Published online May 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i17.2657
Peer-review started: February 8, 2023
First decision: February 16, 2023
Revised: March 3, 2023
Accepted: April 7, 2023
Article in press: April 7, 2023
Published online: May 7, 2023
Processing time: 88 Days and 3.5 Hours
Mucosal patterns (MPs) observed on blue laser imaging in patients with atrophic gastritis can be classified as spotty, cracked, and mottled. Furthermore, we hypothesized that the spotty pattern may change to the cracked pattern after Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) eradication.
To further substantiate and comprehensively investigate MP changes after H. pylori eradication in a larger number of patients.
We included 768 patients who were diagnosed with atrophic gastritis with evaluable MP using upper gastrointestinal endoscopy at the Nishikawa Gas-trointestinal Clinic, Japan. Among them, 325 patients were H. pylori-positive, and of them, 101 patients who underwent upper gastrointestinal endoscopy before and after H. pylori eradication were evaluated for post-eradication MP changes. The patients’ MPs were interpreted by three experienced endoscopists who were blinded to their clinical features.
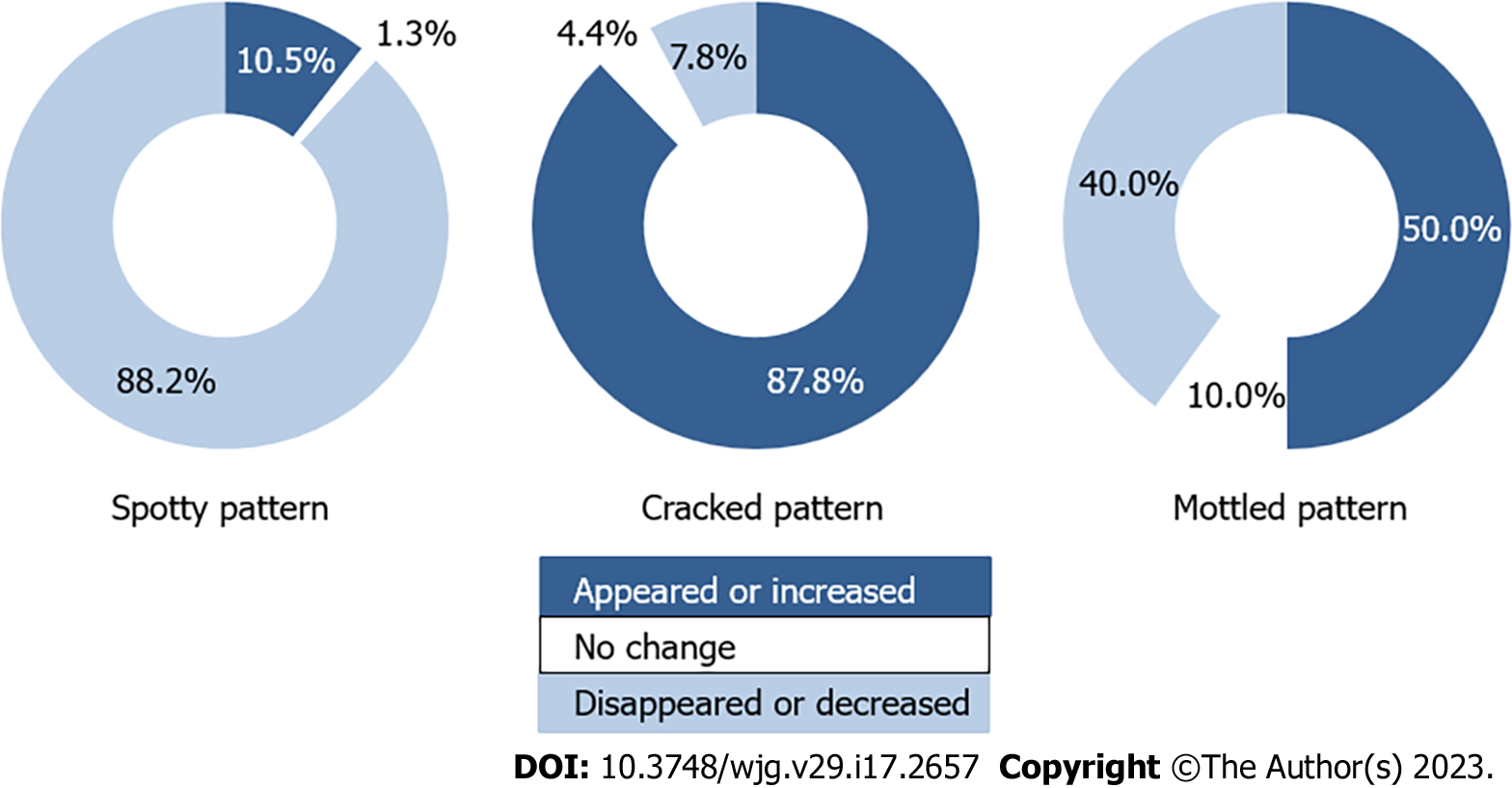
Among 76 patients with the spotty pattern before or after H. pylori eradication, the pattern disappeared or decreased in 67 patients [88.2%, 95% confidence interval (CI): 79.0%-93.6%), appeared or increased in 8 patients (10.5%, 95%CI: 5.4%-19.4%), and showed no change in 1 patient (1.3%, 95%CI: 0.2%-7.1%). In 90 patients with the cracked pattern before or after H. pylori eradication, the pattern disappeared or decreased in 7 patients (7.8%, 95%CI: 3.8%-15.2%), appeared or increased in 79 patients (87.8%, 95%CI: 79.4%-93.0%), and showed no change in 4 patients (4.4%, 95%CI: 1.7%-10.9%). In 70 patients with the mottled pattern before or after H. pylori eradication, the pattern disappeared or decreased in 28 patients (40.0%, 95%CI: 29.3%-51.7%), appeared or increased in 35 patients (50.0%, 95%CI: 38.6%-61.4%), and showed no change in 7 patients (10.0%, 95%CI: 4.9%-19.2%).
After H. pylori eradication, MPs changed from spotty to cracked in most patients, which may help endoscopists easily and precisely evaluate H. pylori-related gastritis status.
Core Tip: We investigated whether the mucosal patterns on blue laser imaging may change from spotty to cracked after Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) eradication. The spotty pattern disappeared or decreased in 88.2% of patients, while the cracked pattern appeared or increased in 87.8% of patients. These suggest that the spotty pattern observed in H. pylori-positive patients is likely to disappear after eradication and may be replaced by the cracked pattern. These observations may help endoscopists easily and precisely evaluate H. pylori-related gastritis status.
- Citation: Nishikawa Y, Ikeda Y, Murakami H, Hori SI, Yoshimatsu M, Nishikawa N. Mucosal patterns change after Helicobacter pylori eradication: Evaluation using blue laser imaging in patients with atrophic gastritis. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(17): 2657-2665
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i17/2657.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i17.2657
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection and related atrophic gastritis is closely associated with the development of gastric cancer[1]. Therefore, it is critical to observe the gastric mucosa to precisely judge the infection status as “current,” “previous,” or “none.” Recently, various types of image-enhanced endoscopy have been used to ensure the accurate evaluation of H. pylori infection[2-6].
In our previous study[7], we classified mucosal patterns (MPs) into three types (spotty, cracked, and mottled) using blue laser imaging (BLI)[8,9] in patients with H. pylori-related gastritis. We found that the spotty pattern indicated the possibility of H. pylori infection, the cracked pattern indicated a post-inflammatory change after H. pylori eradication, and the mottled pattern indicated an intestinal metaplasia resulting from the progression of H. pylori-related gastritis. Thus, we hypothesized that the spotty pattern would disappear or decrease and the cracked pattern would newly appear or increase after H. pylori eradication.
To further explore these changes, we quantitatively analyzed the changes to determine whether each pattern would increase, decrease, or remain unchanged. Since little is known concerning the pattern changes after H. pylori eradication, clarification of these changes may help endoscopists diagnose the existing pattern as being pre- or post-eradication and understand the MP changes more precisely. Thus, this study aimed to clarify the significance and diagnostic viability of each MP using BLI.
A total of 2242 patients underwent upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy at the Nishikawa Gastrointestinal Clinic, Ehime, Japan from April 1, 2015 to March 31, 2017. Of these, 768 patients were endoscopically diagnosed with atrophic gastritis. The presence or absence of H. pylori infection was confirmed. Among them, 325 patients were H. pylori-positive, and of them, 101 patients who underwent H. pylori eradication and subsequent endoscopy were examined for MP changes.
An EG-L580NW nasal upper GI endoscope (FUJIFILM Medical Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) was used orally or nasally. The BLI bright mode was used to evaluate MPs in the intermediate or distant views.
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Ehime University Hospital (No: 1605010; August 22, 2016). Prior to receiving an endoscopic examination, all patients agreed that the data obtained in this study might be published in academic papers.
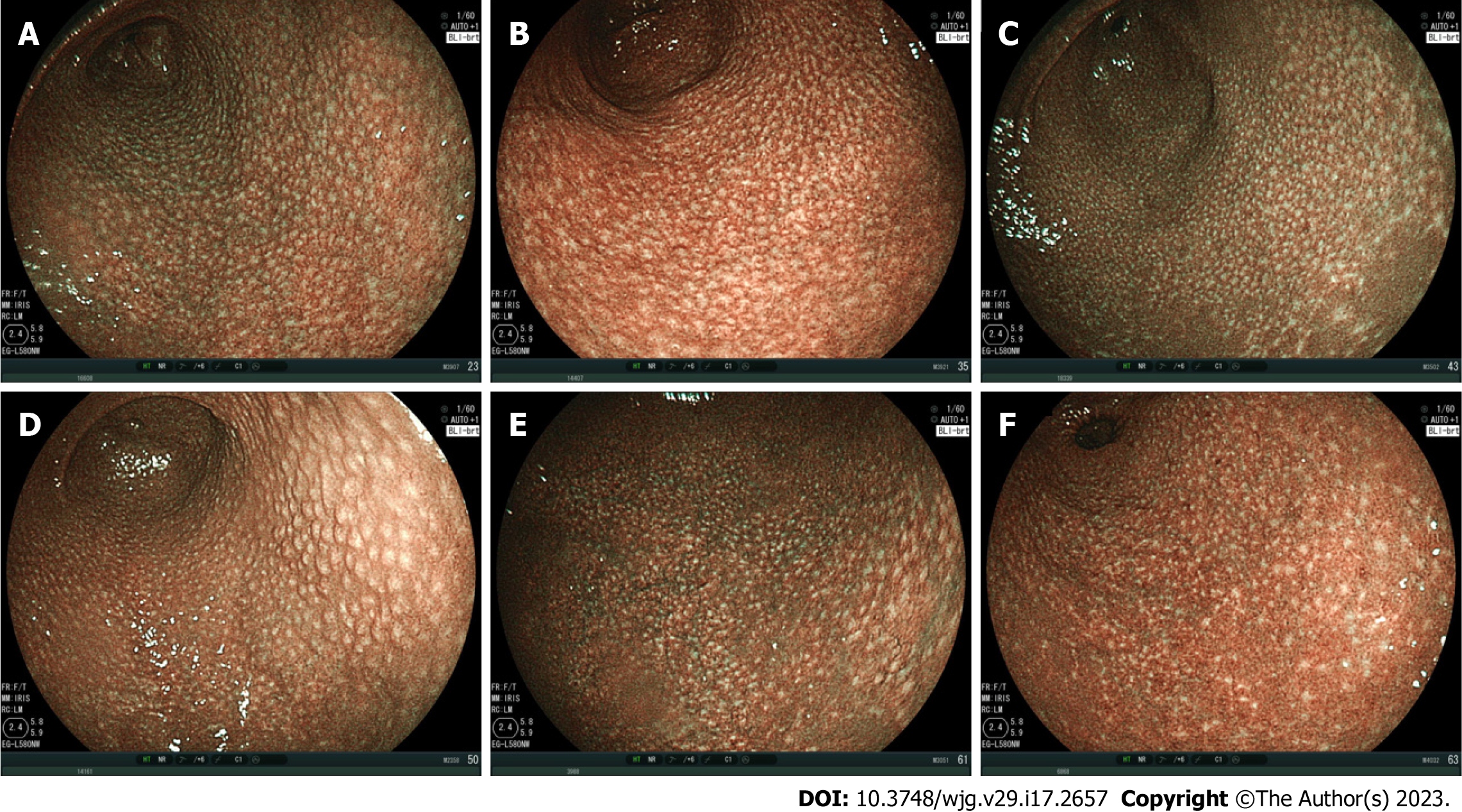
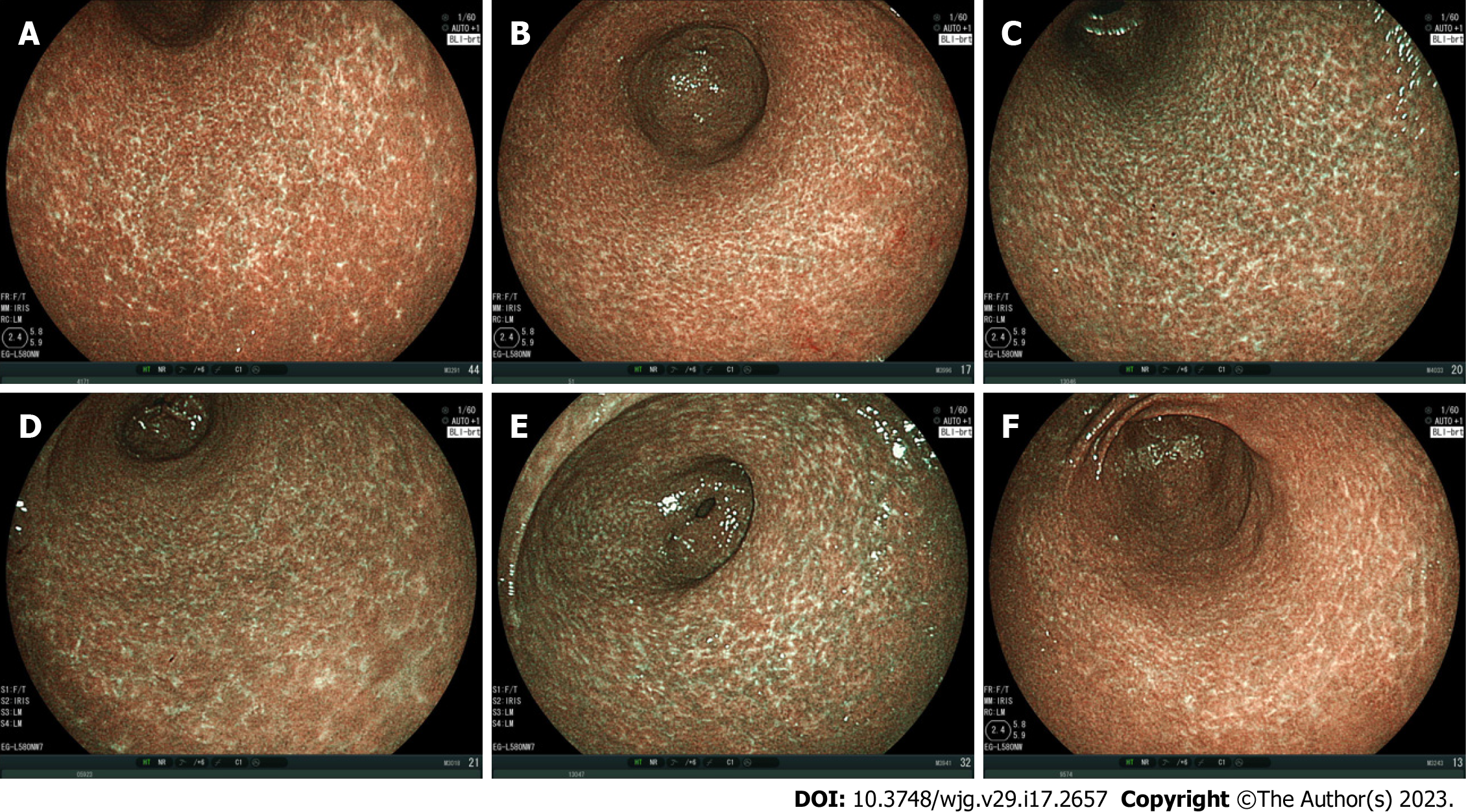
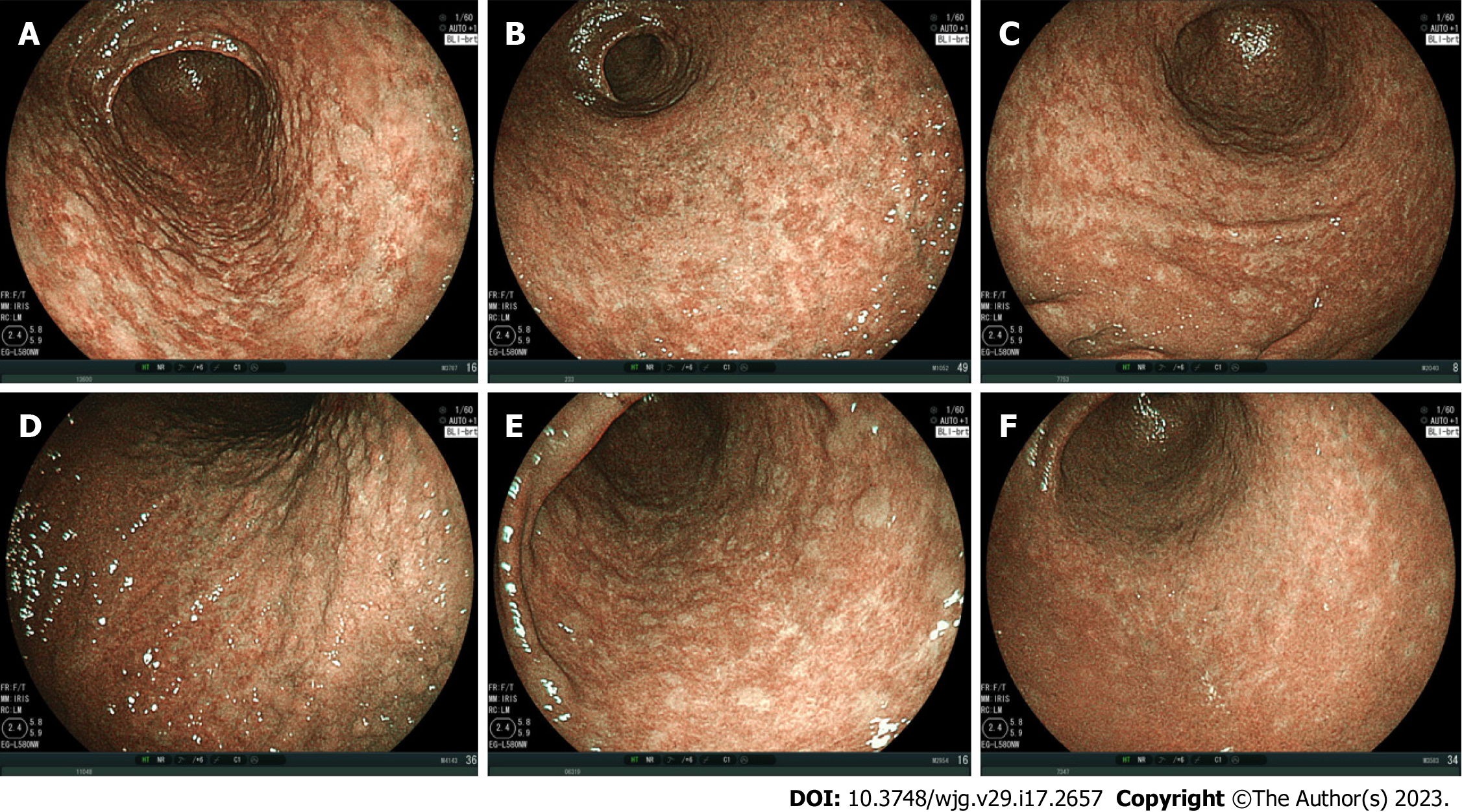
The MPs were classified into three types: The spotty pattern, which consists of 1-2 mm diameter spots (Figure 1); the cracked pattern, which consists of net-like cracks (Figure 2); and the mottled pattern, which has a mottled appearance (Figure 3)[7].
The MP patterns were evaluated as follows: (1) Three expert GI endoscopists, with at least 25 years of experience, evaluated the mucosal changes after H. pylori eradication; (2) They were blinded to the patients’ endoscopic data, including the patterns obtained before and/or after H. pylori eradication; (3) They compared two randomly listed endoscopic image groups and evaluated which image group was dominant, less dominant, equal, or absent for the spotty, cracked, and mottled patterns; (4) When two or all endoscopists agreed on a particular pattern, that pattern was adopted for analysis. When they had conflicting pattern determinations, the final determination was reached through a joint discussion; and (5) H. pylori infection was diagnosed using the anti-H. pylori IgG antibody serology tests[10,11], urea breath tests[12-15], and biopsies.
Student’s t-test was used for the analysis of age, and the χ2 test was used for the analyses of other variables. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05. A 95% confidence interval (CI) was calculated to determine the uncertainty of the sample estimates. All statistical analyses were performed using Microsoft Excel 2016, version 1907, Build 11901.20176 (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, United States), and the statistical methods of this study were reviewed by Dr. Natsumi Yamashita from Clinical Research Center, National Hospital Organization Shikoku Cancer Center.
The number of patients evaluated was 768 (480 females and 288 males) with a mean age of 65.8 ± 12.9 (standard deviation) years. The numbers of patients with and without H. pylori infection were 325 (204 females and 121 males) and 443 (276 females and 167 males), respectively.
The mean ages of patients with and without H. pylori infection were 61.6 ± 14.3 years and 68.9 ± 10.7 years, respectively, with significant differences among them (P < 0.001). No significant difference was observed between the proportions of female and male patients with and without H. pylori infection (P = 0.895; Table 1).
| Item | Patients with atrophic gastritis | Patients with H. pylori infection | Patients underwent both H. pylori eradication and follow up endoscopy |
| No. of patients | 768 | 325 | 101 |
| Age, mean ± SD | 65.8 ± 12.9 | 61.6 ± 14.3 | 57.5 ± 14.1 |
| Female | 480 | 204 | 75 |
| Male | 288 | 121 | 26 |
Upper GI endoscopy was performed for 101 patients (females: 75; males: 26; mean age: 57.5 ± 14.1 years) who successfully underwent H. pylori eradication, and the endoscopic mucosal changes were evaluated. Patients in whom evaluation was difficult because there were no comparable images of the specific parts were excluded from the analysis. The mean interval between H. pylori eradication and post-eradication endoscopy was 27.1 ± 13.1 mo.
In our study, multiple patterns commonly coexisted in many patients, with some patients having all three patterns. Of the 101 patients, 38 patients showed all three patterns (spotty, cracked, and mottled), 59 had two patterns (spotty and cracked, 28; spotty and mottled, 7; and cracked and mottled, 24), and 4 patients presented with only one pattern (spotty, 3; cracked, 0; and mottled, 1) either before or after eradication.
In 76 patients with a spotty pattern before or after H. pylori eradication, the pattern disappeared or decreased in 67 patients (88.2%, 95%CI: 79.0%-93.6%) and appeared or increased in 8 patients (10.5%, 95%CI: 5.4%-19.4%). In 1 patient (1.3%, 95%CI: 0.2%-7.1%), no change was observed after H. pylori eradication.
In 90 patients with a cracked pattern before or after H. pylori eradication, the pattern disappeared or decreased in 7 patients (7.8%, 95%CI: 3.8%-15.2%) and appeared or increased in 79 patients (87.8%, 95%CI: 79.4%-93.0%). In 4 patients (4.4%, 95%CI: 1.7%-10.9%), no change was observed after H. pylori eradication.
In 70 patients with a mottled pattern before or after H. pylori eradication, the pattern disappeared or decreased in 28 patients (40.0%, 95%CI: 29.3%-51.7%) and appeared or increased in 35 patients (50.0%, 95%CI: 38.6%-61.4%). In 7 patients (10.0%, 95%CI: 4.9%-19.2%), no change was observed after H. pylori eradication (Figure 4).
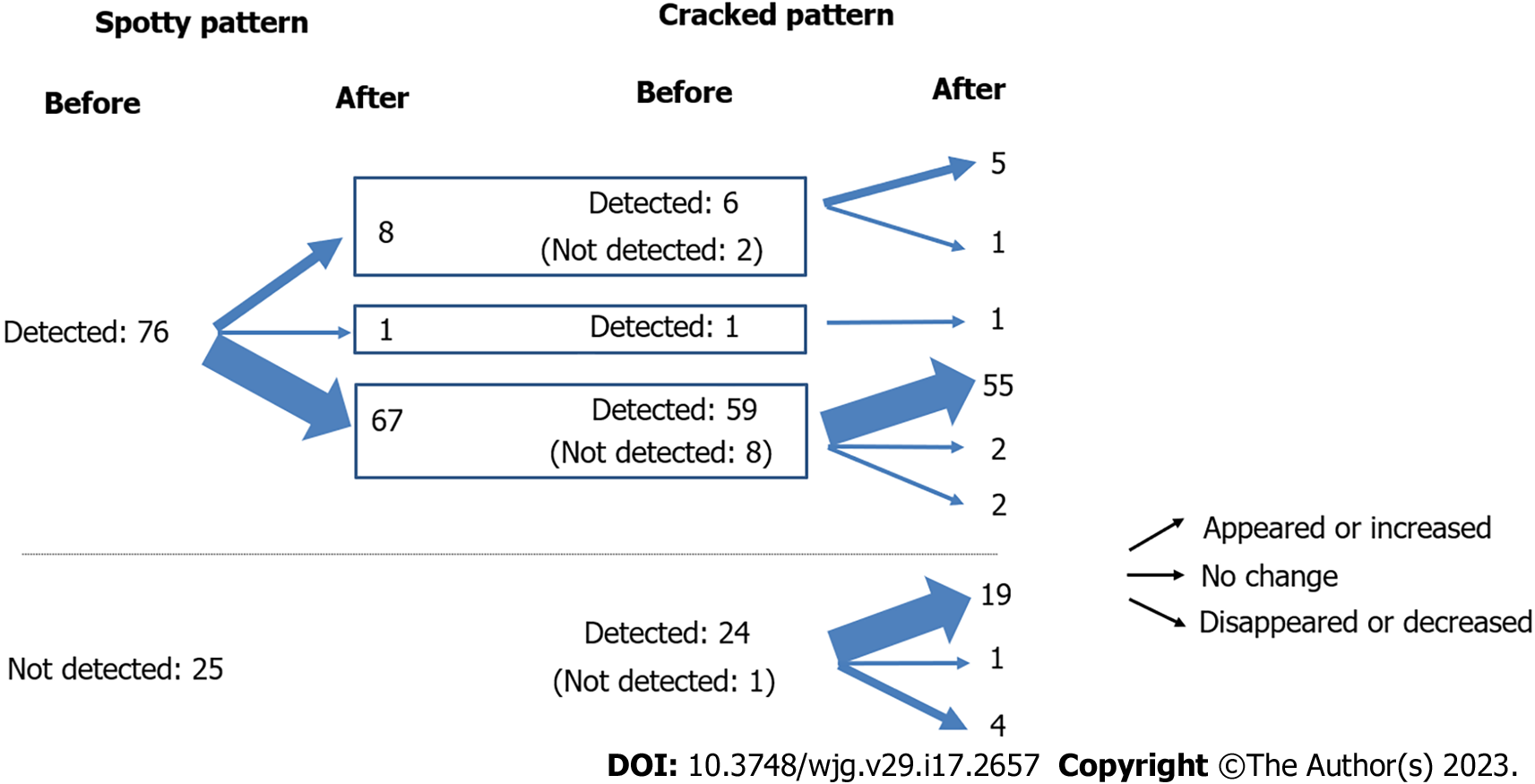
We investigated the relationship between the spotty and cracked patterns before and after eradication. The spotty pattern disappeared or decreased in 67 out of the 76 patients who had a spotty pattern before or after eradication. Of the 67 patients, the cracked pattern appeared or increased in 55 patients. Among the 8 patients with spotty patterns that appeared or increased after eradication, the cracked pattern appeared or increased in 5 patients. The cracked pattern appeared or increased in most of the 25 patients who did not have a spotty pattern before or after eradication (Figure 5).
We further investigated the difference in MP changes due to H. pylori eradication between the short-term (8-24 mo) and long-term (25-60 mo) observation groups. The spotty pattern disappeared or decreased in 88.6% and 87.8% (short-term vs long-term) of the patients. The cracked pattern newly appeared or increased in 88.9% and 86.7% (short-term vs long-term) of the patients. No significant differences were observed between the patients under short-term and long-term observations.
We investigated the use of BLI, an image-enhanced endoscopy, for the diagnosis of H. pylori-related gastritis, with a focus on the MP changes after H. pylori eradication. The Kyoto Classification of Gastritis was established in 2014 for the endoscopic diagnosis of H. pylori-related gastritis[16,17]. The classification of MPs observed on BLI in this study is simpler and easier to use in endoscopic assessment than the Kyoto classification and thus has the potential to become a new standard method with the addition of new diagnostic information to the Kyoto classification. We previously reported the efficacy of MPs on BLI in an intermediate-to-distant view evaluation of H. pylori infection and had the benefits of easy detection of atrophic gastritis and easy diagnosis of infection status (current, previous, or no infection)[7].
The results obtained in the current study indicate that the disappearance of the spotty pattern is evidence of H. pylori clearance, while newly-appearing cracked pattern is evidence of post-gastritis healing. The mottled pattern may reflect “intestinal metaplasia,” as identified in our previous study using biopsies.
Knowledge of the endoscopic changes after H. pylori eradication is helpful in clarifying the meaning of each MP. The spotty pattern disappeared or decreased in 88.2% of patients, whereas the cracked pattern appeared or increased in 87.8% of patients after H. pylori eradication. The mottled pattern exhibited no specific tendency. As indicated in Figure 5, the spotty pattern observed in H. pylori-positive patients before eradication may disappear and may be replaced by the cracked pattern. Based on these observations, we can diagnose the H. pylori infection status as current, previous, or no infection. No difference was detected between the short-term and long-term observations of MP changes after H. pylori eradication, suggesting that the changes in MP would occur relatively quickly after eradication. The primary tendency of MP changes after H. pylori eradication have been clarified in this study. Irregular pattern changes (those other than spotty to cracked pattern) were observed after eradication in a limited number of patients. Further verification is necessary.
In conclusion, the spotty pattern may indicate H. pylori infection, the cracked pattern may indicate post-inflammatory changes after H. pylori eradication, and the mottled pattern may indicate intestinal metaplasia resulting from the progression of H. pylori-related gastritis. We verified that MPs on BLI may change from a spotty to a cracked pattern after H. pylori eradication. These observations may help endoscopists easily and precisely evaluate the status of H. pylori-related gastritis. We hope that MP changes on BLI will be routinely used to confirm the diagnosis of H. pylori-related gastritis in the future.
Determination of the presence or absence of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is important in the diagnosis of atrophic gastritis. Various studies have been conducted to distinguish these two conditions.
In our previous study, we reported that H. pylori eradication may lead to the disappearance of the spotty pattern and the appearance of the cracked pattern.
To further substantiate and comprehensively investigate mucosal pattern changes after H. pylori eradication in a larger number of patients.
Among the patients with atrophic gastritis in whom H. pylori positivity was confirmed, we investigated 101 patients who underwent both H. pylori eradication and follow-up endoscopy and evaluated the change of patterns before and after eradication.
The spotty pattern tended to disappear or decrease, and the cracked pattern tended to appear or increase after H. pylori eradication, while the mottled pattern exhibited no specific tendency.
The spotty pattern likely changes to the cracked pattern after H. pylori eradication.
In future studies, it will be necessary to examine the morphological and histological changes of each mucosal pattern, compare these pattern changes with the Kyoto classification, examine the relationship with other classifications of atrophic gastritis, and clarify the meaning of the mucosal pattern changes.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Corresponding Author’s Membership(s) in Professional Societies: American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: Japan
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C, C
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Kotelevets SM, Russia; Senchukova M, Russia S-Editor: Yan JP L-Editor: A P-Editor: Chen YX
| 1. | Uemura N, Okamoto S, Yamamoto S, Matsumura N, Yamaguchi S, Yamakido M, Taniyama K, Sasaki N, Schlemper RJ. Helicobacter pylori infection and the development of gastric cancer. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:784-789. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3126] [Cited by in RCA: 3183] [Article Influence: 132.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Dohi O, Majima A, Naito Y, Yoshida T, Ishida T, Azuma Y, Kitae H, Matsumura S, Mizuno N, Yoshida N, Kamada K, Itoh Y. Can image-enhanced endoscopy improve the diagnosis of Kyoto classification of gastritis in the clinical setting? Dig Endosc. 2020;32:191-203. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 5.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Glover B, Teare J, Patel N. A systematic review of the role of non-magnified endoscopy for the assessment of H. pylori infection. Endosc Int Open. 2020;8:E105-E114. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 3.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Alaboudy AA, Elbahrawy A, Matsumoto S, Yoshizawa A. Conventional narrow-band imaging has good correlation with histopathological severity of Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Dig Dis Sci. 2011;56:1127-1130. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Tongtawee T, Kaewpitoon S, Kaewpitoon N, Dechsukhum C, Loyd RA, Matrakool L. Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic Patterns and Histopathological Severity of Helicobacter pylori Associated Gastritis Using Conventional Narrow Band Imaging Gastroscopy. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:808505. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Takeda T, Asaoka D, Nojiri S, Nishiyama M, Ikeda A, Yatagai N, Ishizuka K, Hiromoto T, Okubo S, Suzuki M, Nakajima A, Nakatsu Y, Komori H, Akazawa Y, Nakagawa Y, Izumi K, Matsumoto K, Ueyama H, Sasaki H, Shimada Y, Osada T, Hojo M, Kato M, Nagahara A. Linked Color Imaging and the Kyoto Classification of Gastritis: Evaluation of Visibility and Inter-Rater Reliability. Digestion. 2020;101:598-607. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 8.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Nishikawa Y, Ikeda Y, Murakami H, Hori SI, Hino K, Sasaki C, Nishikawa M. Classification of atrophic mucosal patterns on Blue LASER Imaging for endoscopic diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori-related gastritis: A retrospective, observational study. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0193197. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Yoshida N, Yagi N, Inada Y, Kugai M, Okayama T, Kamada K, Katada K, Uchiyama K, Ishikawa T, Handa O, Takagi T, Konishi H, Kokura S, Yanagisawa A, Naito Y. Ability of a novel blue laser imaging system for the diagnosis of colorectal polyps. Dig Endosc. 2014;26:250-258. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 87] [Cited by in RCA: 85] [Article Influence: 7.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Osawa H, Yamamoto H. Present and future status of flexible spectral imaging color enhancement and blue laser imaging technology. Dig Endosc. 2014;26 Suppl 1:105-115. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 101] [Cited by in RCA: 110] [Article Influence: 10.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Feldman RA, Deeks JJ, Evans SJ. Multi-laboratory comparison of eight commercially available Helicobacter pylori serology kits. Helicobacter pylori Serology Study Group. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1995;14:428-433. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 74] [Cited by in RCA: 71] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Loy CT, Irwig LM, Katelaris PH, Talley NJ. Do commercial serological kits for Helicobacter pylori infection differ in accuracy? Am J Gastroenterol. 1996;91:1138-1144. [PubMed] |
| 12. | Graham DY, Klein PD, Evans DJ Jr, Evans DG, Alpert LC, Opekun AR, Boutton TW. Campylobacter pylori detected noninvasively by the 13C-urea breath test. Lancet. 1987;1:1174-1177. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 505] [Cited by in RCA: 445] [Article Influence: 11.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Logan RP, Polson RJ, Misiewicz JJ, Rao G, Karim NQ, Newell D, Johnson P, Wadsworth J, Walker MM, Baron JH. Simplified single sample 13Carbon urea breath test for Helicobacter pylori: comparison with histology, culture, and ELISA serology. Gut. 1991;32:1461-1464. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 145] [Cited by in RCA: 152] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Ohara S, Kato M, Asaka M, Toyota T. Studies of 13C-urea breath test for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection in Japan. J Gastroenterol. 1998;33:6-13. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 87] [Cited by in RCA: 92] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Gisbert JP, Pajares JM. Review article: 13C-urea breath test in the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection -- a critical review. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004;20:1001-1017. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 237] [Cited by in RCA: 257] [Article Influence: 12.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Haruma K, Kato M, Inoue K, Murakami K, Kamada T. Kyoto Classification of Gastritis. Tokyo: Nihon Medical Center, Ltd., 2014. |
| 17. | Toyoshima O, Nishizawa T, Koike K. Endoscopic Kyoto classification of Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric cancer risk diagnosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2020;26:466-477. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 101] [Cited by in RCA: 79] [Article Influence: 15.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |