修回日期: 2022-01-04
接受日期: 2022-02-23
在线出版日期: 2022-02-28
蒺藜皂苷是从中药蒺藜内提取的活性成分, 具有抗癌、抗炎、调节免疫、等多种药理活性, 已有研究表明蒺藜皂苷能抑制胃癌细胞生长和诱导凋亡, 本研究主要探究蒺藜皂苷可能抑制胃癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭.
探讨蒺藜皂苷通过调控Wnt3a/β-catenin信号通路抑制胃癌细胞增殖、迁移侵袭的机制研究.
以胃癌细胞HGC-27为体外研究对象, 用浓度0、20 mg/L、40 mg/L蒺藜皂苷进行处理, 记为对照组(Control)、蒺藜皂苷20 mg/L组、蒺藜皂苷40 mg/L组; 将siRNA NC、siRNA Wnt3a转染胃癌细胞中, 用40 mg/L蒺藜皂苷处理, 记为蒺藜皂苷+siRNA NC组、蒺藜皂苷+siRNA Wnt3a组. 用噻唑蓝(methylthiazolyldiphenyl-tetrazolium bromide, MTT)检测细胞增殖活性; 伤口愈合实验检测细胞迁移; Transwell小室检测细胞侵袭; 蛋白免疫印迹法(Western blot)检测p21、细胞增殖核抗原-67(proliferating nuclear antigen-67, Ki67)、上皮性钙黏附素(epithelical cadherin, E-cadherin)、神经性钙黏附素(neural cadherin, N-cadherin)、波形蛋白(Vimentin)、Wnt3a、β-catenin蛋白表达.
与Control组比较, 蒺藜皂苷20 mg/L组、蒺藜皂苷40 mg/L组胃癌细胞活性、迁移率、侵袭细胞数显著降低, p21、E-cadherin蛋白表达增加, Ki67、N-cadherin、Vimentin、Wnt3a、β-catenin蛋白表达降低. 与蒺藜皂苷+siRNA NC组组相比, 蒺藜皂苷+siRNA Wnt3a组胃癌细胞活性、迁移率、侵袭细胞数显著降低, Wnt3a、β-catenin、Ki67、N-cadherin、Vimentin蛋白表达降低, p21、E-cadherin蛋白表达增加.
蒺藜皂苷可能通过抑制Wnt3a/β-catenin信号通路抑制胃癌细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭和上皮间质转化.
核心提要: 蒺藜皂苷药理活性广泛, 抗肿瘤效果明显, 研究证实蒺藜皂苷对结直肠癌、卵巢癌等癌症有抑制作用, 也能抑制胃癌细胞生长和诱导凋亡, 但是对胃癌细胞迁移、侵袭作用不明确.
引文著录: 曹斌, 姚林华, 冯昕. 蒺藜皂苷通过调控Wnt3a/β-catenin信号通路抑制胃癌细胞增殖、迁移侵袭的机制研究. 世界华人消化杂志 2022; 30(4): 191-197
Revised: January 4, 2022
Accepted: February 23, 2022
Published online: February 28, 2022
Tribulus terrestris saponins are active ingredients extracted from the traditional Chinese medicine tribulus terrestris, which have anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, immune regulation, and other pharmacological activities. Studies have shown that tribulus terrestris saponins can inhibit the growth of gastric cancer cells and induce apoptosis.
To investigate the mechanism of tribulus terrestris saponins to inhibit the proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells.
Gastric cancer cell line HGC-27 was used in this study. HGC-27 cells were treated with 0, 20 mg/L, and 40 mg/L tribulus terrestris saponins. Meanwhile, HGC-27 cells were transfected with Wnt3a siRNA and control siRNA (NC) and then treated with 40 mg/L tribulus terrestris saponins. MTT assay, wound healing assay, and Transwell assay were used to detect cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, respectively. Western blot was used to detect the protein expression of p21, proliferating nuclear antigen-67 (Ki67), epithelial cadherin (E-cadherin), neural cadherin (N-cadherin), Vimentin, Wnt3a, and β-catenin in the treated cells.
Compared with the blank control group, the proliferation activity, migration rate, and number of invaded gastric cancer cells in the tribulus terrestris saponins 20 mg/L and 40 mg/L groups were significantly reduced, p21 and E-cadherin protein expression increased, and Ki67, N-cadherin, Vimentin, Wnt3a, and β-catenin protein expression decreased. Compared with the tribulus terrestris saponins + NC siRNA group, the tribulus terrestris saponins + Wnt3a siRNA group had significantly lower proliferation activity, migration rate, and number of invaded cells, the expression of Wnt3a, β-catenin, Ki67, N-cadherin, and Vimentin decreased, and the expression of p21 and E-cadherin protein increased.
Tribulus terrestris saponins may inhibit the proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting the Wnt3a/β-catenin signaling pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
- Citation: Cao B, Yao LH, Feng X. Tribulus saponins inhibit proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating Wnt3a/β-catenin signaling pathway. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi 2022; 30(4): 191-197
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1009-3079/full/v30/i4/191.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.11569/wcjd.v30.i4.191
胃癌是临床消化科常见的恶性肿瘤, 受饮食习惯、工作方式等影响, 导致胃癌患者倾向年轻化趋势发展, 给人类社会带来不利的影响[1]. 目前, 关于胃癌治疗方式以外科手术, 辅以结合放疗、化疗, 胃癌患者的5年生存期限虽然得到延长, 但是患者复发、转移等问题未得到解决[2,3]. 最近研究表明[4], 中国传统医药用于治疗癌症的研究包括胃癌在内的人类癌症取得了进步. 蒺藜是蒺藜科植物蒺藜属植物, 药用价值较高, 蒺藜皂苷是从蒺藜内提取的主要活性成分, 具有抗癌、治疗心脑血管疾病、调节免疫、保护视神经等药理活性[5]. 最近的研究发现, 蒺藜皂苷通过降低细胞周期蛋白D1(Cyclin D1)、增加活化的含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶3(activated cysteine-containing aspartate proteolytic enzyme 3, cleaved caspase 3)蛋白表达抑制胃癌细胞增殖和阻滞细胞周期, 并诱导细胞的凋亡[6], 但是胃癌细胞迁移、侵袭的研究机制尚不清楚. Wnt/β-catenin通路与多种人类癌症发展密切相关, 能参与癌细胞生长分化、迁移和侵袭等过程影响癌症进展. 关于蒺藜皂苷与Wnt/β-catenin通路的调控作用在胃癌研究中尚不清楚, 因此, 本研究通过探讨蒺藜皂苷对胃癌细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭的研究及其可能相关的Wnt/β-catenin信号通路.
胃癌细胞HGC-27购于中国科学院上海细胞库; 胎牛血清、DMEM培养基购于美国HyClone公司; 蒺藜皂苷购于上海同田生物技术股份有限公司; siRNA NC序列、siRNA Wnt3a序列由上海吉玛公司设计合成; Lipofectamine 2000试剂盒购于上海研卉生物科技有限公司; MTT试剂盒购于碧云天生物; Transwell小室、Matrigel胶购于美国Corning; p21抗体、Ki67抗体、E-cadherin抗体、N-cadherin抗体、Vimentin抗体、Wnt3a抗体、β-catenin抗体购于自美国Santa Cruz Biotechnology公司; 二抗购于北京中杉金桥公司; BCA试剂盒购于上海吉至生化科技有限公司; 电化学发光液购于北京索莱宝科技有限公司.
将胃癌细胞HGC-27培养至含有10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基内, 并放置37 ℃、5% CO2恒温培养箱内进行孵育, 观察细胞生长情况, 细胞融合率为85%时, 加入胰酶消化培养, 每2 d换一次培养液. 取对数期胃癌细胞HGC-27, 用蒺藜皂苷浓度为0、20 mg/L、40 mg/L处理细胞, 记为Control组、蒺藜皂苷 20 mg/L组、蒺藜皂苷40 mg/L组; 将siRNA NC序列、siRNA Wnt3a序列转染胃癌细胞HGC-27中, 用40 mg/L蒺藜皂苷进行处理, 记为蒺藜皂苷+siRNA NC组、蒺藜皂苷+siRNA Wnt3a组.
取各组胃癌细胞HGC-27, 然后以2×104/孔接种至96孔板中, 固定培养48 h、72 h后, 每孔内添加MTT溶液20 μL, 培养4 h以每孔内150 μL添加DMSO溶液, 观察结晶是否溶解, 溶解后置于酶标仪490 nm处检测细胞吸光度值(Absorbance, A), 细胞活性(%) = 实验组A值/对照组A值×100%.
取培养48 h各组胃癌细胞HGC-27并接种在6孔板中, 然后采用无菌枪头垂直划线, 倒置显微镜下拍照, 放入恒温培养箱内培养24 h并拍照, 观察伤口愈合情况, 即为细胞迁移情况.
实验开始前将Matrigel胶解冻. 取各组胃癌细胞HGC-27用不含血清的培养基重悬细胞, Transwell小室上室内加入Matrigel胶50 μL, 下室加入含有血清的培养基500 μL, 放入恒温培养箱中培养24 h, 取出小室擦去未进行侵袭的细胞, 采用甲醛、结晶紫固定及染色, 显微镜下观察视野明亮区域, 并计数.
取培养48 h各组胃癌细胞HGC-27, 与蛋白裂解液在冰上裂解20 min, 使用BCA法检测蛋白浓度. 将蛋白样品加至SDS-PAGE上样孔中, 80 V电泳30 min, 110 V电泳2 h, 转膜, 封闭培养2 h, 将PVDF膜与一抗(稀释浓度1:800)4 ℃过夜孵育, 室温下与二抗(稀释浓度1:2000)孵育2 h, 用电化学发光液显色. 采用Image J分析蛋白条带灰度值, 以GAPDH作为内参.
统计学处理 采用SPSS 19.0统计学软件分析处理数据, 计量结果以(mean±SD)表示, 单因素方差分析用于多组间比较, t检验用于两组间比较. P<0.05表示差异具有统计学意义.
与Control组比较, 蒺藜皂苷 20 mg/L组、蒺藜皂苷40 mg/L组胃癌细胞活性在48 h、72 h明显降低, 差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05), 表1.
与Control组比较, 蒺藜皂苷 20 mg/L组、蒺藜皂苷 40 mg/L组胃癌细胞迁移率、侵袭细胞数目明显减少, 差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05), 表2.
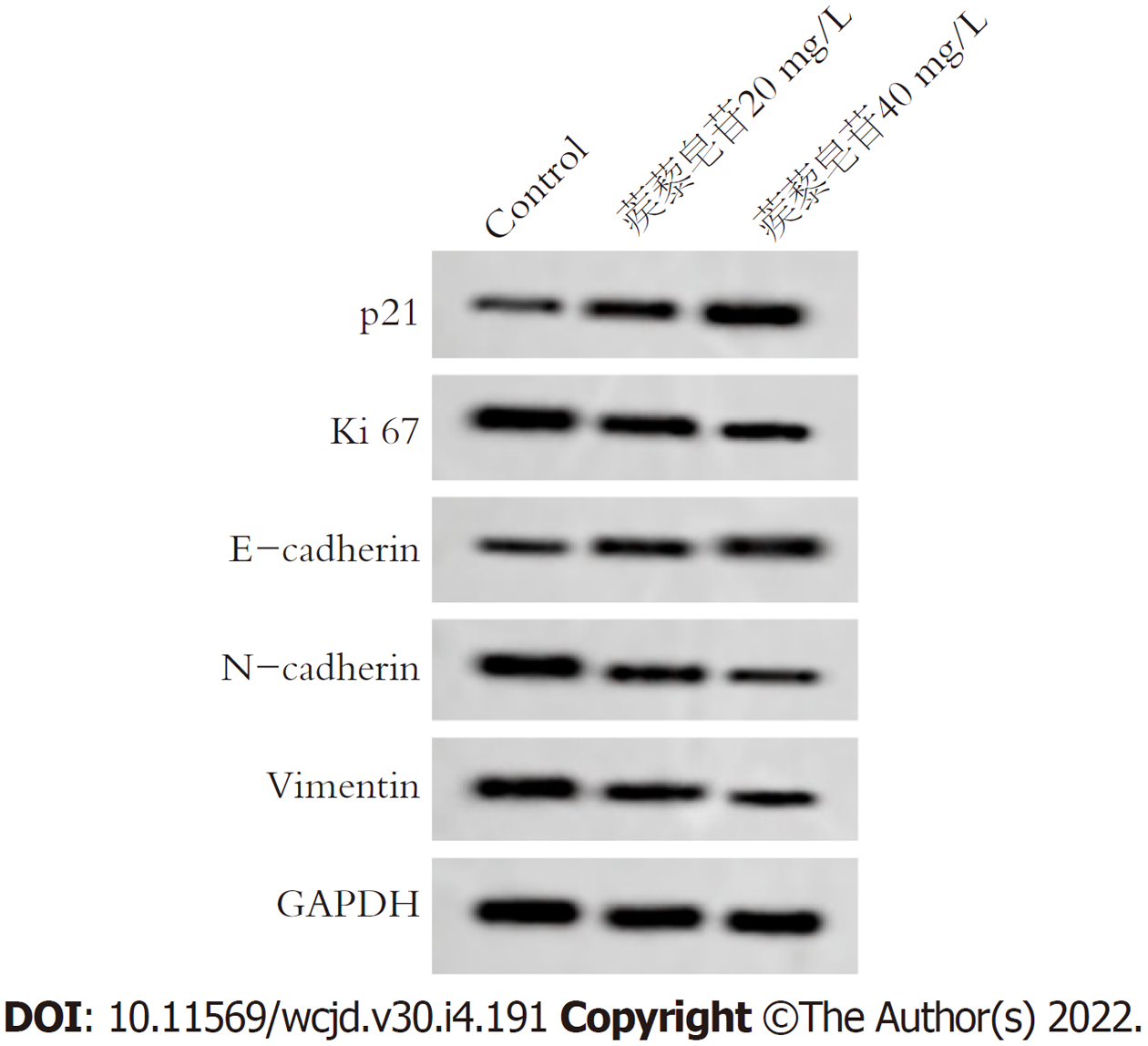
与Control组比较, 蒺藜皂苷20 mg/L组、蒺藜皂苷40 mg/L组胃癌细胞p21、E-cadherin蛋白表达明显增加, Ki67、N-cadherin、Vimentin蛋白表达明显降低, 差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05), 图1和表3.
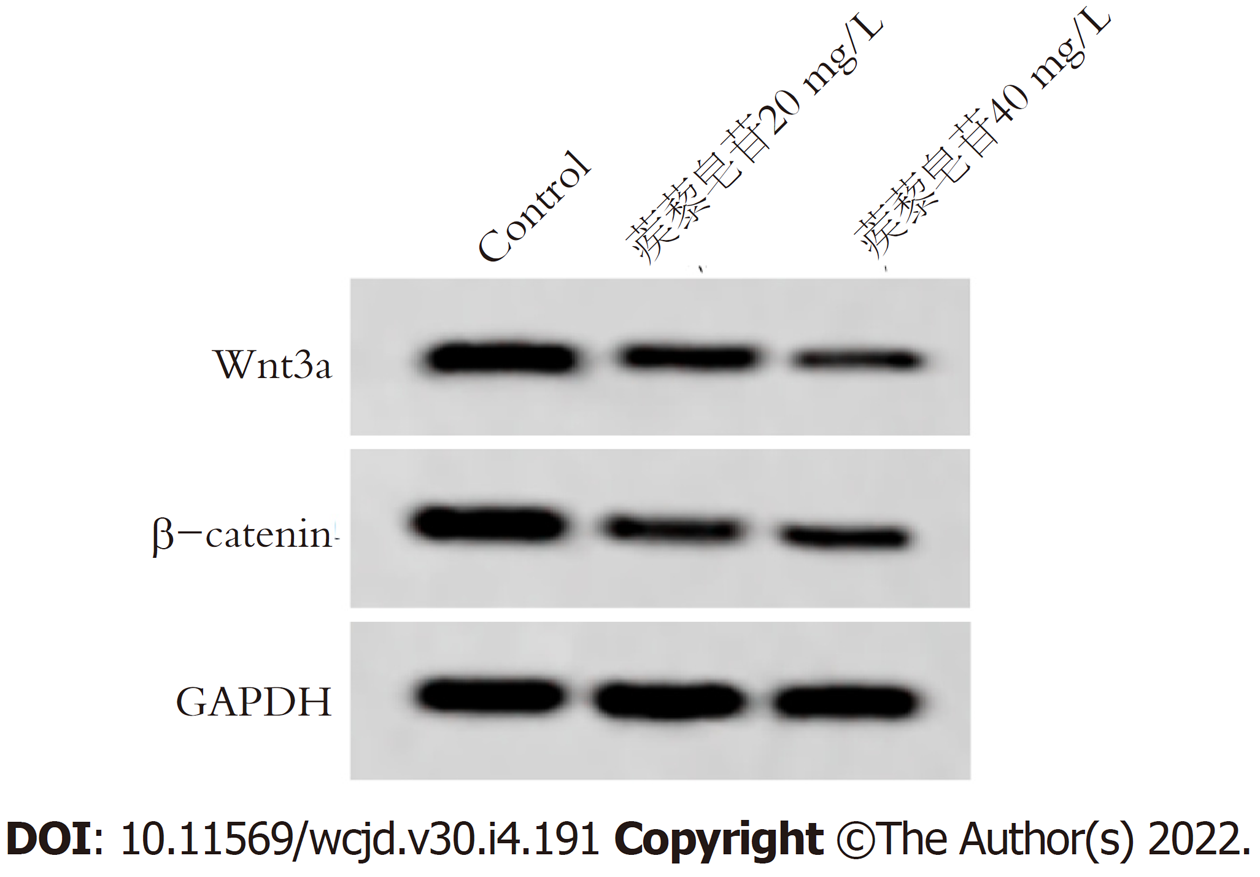
与Control组比较, 蒺藜皂苷 20 mg/L组、蒺藜皂苷 40 mg/L组、蒺藜皂苷40 mg/L+抑制剂组胃癌细胞Wnt3a、β-catenin蛋白表达明显降低, 差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05), 图2和表4.
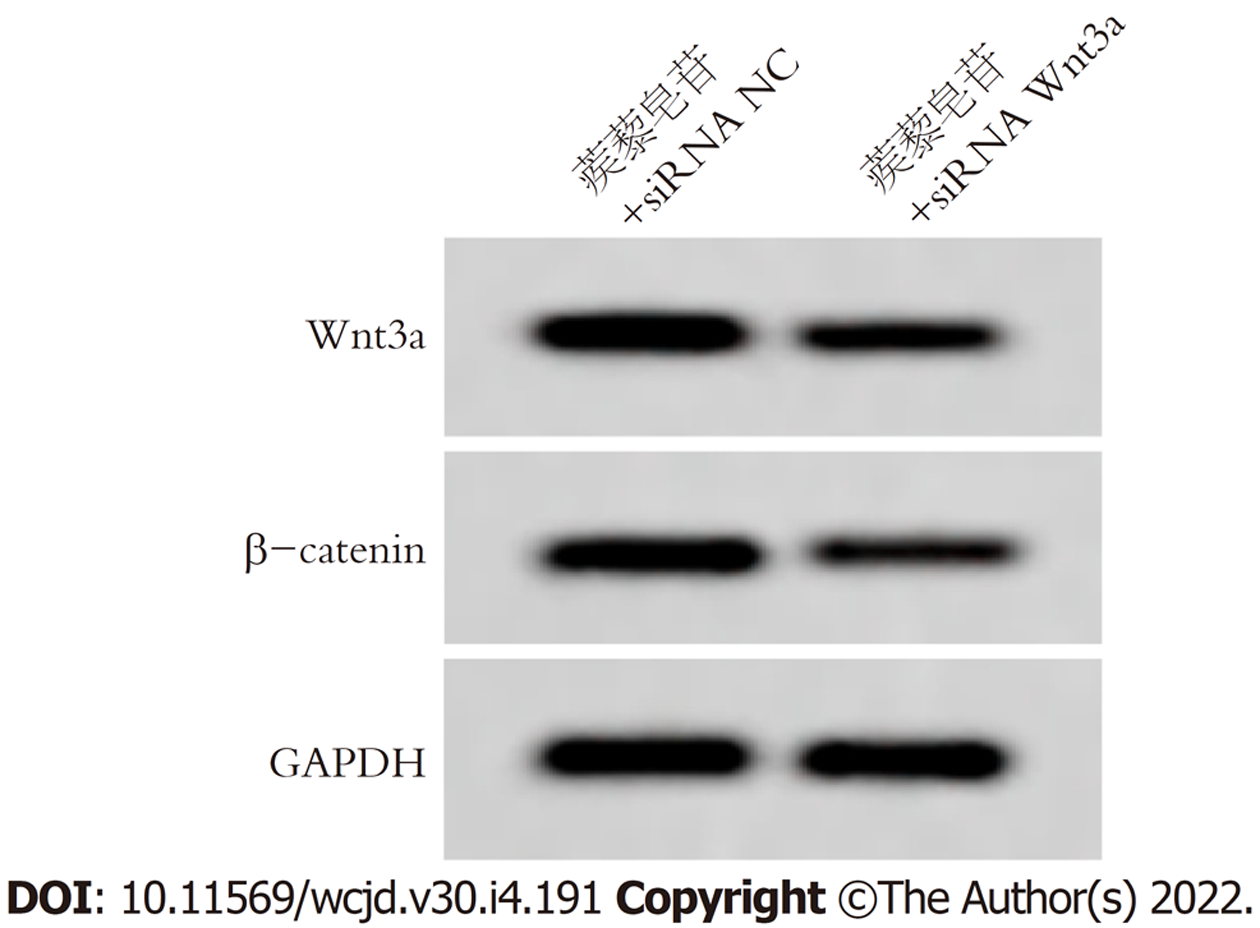
与蒺藜皂苷+siRNA NC组比较, 蒺藜皂苷+siRNA Wnt3a组胃癌细胞Wnt3a、β-catenin蛋白表达明显降低, 差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05), 图3和表5.
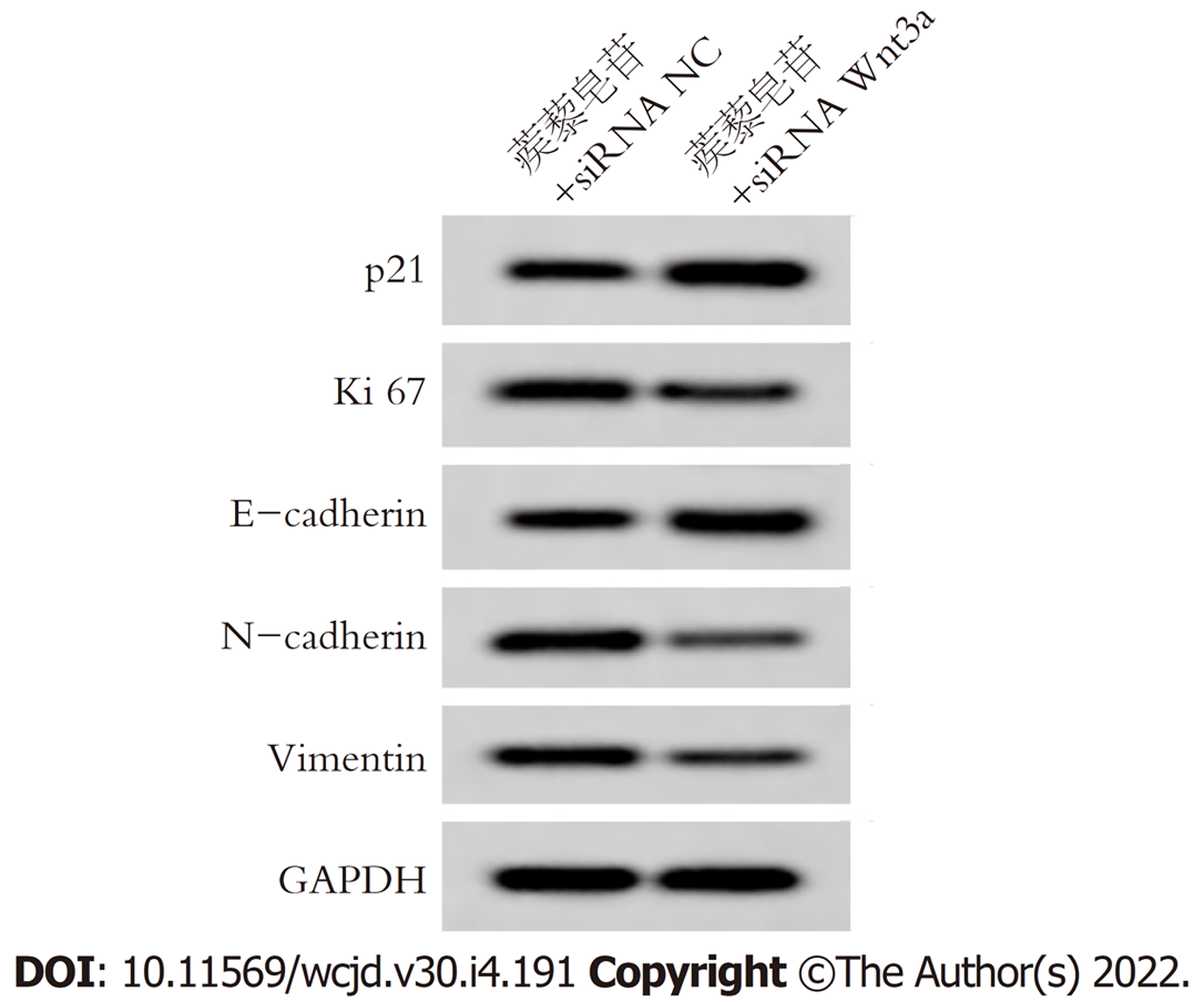
与蒺藜皂苷+siRNA NC组相比, 蒺藜皂苷+siRNA Wnt3a组胃癌细胞活性在48 h、72 h明显降低, 迁移率、侵袭细胞数明显减少, 差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05), 表6.
蒺藜作为蒺藜属植物, 种植广泛, 含有丰富的化学成分, 包括黄酮类、皂苷类、生物碱类化合物、醌类等, 其中皂苷类化合物较为丰富[8], 国内外研究表明蒺藜皂苷具有降血糖、抗癌、治疗心血管疾病等药理作用[9,10]. 陈志伟等[11]研究结果显示, 蒺藜皂苷能抑制卵巢癌细胞增殖, 阻滞细胞周期发展, 并诱导细胞凋亡. 肺癌研究中发现, 蒺藜皂苷通过降低Cyclin D1蛋白表达, 增加p27、cleaved caspase 3蛋白表达, 以起到抑制细胞增殖和诱导细胞凋亡的作用[12]. 之前的研究结果显示, 蒺藜皂苷能抑制胃癌细胞增殖和诱导细胞凋亡[6], 但是胃癌细胞的迁移、侵袭作用机制尚不清楚. 本研究通过不同浓度蒺藜皂苷处理胃癌细胞, 观察蒺藜皂苷对胃癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的作用. 研究结果显示, 蒺藜皂苷 20 mg/L组、蒺藜皂苷40 mg/L组能降低胃癌细胞增殖活性, 减少细胞侵袭数, 抑制细胞迁移率. p21蛋白是近年发现的细胞周期蛋白抑制基因, Ki67是细胞增殖抗原, 与细胞有丝分裂相关, p21、Ki67与细胞增殖密不可分[13]. 上皮间质转化主要是上皮细胞间质转化现象, 是获得癌细胞迁移、侵袭重要过程; E-cadherin、N-cadherin、Vimentin是上皮间质转化(epithelial mesenchymal transition, EMT)相关标志物, 与癌细胞转移有关[14,15]. 本研究结果显示, 蒺藜皂苷增加了胃癌细胞p21、E-cadherin蛋白表达, 降低Ki67、N-cadherin、Vimentin蛋白表达, 提示蒺藜皂苷能抑制胃癌细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭和上皮间质转化.
Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在胃癌细胞生长、迁移侵袭等生物学过程有关, 也是EMT重要的调控途径, Wnt转录因子激活时, 与跨膜受体蛋白结合形成复合物, β-catenin产生磷酸化, 调节下游基因的表达[16-18]. 研究结果显示[19], 姜黄素抑制胃癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭, 并下调胃癌细胞中N-cadherin、snail1、Wnt3a、β-catenin, 上调E-cadherin蛋白表达, 说明其作用机制可能与Wnt3a/β-catenin/EMT通路有关. 赵鹏等[20]研究结果显示, RBMS3通过抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路进而抑制胃癌细胞侵袭和上皮间质转化. 本研究结果显示, 不同浓度蒺藜皂苷处理胃癌细胞后, Wnt3a、β-catenin蛋白表达下调, 提示蒺藜皂苷抑制胃癌增殖、迁移和侵袭可能与Wnt3a/β-catenin有关. 将siRNA Wnt3a转染胃癌细胞后, 使用蒺藜皂苷处理胃癌细胞内, 结果显示, Wnt3a、β-catenin蛋白表达, 细胞活性、迁移率降低, 侵袭细胞数目减少, p21、E-cadherin蛋白表达上调, Ki67、N-cadherin、Vimentin蛋白表达下调, 提示蒺藜皂苷可能通过抑制Wnt3a/β-catenin信号通路影响胃癌细胞增殖、迁移侵袭和上皮间质转化.
综上所述, 蒺藜皂苷能抑制胃癌细胞增殖、迁移侵袭和上皮间质转化, 其作用机制可能与抑制Wnt3a/β-catenin信号通路有关.
蒺藜皂苷能抑制胃癌细胞增殖和诱导细胞凋亡, 并阻滞胃癌细胞周期进展, 而Wnt3a/β-catenin信号通路研究与胃癌密不可分, 对胃癌细胞生长、转移有抑制作用.
本研究主要探究蒺藜皂苷与Wnt3a/β-catenin信号通路调控作用对胃癌细胞增殖、转移的影响, 拟解决蒺藜皂苷对胃癌细胞迁移、侵袭的影响, 及其相关的Wnt3a/β-catenin信号通路, 为胃癌研究提供新的研究方向.
本研究主要探究蒺藜皂苷对胃癌有抑制作用, 且可能与Wnt3a/β-catenin信号通路有关, 本研究证明了蒺藜皂苷可能通过Wnt3a/β-catenin信号通路抑制胃癌细胞增殖、转移, 为胃癌研究提供合理的数据支撑.
以胃癌细胞HGC-27为体外研究对象, 用浓度0、20 mg/L、40 mg/L蒺藜皂苷进行处理, 记为对照组(Control)、蒺藜皂苷 20 mg/L组、蒺藜皂苷40 mg/L组; 将siRNA NC、siRNA Wnt3a转染胃癌细胞中, 用40 mg/L蒺藜皂苷处理. MTT检测细胞增殖活性; 伤口愈合、Transwell小室实验检测细胞迁移与侵袭能力; Western blot检测p21、Ki67、E-cadherin、N-cadherin、Vimentin、Wnt3a、β-catenin蛋白表达.
蒺藜皂苷呈浓度依赖性降低胃癌细胞活性、迁移率、侵袭细胞数, 增加p21、E-cadherin蛋白表达, 降低Ki67、N-cadherin、Vimentin、Wnt3a、β-catenin蛋白表达. 与蒺藜皂苷+siRNA NC组组相比, 蒺藜皂苷+siRNA Wnt3a组胃癌细胞活性、迁移率、侵袭细胞数显著降低, Wnt3a、β-catenin、Ki67、N-cadherin、Vimentin蛋白表达降低, p21、E-cadherin蛋白表达增加.
蒺藜皂苷抑制胃癌细胞增殖、迁移侵袭和上皮间质转化, 并与抑制Wnt3a/β-catenin信号通路有关.
本研究发现, 蒺藜皂苷与Wnt3a/β-catenin信号通路调控作用对胃癌细胞生长、转移有抑制作用, 为胃癌的临床治疗可能提供了帮助. 但是本研究只注重体外实验研究, 关于体内动物实验需要进一步开展实验证明.
学科分类: 胃肠病学和肝病学
手稿来源地: 浙江省
同行评议报告学术质量分类
A级 (优秀): 0
B级 (非常好): 0
C级 (良好): C, C
D级 (一般): D
E级 (差): 0
科学编辑: 张砚梁 制作编辑:张砚梁
| 1. | Machlowska J, Baj J, Sitarz M, Maciejewski R, Sitarz R. Gastric Cancer: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Classification, Genomic Characteristics and Treatment Strategies. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 2. | Song Z, Wu Y, Yang J, Yang D, Fang X. Progress in the treatment of advanced gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 2017;39:1010428317714626. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 3. | Johnston FM, Beckman M. Updates on Management of Gastric Cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. 2019;21:67. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 4. | Pan X, Tao H, Nie M, Liu Y, Huang P, Liu S, Sun W, Wu J, Ma T, Dai A, Lu J, Liu B, Zou X, Sun Q. A clinical study of traditional Chinese medicine prolonging the survival of advanced gastric cancer patients by regulating the immunosuppressive cell population: A study protocol for a multicenter, randomized controlled trail. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99:e19757. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 7. | Gao J, Zhao C, Liu Q, Hou X, Li S, Xing X, Yang C, Luo Y. Cyclin G2 suppresses Wnt/β-catenin signaling and inhibits gastric cancer cell growth and migration through Dapper1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37:317. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 9. | Wang Y, Zhao H, Liu Y, Guo W, Bao Y, Zhang M, Xu T, Xie S, Liu X, Xu Y. GC-MS-Based Metabolomics to Reveal the Protective Effect of Gross Saponins of Tribulus terrestris Fruit against Ischemic Stroke in Rat. Molecules. 2019;24. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 13. | Hardwick LJA, Kortum AJ, Constantino-Casas F, Watson PJ. Breed-related expression patterns of Ki67, γH2AX, and p21 during ageing in the canine liver. Vet Res Commun. 2021;45:21-30. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 14. | Lamouille S, Xu J, Derynck R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:178-196. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 15. | Higashimori A, Dong Y, Zhang Y, Kang W, Nakatsu G, Ng SSM, Arakawa T, Sung JJY, Chan FKL, Yu J. Forkhead Box F2 Suppresses Gastric Cancer through a Novel FOXF2-IRF2BPL-β-Catenin Signaling Axis. Cancer Res. 2018;78:1643-1656. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 16. | Dongre A, Weinberg RA. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20:69-84. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 17. | Arend RC, Londoño-Joshi AI, Straughn JM, Buchsbaum DJ. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway in ovarian cancer: a review. Gynecol Oncol. 2013;131:772-779. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 18. | Gonzalez DM, Medici D. Signaling mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci Signal. 2014;7:re8. [PubMed] [DOI] |