修回日期: 2008-02-25
接受日期: 2008-03-08
在线出版日期: 2008-03-28
目的: 研究异甘草酸镁(MI)对CCl4诱导急性肝损伤小鼠的保肝降酶作用与及其对肝组织中核因子-κB(nuclear factor kappa B, NF-κB)、细胞间黏附分子-1(ICAM-1)表达的影响.
方法: 30只♂昆明小鼠(28±2.2 g), 随机分为3组, 即正常对照组、模型组和异甘草酸镁组. 正常对照组ip生理盐水(0.1 mL/10 g), 模型组ip 0.1% CCl4(0.1 mL/10g), 异甘草酸镁组于ip 0.1% CCl4(0.1 mL/10 g)前15 min予MI(15 mg/kg体质量) ip, 1次/d, 共5次. 采用生化法测定血清ALT、AST及肝组织MDA和SOD含量. 采用HE染色观察肝组织病理损伤. SP免疫组化染色检测NF-κB、ICAM-1表达.
结果: 肝损伤组ALT、AST及MDA较正常组显著升高(465.10±35.90 kU/L vs 47.40±4.13 kU/L; 582.37±25.63 kU/L vs 116.06±12.82 kU/L; 4.07±0.38 nmol/mg vs 1.39±0.03 nmol/mg; 均P<0.01), SOD明显降低(29.71±2.25 U/mg vs 87.02±4.84 U/mg, P<0.01). 在正常组织中无NF-κB、ICAM-1表达, 肝损伤模型组中NF-κB有较强表达, ICAM-1在肝坏死区强表达. MI组ALT、AST及MDA(263.51±22.89 kU/L, 292.56±26.01 kU/L, 2.17±0.03 nmol/mg)较肝损伤组显著降低(P<0.01), SOD(58.04±2.56 U/mg)明显升高(P<0.05), NF-κB、ICAM-1表达均较肝损伤组减弱, 肝组织坏死程度也轻.
结论: NF-κB、ICAM-1在CCl4诱导小鼠急性肝损伤中表达明显增强, MI可减少NF-κB及ICAM-1表达并减轻肝损伤程度.
引文著录: 鲍启德, 杨兰兰, 王利, 崔东来. 异甘草酸镁对CCl4诱导小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用. 世界华人消化杂志 2008; 16(9): 1004-1007
Revised: February 25, 2008
Accepted: March 8, 2008
Published online: March 28, 2008
AIM: To investigate the effect of magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate (MI) on acute liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) in mice and its relationship with the expression of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in liver tissues.
METHODS: Thirty male Kunming mice (28 ± 2.2 g) were divided randomly into 3 groups: model group, normal control group and MI-treated group. The model of acute liver injury was established by intraperitoneal injection of 1% CCl4 (0.1 mL/10 g). The mice in normal control group and MI-treated group were injected with sterile saline, and furthermore, the MI-treated mice were intraperitoneally injected with MI (15 mg/kg, once per day for five days) 15 min before CCl4 injection. Serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and tissue contents of malondialdehyde (MDA) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) were measured using biochemical method. SP immunohistochemistry was used to detect NF-κB and ICAM-1 expression. The pathological alterations were observed after HE staining.
RESULTS: The serum levels of AST, ALT and tissue content of MDA were significantly increased in model group as compared with those in normal control group (465.10 ± 35.90 kU/L vs 47.40 ± 4.13 kU/L; 582.37 ± 25.63 kU/L vs 116.06 ± 12.82 kU/L; 4.07 ± 0.38 nmol/mg vs 1.39 ± 0.03 nmol/mg; all P < 0.01), but tissue content of SOD was significantly decreased (29.71 ± 2.25 U/mg vs 87.02 ± 4.84 U/mg, P < 0.01). NF-κB and ICAM-1 were not expressed in normal control group, but obviously expressed in model group. In comparison with those in model group, the tissue expression of NF-κB and ICAM-1 in MI-treated group were decreased in concurrence with the alleviation of liver injury as well as a statistically significant decrease in AST (263.51 ± 22.89 kU/L), ALT (292.56 ± 26.01 kU/L) and MDA (2.17 ± 0.03 nmol/mg, P < 0.05) and increase in SOD (58.04 ± 2.56 U/mg, P < 0.01) in hepatic homogenate.
CONCLUSION: NF-κB and ICAM-1 are strongly expressed in acute liver injury in mice. MI can protect mice against CCl4-induced acute liver injury by suppressing NF-κB activation and subsequent expression of ICAM-1.
- Citation: Bao QD, Yang LL, Wang L, Cui DL. Protective effects of magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in mice. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi 2008; 16(9): 1004-1007
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1009-3079/full/v16/i9/1004.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.11569/wcjd.v16.i9.1004
近年来研究发现核因子-κB(nuclear factor kappa B, NF-κB)、细胞间黏附分子-1(intercellular adhesion molecule-1, ICAM-1)过度表达在各种肝脏炎症、纤维化的发生、发展中起重要作用[1]. 异甘草酸镁(magnesium isoglycyrrhizina, MI)为甘草酸中的有效成分, 是单一构型的甘草酸α体, 其含量达98%以上, 具有较强的抗炎、保护肝细胞膜、解毒、抗生物氧化及改善肝功能作用[2]. 本文旨在探讨MI对CCl4诱导小鼠急性肝损伤的保护机制与肝组织中NF-κB、ICAM-1表达的关系.
成年健康清洁级♂昆明小鼠30只, 体质量28±2.2 g, 购自河北医科大学实验动物中心, 自由进食水. 兔抗ICAM-1 pAb购自武汉博士德生物工程公司, 小鼠抗NF-κB mAb购自美国Stanta Cruz公司. 兔和小鼠SP试剂盒购自北京中山生物技术公司. MI由江苏正大天晴药业生产.
1.2.1 分组及造模: 全部动物随机分成3组, 每组10只, 分别为正常对照组、模型组和MI组. 正常对照组动物ip生理盐水(0.1 mL/10 g); 模型组和MI组ip 0.1% CCl4(0.1 mL/10 g), 且MI组于ip 0.1% CCl4( 0.1 mL/10 g)前15 min予以MI(15 mg/kg, 相当于正常成人用量的15倍)ip, 1次/d, 共5 d. d 5所有动物摘眼球取血, 静置2 h, 3000 r/min离心15 min, 取血清保存于-20冰箱中, 以备ALT、AST测定; 取肝右叶保存-70℃冰箱中, 以备MDA、SOD测定; 取部分肝左叶40 g/L甲醛固定, 用于HE染色、免疫组织化学染色.
1.2.3 检测方法: 血清ALT、AST的测定采用生化法. 肝组织MDA和SOD含量按说明书测定. 采用HE染色观察肝组织病理损伤. NF-κB、 ICAM-1免疫组织化学染色采用SP法.
统计学处理 数据用mean±SD表示, 两组间均数间分析采用t检验, P<0.05认为有统计学意义.
模型组ALT、AST活性显著高于正常对照组; MI组ALT、AST活性低于模型组, 两者相比具有显著统计学差异(P<0.01), 提示MI可降低CCl4所致急性肝损伤小鼠血清ALT、AST活性(表1).
| ALT(kU/L) | AST(kU/L) | MDA(nmol/mg) | SOD(U/mg) | NF-κB | ICAM-1 | |
| 正常对照组 | 47.40±4.13 | 116.06±12.82 | 1.39±0.03 | 87.02±4.84 | 0 | 0 |
| 肝损伤组 | 465.10±35.90b | 582.37±25.63b | 4.07±0.38b | 29.71±2.25b | 82.47±5.60 | 45.09±6.30 |
| MI组 | 263.51±22.89d | 292.56±26.01d | 2.17±0.03d | 58.04±2.56c | 50.71±4.90d | 13.30±4.57d |
模型组与正常对照组比较, MDA明显升高(P<0.01), SOD活力明显下降(P<0.01). MI组与模型组比较MDA明显升高(P<0.01), SOD活力明显下降(P<0.05), 提示MI可提高肝组织SOD活力, 降低MDA含量(表1).
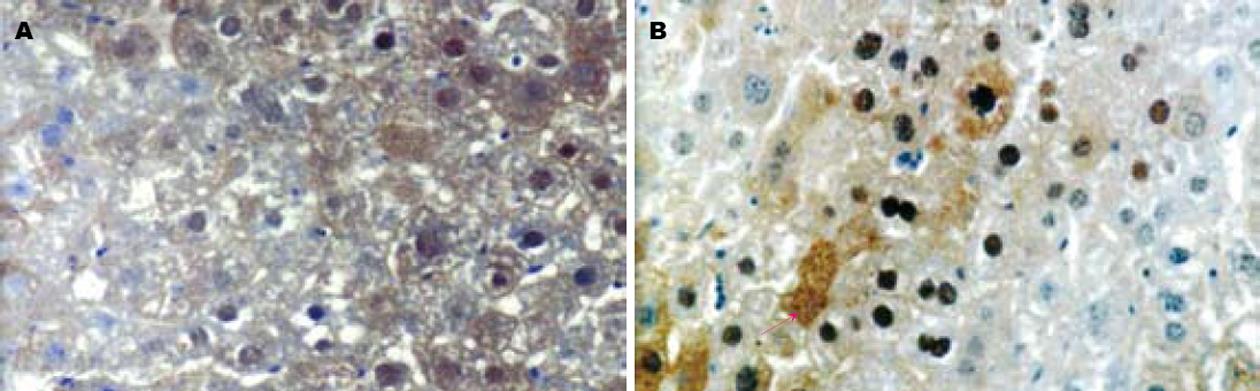
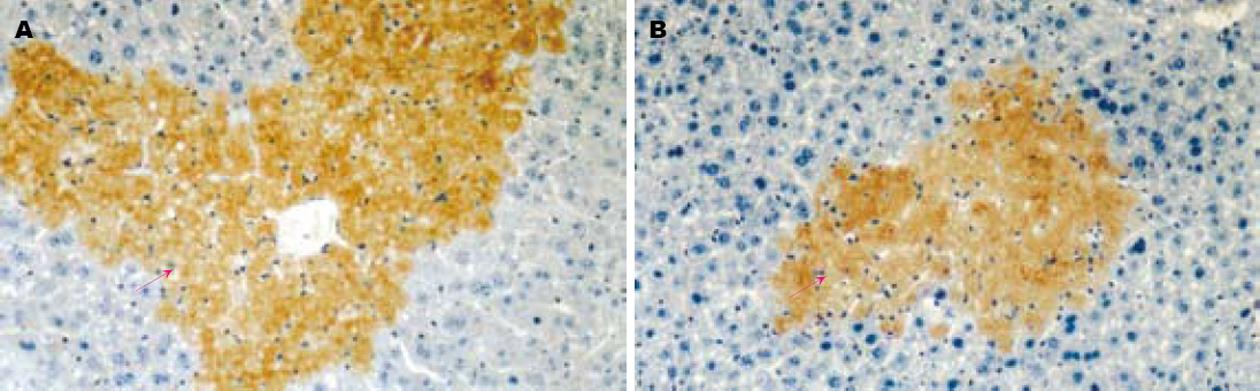
正常肝组中 NF-κB无表达. 模型组中NF-κB表达强烈, 主要表达在坏死区周围的肝细胞的胞核中, 呈棕黄色, 胞质也有表达, MI组表达明显减弱, 阳性面积明显减小(P<0.01, 表1), 表明MI明显抑制NF-κB活性(图1).
近年来发现, NF-κB、ICAM-1等细胞因子在CCl4诱导小鼠急性肝损伤发病机制中可能起重要作用, 并有可能成为防治急性肝损伤的新靶位[3-4]. NF-κB是真核细胞中普遍存在的一种转录因子, 活化后可激活多种相关基因的转录和表达. 研究表明, 在缺血再灌注[5]、刀豆素A[6]及CCl4[7]等所致肝损伤中NF-κB表达均明显上调, 并促进多种炎症介质的转录表达, 加重肝损伤. 抑制NF-κB活性可减轻CCl4等所致肝损伤[8].
活化的NF-κB可诱导ICAM-1基因转录. ICAM-1是免疫球蛋白超家族的细胞黏附糖蛋白, 作为一种配体介导白细胞的黏附及迁移, 大量白细胞聚集造成微循环障碍, 通过呼吸暴发产生大量氧自由基, 破坏生物膜, 引起或加重组织损伤[9]. 研究表明在CCl4诱导急性肝损伤中, ICAM-1的表达明显上调, 且ICAM-1表达强弱与肝细胞坏死程度密切相关, 并认为ICAM-1的上调和炎症细胞的积累可能是其致肝损伤的关键[10-11].
SOD是超氧阴离子自由基的清除剂, 可抑制自由基启动的脂质过氧化反应, 对机体的氧化与抗氧化平衡起着至关重要的作用[12]. MDA脂质过氧化的最终产物自由基可诱发和增强机体内脂质过氧化作用, 导致细胞膜系统损伤及其功能丧失.
CCl4诱导小鼠急性肝损伤中NF-κB激活机制尚不十分清楚, 一般认为与CCl4造成氧应激有关. 后者可诱导NF-κB活化, 表达上调, 同时促进ICAM-1基因转录. 本研究也显示CCl4诱导急性肝损伤组小鼠ALT、AST、MDA升高, SOD活力下降, 肝组织病理损伤明显, 在肝细胞坏死区NF-κB、ICAM-1表达明显上调, 并与肝细胞损伤严重程度分布一致, 而应用MI后, 肝损伤的酶学指标显著下降, 病理上肝组织损伤程度显著减轻, 肝组织内NF-κB及ICAM-1蛋白表达量亦相应降低, 这证实NF-κB参与了CCl4诱导小鼠急性肝损伤的发病机制, 通过抑制NF-κB活性, 可抑制黏附因子的表达, 减轻肝组织损伤程度.
MI是一种肝细胞保护剂, 具有抗炎、保护肝细胞膜及改善肝功能的作用, 其有效成分是单-18α异构体甘草酸, 具有更强的保肝抗炎、免疫抑制、抗生物氧化等多种功效, 能稳定肝细胞膜, 清除体内氧自由基, 减轻肝细胞的炎症和坏死, 促进肝细胞的再生和修复[13-14]. 最近研究发现MI对大鼠肝星状细胞增殖有明显抑制作用, 且存在剂量时间依存关系, 提高肝星状细胞的SOD活性, 降低异常升高的MDA含量, 在治疗肝纤维化方面具有良好的应用前景[15].
本研究表明MI对CCl4引起的小鼠急性肝损伤具有保护作用, 其机制可能与增强机体对氧化应激的防御能力, 保护肝细胞免受脂质过氧化损害, 从而减少肝组织内NF-κB过度表达而诱发的炎症反应有关. 因此MI可通过清除氧自由基, 调控NF-κB或ICAM-1表达来防治肝损伤.
甘草酸制剂具有明显的抗病毒、降低转氨酶、减低血清胆红素、抗纤维化、抗氧化、抗细胞凋亡等作用, 临床上已经广泛用于治疗肝脏疾病, 异甘草酸镁作为新一代甘草酸制剂显示有更好的临床疗效.
宣世英, 教授, 山东省青岛市市立医院肝病内科.
异甘草酸镁应用临床时间尚短, 对其进行基础实验研究可为临床提供应用实验依据. 但相关研究尚少.
有研究表明异甘草酸镁对肝星状细胞的增殖和氧化应激、对CCl4诱导的慢性肝损伤、D-氨基半乳糖诱导的急性肝损伤有保护作用.
本研究设计合理, 数据可靠, 具有一定的创新性和科学性.
编辑: 李军亮 电编:郭海丽
| 1. | Liu SL, Degli Esposti S, Yao T, Diehl AM, Zern MA. Vitamin E therapy of acute CCl4-induced hepatic injury in mice is associated with inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B binding. Hepatology. 1995;22:1474-1481. [PubMed] |
| 3. | Nagata K, Suzuki H, Sakaguchi S. Common pathogenic mechanism in development progression of liver injury caused by non-alcoholic or alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Toxicol Sci. 2007;32:453-468. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 4. | Kawasuji A, Hasegawa M, Horikawa M, Fujita T, Matsushita Y, Matsushita T, Fujimoto M, Steeber DA, Tedder TF, Takehara K. L-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 regulate the development of Concanavalin A-induced liver injury. J Leukoc Biol. 2006;79:696-705. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 5. | Frangogiannis NG. Chemokines in ischemia and reperfusion. Thromb Haemost. 2007;97:738-747. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 6. | Ma XL, Li YH, Gao JX, Li J, Guo L, Wu CZ. Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in the liver is under the control of nuclear factor kappa B in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;. [PubMed] |
| 7. | Son G, Iimuro Y, Seki E, Hirano T, Kaneda Y, Fujimoto J. Selective inactivation of NF-kappaB in the liver using NF-kappaB decoy suppresses CCl4-induced liver injury and fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007;293:G631-G639. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 9. | Ramaiah SK, Jaeschke H. Role of neutrophils in the pathogenesis of acute inflammatory liver injury. Toxicol Pathol. 2007;35:757-766. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 10. | Ledebur HC, Parks TP. Transcriptional regulation of the intercellular adhesion molecule-1 gene by inflammatory cytokines in human endothelial cells. Essential roles of a variant NF-kappa B site and p65 homodimers. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:933-943. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 11. | Neubauer K, Eichhorst ST, Wilfling T, Buchenau M, Xia L, Ramadori G. Sinusoidal intercellular adhesion molecule-1 up-regulation precedes the accumulation of leukocyte function antigen-1-positive cells and tissue necrosis in a model of carbontetrachloride-induced acute rat liver injury. Lab Invest. 1998;78:185-194. [PubMed] |
| 12. | Ahn TH, Yang YS, Lee JC, Moon CJ, Kim SH, Jun W, Park SC, Kim JC. Ameliorative effects of pycnogenol on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic oxidative damage in rats. Phytother Res. 2007;21:1015-1019. [PubMed] [DOI] |