Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
基因芯片法筛选萎缩性胃炎相关的差异表达基因
徐俊荣, 崔大祥, 张沥, 张玲霞, 贾长河, 张宁霞, 江梅, 曹广周
徐俊荣, 张沥, 张玲霞, 贾长河, 张宁霞, 江梅, 曹广周, 西安市中心医院消化内科 陕西省西安市 710003
崔大祥, 中国人民解放军第四军医大学基因诊断技术研究所 陕西省西安市 710033
徐俊荣, 女, 1970-02-15生, 陕西省西安市人, 汉族.1993年西安医科大学临床医学系本科毕业, 2001年第四军医大学研究生课程班毕业. 硕士, 主治医师, 主要从事幽门螺杆菌及消化系疾病研究, 发表论文7篇.
ORCID number: $[AuthorORCIDs]
电话: 029-7582637
收稿日期: 2002-07-08
修回日期: 2002-07-10
接受日期: 2002-07-22
在线出版日期: 2003-01-15
目的: 建立大鼠萎缩性胃炎模型, 用高密度基因芯片筛选萎缩性胃炎相关的差异表达基因.
方法: 采用热盐水、盐水、热水灌胃的方法建立大鼠萎缩性胃炎模型, 并设立正常对照组、正常喂养组作为对照. 提取标本的总RNA, 定量后并反转录成cDNA, 萎缩性胃炎标本标记上Cy5, 正常对照标本标记上Cy3, 与含有8248个大鼠基因的cDNA芯片进行杂交, 常规洗片, 扫描, 分析杂交结果.
结果: 热盐水组灌胃12 wk的大鼠经病理诊断已存在萎缩性胃炎的特征, 盐水、热水组灌胃的大鼠在24 wk时经病理诊断也存在萎缩性胃炎的特征; 热盐水组与正常对照组之间的差异基因共有436个, 145个基因在萎缩性病变组织中呈高表达, 291个基因在正常组织中呈高表达; 热水组与正常对照组之间的差异表达基因共有398个, 98个基因在萎缩性病变组织中呈高表达, 300个基因在正常组织中呈高表达; 热盐水组与盐水组之间差异表达基因共有36个, 其中23个在热盐水组中呈高表达, 13个基因在盐水对照组中呈高表达.
结论: 成功地建立了大鼠萎缩性胃炎的模型; 筛选出了与热盐水、盐水、热水诱发的萎缩性胃炎发生有关的差异表达基因.
关键词: N/A
引文著录: 徐俊荣, 崔大祥, 张沥, 张玲霞, 贾长河, 张宁霞, 江梅, 曹广周. 基因芯片法筛选萎缩性胃炎相关的差异表达基因. 世界华人消化杂志 2003; 11(1): 47-50
Screening of differentially expressed genes associated with atrophic gastritis by high density cDNA microarrays
Jun-Rong Xu, Da-Xiang Cui, Li Zhang, Ling-Xia Zhang, Chang-He Jia, Ning-Xia Zhang, Mei Jiang, Guang-Zhou Cao.
Jun-Rong Xu, Li Zhang, Ling-Xia Zhang, Chang-He Jia, Ning-Xia Zhang, Mei Jiang, Guang-Zhou Cao, Department of Gastroenterology, Xi'an Municipal Central Hosital, Xi'an 710003, Shaanxi Province, China
Da-Xiang Cui, Institute of Genetic Diagnosis, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an 710033, Shaanxi Province, China
Correspondence to: Jun-Rong Xu, Xi'an Municipal Central Hospital, Xi'an 710003, Shaanxi Province, China. xujunrong@netease.com
Received: July 8, 2002
Revised: July 10, 2002
Accepted: July 22, 2002
Published online: January 15, 2003
AIM: To establish the rat model and to screen differentially expressed genes closely associated with atrophic gastritis.
METHODS: The rat atrophic gastritis model was induced by intragastrically giving hot high salt water, hot water and high salt water. Normal raising group and normal control group were used as control. Total RNAs of specimens were extracted, quantified, and reversely transcripted into cDNA. cDNAs from atrophic gastritis were labeled with Cy5, and cDNAs from the normal control group were labeled with Cy3, which were mixed with cDNAs from the control group with equal quantity, then hybridized with cDNA chips containing 8 248 genes. Chips were washed, scanned and analyzed.
RESULTS: There were atrophic lesions in rat gastric sinus confirmed by pathological examination in the hot high salt water group at the 12th week, but in the high salt water group and the hot water group, there were atrophic lesions at the 24th week. A total of 436 differentially expressed genes were identified by cDNA chip between the hot high salt water group and the normal control group, 145 genes were highly expressed in the hot high salt water group and 291 genes were highly expressed in the normal control group; 398 differentially expressed genes were identified in the hot water group and the normal control group, 98 genes were highly expressed in the hot water group, and 300 genes were highly expressed in the normal control group; and 36 differentially expressed genes were confirmed between the hot high salt water group and the high salt water group, 23 genes were highly expressed in the hot high salt water group and 13 genes were highly expressed in the high salt water group.
CONCLUSION: Rat atrophic gastritis models were established successfully, differentially expressed genes associated with atrophic gastritis induced respectively by hot high salt water, high salt water and hot water were identified by way of high density cDNA chip.
Key Words: N/A
0 引言
萎缩性胃炎是人类发病率最高的胃癌前病变, 是胃癌发生过程中的一个非常关键的环节. 建立简单可靠的萎缩性胃炎动物模型并阐明其发生机制, 对胃癌发生过程的研究具有十分重要的现实意义. 我们自1995年以来, 一直致力于胃癌早期诊断体系的研究, 对癌前病变至胃癌过程的差异表达基因进行了筛选与克隆, 初步建立了胃癌早期诊断芯片与预警体系[1-5]. 但是, 对正常胃黏膜至萎缩性胃炎过程缺少深入研究. 我们以人类饮食中不可缺少的两大因素-食物的热度与咸度, 作为参量, 建立大鼠萎缩性胃炎模型, 并用含8 248个基因的鼠cDNA芯片对萎缩性胃炎模型的胃窦黏膜组织和正常大鼠胃窦黏膜组织之间的差异表达基因进行了筛选, 获取了正常胃黏膜与萎缩性胃炎之间的差异表达基因, 为进一步阐明萎缩性胃炎的分子机制奠定了坚实的基础.
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料
体质量为200-250 g、7 周龄健康、性成熟的♂SD大鼠96只及饲料购自第四军医大学动物实验中心; 总RNA提取试剂盒采用Promega公司的 总RNA提取试剂盒; 反转录试剂盒采用Clontech 公司的Smart PCR cDNA synthesis kit; Cy3-dUTP, Cy5-dUTP 购自 Pharmacia 公司; 氯化钠等化学试剂购自西安化学试剂公司; 含8248个基因的高密度基因芯片M80S购自上海联合基因集团博道公司, 基因名称与序列见http://www.biodo.com; 芯片扫描采用Affymetrix公司的428TM Array Scanner; 图像采用ImageGene 3.0 Software(BioDiscovery Inc.)进行定量分析. 杂交试剂与洗涤芯片试剂按照要求配制.
1.2 方法
采用热盐水、盐水、热水灌胃的方法建立大鼠萎缩性胃炎模型, 并设立正常对照组、正常喂养组作为对照. 造模方法参见参考文献[6]. 分别采取灌胃24 wk的盐水组、热水组, 灌胃12 wk的热盐水组、正常组大鼠的胃窦部黏膜组织, 按照试剂盒说明书提取标本的mRNA, 按组混合在一起, 紫外线定量, 反转录并标记上荧光探针, 实验标本mRNA在反转录时标记上Cy5-dUTP, 正常对照标本在反转录时标记上Cy3-dUTP. 高密度芯片检测实验分为两组. 第一组(芯片1)的对照组为盐水组大鼠胃窦部组织mRNA, Cy3标记; 实验组为热盐水组大鼠胃窦部组织mRNA, Cy5标记. 第二组(芯片2)的对照组为正常组大鼠胃窦部组织mRNA, Cy3标记; 实验组为热水组大鼠胃窦部组织mRNA, Cy5标记. 把标记的探针在95 ℃变性5 min, 然后把实验组与对照组探针等量混合后, 加到芯片上, 盖上杂交盖, 在42 ℃杂交17 h. 然后, 取出芯片, 分别在2×SS+2 g/L SDS, 0.1×SSC+ 2 g/L SDS与0.1×SSC液体中, 浸洗10 min, 然后在室温自然凉干. 芯片杂交结果用芯片扫描仪进行双波长扫描, 所获图像采用ImageGene 3.0 Software(BioDiscovery Inc.)进行定量分析, 分别计算热水组、Cy5与正常组Cy3比率, 计算热盐水组Cy5与盐水组Cy3比率. 实验组与对照组之间的差异表达基因筛选标准: P<0.05, Cut off 值设定为80, Cy5/Cy3比率为±2.0以上.
2 结果
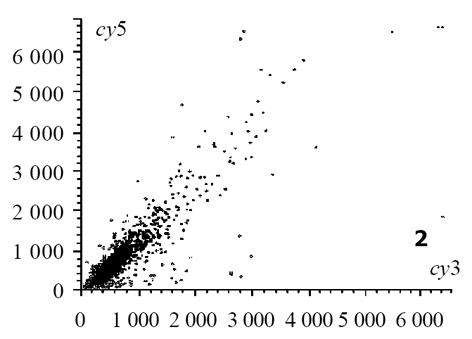
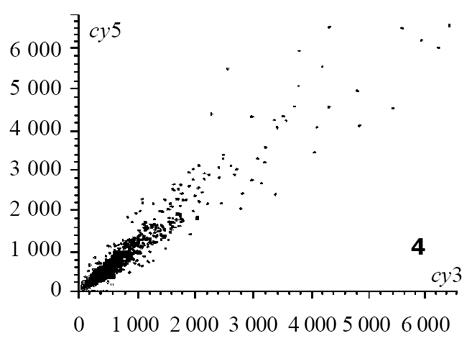
热盐水灌胃12 wk出现胃黏膜萎缩; 盐水、热水灌胃12 wk, 两组大鼠胃黏膜均未见萎缩改变, 但延长灌胃至24 wk时可见胃黏膜出现萎缩改变[6]. 以正常组胃窦部黏膜组织作为对照, 热水组24 wk时诱导的萎缩性胃炎病变作为实验组, 芯片杂交扫描结果见图1, 热水组与正常组杂交信号迭加后强度散点图见图2. 根据差异表达基因筛选标准, 符合条件的差异表达基因共有398个, 98个基因在萎缩性病变组织中呈高表达, 300个基因在正常组织中呈高表达, 这些基因及对应蛋白与萎缩性胃炎的发生可能密切相关. 灌胃12 wk热盐水组与正常对照组芯片杂交结果图迭加后, 扫描分析结果显示, 符合标准的差异表达基因共有436个, 145个在基因在萎缩性病变组织中呈高表达, 291个基因在正常组织中呈高表达. 这些基因中包括246个热水组中的差异表达基因, 包括了36个热盐水组与盐水组之间差异表达基因, 剩下基因可能与盐水组引起的萎缩性胃炎病变有关. 灌胃24 wk热盐水组与盐水对照组芯片杂交扫描结果见图3, 杂交信号强度散点图见图4. 根据差异表达基因筛选标准, 两组之间差异表达基因共有36个, 其中23个在热盐水组中呈高表达, 13个基因在盐水对照组中呈高表达; 此结果表明, 热盐水诱导的萎缩性胃炎与盐水诱导的萎缩性胃炎发生机制可能存在一定差异, 这种差异与这36个基因的功能密切相关.
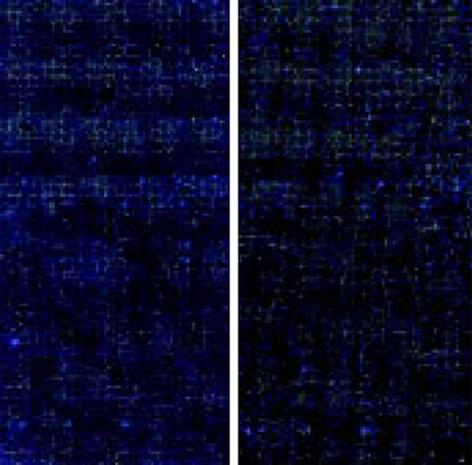
图1 灌胃至24 wk时热水组与正常对照组杂交扫描结果.
正常组杂交扫描图(cy3标记); 热水组杂交扫描图(cy5标记).
图2 不同组织(热水组+正常组)杂交信号强度散点图.
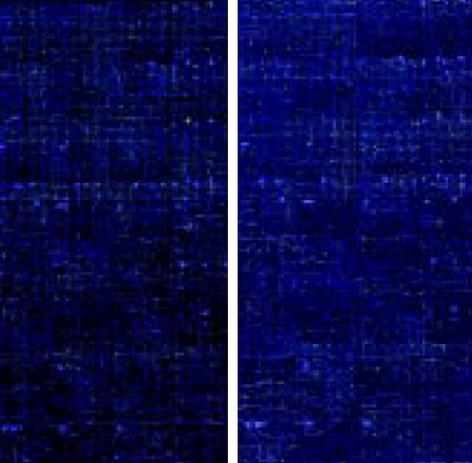
图3 热盐水组与盐水组芯片杂交扫描结果.
热盐水组杂交扫描图(cy5标记); 盐水组杂交扫描图(cy3标记).
3 讨论
慢性萎缩性胃炎是胃主要的癌前病变之一[7-28], 他的发生发展机制不十分清楚. 建立萎缩性胃炎动物模型对研究萎缩性胃炎的发生机制具有十分重要的现实意义[29,30]. 我们以大鼠为研究对象, 以食物(水)的热度与咸度两种因素单独及共同作用作为影响因素, 建立大鼠萎缩性胃炎模型. 结果表明, 热盐水在短期内(12 wk)即可造成大鼠胃黏膜萎缩, 同期实验的正常组、热水组、盐水组均未出现类似现象, 证明了水的热度与咸度两种因素共同作用可短期内造成胃黏膜的损伤, 引起胃黏膜萎缩. 热水组、盐水组在灌胃24 wk后, 大鼠胃黏膜也出现了萎缩, 说明单一因素(热度、咸度)长期作用也可造成胃黏膜的萎缩.
为了进一步探讨大鼠萎缩性胃炎的分子机制, 我们采用了含8428个基因的高密度芯片, 对这些胃窦部萎缩性胃炎标本进行了与正常胃黏膜之间的差异表达基因的筛选. 众所周知, 基因芯片技术具有高通量、高效率、高准确性特点, 一次可同步监测数以千计的基因的变化, 与传统技术相比, 具有无比的优越性[31]. 本研究结果显示, 热水引起的萎缩性胃炎中, 存在398个高度差异表达基因, 98个在萎缩性胃炎中呈高表达, 300个在正常胃黏膜组织中呈高表达; 在热盐水引起的萎缩性胃炎中, 存在436个差异表达基因, 145个基因在萎缩性病变组织中呈高表达, 291个基因在正常组织中呈高表达. 这些基因中包括246个热水组中的差异表达基因, 包括了36个热盐水组与盐水组之间差异表达基因, 剩下基因可能与盐水组引起的萎缩性胃炎病变有关. 进一步分析显示, 这些基因涉及到原癌基因和抑癌基因、离子通道和运输蛋白、细胞周期蛋白类、外压反应蛋白、细胞骨架和运动、细胞凋亡相关蛋白、细胞受体、免疫相关、代谢、蛋白翻译合成、翻译相关基因等.
我们也进行了盐水引起的萎缩性胃炎与热盐水引起的萎缩性胃炎的差异表达基因的筛选, 结果显示仅存在36个差异表达基因, 进一步分析发现, 这些基因与细胞的异常增生关系不大, 这说明两组大鼠虽采用不同的方法来灌胃, 但由于灌胃至24 wk时均有明显的萎缩性胃炎的改变, 虽然造成萎缩的因素和时间长短不同, 形成萎缩后的差异表达基因虽然存在36个, 但与实验组及正常对照组比较, 差异很小, 此结果表明, 热盐水与盐水引起的萎缩性胃炎在发生机制上可能存在相同性步骤. 本研究结果表明, 热水、盐水与热盐水能使正常胃黏膜在一定时间内形成萎缩, 在此过程中引起许多基因出现表达水平的变化, 这些不同的差异表达基因及其对应蛋白是如何使正常胃黏膜逐渐演变成萎缩性胃炎还不清楚, 这些差异表达基因在胃黏膜到胃癌的发生发展过程中究竟扮演何角色, 还有待于深入研究.