Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2019; 11(8): 476-490
Published online Aug 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i8.476
Published online Aug 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i8.476
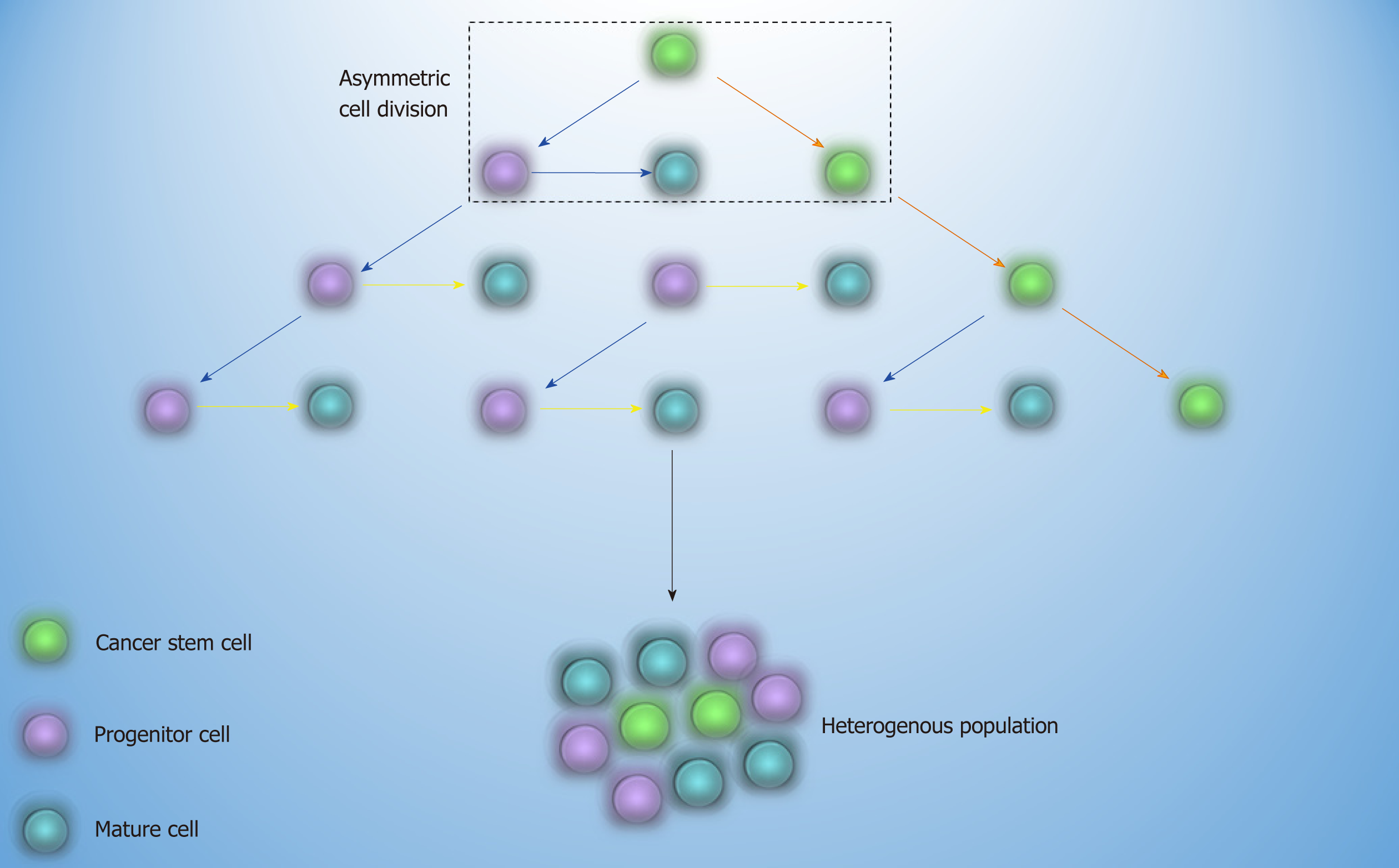
Figure 1 Cancer stem cell theory.
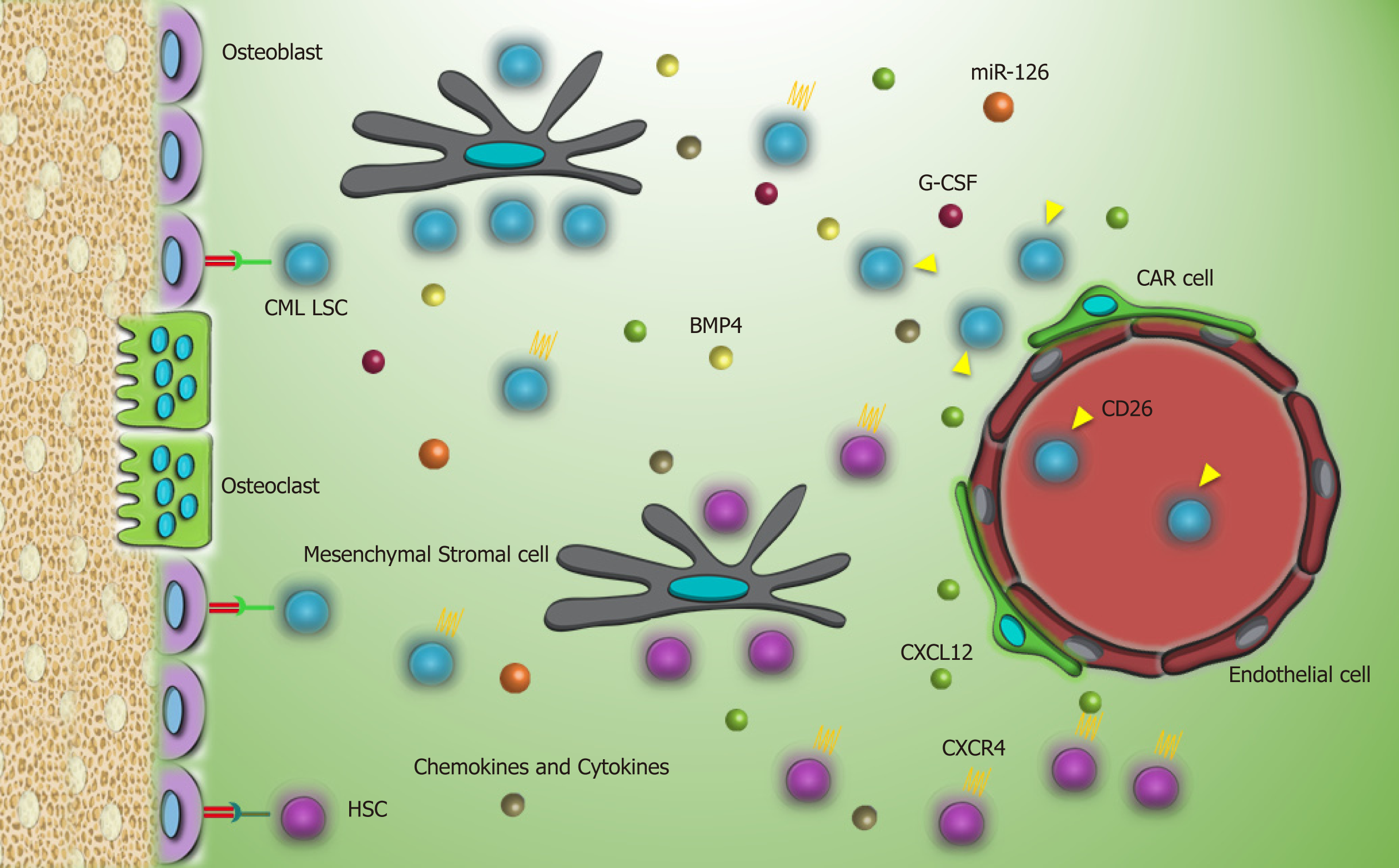
Figure 2 CML LSCs and their interaction with the bone marrow microenvironment.
Expression of CXCR4 is downregulated by kinase activity of P210BCRABL1, and secretion of G-CSF and expression of CD26 by CML LSCs altogether lead to mobilization of CML LSCs into the blood. At the same time, secretion of some proteins such as bone morphogenetic protein 4, miR-126, and other chemokines and cytokines through autocrine or paracrine mechanisms may support dormancy, growth, and drug resistance of CML LSCs. CML LSC: Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cell; HSC: Hematopoietic stem cell; CAR cell: CXCL12-abundant reticular cell; G-CSF: Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor; CXCL12: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12; CXCR4: C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; BMP4: Bone morphogenetic protein 4.
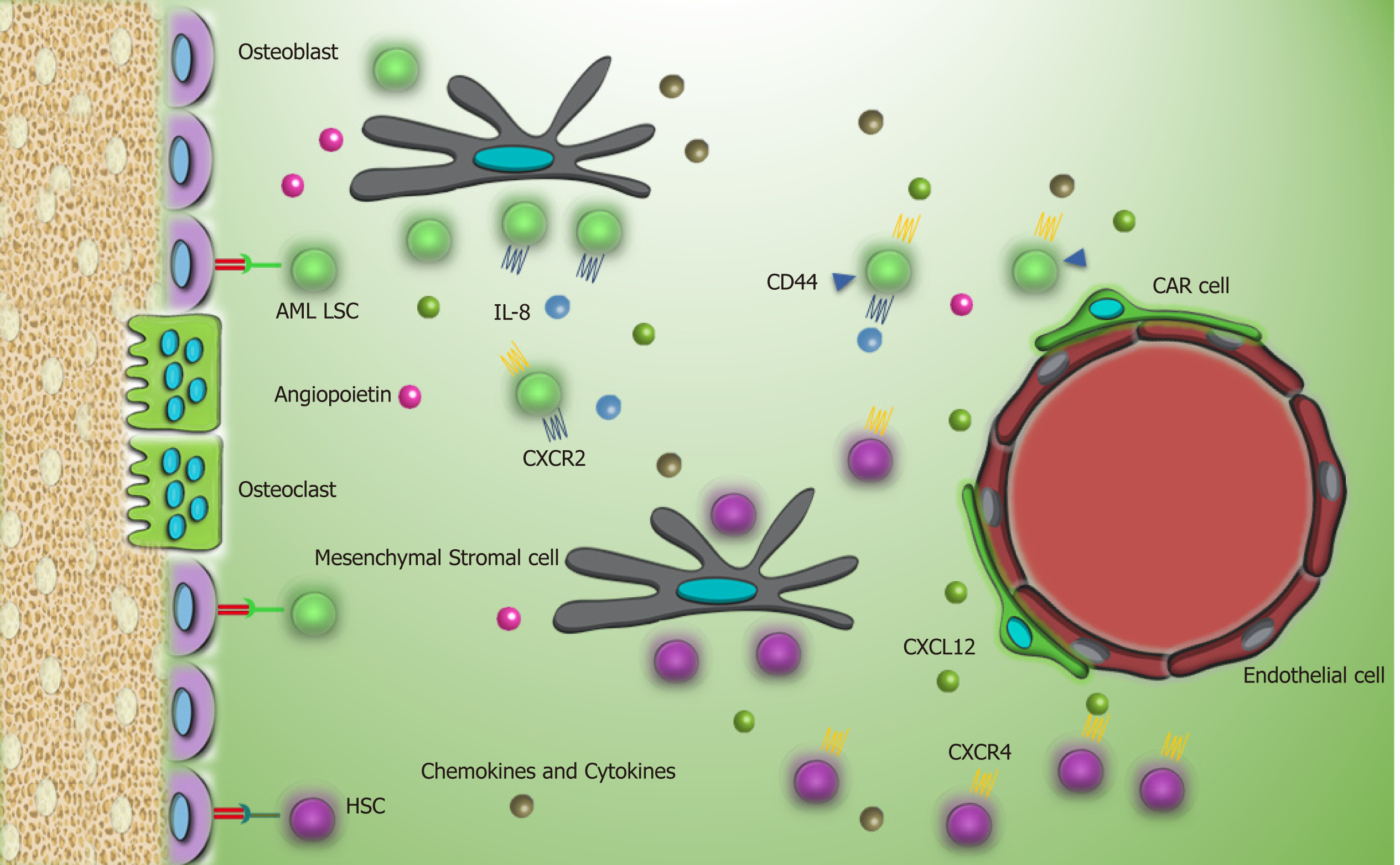
Figure 3 AML LSCs and their interaction with the bone marrow microenvironment in contrast to chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells, AML LSCs have high expression of CXCR4 that help them to reside in the bone marrow microenvironment.
Meanwhile, autocrine secretion of IL-8 by AML LSCs increases their survival. Enhanced secretion of pro-angiogenesis factors via autocrine and paracrine mechanism extends angiogenesis, which by providing metabolites and oxygen for AML LSCs leads to leukemia progression. AML LSCs: Acute myeloid leukemia stem cell; HSC: Hematopoietic stem cell; CAR cell: CXCL12-abundant reticular cell; CXCL12: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12; CXCR4: C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; CXCR2: C-X-C chemokine receptor type 2; IL-8: Interleukin-8.
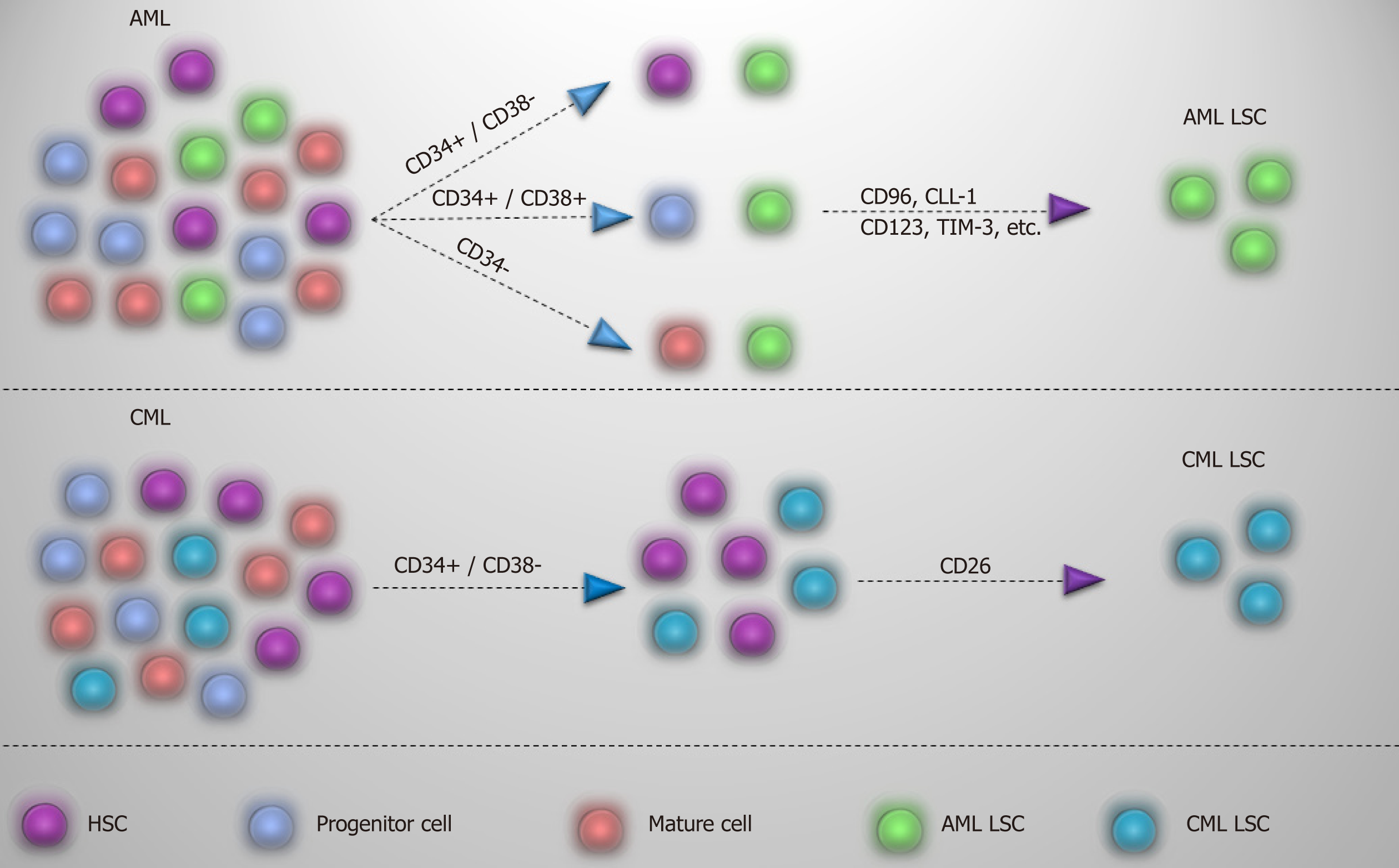
Figure 4 Detection of AML and CML LSCs.
While CML LSCs in chronic phase are in CD34+/CD38-, using CD26 helps to segregate them from normal hematopoietic stem cells. In AML, CD34 is not a fixed marker for detection of AML LSCs, and due to the heterogeneity of AML LSC populations, other markers are needed to identify these cells. CLL-1: C-type lectin-like molecule-1; TIM-3: T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-3; AML LSCs: Acute myeloid leukemia stem cell; HSC: Hematopoietic stem cell; CML LSCs: Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells.
- Citation: Houshmand M, Blanco TM, Circosta P, Yazdi N, Kazemi A, Saglio G, Zarif MN. Bone marrow microenvironment: The guardian of leukemia stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2019; 11(8): 476-490
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v11/i8/476.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v11.i8.476