Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2015; 21(18): 5465-5472
Published online May 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i18.5465
Published online May 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i18.5465
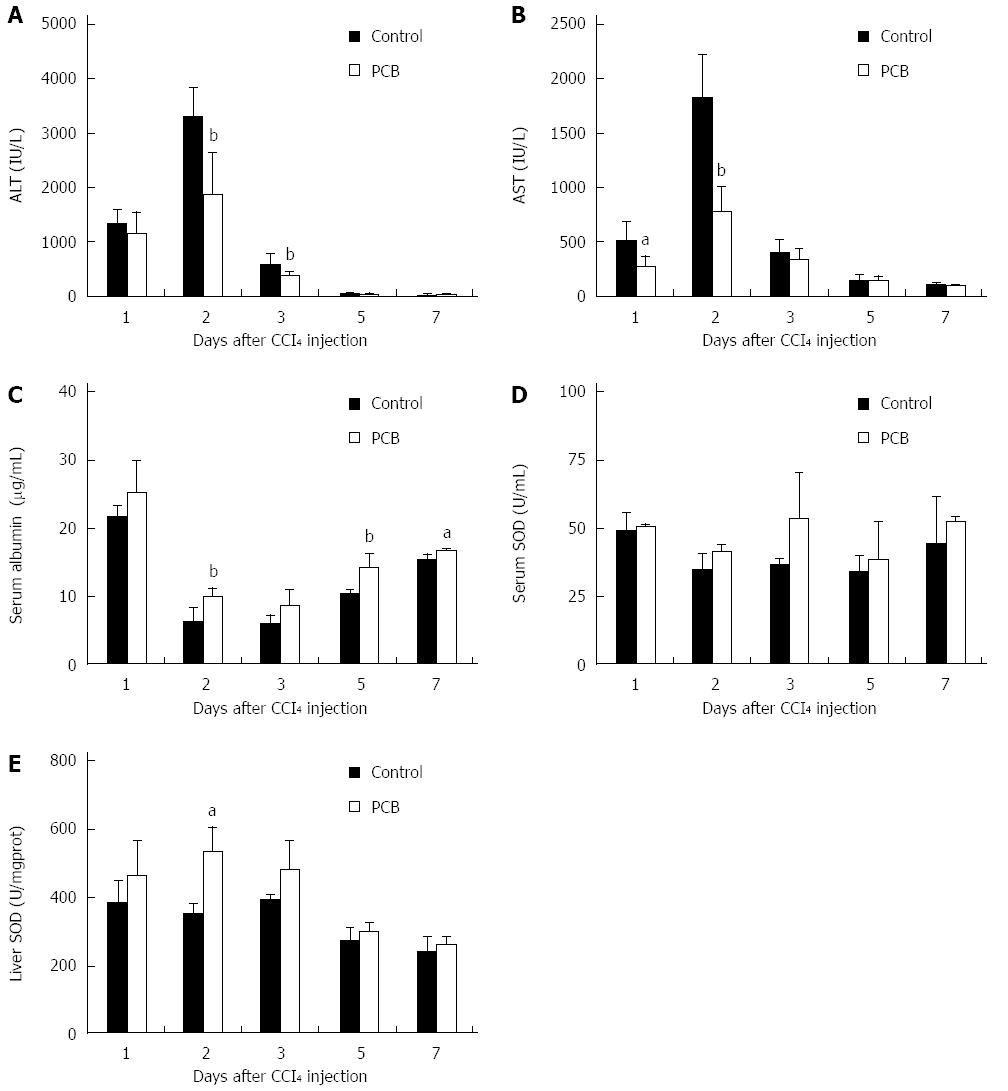
Figure 2 Phycocyanobilin protects mice against acute hepatocellular damage.
After CCl4 injection, mice were intragastrically administered with PCB or CMC-Na solution only. Then serum ALT, AST, albumin, SOD and liver SOD of mice were measured at indicated time points to monitor the indicator change-related acute hepatocellular damage. A: Serum ALT; B: Serum AST; C: Serum Albumin; D: Serum SOD; E: Liver SOD. Values represent mean ± SE (n = 6). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control. PCB: Phycocyanobilin; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; CMC-Na: Sodium carboxymethylcellulose.
- Citation: Liu J, Zhang QY, Yu LM, Liu B, Li MY, Zhu RZ. Phycocyanobilin accelerates liver regeneration and reduces mortality rate in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury mice. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(18): 5465-5472
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i18/5465.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i18.5465