Published online Sep 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i36.10435
Peer-review started: January 21, 2015
First decision: February 10, 2015
Revised: April 12, 2015
Accepted: July 8, 2015
Article in press: July 8, 2015
Published online: September 28, 2015
Processing time: 250 Days and 23 Hours
AIM: To evaluate the efficacy of sequential vs hybrid therapy in patients with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection.
METHODS: From March 2013 to May 2014, one hundred and seventy-five H. pylori infected patients who had not been treated for H. pylori before were randomized to receive either sequential therapy (rabeprazole 20 mg and amoxicillin 1 g twice daily for 5 d, followed by rabeprazole 20 mg, clarithromycin 500 mg and metronidazole 500 mg twice daily for 5 d) or hybrid therapy (rabeprazole 20 mg and amoxicillin 1 g for 7 d, followed by rabeprazole 20 mg, amoxicillin 1 g, clarithromycin 500 mg and metronidazole 500 mg twice daily for 7 d). H. pylori status was confirmed by positive results of both rapid urease test and histology examination or a positive result of culture. Eradication efficacy was assessed by follow-up endoscopy with rapid urease test and histological examination 8 wk after the end of anti-H. pylori therapy, or 13C-urea breath test at least 4 wk after completion of treatment. The primary outcome was H. pylori eradication by intension-to-treat (ITT) and per-protocol (PP) analyses.
RESULTS: One hundred and sixty-seven patients (83 patients in the sequential group and 84 patients in the hybrid group) completed the study. The compliance rates were 97.6% and 97.7% for the two groups, respectively. The eradication rate was 78.2% for the sequential group and 92% for the hybrid group by ITT analysis (P = 0.01). The eradication rate was 81.9% for the sequential group and 96.4% for the hybrid group by PP analysis (P = 0.01). Univariate analysis for the clinical and bacterial factors did not identify any risk factors associated with treatment failure. Severe adverse events were observed in 2.3% of patients in the sequential group and 2.4% of those in the hybrid group.
CONCLUSION: Due to a grade A (> 95%) success rate for H. pylori eradication by PP analysis, similar compliance and adverse events, hybrid therapy seems to be an appropriate eradication regimen in Taiwan.
Core tip: The ideal therapy regimen for Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection should achieve an eradication rate ≥ 90% on per-protocol analysis. Both the hybrid and sequential therapies have shown eradication rates superior to the standard triple therapy in several studies. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study on the comparison between hybrid therapy and sequential therapy in Taiwan population. Hybrid regimen is a more effective therapy for H. pylori eradication than sequential regimen.
-
Citation: Chen KY, Lin TJ, Lin CL, Lee HC, Wang CK, Wu DC. Hybrid
vs sequential therapy for eradication ofHelicobacter pylori in Taiwan: A prospective randomized trial. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(36): 10435-10442 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i36/10435.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i36.10435
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is very common worldwide, occurring in 40% to 50% of the population in developed countries, in 80% to 90% of the population in developing regions[1,2], and about 50% of the population in Taiwan[2]. H. pylori infection causes chronic gastritis which significantly increases the risk of developing gastric or duodenal ulcers[3,4], gastric adenocarcinoma, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma[5,6]. Eradication of H. pylori infection prevents ulcer recurrence[7,8], leads to a significant reduction of gastric cancer, decreases intestinal type gastric cancer recurrence in patients who underwent endoscopic resection[9], and results in complete regression of 60%-83% of MALTomas[10].
Until recently, the gold standard regimen for H. pylori eradication consisted of triple therapy with a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) plus clarithromycin and amoxicillin or metronidazole, administered for 7-14 d[11,12]. The failure rates of these standard therapies range from 5% to 35%[13-15]. The main reasons for eradication failure are poor patient compliance, resistant bacteria, low gastric pH and a high bacterial load[16,17].
Sequential therapy, as originally defined, starts with a simple double regimen of a PPI plus amoxicillin for 5 d, followed by a triple regimen of a PPI, clarithromycin, and tinidazole for the next 5 d[18]. Recent studies with antimicrobial susceptibility testing have confirmed that the superiority of sequential therapy over standard triple therapy is primarily because of an improved outcome with clarithromycin-resistant strains[19]. However, sequential therapy was not demonstrated to achieve a per-protocol (PP) eradication rate of 95%.
In 2011, Hsu et al[20] report a study using a hybrid regimen, starting with PPI plus amoxicillin for 7 d, followed by a quadruple regimen of a PPI, amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and metronidazole for the next 7 d. The eradication rate was 99.1% by PP analysis and 97.4% by intension-to-treat (ITT) analysis. The ITT eradication rates achieve grade A success based on grading success (≥ 95% = A, 90%-94% = B, 85%-89% = C, 81%-84% = D, and ≤ 80% = F[21]).
Fewer studies compared sequential therapy with hybrid therapy. Two studies from Italy and Iran that compared sequential therapy for 10 d with hybrid therapy for 14 d showed contradictory results[22,23]. The reason was unknown because susceptibility tests were not done. Therefore, we did a randomized controlled trial to compare sequential regimen and hybrid regimen for the treatment of H. pylori infection. We assessed the antibiotic resistance that might affect the eradication rate. In Taiwan, the rate of resistance to metronidazole is generally high and that to clarithromycin is increasing, allowing the opportunity to compare sequential therapy and hybrid therapy in patients with single or dual antibiotic resistance.
We surveyed patients who visited the gastroenterology clinics of Taipei City Hospital between March 2013 and May 2014. Patients with H. pylori infection were enrolled in this study. Pre-enrollment procedures included biopsy of the gastric mucosa where the presence of H. pylori was assessed by rapid urease test, culture and histological examination of the tissue. The presence of H. pylori was defined as: (1) positive results of both rapid urease test and histology examination; or (2) a positive result of culture. Blood samples were taken for laboratory tests including renal and liver function tests to ascertain that there were no abnormal tests that would preclude entry into the trial.
Criteria for exclusion included: (1) use of antibiotics within the preceding 30 d; (2) regular use of a PPI (> 3 times per week) in the 30 d before enrollment; (3) previous surgery of the stomach; (4) patients previously treated for H. pylori infection; (5) use of concomitant medication; (6) presence of a serious medical condition; (7) known to interact with study medication; (8) pregnancy or lactation; (9) allergy to any medication in this study; and (10) presence of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. All participants gave written informed consent. Our study was approved by the ethic committee of Taipei City Hospital (TCHIRB-1011111).
The participants were randomly assigned to 10-d sequential therapy (rabeprazole 20 mg and amoxicillin 1 g twice daily for 5 d, followed by rabeprazole 20 mg, clarithromycin 500 mg and metronidazole 500 mg twice daily for 5 d) or 14-d hybrid therapy (rabeprazole 20 mg and amoxicillin 1 g for 7 d, followed by rabeprazole 20 mg, amoxicillin 1 g, clarithromycin 500 mg and metronidazole 500 mg twice daily for 7 d).
A trained interviewer used a standardized questionnaire to obtain demographic data and medical history. Patients were given a written handout with instructions on how to take the medications correctly.
Patients were asked to return 2 wk after the start of drug administration to assess drug compliance and adverse events. Drug compliance was assessed via pill counts. Compliance termed as good was defined as taking more than 80% of the total medication or poor by counting unused medication after the treatment was completed. Eradication efficacy was assessed by (1) follow-up endoscopy with rapid urease test and histological examination 8 wk after the end of anti-H. pylori therapy; or (2) 13C-urea breath test at least 4 wk after completion of treatment. Eradication was defined as either negative results of both urease test and histology or a negative result of the urea breath test.
A complete medical history and demographic data were obtained from each patient, including age, sex, medical history, history of smoking, and alcohol, coffee and tea consumption. Smokers were defined as those who consumed more than 1 pack of cigarettes a week, and drinkers were those who drank more than 1 cup of alcoholic beverage per day. The adverse events evaluated including diarrhea, constipation, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, skin rash, headache, dizziness, bitter taste and fatigue. We assessed adverse events according to a 4-point scale system: none; mild (discomfort annoying but not interfering with daily life); moderate (discomfort resulting in interference with daily life); severe (discomfort resulting in discontinuation of eradication drug).
The results of rapid urease test (Delta West Bently, Western, Australia) were interpreted as positive if the color of the gel turned pink or red 6 h after examination at room temperature. The 13C-urea was manufactured by the Wagner Analysen Technik Vertriebs GmbH, Germany. 75 mg 13C-urea mixed with 100 mL water was used as the test drink. The staffs who were blinded to the H. pylori status performed the tests.
Gastric specimens were taken, including one specimen from the lesser curvature site of the antrum and another from the lesser curvature site of the corpus for histological examination. The specimens were fixed with formalin, embedded in paraffin, and stained with hematoxylin and erosin. The result of Gram staining was considered positive when a curvy, gram-negative bacterium was found. The histological features of the gastric mucosa were graded according to the updated Sydney System[24]. The histopathologists were blinded to patient status and the results of other laboratory tests.
Biopsy specimens were rubbed on the surface of a Columbia blood agar plate and then incubated at 35 °C under microaerobic conditions for 4-5 d. Culture of H. pylori was considered positive if 1 or more colonies showed gram-negativity, oxidase (+), catalase (+), urease (+), and spiral or curved rods in morphology.
One antral gastric biopsy specimen was obtained for isolation of H. pylori. H. pylori subculturing was done by rubbing the specimens on the surface of a Campy-BAP agar plate (Brucella agar; Difco, Sparks, Maryland) + IsoVitalex (Gibco, Grand Island, New York) + 10% whole sheep blood) followed by incubation at 37 °C under microaerobic conditions (5% O2, 10% CO2, and 85% N2) for 4-5 d. H. pylori strains were tested for clarithromycin, tetracycline, metronidazole, amoxicillin, and levofloxacin susceptibility using E-test (AB Biodisck, Solna, Sweden). H. pylori strains with a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) value > 1 μg/mL, > 4 μg/mL, > 8 μg/mL, > 0.5 μg/mL, and > 1 μg/mL were defined as resistance to clarithromycin, tetracycline, metronidazole, amoxicillin, and levofloxacin, respectively.
The variables of primary outcome were the rates of eradication, adverse events and compliance. The difference of patients’ age in two groups was examined using Student’s t-test. A two-sided P-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The distribution of gender, smoking, alcohol consumption, coffee ingestion, NSAID user and initial endoscopic diagnosis between subjects in sequential and hybrid groups were compared by χ2 test. The same method was applied to compare the treatment efficacy and the frequency of side effects of the two regimens. The data were analyzed using the IBM SPSS statistics (version 22; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, United States).
Eradication rates were examined by ITT and PP analyses. ITT analysis included all randomly assigned patients who had taken at least one dose of medication. Patients with unknown H. pylori infection status after treatment were considered treatment failures for the purposes of ITT analyses. Patients with unknown H. pylori infection status or with major protocol violations were excluded for the PP analyses. A two-sided P-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
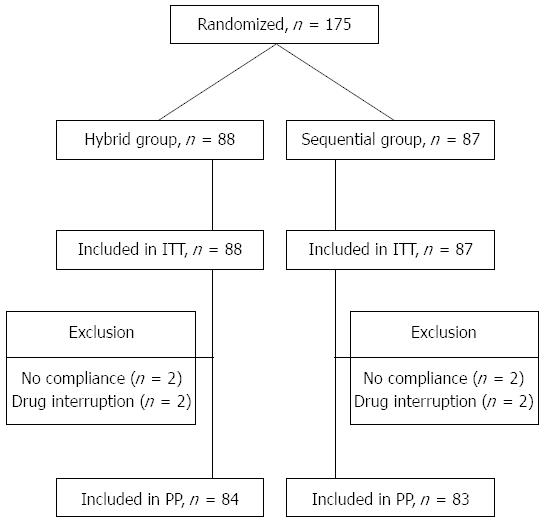
A total of 175 patients with H. pylori infection were randomly assigned to sequential (n = 87) or hybrid (n = 88) therapy. The first patient was randomized on March 18, 2013 and the last ended treatment on May 1, 2014. All subjects were included in the ITT analysis for H. pylori eradication. The baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of patients at entry are summarized in Table 1. The two groups had comparable age, history of smoking, alcohol consumption, ingestion of coffee, NSAID user, underlying diseases, endoscopic finding and H. pylori density. Among the subjects, four with poor compliance and four lost to follow-up were excluded from PP analysis for H. pylori eradication. Figure 1 summarizes the patient disposition.
| Characteristic | Hybrid therapy (n = 88) | Sequential therapy (n = 87) | P value |
| Age (mean ± SD), yr | 52.1 ± 13.0 | 54.6 ± 13.2 | 0.26 |
| Gender (male/female) | 39/49 | 25/62 | 0.04 |
| Smoking | 14 | 6 | 0.10 |
| Alcohol consumption | 20 | 18 | 0.74 |
| Ingestion of coffee | 61 | 57 | 0.59 |
| NSAID user | 8 | 8 | 0.96 |
| Underlying diseases | 26 | 23 | 0.77 |
| Endoscopic finding (Peptic ulcer/non-ulcer dyspepsia) | 46/42 | 32/55 | 0.06 |
| Helicobacter pylori density (mild/moderate/marked) | 8/42/38 | 4/57/26 | 0.26 |
The therapeutic outcomes are shown in Table 2. PP analysis demonstrated that hybrid therapy achieved a better eradication rate than sequential therapy [sequential, 81.9% (68/83), 95%CI: 73.6%-90.2% vs hybrid, 96.4% (81/84), 95%CI: 92.5%-100.4%, P = 0.01). For ITT analysis, the result was similar [sequential, 78.2% (68/87), 95%CI: 69.5%-86.8% vs hybrid, 92% (81/88), 95%CI: 86.4%-97.7%, P = 0.01].
| Variable | Hybrid therapy | Sequential therapy | P value | ||||
| Patients | Eradication rate | 95%CI | Patients | Eradication rate | 95%CI | ||
| Intension-to-treat analysis | 88 | 92.0% | 86.4-97.7 | 87 | 78.2% | 69.5-86.8 | 0.01 |
| Per-protocol analysis | 84 | 96.4% | 92.5-100.4 | 83 | 81.9% | 73.6-90.2 | 0.01 |
Both groups displayed good compliance rates (sequential, 97.6% vs hybrid, 96.5%, P = 0.99). The results were the same when compliance was defined as taking > 80% of the study medications.
Adverse events were reported in 112 (64%) of the 175 patients (Table 3); 69% (60/87) of patients in the sequential group and 59% (52/88) in the hybrid group report at least one adverse event during eradication therapy. The frequency was similar between the two groups (P = 0.164). Bitter taste (40%) and diarrhea (18.9%) were the most common adverse events. Four patients discontinued the treatments owing to adverse events (< 80% of total medicine), including two patients (2.3%) from the sequential group (diarrhea, one patients; headache, one patient) and two patients (2.4%) from the hybrid group (nausea, one patient; headache, one patient). Overall, four patients had poor drug compliance.
| Hybrid therapy | Sequential therapy | P value | |
| Compliance, n (%) | 84 (97.7) | 83 (97.6) | 0.99 |
| Side effects, n (%) | 52 (59) | 60 (69) | 0.22 |
| Diarrhea | 16/1/11 | 15/0/0 | 0.42 |
| Constipation | 1/0/0 | 2/0/0 | 0.50 |
| Anorexia | 0 | 1/0/0 | 0.70 |
| Nausea | 4/1/0 | 9/0/1 | 0.92 |
| Vomiting | 5/2/0 | 3/1/0 | 0.57 |
| Abdominal pain | 5/0/0 | 9/0/0 | 0.87 |
| Skin rash | 3/2/0 | 1/2/0 | 0.74 |
| Headache | 9/1/1 | 16/1/1 | 0.41 |
| Dizziness | 6/1/0 | 9/0/0 | 0.70 |
| Bitter taste | 25/6/0 | 36/3/0 | 0.17 |
| Fatigue | 3/0/0 | 4/0/0 | 0.30 |
H. pylori strain was successfully isolated from 124 (70.9%) of all enrolled patients who underwent bacterial culture during the initial endoscopy. The rates of resistance were as follows: amoxicillin, 0% (0/124); metronidazole, 37.9% (47/124); clarithromycin, 15.3% (19/124); tetracycline, 0.8% (1/124); levofloxacin, 16.9% (21/124). The dual antibiotic resistance rate (metronidazole and clarithromycin) was 8.9% (11/124).
The clinical and bacterial factors influencing the efficacy of therapy are shown in Table 4. Univariate analysis for the clinical and bacterial factors did not identify any risk factors associated with treatment failure. Those with single or dual (metronidazole and clarithromycin) antibiotic resistance were not a predictor of eradication in both groups. Compliance, smoking and alcohol consumption did not affect the result in either group.
| Variable | Sequential therapy | P value | Hybrid therapy | P value |
| Resistance (n = 124) | n = 59 | n = 65 | ||
| Metronidazole | 0.22 | 0.74 | ||
| Susceptible | 32 (84.2) | 37 (94.9) | ||
| Resistant | 14 (66.7) | 25 (96.1) | ||
| Clarithromycin | 0.73 | 0.51 | ||
| Susceptible | 37 (77.1) | 54 (94.7) | ||
| Resistant | 9 (81.8) | 8 (100) | ||
| Tetracycline | 0.59 | NA | ||
| Susceptible | 45 (77.6) | 62 (95.4) | ||
| Resistant | 1 (100) | |||
| Levofloxacin | 0.46 | 0.45 | ||
| Susceptible | 36 (75.0) | 52 (94.5) | ||
| Resistant | 10 (90.9) | 10 (100) | ||
| Amoxicillin | NA | NA | ||
| Susceptible | 46 (78.0) | 62 (95.4) | ||
| Resistant | ||||
| Dual resistance | 0.66 | 0.65 | ||
| Present | 5 (71.4) | 4 (100) | ||
| Absent | 41 (78.8) | 58 (95.0) | ||
| Compliance | 0.47 | 0.66 | ||
| Good | 66 (79.5) | 78 (94.0) | ||
| Poor | 2 (100) | 3 (100) | ||
| Smoking | 0.2 | 0.31 | ||
| Present | 6 (100) | 14 (100) | ||
| Absent | 62 (78.5) | 67 (93.1) | ||
| Alcohol | 0.29 | 0.21 | ||
| Present | 16 (88.9) | 20 (100) | ||
| Absent | 52 (77.6) | 61 (92.4) | ||
| Gastroduodenal disease | 0.91 | 0.57 | ||
| Non-ulcer dyspepsia | 43 (79.6) | 38 (92.7) | ||
| Peptic ulcer | 25 (80.6) | 43 (95.6) | ||
| Bacterial density | 0.31 | 0.4 | ||
| Mild | 4 (100) | 7 (87.5) | ||
| Moderate/marked | 64 (79.0) | 74 (94.9) |
The standard triple therapy is the most used treatment in routine clinical practice. However, the raising prevalence of clarithromycin and metronidazole resistance in recent year has caused a corresponding decrease in the eradication rates of H. pylori infection. It is clear that alternative regimens, particular for patients with clarithromycin-resistant strains of H. pylori, are urgently needed. We conducted a randomized, controlled trial to assess sequential and hybrid therapies for H. pylori infection. The finding of this study demonstrated a significantly higher eradication rate of hybrid therapy than sequential therapy, regardless of using ITT (92% vs 78.2%) or PP (96.4% vs 81.9%) analysis.
The reported eradication rate of sequential therapy varies between 78% and 97%[18]. Most of the studies conducted in Italy showed that the sequential therapy was more effective than triple therapy. Conversely, the studies from Latin America and South Korea reported that sequential therapy was not superior to triple therapy[25,26]. The difference in the prevalence of antibiotic resistance between the studies was probably the most important explanation. Although Zullo et al[27] found that the sequential therapy was not affected by metronidazole and clarithromycin resistance, except in the presence of dual metronidazole and clarithromycin resistance. Another study from Liou et al[28] noted the 10-d sequential therapy was affected by metronidazole or clarithromycin resistance. The eradication rate was 73% (32/44) in metronidazole resistant group and 59% (10/17) in clarithromycin resistant group. The sensitivity test of our study showed that the rates of resistance to clarithromycin and metronidazole were 15.3% and 37.9%, respectively. We did not find a significant effect of metronidazole and clarithromycin resistance. However, the eradication rate was 66.7% in the presence of metronidazole resistance.
According to Maastricht IV consensus report, bismuth-containing quadruple or sequential therapy should be used empirically in the first-line therapy, when the clarithromycin resistance rate is higher than 15%-20%[29]. Nevertheless, our data did not lend support to the use of sequential therapy as first-line therapy due to the acceptable eradication rate (81.9%). Taken the latest results into consideration, a more efficient therapy should be needed.
Hsu et al[20] reported a 99.1% eradication rate with hybrid regimen by PP analysis. They concluded that the high eradication rate of hybrid regimen can be attributed to the treatment duration extending and continuing the amoxicillin through the entire 14 d therapy. In particular, the eradication rate of hybrid therapy for those with dual resistance was 100%. Sardarian et al[23] reported an eradication rate of 92.9% with hybrid regimen compared to 76.7% with the sequential regimen (P = 0.001). In our study, hybrid therapy achieved a 96.4% eradication rate (grade A success) by PP analysis.
It has previously been suggested that sequential therapy was likely to fail in the presence of dual clarithromycin and metronidazole resistance. A study by Wu et al[30] reported three patients in the sequential group had strains of H. pylori with dual resistance, and the eradication rate was 33.3% (1/3). Another study from Vaira et al[31] reported that none of the 4 patients with dual resistance strains achieved eradication with the sequential treatment. Our data showed that sequential therapy achieved a 71.4% (5/7) eradication rate in patients with dual resistance strains. On the other hand, hybrid therapy achieved a 100% (4/4) eradication rate, which is consistent with the study report from Hsu et al[20]. These arguments are based on the results from a very small subset of patients in a single study and, therefore, more studies are needed.
Smoking had been showed to reduce the effectiveness of treatment and appeared possibly important in some sequential trials[32-35]. In our study, there was no significant effect of smoking in both groups. Even so, the prevalence of smoking was relatively low in our study population. Our study also demonstrated that the eradication rate was not affected by bacterial density, alcohol consumption, compliance, gastroduodenal disease and antibiotic resistance in both groups.
In this study, both regimens were well tolerated and exhibited good compliance. Fifty-nine percent of patients in the hybrid group and 69% in the sequential group reported at least one adverse event during the eradication therapy. The frequency was similar between the two groups (P = 0.22). Most adverse events were mild, and only four patients (hybrid group, two patients; sequential group, two patients) discontinued therapy due to severe adverse events. The most common adverse event was bitter taste in both groups, which affected 31 (36%) patients in the hybrid and 39 (45.9%) patients in the sequential group. However, it did not result in any therapy discontinuation. Sardarian et al[23] compared the adverse events between hybrid therapy and sequential therapy, and they also reported a similar side effect rate with bad taste having the most common incidence.
Both hybrid and sequential therapies had similar patient compliance in our study (97.6% vs 97.5%, P = 0.99). This is in accordance with other study reports. Sardarian et al[23] reported a 96.7% adherence rate in the hybrid therapy group and 98.6% in the sequential therapy group. The relative complexity of the hybrid regimen did not affect the compliance.
Some limitations should be acknowledged in our study. First, this is a single-center study comprising a relatively small sample size. A large, multicenter, randomized study is probably necessary to confirm the efficacy of those therapies. Second, antibiotic susceptibility data were available in only 70.9% of patients, which might raise the possibility of selection bias. This percentage was mainly related to the fact that the culture rate of H. pylori is less than perfect[36].
In conclusion, due to a grade A (> 95%) successful rate for H. pylori eradication, similar compliance and side events, hybrid therapy seems to be an appropriate eradication regimen in Taiwan.
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection causes chronic gastritis which significantly increases the risk of developing peptic ulcers and gastric malignancy. The failure rates of standard triple therapies are increasing. Sequential therapy and hybrid therapy have a better eradication rate of H. pylori infection than standard triple therapy. However, little data exist on the comparison between sequential therapy and hybrid therapy.
Sequential regimen and hybrid regimen for the treatment of H. pylori infection were compared.
In this study, a head-to-head comparison between hybrid therapy and sequential therapy was performed. Bacterial eradication was achieved in 92% and 78.2% at intension-to-treat, respectively, and 96.4% and 81.9% at per-protocol analysis, respectively, with comparable prevalence of side events, and comparable compliance to the therapy.
The results in this paper suggest that hybrid therapy seems to be an appropriate eradication regimen than sequential therapy. Larger studies and studies in different regions are needed to confirm this finding.
Hybrid therapy starts with a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) plus amoxicillin for 7 d, followed by a quadruple regimen of a PPI, amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and metronidazole for the next 7 d. Sequential therapy starts with a PPI plus amoxicillin for 5 d, followed by a triple regimen of a PPI, clarithromycin, and metronidazole for the next 5 d.
This is an interesting paper that compares the efficacy of sequential and hybrid therapy for H. pylori infection in Taiwan. The authors should indicate in the abstract that the treatment comparisons were carried out on patients that had not been treated for H. pylori before. Also in the conclusion of the abstract and the main body of the paper, indicate that the “grade A (> 95%) success rate for H. pylori eradication” was by per protocol analysis.
P- Reviewer: Engin AB, Smith SM S- Editor: Ma YJ L- Editor: Wang TQ E- Editor: Ma S
| 1. | Vaira D, Miglioli M, Mulè P, Holton J, Menegatti M, Vergura M, Biasco G, Conte R, Logan RP, Barbara L. Prevalence of peptic ulcer in Helicobacter pylori positive blood donors. Gut. 1994;35:309-312. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 54] [Cited by in RCA: 58] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Lin JT, Wang JT, Wang TH, Wu MS, Lee TK, Chen CJ. Helicobacter pylori infection in a randomly selected population, healthy volunteers, and patients with gastric ulcer and gastric adenocarcinoma. A seroprevalence study in Taiwan. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1993;28:1067-1072. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 78] [Cited by in RCA: 77] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Marshall BJ. Helicobacter pylori. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994;89:S116-S128. [PubMed] |
| 4. | Rauws EA, Tytgat GN. Cure of duodenal ulcer associated with eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Lancet. 1990;335:1233-1235. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 681] [Cited by in RCA: 626] [Article Influence: 17.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Asghar RJ, Parsonnet J. Helicobacter pylori and risk for gastric adenocarcinoma. Semin Gastrointest Dis. 2001;12:203-208. [PubMed] |
| 6. | Sipponen P. Gastric cancer: pathogenesis, risks, and prevention. J Gastroenterol. 2002;37 Suppl 13:39-44. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Gillen D, McColl KE. Gastroduodenal disease, Helicobacter pylori, and genetic polymorphisms. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;3:1180-1186. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Ernst PB, Peura DA, Crowe SE. The translation of Helicobacter pylori basic research to patient care. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:188-206; quiz 212-213. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 99] [Cited by in RCA: 106] [Article Influence: 5.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Uemura N, Okamoto S. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on subsequent development of cancer after endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer in Japan. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2000;29:819-827. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 63] [Cited by in RCA: 65] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | II United European Gastroenterology Week. Barcelona, Spain, July 19-24, 1993. Abstracts. Gut. 1993;34:S1-49. [PubMed] |
| 11. | Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, O’Morain C, Bazzoli F, El-Omar E, Graham D, Hunt R, Rokkas T, Vakil N, Kuipers EJ. Current concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection: the Maastricht III Consensus Report. Gut. 2007;56:772-781. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1396] [Cited by in RCA: 1350] [Article Influence: 75.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 12. | Graham DY, Fischbach L. Helicobacter pylori treatment in the era of increasing antibiotic resistance. Gut. 2010;59:1143-1153. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 652] [Cited by in RCA: 735] [Article Influence: 49.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 13. | Egan BJ, Marzio L, O’Connor H, O’Morain C. Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter. 2008;13 Suppl 1:35-40. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 44] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Hsu PI, Lai KH, Lin CK, Chen WC, Yu HC, Cheng JS, Tsay FW, Wu CJ, Lo CC, Tseng HH. A prospective randomized trial of esomeprazole- versus pantoprazole-based triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100:2387-2392. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 49] [Cited by in RCA: 48] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Wu IC, Wu DC, Hsu PI, Lu CY, Yu FJ, Wang TE, Chang WH, Chen JJ, Kuo FC, Wu JY. Rabeprazole- versus esomeprazole-based eradication regimens for H. pylori infection. Helicobacter. 2007;12:633-637. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Houben MH, van de Beek D, Hensen EF, de Craen AJ, Rauws EA, Tytgat GN. A systematic review of Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy--the impact of antimicrobial resistance on eradication rates. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1999;13:1047-1055. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 251] [Cited by in RCA: 226] [Article Influence: 8.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Padol S, Yuan Y, Thabane M, Padol IT, Hunt RH. The effect of CYP2C19 polymorphisms on H. pylori eradication rate in dual and triple first-line PPI therapies: a meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:1467-1475. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 112] [Cited by in RCA: 116] [Article Influence: 6.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Gisbert JP, Calvet X, O’Connor A, Mégraud F, O’Morain CA. Sequential therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a critical review. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010;44:313-325. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 127] [Cited by in RCA: 139] [Article Influence: 9.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Gatta L, Vakil N, Leandro G, Di Mario F, Vaira D. Sequential therapy or triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials in adults and children. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:3069-379; quiz 1080. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 209] [Cited by in RCA: 219] [Article Influence: 13.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Hsu PI, Wu DC, Wu JY, Graham DY. Modified sequential Helicobacter pylori therapy: proton pump inhibitor and amoxicillin for 14 days with clarithromycin and metronidazole added as a quadruple (hybrid) therapy for the final 7 days. Helicobacter. 2011;16:139-145. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 142] [Cited by in RCA: 147] [Article Influence: 10.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Graham DY, Lu H, Yamaoka Y. A report card to grade Helicobacter pylori therapy. Helicobacter. 2007;12:275-278. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 244] [Cited by in RCA: 314] [Article Influence: 17.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Zullo A, Scaccianoce G, De Francesco V, Ruggiero V, D’Ambrosio P, Castorani L, Bonfrate L, Vannella L, Hassan C, Portincasa P. Concomitant, sequential, and hybrid therapy for H. pylori eradication: a pilot study. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2013;37:647-650. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 67] [Cited by in RCA: 71] [Article Influence: 5.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Sardarian H, Fakheri H, Hosseini V, Taghvaei T, Maleki I, Mokhtare M. Comparison of hybrid and sequential therapies for Helicobacter pylori eradication in Iran: a prospective randomized trial. Helicobacter. 2013;18:129-134. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 82] [Cited by in RCA: 84] [Article Influence: 7.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Stolte M, Meining A. The updated Sydney system: classification and grading of gastritis as the basis of diagnosis and treatment. Can J Gastroenterol. 2001;15:591-598. [PubMed] |
| 25. | Greenberg ER, Anderson GL, Morgan DR, Torres J, Chey WD, Bravo LE, Dominguez RL, Ferreccio C, Herrero R, Lazcano-Ponce EC. 14-day triple, 5-day concomitant, and 10-day sequential therapies for Helicobacter pylori infection in seven Latin American sites: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2011;378:507-514. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 181] [Cited by in RCA: 206] [Article Influence: 14.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Kim YS, Kim SJ, Yoon JH, Suk KT, Kim JB, Kim DJ, Kim DY, Min HJ, Park SH, Shin WG. Randomised clinical trial: the efficacy of a 10-day sequential therapy vs. a 14-day standard proton pump inhibitor-based triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori in Korea. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011;34:1098-1105. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Zullo A, De Francesco V, Hassan C, Morini S, Vaira D. The sequential therapy regimen for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a pooled-data analysis. Gut. 2007;56:1353-1357. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 209] [Cited by in RCA: 211] [Article Influence: 11.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Liou JM, Chen CC, Chen MJ, Chen CC, Chang CY, Fang YJ, Lee JY, Hsu SJ, Luo JC, Chang WH. Sequential versus triple therapy for the first-line treatment of Helicobacter pylori: a multicentre, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet. 2013;381:205-213. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 197] [Cited by in RCA: 199] [Article Influence: 16.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, O’Morain CA, Atherton J, Axon AT, Bazzoli F, Gensini GF, Gisbert JP, Graham DY, Rokkas T. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection--the Maastricht IV/ Florence Consensus Report. Gut. 2012;61:646-664. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1719] [Cited by in RCA: 1588] [Article Influence: 122.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (5)] |
| 30. | Wu DC, Hsu PI, Wu JY, Opekun AR, Kuo CH, Wu IC, Wang SS, Chen A, Hung WC, Graham DY. Sequential and concomitant therapy with four drugs is equally effective for eradication of H pylori infection. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;8:36-41.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 176] [Cited by in RCA: 189] [Article Influence: 12.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Vaira D, Zullo A, Vakil N, Gatta L, Ricci C, Perna F, Hassan C, Bernabucci V, Tampieri A, Morini S. Sequential therapy versus standard triple-drug therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2007;146:556-563. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 209] [Cited by in RCA: 211] [Article Influence: 11.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Treiber G, Wittig J, Ammon S, Walker S, van Doorn LJ, Klotz U. Clinical outcome and influencing factors of a new short-term quadruple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a randomized controlled trial (MACLOR study). Arch Intern Med. 2002;162:153-160. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 84] [Cited by in RCA: 86] [Article Influence: 3.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Moayyedi P. Sequential regimens for Helicobacter pylori eradication. Lancet. 2007;370:1010-1012. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 44] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Suzuki T, Matsuo K, Ito H, Sawaki A, Hirose K, Wakai K, Sato S, Nakamura T, Yamao K, Ueda R. Smoking increases the treatment failure for Helicobacter pylori eradication. Am J Med. 2006;119:217-224. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 119] [Cited by in RCA: 129] [Article Influence: 6.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Broutet N, Tchamgoué S, Pereira E, Lamouliatte H, Salamon R, Mégraud F. Risk factors for failure of Helicobacter pylori therapy--results of an individual data analysis of 2751 patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003;17:99-109. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 150] [Cited by in RCA: 163] [Article Influence: 7.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Ricci C, Holton J, Vaira D. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori: invasive and non-invasive tests. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2007;21:299-313. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 129] [Cited by in RCA: 143] [Article Influence: 7.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |