Published online Dec 15, 1999. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v5.i6.538
Revised: June 20, 1999
Accepted: September 13, 1999
Published online: December 15, 1999
- Citation: Zhou Q, Xu TR, Fan QH, Zhen ZX. Clinicopathologic study of primary intestinal B cell malignant lymphoma. World J Gastroenterol 1999; 5(6): 538-540
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v5/i6/538.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v5.i6.538
Primary intestinal B cell lymphoma is one of the most common extra-nodal lymphomas, which includes two types: intestinal mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lym phoma ( IMALToma ) and lymphomatous polyposis ( LP ). Both have characteristic pathologic features, immunophen-otypes and biological behaviors. In this article, twenty-five cases were retrospectively analyzed with regard to criteria of diagnosis and clinicopathologic characteristics.
All 25 tissue specimens obtained from surgical operation, were embedded in paraffin, sectioned and stained by haematoxylin-eosin and immunohistochemical stains ( ABC method ). The first antibody ( CD20, CD45, CD45R0, CD68, CD30, K, λ, IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD and bcl-2 ), second an tibody and ABC Kit were produced by Dako and Vector Co.PBS buffer solution was substituted for the first antibodies as the negative control, whereas the lympho ma cases were used for positive control.
There were 21 cases of IMALToma, in which 16 were males and 5 females, age ranged 9-70 years, mean age 39.6 years. Location of tumors, 10 were situated in ileum, 2 at jejunum, 6 in colon, 1 at rectum and 2 in both ileum and colon; there were 4-cases of LP, 3 men and 1 woman, age 30-47 (average 38.8 ) years, all were located at the terminal ileum. Clinical manifestations of IMALToma were similar to LP with abdominal pain and mass, melena and mucous stool, intestinal intussece ption and intestinal obstruction, fever, loose bowel movement.
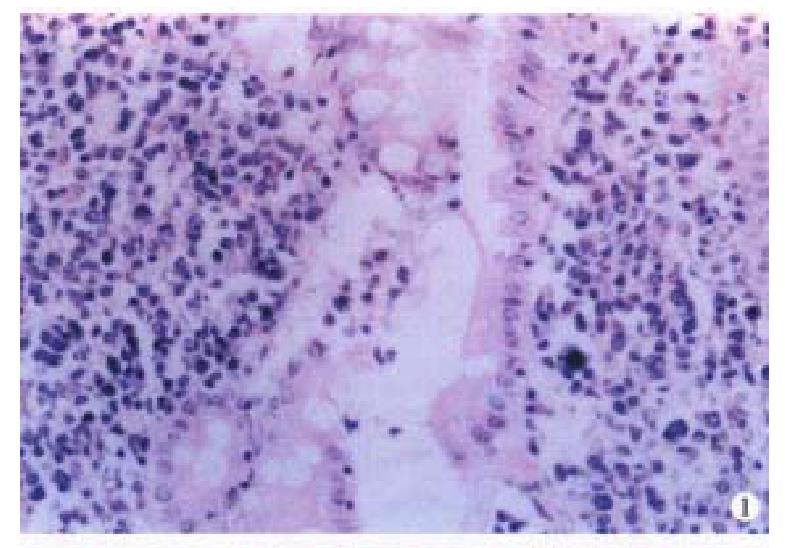
Macroscopically, the IMALToma could be categorized into mushroom, constrictive and ulcerative types; the size of tumor varied from 2 cm × 1 cm × 1 cm to 20 cm × 10 cm × 3.5 cm. Sixteen cases had single nodule, five were multiple. The lymphomatous cells infiltrated in the mucosa, sub-mucosa and muscular layer diffusely or focally. Lymphoid follicles were seen in 7 cases. In 9 cases, the germinal centers were partly or entirely replaced by lymphoma cells. Dendritic cells and macrophages with chromophilic bodies disappeared. This phenomenon is called follicular colonization ( FC). 9 cases showed lymphoepith elial lesion (LEL) in which there were clusters of lymphomatous cells infiltrate d focally at the surface epithelium and/or glands (Figure 1). The glandular epithelia were destroyed. The neoplastic cells presented a serial cell lineage of small lymphocyte, centrocyte-like cell (CCL), monocyte-like B cell (MCB) and lymphoplasma cell (LPC), and also centroblast like cells (CBL). All these cells, several kinds were in a mixed distribution, but usually one kind was predominant. IMALToma was divided into following subtypes:
(1) CCL subtype seen in 11 cases. The tumor cells were medium and small in size, with less cytoplasm, irregular and angular nuclei of dark staining, which looked like centrocytes.
(2) MCB subtype seen in 4 cases. The tumor cells were of medium size, their cytoplasm was abundant, lightly stained and clear. The nuclei were round, with visible nuclear membrane, fine chromatin and small nucleoli.
(3) LPC subtype seen in 2 cases. The cytoplasm tumor cells looked like plasma cells and nuclei like small lymphocytes. The cytoplasm was abundant and stained red, in some, the cytoplasm contained immunoglobulin inclusions. The nuclei of tumor cells were round, dark stained, similar to small lymphocyte.
(4) CBL subtype: CBL cells were more than 50% in four cases, medium size with light stained cytoplasm and round vacuolated nuclei, and 1-3 basophilic nucleoli nearby the nuclear membrane. CBL cells were focally distributed with a few CCL cells scattering or clustering around the CBL cells. Transition could be shown between CBL and CCL cells. Mitoses were easily found, especially the pathologic mitoses.
In the above 3 subtypes, 14 with few or none of CBL cells were low-grade malignant. Another 2 of CCL type and 1 MCB type was low-grade malignant but with high-grade malignant component, of which the proportion of CBL cells was more than 25%. Four CBL types having more than 50% CBL cells were highly malignant. Lymph node metastases were seen in 3 of 14 cases of low grade malignancy, 2 low grade malignancy with high-grade malignant component and 4 high grade malignant IMALToma.
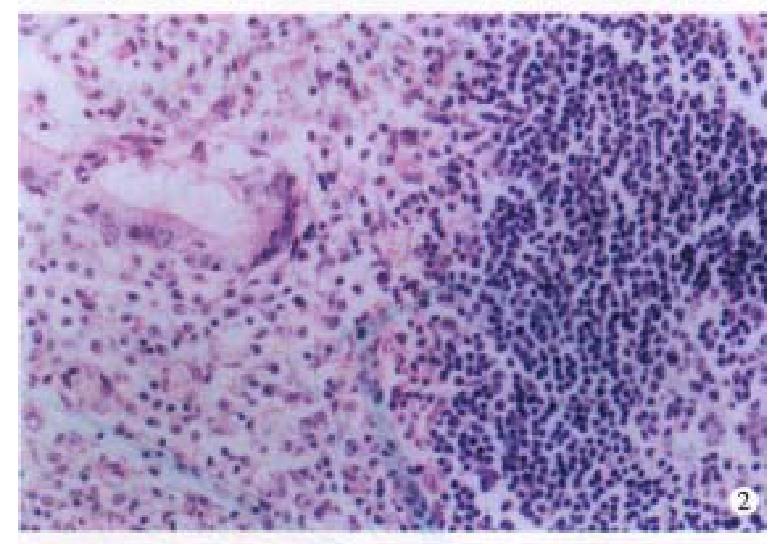
Four cases of LP were located at terminal ileum within the range of 20 cm-40 cm. They were hundreds stalkless polyps, varied from millet to broad bean. Three-fourth were mushroom-like or narrow masses, which were 1 cm × 1 cm × 1 cm-6 cm × 4 cm × 2.5 cm in size; with ulceration on the surface. Histologically, the lymph follicles were surrounded by numerous layers of lymphomatous lymphocytes, infiltrating into the germinal centers. The dendri tic cells and macrophages with chromophilic bodies decreased and even disappeared. Neoplastic cells infiltrated diffusely, forming nodular and mantle-like growth pattern. The nuclei of the lymphomatous cells were round or irregularly angular with thick nuclear membrane and condensed chromatin (Figure 2). One case showed blast cell transformation.
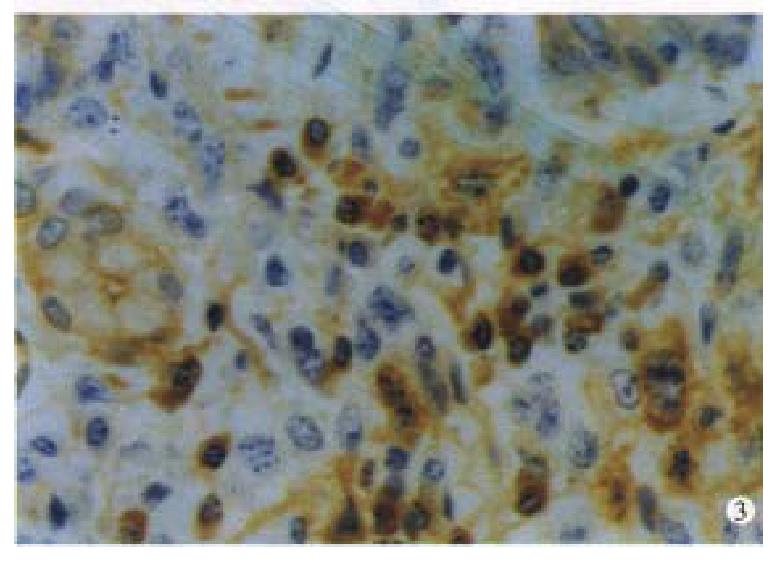
Immunohistochemically, twenty one cases of IMALToma and four cases of LP were CD45 and CD20 positive( Figure 3 ). The reactive lymph follicles we re polyclonal, while LEL and FC were monoclonal; one case of CBL lymphoma was negative for bcl-2. Ten cases and 5 cases were positive in CD68 and CD45R0, in reactive histocytes and small lymphocytes, respectively.
The significance of the LEL and FC pathological diagnosis of IMALToma.
LEL is considered a characteristic feature of IMALToma[1]. In our data, less than 50% (9/21) had LEL. The nest formation could also be found in the in flammatory and reactive status, it might be difficult to distinguish them from the real LEL, in such case, immunohistochemistry may be helpful. The former is several leukocytes with poly-clone and the latter is the lymphocytes with mono-clone. FC, appeared in 9 cases, is easy to misjudge as reactive follicles. The following morphological characteristics and immuno-phenotype may be helpful for the differentiation: (1) FC has no dendritic cells or macrophages with chromophilic bodies. (2) CCL cell is the immunophenotype of B cells in the marginal ar ea, rather than at the germinal center[2].
Both LEL and FC were characteristic features for diagnosis[3], but they could only be seen in some of the cases, then, immunohistochemistry and molecular biology technique should be done.
Fourteen were of low-grade malignancy, including CCL, MCB and LPC subtypes. The proportion of CBL cells was more than 25% in two CCL lymphoma and one MCB lymphoma, one should pay attention to transformation from low-to high-grade malign ancy. Four CBL lymphomas were of high-grade malignancy, in which the CBL cells were > 50%, distributing around the FC in fused clusters or trabeculae, and Igmight be positive and bcl-2 negative[4,5]. The rates of metastasis of the above three types of lymphoma were 28.5%, 66.7% and 100%, respectively, which proved that histological grading and the clinical staging were intimately related to prognosis.
The lymphomatous polyps were first described, and named LP by Corn in 1961. The origination of LP was argued for a long time. Only recently, LP could be defined as originating from both mantle cells and the centrocytes, which were similar in morphology[6]. The former was positive in IgD, CD5 and cycl in D1 without blastocyte transformation, while the latter was positive in IgM and CD10 with blastocyte transformation[7,8]. In our group, three cases had the morphologic feature of mantle cells, one was originated from germinal center, which was transformed from centrocytes to centroblastocytes. Thus the term LP could not reflect the origination and the nature. LP has two patterns, showing similar macroscopic and histologic features here we suggest a better terms for LP: mucosal mantle cell lymphoma and mucosal follicular lymphoma.
Edited by Xie-Ning Wu
Proofread by Qi-Hong Miao
| 1. | Isaacson PG. Gastrointestinal lymphoma. Hum Pathol. 1994;25:1020-1029. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 261] [Cited by in RCA: 233] [Article Influence: 7.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Isaacson PG. Malignant lymphomas with a follicular growth pattern. Histopathology. 1996;28:487-495. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 41] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Montalbán C, Manzanal A, Castrillo JM, Escribano L, Bellas C. Low grade gastric B-cell MALT lymphoma progressing into high grade lymphoma. Clonal identity of the two stages of the tumour, unusual bone involvement and leukemic dissemination. Histopathology. 1995;27:89-91. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 57] [Cited by in RCA: 46] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Navratil E, Gaulard P, Kanavaros P, Audouin J, Bougaran J, Martin N, Diebold J, Mason DY. Expression of the bcl-2 protein in B cell lymphomas arising from mucosa associated lymphoid tissue. J Clin Pathol. 1995;48:18-21. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Ashton-Key M, Biddolph SC, Stein H, Gatter KC, Mason DY. Heterogeneity of bcl-2 expression in MALT lymphoma. Histopathology. 1995;26:75-78. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Moynihan MJ, Bast MA, Chan WC, Delabie Jan RS, Wu G, Weisenburger DD. Lymphomatous polyposis. A neoplasm of either follicular mantle or germinal center cell origin. Am J Surg Pathol. 1996;20:442-452. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Fraga M, Lloret E, Sanchez-Verde L, Orradre JL, Campo E, Bosch F, Piris MA. Mucosal mantle cell (centrocytic) lymphomas. Histopathology. 1995;26:413-422. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 35] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Robert ME, Kuo FC, Longtine JA, Sklar JL, Schrock T, Weidner N. Diffuse colonic mantle cell lymphoma in a patient with presumed ulcerative colitis: detection of a precursor monoclonal lymphoid population using polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry. Am J Surg Pathol. 1996;20:1024-1031. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |