Published online Jun 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i23.5422
Peer-review started: March 13, 2016
First decision: March 31, 2016
Revised: April 12, 2016
Accepted: May 4, 2016
Article in press: May 4, 2016
Published online: June 21, 2016
Processing time: 91 Days and 21.5 Hours
AIM: To investigate the expression of endocan in tumour vessels and the relationships between endocan and the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and prognosis in gastric cancer.
METHODS: This study included 142 patients with confirmed gastric cancer in a single cancer centre between 2008 and 2009. Clinicopathologic features were determined, and an immunohistochemical analysis of endocan-expressing microvessel density (MVD) (endocan-MVD), VEGF and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) was performed. Potential relationships between endocan-MVD and clinicopathological variables were assessed using a Student’s t-test or an analysis of variance test. Spearman’s rank correlation was applied to evaluate the relationship between endocan-MVD and the expression of VEGF/VEGFR2. Long-term survival of these patients was analysed using univariate and multivariate analyses.
RESULTS: Positive staining of endocan was observed in most of the gastric cancer tissues (108/142) and in fewer of the normal gastric tissues. Endocan-MVD was not associated with gender or histological type (P > 0.05), while endocan-MVD was associated with tumour size, Borrmann type, tumour differentiation, tumour invasion, lymph node metastasis and TNM stage (P < 0.05). According to the Spearman’s rank correlation analysis, endocan-MVD had a positive correlation with VEGF (r = 0.167, P = 0.047) and VEGFR2 (r = 0.410, P = 0.000). The univariate analysis with a log-rank test indicated that the patients with a high level of endocan-MVD had a significantly poorer overall survival rate than those with a low level of endocan-MVD (17.9% vs 64.0%, P = 0.000). The multivariate analysis showed that a high level of endocan-MVD was a valuable prognostic factor.
CONCLUSION: Endocan-MVD significantly correlates with the expression of VEGF and VEGFR2 and is a valuable prognostic factor for survival in human gastric cancer.
Core tip: Angiogenesis plays an important role in the progression of gastric cancer. In the present study, we first found that endocan-expressing microvessel density (MVD) (endocan-MVD) had a positive correlation with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and VEGFR2 in gastric cancer tissues. Patients with a high level of endocan-MVD had a significantly poorer overall survival rate than those with a low level of endocan-MVD. Based on our research, we suggest that endocan-MVD may act as a valuable prognostic factor for survival in patients with gastric cancer.
- Citation: Chang Y, Niu W, Lian PL, Wang XQ, Meng ZX, Liu Y, Zhao R. Endocan-expressing microvessel density as a prognostic factor for survival in human gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(23): 5422-5429
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i23/5422.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i23.5422
Gastric cancer, a malignancy that remains the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide and causes high morbidity and mortality, is one of the most common malignancies in the world[1]. Compared to developed countries, developing countries have higher morbidity and mortality rates. Worldwide, more than 70% of new cases of gastric cancer and related deaths occur in developing countries, such as in Eastern Europe, East Asia and South America[2]. In particular, in China, there are approximately 400000 new cases annually, which account for 42% of the total global cases, and the death toll in China is 300000[3]. Therefore, identifying a new potential therapeutic target can benefit diagnosis and treatment. It is critical to investigate new factors that are closely associated with the initiation and development of gastric cancer.
Endocan, previously called the endothelial cell specific molecule-1, which is a new member of the proteoglycan family, plays an extremely important role in the transformation, survival, proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis and metastasis of tumours[4-7]. Previous in vivo and in vitro studies have demonstrated that endocan is overexpressed in human tumours, such as in colon cancer, kidney cancer and prostate cancer[8-10]. Consistently, elevated blood levels of endocan have also been observed in patients with lung cancers[11]. In particular, in liver cancer and gastric cancer[12,13], serum levels of endocan are significantly changed after treatment; thus, endocan is a biomarker of tumour progression as well as a validated therapeutic target.
It has been extensively reported that the secretion of endocan by cultured endothelial cells is strongly upregulated in the presence of proangiogenic molecules such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)[14]. Endocan has been shown to be activated by VEGF through the PKC and PI3K signalling pathways in human umbilical vein endothelial cells, and this process can be inhibited by PI3K pathway blockers[15]. Furthermore, the blockade of VEGFR2 by specific antibodies completely prevented VEGFC-mediated induction of endocan expression in endothelial cells[16]. Data obtained from cancer tissue samples have shown that endocan can be visualized in newly growing tumour vessels of endothelial cells. Thus, endocan-expressing microvessel density (MVD) is likely to be valuable for assessing the prognosis of malignancy. Vascular endocan, as a biomarker of neoangiogenesis, is found inside the vessels in different types of tumours, such as colon, kidney, prostate and brain cancers, but not in gastric cancer[8-10,17]. Thus, endocan immunolabelling was explored in this study to understand the progression of gastric cancer.
The aim of this study was to examine the expression of endocan in gastric cancer vessels, to investigate the relationship between endocan-MVD and the expression of VEGF and VEGFR2, and to determine whether endocan-MVD could be used to predict the outcomes of patients with gastric cancer.
A total of 142 patients with gastric cancer who had undergone gastrectomy were enrolled in this study between January 2008 and April 2009 at the Qilu Hospital of Shandong University. All patients had undergone primary curative gastrectomy, and none of them had received chemotherapy or radiotherapy before surgery. Meanwhile, 142 specimens of adjacent tissues were obtained from these patients to serve as the paired controls. The tissues were embedded in paraffin after 16 h of formalin fixation. Of the patients enrolled in this study, 93 (65.4%) were male and 49 (34.5%) were female, with a median age of 56.8 years (ranging from 24 to 79 years). The cut-off date for follow-up was April 2015, and the median follow-up duration was 39 mo (ranging from 6 to 72 mo). The clinicopathological features of the patients examined included gender, age, Borrmann type, tumour size, tumour histological morphology, tumour differentiation (according to the WHO classification for gastric cancer in 2000), tumour invasion, lymph node metastasis, TNM stage (TNM 7th edition by the American Joint Committee on Cancer) and vascular invasion. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Qilu Hospital, Shandong University, and all study participants signed an informed consent form. The clinicopathological characteristics of the patients are summarized in Table 1.
| Clinicopathologic feature | n | Endocan-MVD | P value1 |
| Gender | 0.27 | ||
| Male | 93 | 18.19 ± 8.240 | |
| Female | 49 | 19.79 ± 8.203 | |
| Age (yr) | 0.32 | ||
| < 60 | 78 | 19.36 ± 8.436 | |
| ≥ 60 | 64 | 18.00 ± 7.982 | |
| Tumour size (cm) | 0.000a | ||
| < 5 | 79 | 16.48 ± 9.170 | |
| ≥ 5 | 63 | 21.58 ± 5.799 | |
| Borrmann type | 0.000a | ||
| I | 18 | 11.33 ± 3.970 | |
| II | 15 | 11.93 ± 4.651 | |
| III | 81 | 21.17 ± 8.122 | |
| IV | 28 | 20.14 ± 7.437 | |
| Histology | 0.25 | ||
| Adenocarcinoma | 118 | 19.11 ± 8.183 | |
| Signet ring cell carcinoma | 8 | 16.55 ± 2.554 | |
| Mixed carcinoma | 15 | 17.13 ± 10.602 | |
| Differentiation | 0.000a | ||
| High/moderate | 36 | 11.66 ± 4.623 | |
| Low/undifferentiated | 106 | 21.15 ± 7.803 | |
| Tumour invasion | 0.000a | ||
| T1 | 2 | 6.33 ± 0.577 | |
| T2 | 30 | 10.30 ± 4.822 | |
| T3 | 4 | 16.33 ± 0.577 | |
| T4 | 106 | 21.56 ± 7.168 | |
| Lymph node metastasis | 0.000a | ||
| N0 | 33 | 12.60 ± 7.314 | |
| N1 | 21 | 17.521 ± 5.662 | |
| N2 | 30 | 16.96 ± 7.420 | |
| N3 | 58 | 23.62 ± 7.053 | |
| TNM stage | 0.000a | ||
| I | 15 | 8.80 ± 3.764 | |
| II | 18 | 11.38 ± 5.679 | |
| III | 99 | 20.85 ± 7.331 | |
| IV | 10 | 26.10 ± 2.960 | |
| VEGF expression | 0.001a | ||
| Negative | 58 | 16.32 ± 6.227 | |
| Positive | 84 | 20.43 ± 9.015 | |
| VEGFR2 expression | 0.000a | ||
| Negative | 66 | 12.48 ± 5.239 | |
| Positive | 76 | 24.19 ± 6.222 |
Paraffin-embedded tissues containing primary tumours and paired controls were obtained from the archives of the Department of Pathology of our hospital. Successive sections at 1 mm intervals from each paraffin block were used for evaluation. Anti-endocan mouse monoclonal antibody (ab56914, Abcam, Cambridge, MA, United States), anti-VEGF mouse monoclonal antibody (sc-7269, Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, United States) and anti-VEGFR2/Flk-1 mouse monoclonal antibody (sc-6251, Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, United States) were used for the immunohistochemical staining of endocan, VEGF and VEGFR2, respectively.
The immunohistochemical staining was performed using the streptavidin peroxidase complex method. The slides were deparaffinized with xylene and washed with PBS. After antigen retrieval, the slides were incubated with 0.3% blocking serum for 30 min at 37 °C to reduce nonspecific binding. The sections were incubated overnight at 4 °C with primary antibody against endocan (dilution: 1:100), VEGF (dilution: 1:150) or VEGFR2 (dilution: 1:150). The tissue sections were rinsed in TBS and then detected using biotinylated goat anti-mouse immunoglobulin as secondary antibody. After rinsing with TBS, the sections were incubated with 3,3’-diaminobenzidine solution until the desired staining was achieved. The slides were counterstained with haematoxylin, dehydrated, cleared and mounted. Negative controls were created by omitting the primary antibodies.
The immunohistochemical staining was evaluated independently by two pathologists who were blinded to the clinical information and the nature of the specimens. Quantitative analysis of MVD was performed in the sections that were stained for endocan. The most vascularized areas within the tumours (“hot spots”) were chosen at low magnification (× 40), and the vessels were counted at representative high magnification (× 400). All brown-stained endothelial cells that were clearly separated from connective tissue elements were considered microvessels. MVD was counted in three fields and was recorded as a total number per unit area. Endocan-MVD was divided into four groups (0, 1, 2 and 3) based on quartiles of endocan-MVD numbers, which were 12.51, 18.86 and 25.88, respectively. For all cases, the scores (0) and (1) were defined as a low level of endocan-MVD, and (2) and (3) as a high level of endocan-MVD.
The immunohistochemical results of VEGF and VEGFR2 were classified according to the number of positive cells as follows: (-), no cell was stained; (+), < 25% of cells were stained; (++), 25%-50% of cells were stained; and (+++), > 50% of cells were stained. For all cases, the scores (-) and (+) were defined as the negative expression of VEGF and VEGFR2, and (++) and (+++) as positive expression.
The SPSS program (version 16, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, United States) was used for the statistical analyses. Continuous quantitative data with a normal distribution are expressed as the mean ± SD. Potential relationships between endocan-MVD and clinicopathological variables were assessed using a Student’s t-test or an analysis of variance test, as appropriate. Spearman’s rank correlation was applied to evaluate the relationship between endocan-MVD and the expression of VEGF/VEGFR2. A Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to assess patient survival. We conducted a univariate analysis of the prognostic factors with a log-rank test and a multivariate analysis with a Cox’s regression model. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
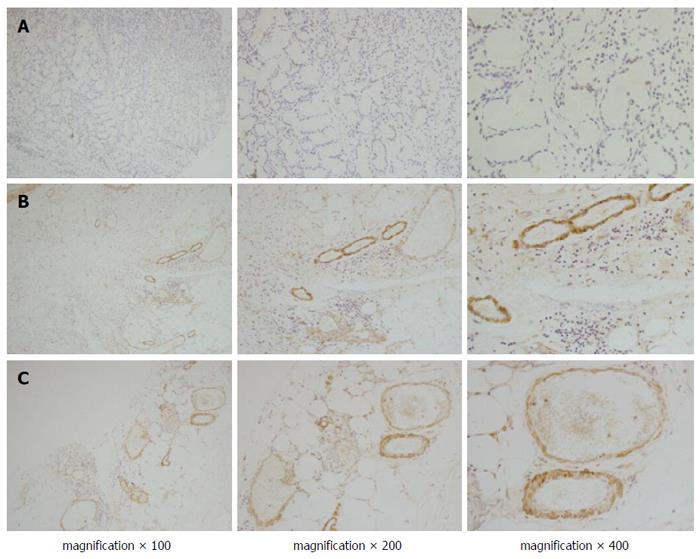
Positive staining of endocan was observed in most of the gastric cancer tissues (108/142) and in fewer of the normal gastric tissues (Figure 1A and B). The expression of endocan was also found in the endothelial cells of tumour vessels. In tumour centres, endocan-expressing endothelial cells of tumour vessels were observed in 78% (85/108) of the gastric cancer tissues stained with the endocan antibody (Figure 1C). In the peritumour vascular endothelium, positive endocan staining was more compact and was observed in most cases of gastric cancer tissues stained with the endocan antibody (100/108; Figure 1B). The endocan-MVD in gastric cancer tissues was 18.8 ± 8.1 and ranged from 4 to 44.
Endocan-MVD was significantly correlated with tumour size, Borrmann type, tumour differentiation, tumour invasion, lymph node metastasis, TNM stage and the expression of VEGF and VEGFR2, whereas it was not correlated with gender, age or histology. These data are summarized in Table 1.
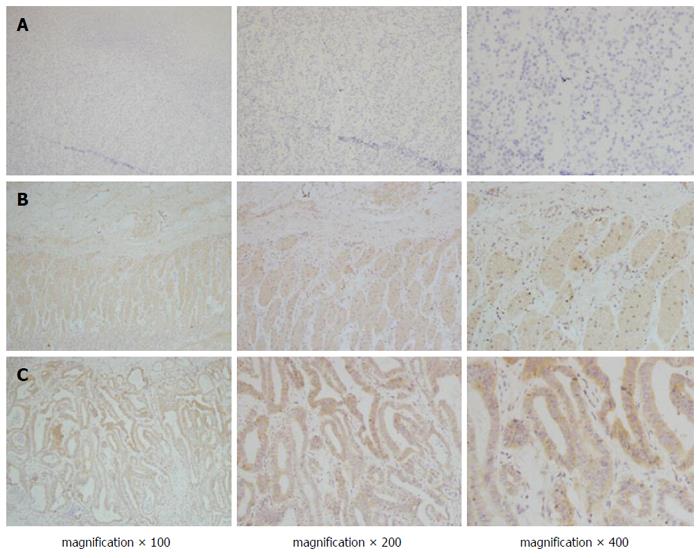
VEGF and VEGFR2 were dispersed granularly within the cytoplasm of the tumour cells (Figure 2). Among the total 142 gastric cancer specimens, VEGF overexpression was detected in 84 (59.1%), and VEGFR2 was overexpressed in 76 (53.5%). A significant association was found between endocan-MVD and the expression of VEGF or VEGFR2 (Spearman’s rank correlation analysis, r = 0.167, P = 0.047 and r = 0.410, P = 0.000, respectively; Table 2).
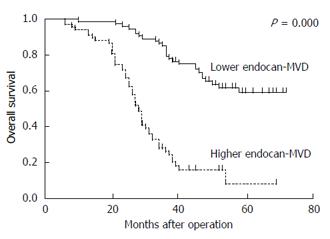
The 142 patients were divided into a low endocan-MVD group (75/142) and a high endocan-MVD group (67/142) using the median value of endocan-MVD (i.e., 18.8). The univariate analysis with a log-rank test indicated that the patients with a high endocan-MVD had a significantly poorer overall survival rate than those with a low endocan-MVD (17.9% vs 64.0%, P = 0.000; Figure 3). Tumour size, Borrmann type, differentiation, tumour invasion, lymph node metastasis, TNM stage and the expression of VEGF and VEGFR2 were significantly associated with the overall survival rate, whereas the other clinicopathologic features were not (Table 3).
| Clinicopathologic feature | n | 5-yr survival rate (%) | P value1 |
| Gender | 0.280 | ||
| Male | 93 | 44.08 | |
| Female | 49 | 38.77 | |
| Age (yr) | 0.580 | ||
| < 60 | 78 | 41.02 | |
| ≥ 60 | 64 | 43.75 | |
| Tumour size (cm) | 0.000a | ||
| < 5 | 79 | 62.02 | |
| ≥ 5 | 63 | 17.46 | |
| Borrmann type | 0.000a | ||
| I + II | 33 | 78.78 | |
| III + IV | 109 | 31.19 | |
| Histology | 0.260 | ||
| Adenocarcinoma | 118 | 40.67 | |
| Others | 23 | 52.17 | |
| Differentiation | 0.000a | ||
| High/moderate | 36 | 69.44 | |
| Low/undifferentiated | 106 | 33.01 | |
| Tumour invasion | 0.000a | ||
| T1-2 | 32 | 84.37 | |
| T3-4 | 110 | 30.00 | |
| Lymph node metastasis | 0.003a | ||
| N0-1 | 54 | 57.40 | |
| N2-3 | 88 | 32.95 | |
| TNM stage | 0.000a | ||
| I-II | 33 | 84.84 | |
| III-IV | 109 | 29.35 | |
| VEGF expression | 0.003a | ||
| Negative | 58 | 56.89 | |
| Positive | 84 | 32.14 | |
| VEGFR2 expression | 0.000a | ||
| Negative | 66 | 68.18 | |
| Positive | 76 | 19.73 | |
| Endocan-MVD | 0.000a | ||
| Low | 75 | 64.00 | |
| High | 67 | 17.91 |
Parameters with P values < 0.05 in the univariate analysis were included in the multivariate analysis using a Cox proportional hazards model. It was revealed that differentiation, TNM stage, endocan-MVD and the expression of VEGF and VEGFR2 were significant prognostic factors in these patients (Table 4).
| Factor | P value | HR | 95%CI |
| Tumour size (cm) | 0.247 | 1.407 | 0.789-2.508 |
| Borrmann type | 0.388 | 1.345 | 0.686-2.636 |
| Differentiation | 0.036a | 3.52 | 1.087-11.394 |
| Tumour invasion | 0.681 | 1.465 | 0.237-9.066 |
| Lymph node metastasis | 0.75 | 1.119 | 0.560-2.235 |
| TNM stage | 0.000a | 4.189 | 1.450-12.102 |
| VEGF expression | 0.001a | 2.827 | 1.508-5.302 |
| VEGFR2 expression | 0.020a | 3.572 | 1.218-10.474 |
| High endocan-MVD | 0.047a | 2.111 | 1.008-4.419 |
Angiogenesis plays an important role in the invasion, growth and metastasis of most tumours in which a number of cytokines are now known to be involved[18]. Among these cytokines is an essential factor for angiogenesis, which is known as VEGF. VEGF not only stimulates the division and migration of vascular endothelial cells but can also induce new vessels, which are thin and susceptible to the invasion of cancer, leading to distant metastases[19]. Microvascular density is used as an objective evaluation index for tumour angiogenesis. Previous studies have shown that endocan is expressed in endothelial cells in colon cancer and kidney cancer, and endocan-MVD is associated with the prognosis of tumours[8-10]. Therefore, in this paper, we performed further research on the relationship between endocan-MVD and VEGF/VEGFR2 and the prognosis of patients with gastric cancer to provide a new therapy for patients with gastric cancer.
Endocan is the product of a gene that is located in the proximal region of the long arm of chromosome 5 (5q11.2)[4]. Recent evidence has implied that endocan plays important roles in several pathophysiological processes, including inflammatory disorders and tumour progression, and in the regulation of major cellular processes, such as adhesion, migration and angiogenesis[4-7]. Numerous studies have focused on endocan expression in tumour tissues, and it is deemed as a new tumour prognostic marker because of its expression in serum[20,21]. However, our studies paid more attention to the expression of endocan in tumour vessels, as well as the relationship between the expression of endocan and tumour clinical features. We have confirmed the expression of endocan in the endothelial cells of tumour centre vessels, and positive endocan showed denser expression in the peritumour vascular endothelium. This showed that endocan is crucial in gastric cancer angiogenesis.
To test whether endocan-MVD can predict the prognosis of gastric cancer after resection, we used immunohistochemical staining to determine endocan expression in tumour specimens and correlated our findings with available follow-up information. We found that positive staining of endocan was preferentially detected in gastric cancer vessels but not in normal gastric tissues. Endocan-MVD in the peritumour vascular endothelium was higher than that in the tumour centre. The data from the current study indicated that endocan-MVD in gastric cancer was significantly associated with tumour size, Borrmann type, differentiation, tumour invasion, lymph node metastasis, TNM stage and the expression of VEGF and VEGFR2. By analysing the potential relationship between endocan-MVD and survival time, we found that patients with high endocan-MVD had a significantly poorer overall survival rate, which is consistent with the results for non-small-cell lung cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma[11,22]. With the Cox proportional hazards regression model, we found that endocan-MVD was an ideal marker to predict the prognosis in patients with gastric cancer.
The expression of endocan is regulated by a number of cytokines and growth factors, such as tumour necrosis factor-α, transforming growth factor-β1 and VEGF[23,24]. Among them, VEGF, as a major proangiogenic factor, has attracted the most attention. Recent studies have suggested that VEGF can induce the expression of endocan in vitro, and the VEGF-mediated induction of endocan mRNA was blocked by BIM (a PKC inhibitor) but not by PD98059 (an MEK1/2 inhibitor)[15]. However, endocan was reported less often in gastric cancer tissues and cells. In this study, we found that endocan-MVD was closely related to the expression of VEGF and VEGFR2 in gastric cancer tissues, which suggested that VEGF and VEGFR2 might induce the expression of endocan. The size of samples enrolled in our study was not large enough, and a subsequent study will employ larger samples based on a multicentre survey for further intervention. Despite this, analysing endocan-MVD might be useful in predicting prognoses and in choosing appropriate therapeutic modalities for patients with gastric cancer.
In conclusion, endocan had a high expression level in the endothelial cells of tumour vessels, and a significant association was found between endocan-MVD and the expression of VEGF or VEGFR2. The patients with high endocan-MVD had a significantly poorer overall survival rate than those with low endocan-MVD. This shows that endocan-MVD may play an important role in the processes of tumour therapy, which can be used as a critical factor for prognosis.
Endocan plays an extremely important role in the angiogenesis of tumours, and endocan-expressing microvessel density (MVD) (endocan-MVD) is likely to be valuable for the prognosis of malignancy. It has been reported that the secretion of endocan is strongly upregulated in the presence of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The exact relationship between endocan-MVD and the expression of VEGF and the value of endocan-MVD as a prognostic factor in patients with gastric cancer have not yet been defined.
Vascular endocan, as a biomarker of neoangiogenesis, is found inside the vessels in different types of tumours, but not in gastric cancer. The exact relationship between endocan-MVD and the expression of VEGF in gastric cancer remains unclear. The research hotspot is to further clarify these issues.
Based on the investigation of clinical characteristics and endocan expression in 142 patients with gastric cancer, we first found that endocan-MVD had a positive correlation with VEGF and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) in gastric cancer tissues. Patients with a high level of endocan-MVD had a significantly poorer overall survival rate than those with a low level of endocan-MVD.
The results of this study may clarify the role of endocan-MVD in the tumour neoangiogenesis in patients with gastric cancer, and provide strategies for the treatment of patients with advanced gastric cancer. Endocan-MVD may act as a valuable prognostic factor for survival in patients with gastric cancer.
Endocan, previously called the endothelial cell specific molecule-1, which is a new member of the proteoglycan family, plays an extremely important role in the transformation, survival, proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis and metastasis of tumours. Microvascular density (MVD) is used as an objective evaluation index for tumour angiogenesis.
This is an interesting study about the expression of endocan in cancer vessels and the relationships between endocan and the expression of VEGF and prognosis in gastric cancer.
P- Reviewer: Gilbert MR, Ishibashi H S- Editor: Gong ZM L- Editor: Wang TQ E- Editor: Wang CH
| 1. | Bray F, Jemal A, Grey N, Ferlay J, Forman D. Global cancer transitions according to the Human Development Index (2008-2030): a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:790-801. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1245] [Cited by in RCA: 1401] [Article Influence: 107.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Stewart BW, Coates AS. Cancer prevention: a global perspective. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:392-403. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Lin Y, Ueda J, Kikuchi S, Totsuka Y, Wei WQ, Qiao YL, Inoue M. Comparative epidemiology of gastric cancer between Japan and China. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:4421-4428. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 119] [Cited by in RCA: 133] [Article Influence: 9.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Roudnicky F, Poyet C, Wild P, Krampitz S, Negrini F, Huggenberger R, Rogler A, Stöhr R, Hartmann A, Provenzano M. Endocan is upregulated on tumor vessels in invasive bladder cancer where it mediates VEGF-A-induced angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2013;73:1097-1106. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 114] [Cited by in RCA: 143] [Article Influence: 11.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Sanderson RD, Yang Y, Suva LJ, Kelly T. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans and heparanase--partners in osteolytic tumor growth and metastasis. Matrix Biol. 2004;23:341-352. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 154] [Cited by in RCA: 148] [Article Influence: 7.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Reed CC, Waterhouse A, Kirby S, Kay P, Owens RT, McQuillan DJ, Iozzo RV. Decorin prevents metastatic spreading of breast cancer. Oncogene. 2005;24:1104-1110. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 151] [Cited by in RCA: 166] [Article Influence: 8.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Grant DS, Yenisey C, Rose RW, Tootell M, Santra M, Iozzo RV. Decorin suppresses tumor cell-mediated angiogenesis. Oncogene. 2002;21:4765-4777. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 161] [Cited by in RCA: 182] [Article Influence: 7.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Kim JH, Park MY, Kim CN, Kim KH, Kang HB, Kim KD, Kim JW. Expression of endothelial cell-specific molecule-1 regulated by hypoxia inducible factor-1α in human colon carcinoma: impact of ESM-1 on prognosis and its correlation with clinicopathological features. Oncol Rep. 2012;28:1701-1708. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 42] [Cited by in RCA: 51] [Article Influence: 3.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Leroy X, Aubert S, Zini L, Franquet H, Kervoaze G, Villers A, Delehedde M, Copin MC, Lassalle P. Vascular endocan (ESM-1) is markedly overexpressed in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Histopathology. 2010;56:180-187. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 81] [Cited by in RCA: 100] [Article Influence: 6.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Dieterich LC, Mellberg S, Langenkamp E, Zhang L, Zieba A, Salomäki H, Teichert M, Huang H, Edqvist PH, Kraus T. Transcriptional profiling of human glioblastoma vessels indicates a key role of VEGF-A and TGFβ2 in vascular abnormalization. J Pathol. 2012;228:378-390. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 101] [Cited by in RCA: 122] [Article Influence: 9.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Grigoriu BD, Depontieu F, Scherpereel A, Gourcerol D, Devos P, Ouatas T, Lafitte JJ, Copin MC, Tonnel AB, Lassalle P. Endocan expression and relationship with survival in human non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:4575-4582. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 125] [Cited by in RCA: 148] [Article Influence: 8.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Chen LY, Liu X, Wang SL, Qin CY. Over-expression of the Endocan gene in endothelial cells from hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with angiogenesis and tumour invasion. J Int Med Res. 2010;38:498-510. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 54] [Cited by in RCA: 66] [Article Influence: 4.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Liu N, Zhang LH, Du H, Hu Y, Zhang GG, Wang XH, Li JY, Ji JF. Overexpression of endothelial cell specific molecule-1 (ESM-1) in gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:2628-2639. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 46] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Abid MR, Yi X, Yano K, Shih SC, Aird WC. Vascular endocan is preferentially expressed in tumor endothelium. Microvasc Res. 2006;72:136-145. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 83] [Cited by in RCA: 102] [Article Influence: 5.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Rennel E, Mellberg S, Dimberg A, Petersson L, Botling J, Ameur A, Westholm JO, Komorowski J, Lassalle P, Cross MJ. Endocan is a VEGF-A and PI3K regulated gene with increased expression in human renal cancer. Exp Cell Res. 2007;313:1285-1294. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 91] [Cited by in RCA: 106] [Article Influence: 5.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Shin JW, Huggenberger R, Detmar M. Transcriptional profiling of VEGF-A and VEGF-C target genes in lymphatic endothelium reveals endothelial-specific molecule-1 as a novel mediator of lymphangiogenesis. Blood. 2008;112:2318-2326. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 96] [Cited by in RCA: 114] [Article Influence: 6.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Cornelius A, Cortet-Rudelli C, Assaker R, Kerdraon O, Gevaert MH, Prévot V, Lassalle P, Trouillas J, Delehedde M, Maurage CA. Endothelial expression of endocan is strongly associated with tumor progression in pituitary adenoma. Brain Pathol. 2012;22:757-764. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 50] [Cited by in RCA: 51] [Article Influence: 3.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646-674. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 51728] [Cited by in RCA: 47161] [Article Influence: 3368.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (5)] |
| 19. | Grothey A, Galanis E. Targeting angiogenesis: progress with anti-VEGF treatment with large molecules. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2009;6:507-518. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 276] [Cited by in RCA: 273] [Article Influence: 17.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Yilmaz MI, Siriopol D, Saglam M, Kurt YG, Unal HU, Eyileten T, Gok M, Cetinkaya H, Oguz Y, Sari S. Plasma endocan levels associate with inflammation, vascular abnormalities, cardiovascular events, and survival in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2014;86:1213-1220. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 94] [Cited by in RCA: 121] [Article Influence: 11.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Balta I, Balta S, Koryurek OM, Demirkol S, Mikhailidis DP, Celik T, Cakar M, Kucuk U, Eksioglu M, Kurt YG. Serum endocan levels as a marker of disease activity in patients with Behçet disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:291-296. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 94] [Cited by in RCA: 110] [Article Influence: 9.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Huang GW, Tao YM, Ding X. Endocan expression correlated with poor survival in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 2009;54:389-394. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 54] [Cited by in RCA: 67] [Article Influence: 4.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Gerritsen ME, Tomlinson JE, Zlot C, Ziman M, Hwang S. Using gene expression profiling to identify the molecular basis of the synergistic actions of hepatocyte growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor in human endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2003;140:595-610. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 112] [Cited by in RCA: 127] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Kirwan RP, Leonard MO, Murphy M, Clark AF, O’Brien CJ. Transforming growth factor-beta-regulated gene transcription and protein expression in human GFAP-negative lamina cribrosa cells. Glia. 2005;52:309-324. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 66] [Cited by in RCA: 74] [Article Influence: 3.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |