Copyright
©2009 Baishideng.
World J Stem Cells. Dec 31, 2009; 1(1): 11-21
Published online Dec 31, 2009. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v1.i1.11
Published online Dec 31, 2009. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v1.i1.11
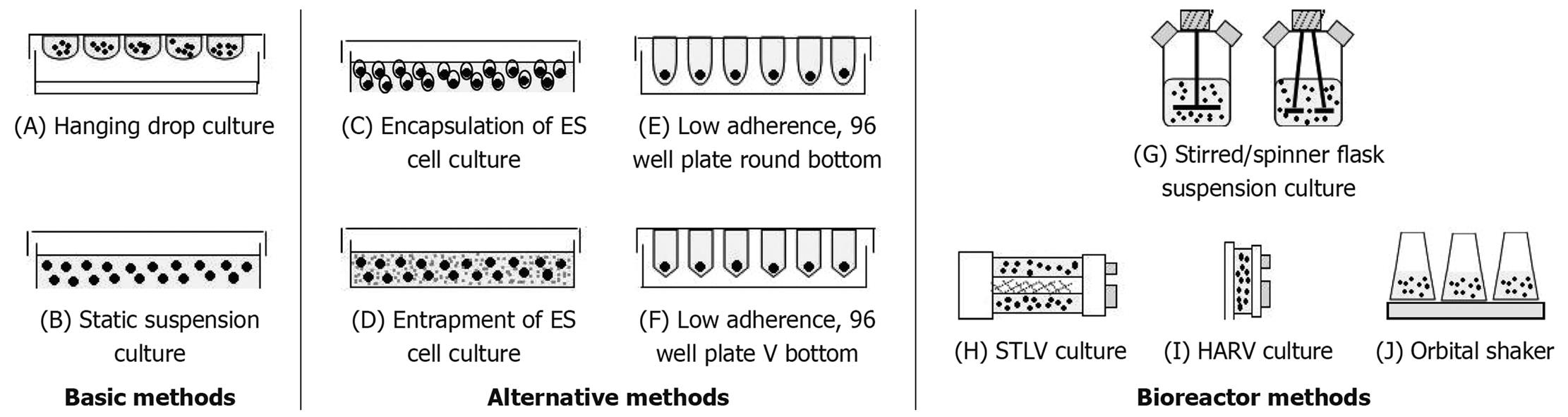
Figure 1 Schematic representation for vessels used in methods to form EBs from ES cells.
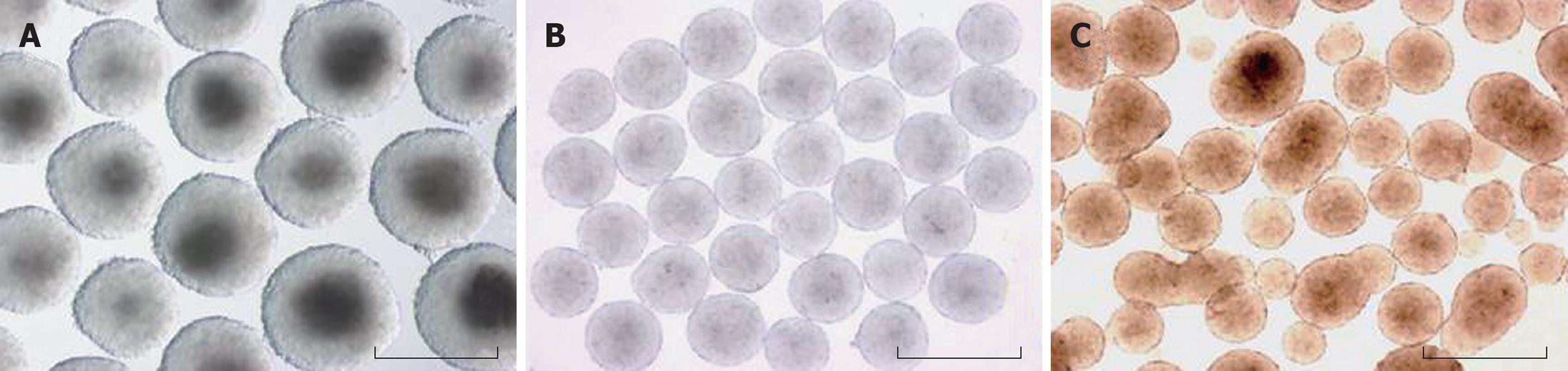
Figure 2 Formation of EBs in various methods.
Gross morphology of EBs derived from slow turning lateral vessel (STLV) (A), hanging drop (B) and suspension culture (C). Scale bars correspond to 500 μm.
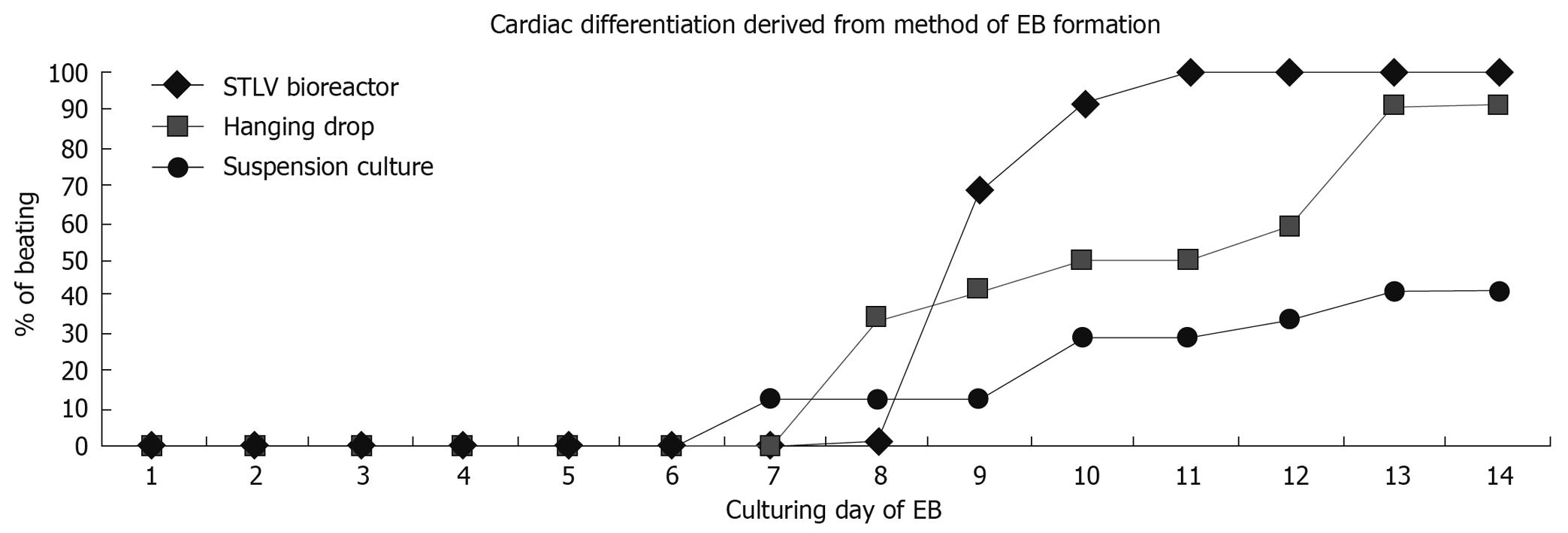
Figure 3 Illustration of the cumulative percentage of EBs containing contracting area derived from STLV, hanging drop and suspension culture.
- Citation: Rungarunlert S, Techakumphu M, Pirity MK, Dinnyes A. Embryoid body formation from embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells: Benefits of bioreactors. World J Stem Cells 2009; 1(1): 11-21
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v1/i1/11.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v1.i1.11