Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2017; 23(17): 3030-3042
Published online May 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i17.3030
Published online May 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i17.3030
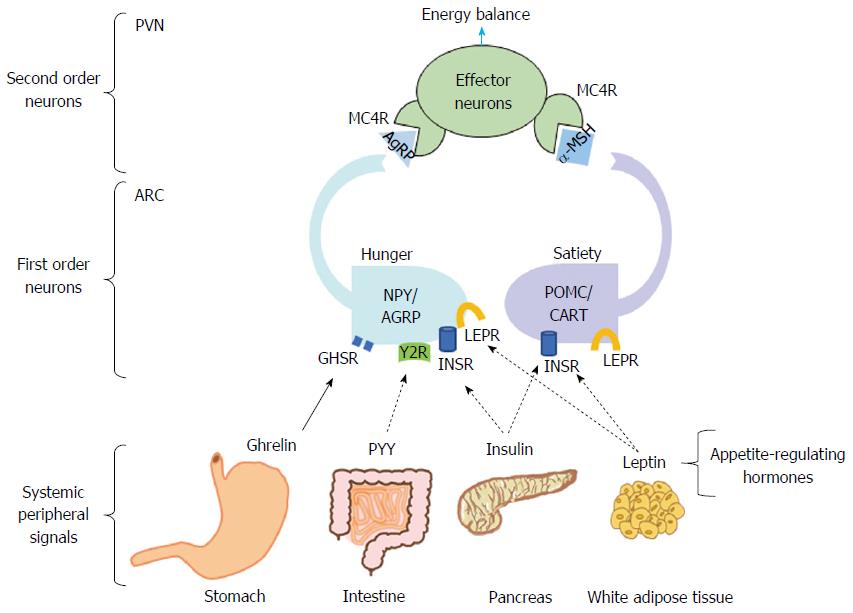
Figure 2 Hunger-satiety circuit and energy balance.
Energy balance depends on the appropriate compensatory signals from the hypothalamic nucleus. Food intake is promoted by the binding of ghrelin to the GHSR in the NPY/AgRP neurons, blocking anorexigenic signaling. Once food consumption occurs, PYY-Y2R binding has an antagonistic effect on the orexigenic pathway. Leptin and insulin bind to their specific receptors in POMC/CART neurons that in turn induces α-MSH to bind to its MC4R, promoting satiety. Furthermore, leptin and insulin in NYP/AGRP neurons inhibit AgRP signaling. GHSR: Growth hormone secretagogue receptor; NPY/AgRP: Neuropeptide Y/Agouti-related receptor protein; PYY: Peptide YY; Y2R: Y2 receptor; POMC/CART: Pro-opiomelanocortin/cocaine and amphetamine regulated transcript; α-MSH: α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone; PVN: Paraventricular nucleus; ARC: Arcuate nucleus.
- Citation: Panduro A, Rivera-Iñiguez I, Sepulveda-Villegas M, Roman S. Genes, emotions and gut microbiota: The next frontier for the gastroenterologist. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(17): 3030-3042
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i17/3030.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i17.3030