp stem cells.
A: Morphology of dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs); B: Neural-like cells differentiated from DPSCs; C: Immunofluorescent staining for Nestin, S100, GFAP, p75, and NF200; D: Osteogenic induction; E: Neural induction assessed by real-time PCR; F: Flow cytometry for CD73, CD90, CD146, CD106, CD31, and CD34. Student’s t test was used to identify statistical significance. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
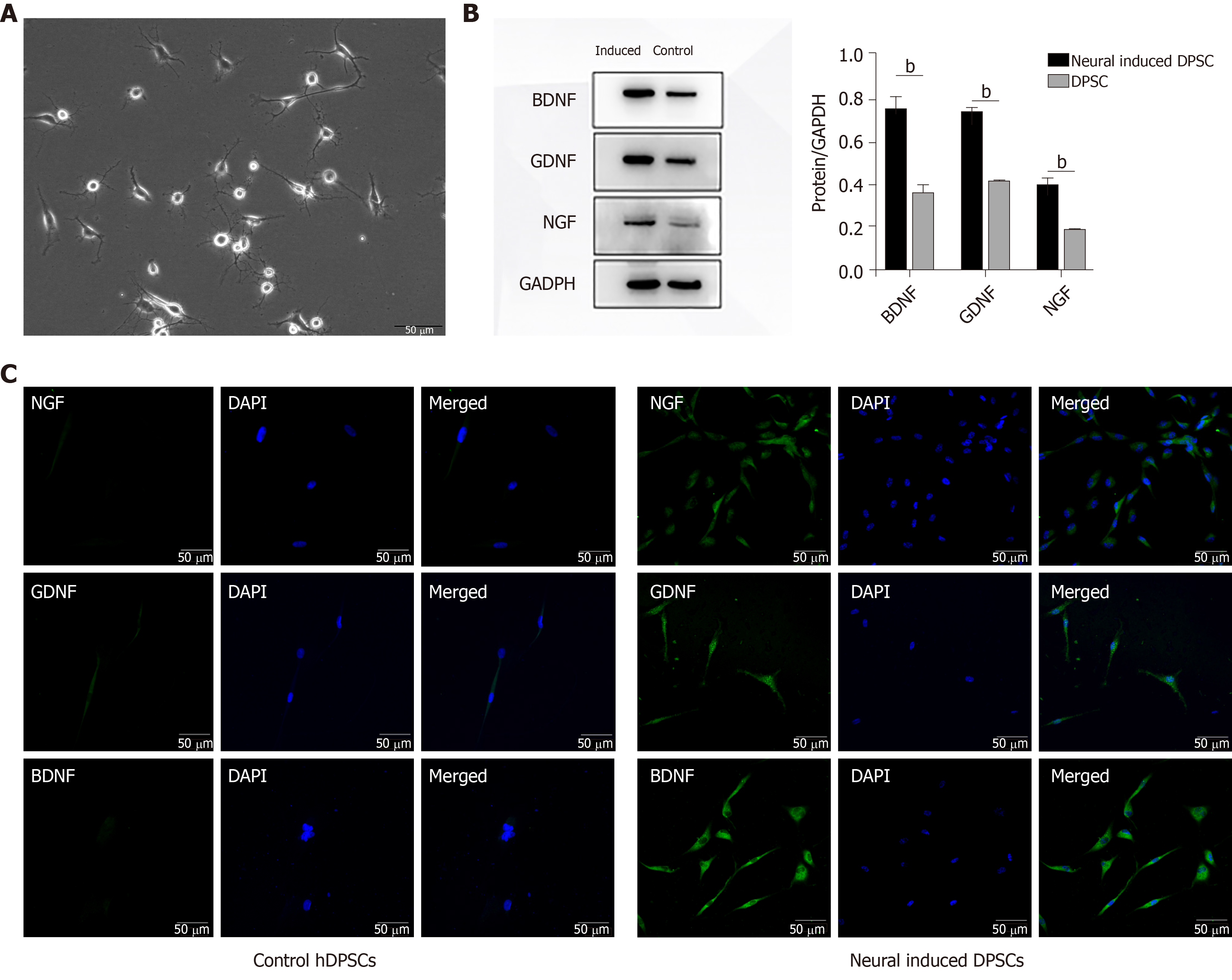
Figure 2 Dental pulp stem cells can differentiate into neural-like cells, and neural-induced dental pulp stem cells are highly positive for neurotrophic factors.
A: Morphology of neural-induced dental pulp stem cells; B: The expression of BDNF, GDNF, and NGF was assessed by Western blot; C: The expression of BDNF, GDNF, and NGF was assessed by immunofluorescent staining. bP < 0.01. DPSC: Dental pulp stem cells; hDPSCs: Human dental pulp stem cells.
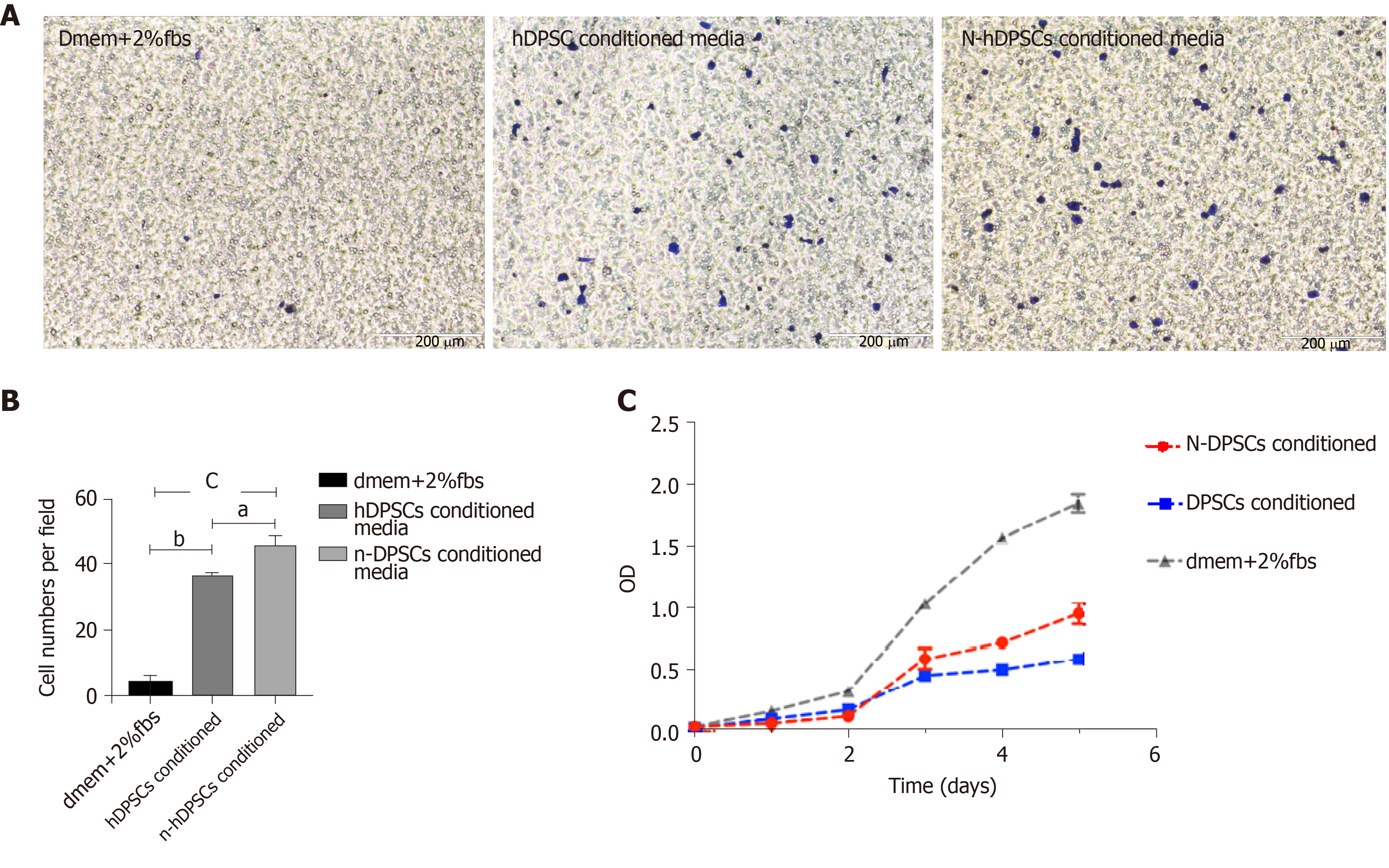
Figure 3 The secretions of neural-induced dental pulp stem cells enhance the proliferation and migration of RSC96 cells.
A: Migration ability assessed by transwell assays; B: Analysis of RSC96 cell migration; C: CCK-8 assays. Student’s t test was used to identify statistical significance. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, and cP < 0.001. N-DPSCs: Neural-induced dental pulp stem cells; DPSC: Dental pulp stem cells; hDPSCs: Human dental pulp stem cells.
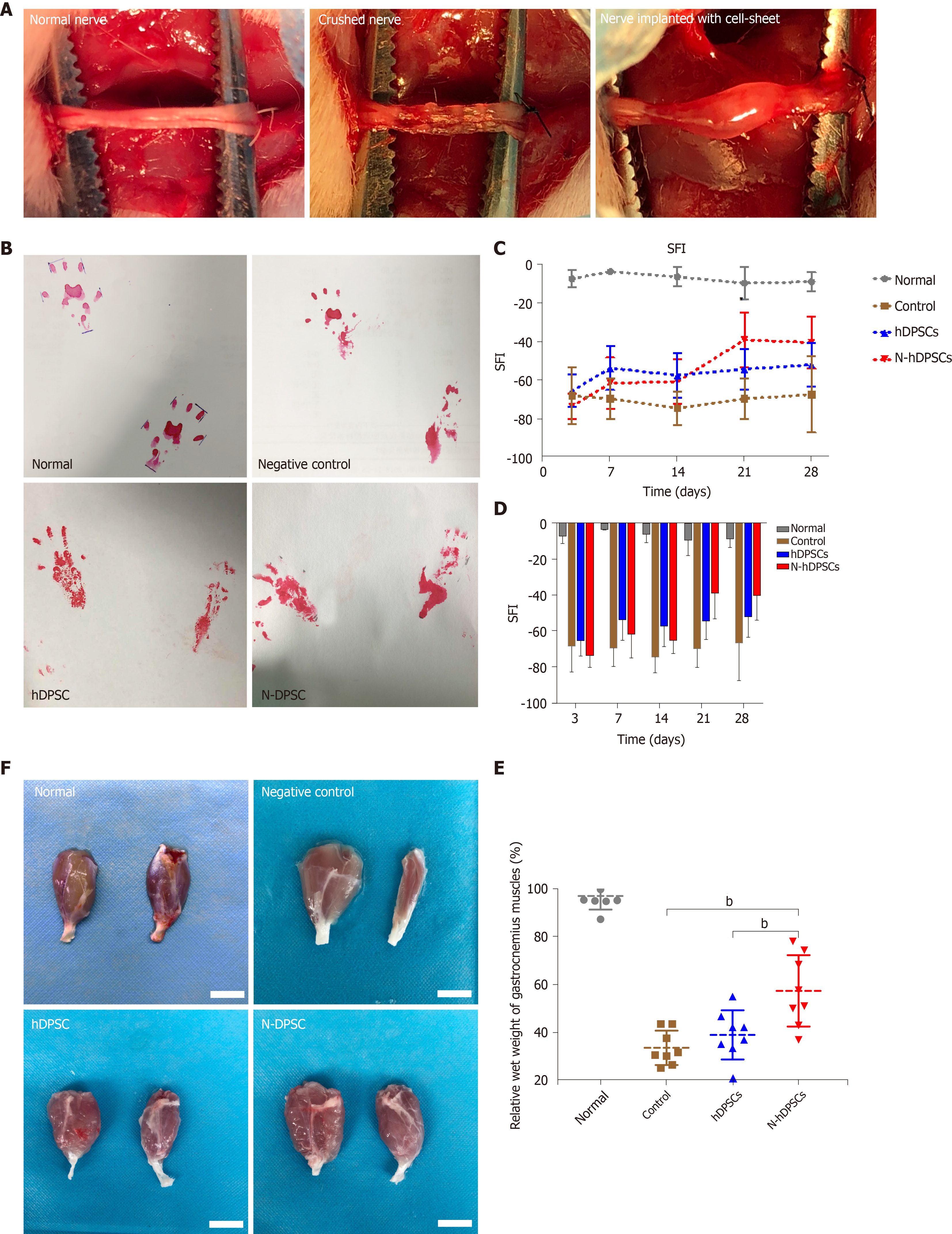
Figure 4 Neural-induced dental pulp stem cells enhance rat functional recovery after nerve crush injury.
A: Nerve crush model of peripheral nerve injury and cell sheet implantation; B: Footprints of the four groups; C and D: Analysis of sciatic function index; E: Wet weight ratio of the gastrocnemius muscles; F: Appearance of the gastrocnemius muscle of four groups. Bar = 1 cm. All data represent the mean ± SD. n = 8 in each group. bP < 0.01. SFI: Sciatic function index; N-DPSCs: Neural-induced dental pulp stem cells; hDPSCs: Human dental pulp stem cells.
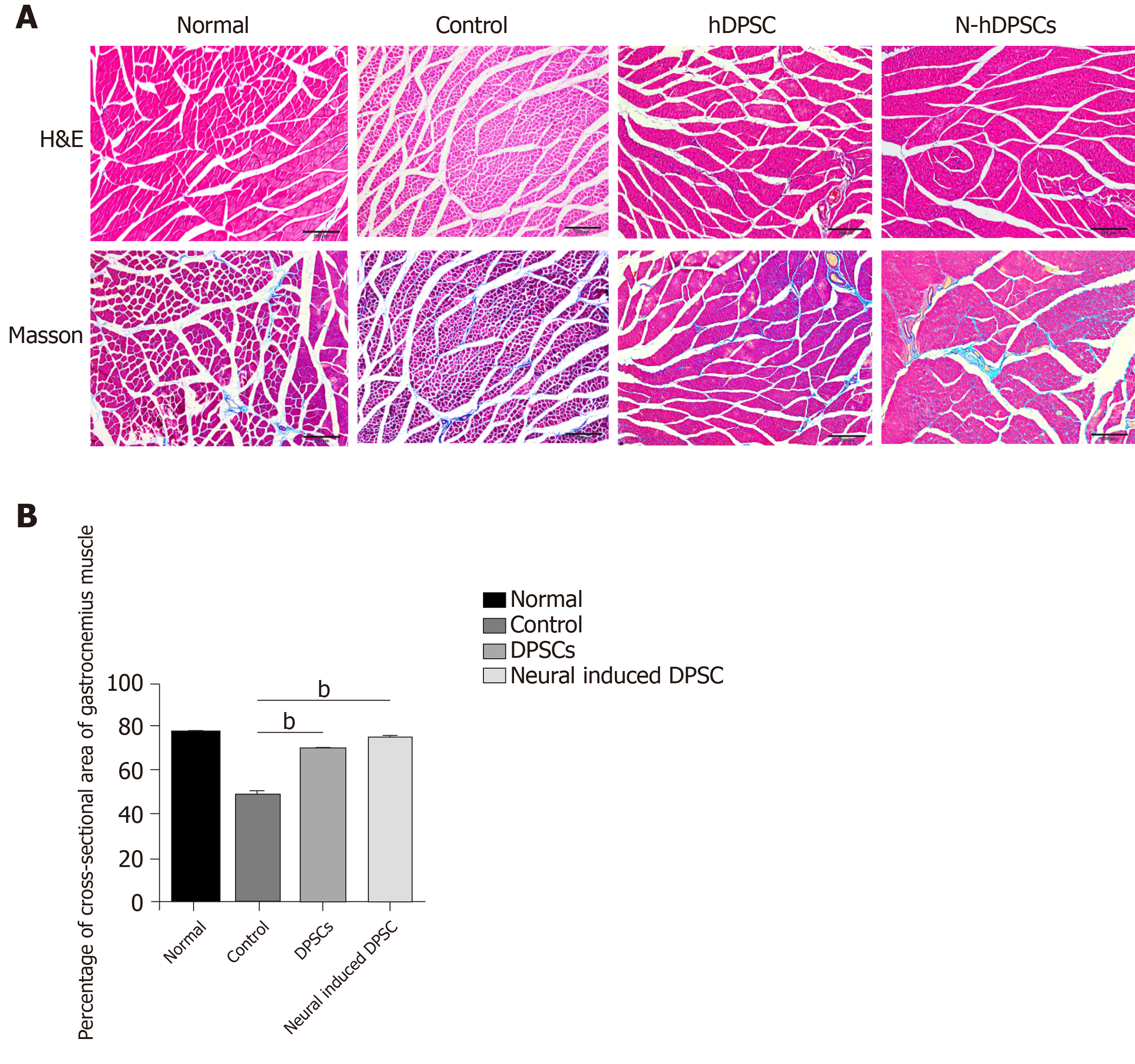
Figure 5 Hematoxylin & eosin staining and Masson staining of cross-sections of muscle fibers showed that neural-induced dental pulp stem cells could alleviate muscle atrophy.
A: The degree of muscle atrophy in the neural-induced dental pulp stem cells (N-DPSC) group was significantly improved, as shown by the larger area ratio of well-organized muscle fibers compared with those of the control and DPSC groups; B: Histograms presenting the percentage of area of muscle fiber. bP < 0.01. H&E: Hematoxylin & eosin staining; DPSC: Dental pulp stem cells.
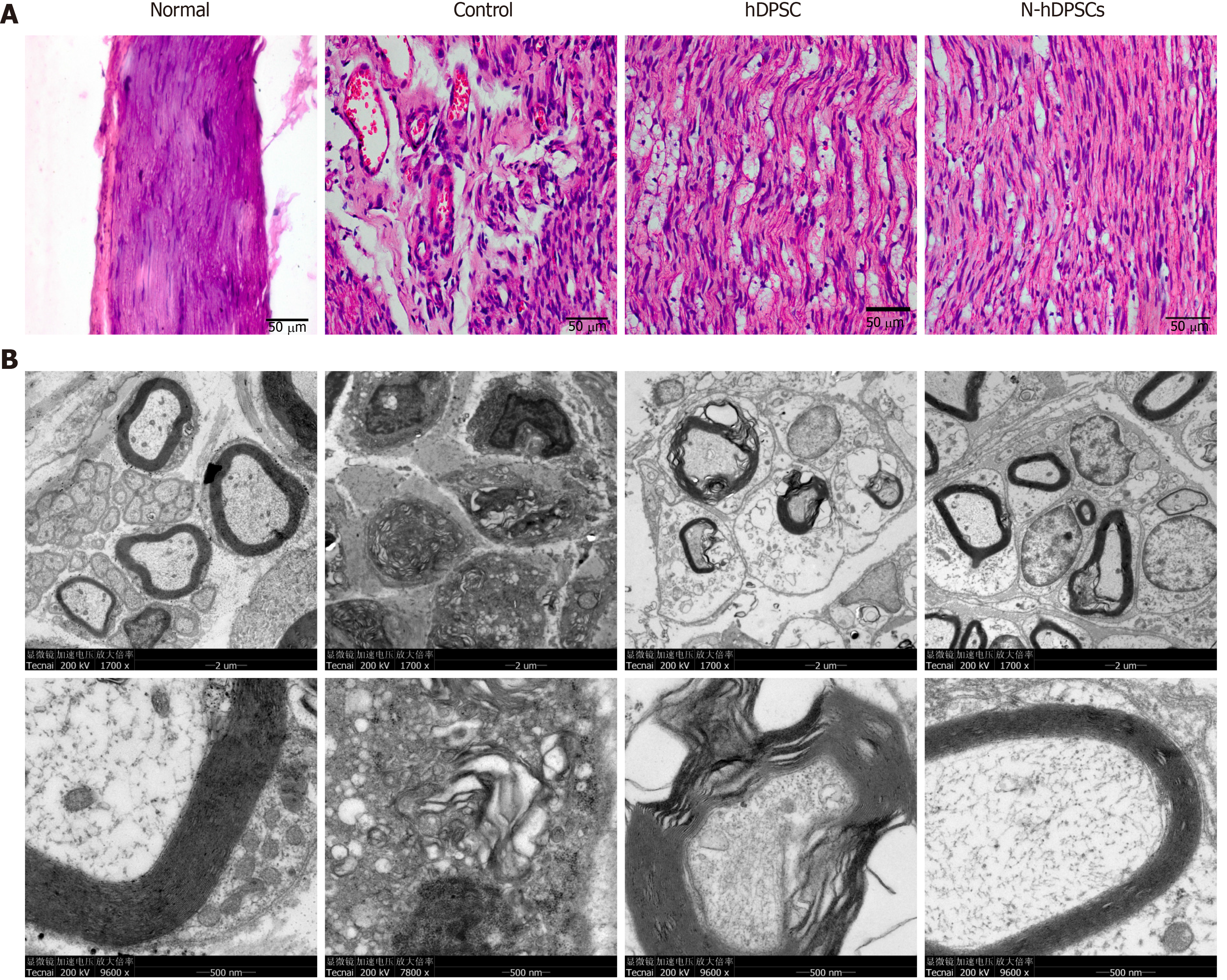
Figure 6 Histological and transmission electron microscopic evaluation showed that neural-induced dental pulp stem cells could help nerve reorganization and regeneration.
A: Hematoxylin & eosin staining of longitudinal sections of crushed nerves; B: Transmission electron microscopy of the nerve myelin sheath. n = 8. Bar = 50 μm. hDPSC: Dental pulp stem cells; N-hDPSCs: Neural-induced human dental pulp stem cells.
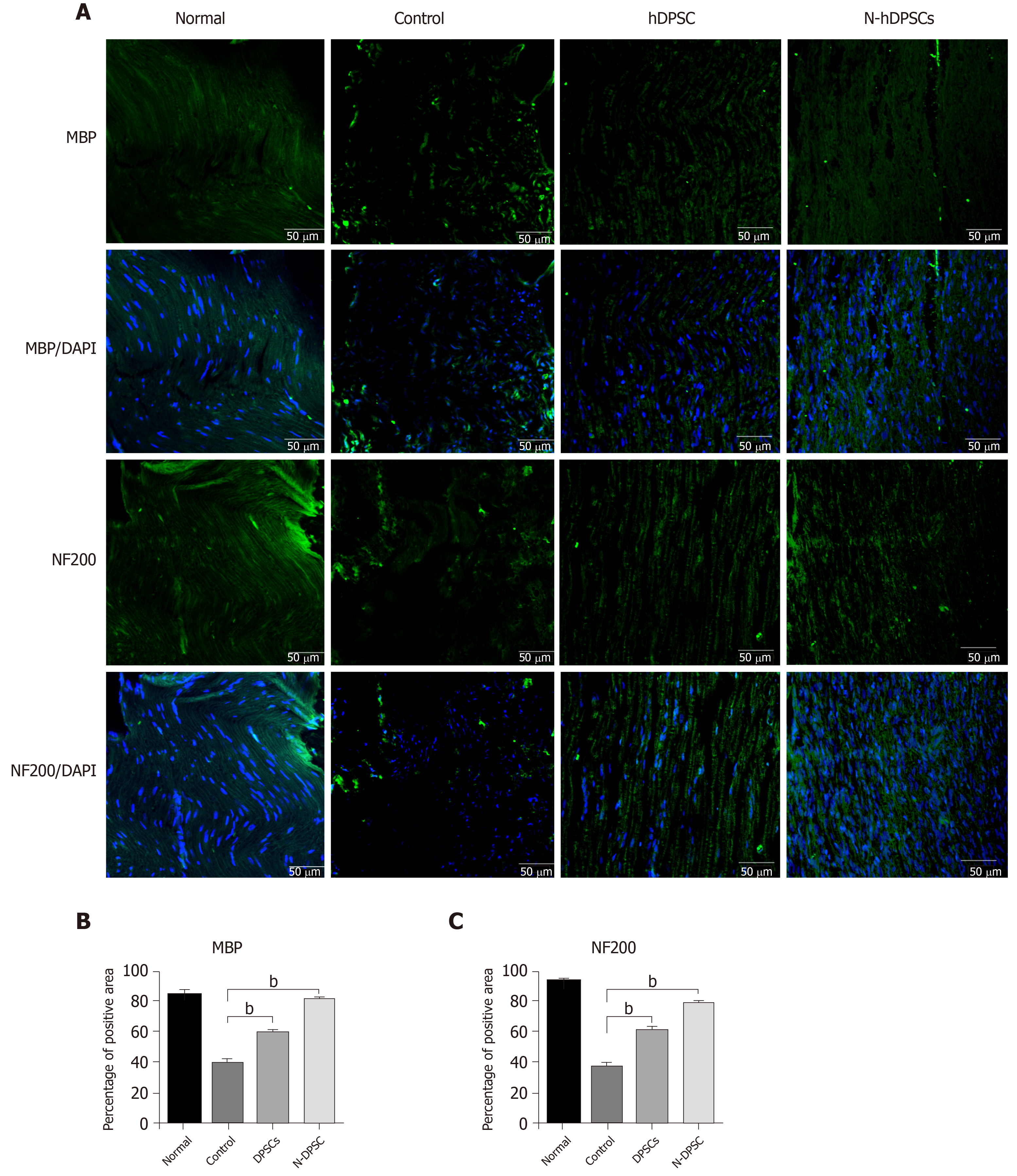
Figure 7 Immunofluorescence staining of crushed nerves for Myelin basic protein and NF-200 implied that neural-induced dental pulp stem cells help nerve regeneration.
A: Myelin basic protein (MBP) and NF200 staining; B and C: Percentage of positive area of MBP and NF200 staining. n = 8. Bar = 50 μm. bP < 0.01. MBP: Myelin basic protein; hDPSC: Dental pulp stem cells; N-hDPSCs: Neural-induced human dental pulp stem cells.
- Citation: Wang DR, Wang YH, Pan J, Tian WD. Neurotrophic effects of dental pulp stem cells in repair of peripheral nerve after crush injury. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(10): 1196-1213
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i10/1196.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1196