Published online Mar 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i12.3731
Peer-review started: September 5, 2014
First decision: October 14, 2014
Revised: November 4, 2014
Accepted: December 1, 2014
Article in press: December 1, 2014
Published online: March 28, 2015
Processing time: 206 Days and 2.2 Hours
A 21-year-old male with no significant past medical history, presented with right upper quadrant (RUQ) abdominal pain along with fevers and chills. Lab work revealed leukocytosis, anemia, and slightly elevated alkaline phosphatase. Viral serology for hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, and human immunodeficiency virus were negative and he was immunocompetent. Computed tomography imaging revealed hepatic abscesses, the largest measuring 9.5 cm. Empiric antibiotics were started and percutaneous drains were placed in the abscesses. Anaerobic cultures from the abscesses grew Fusobacterium nucleatum. This is a gram negative anaerobic bacteria; a normal flora of the oral cavity. Fusobacterium is most commonly seen in Lemiere’s disease, which is translocation of oral bacteria to the internal jugular vein causing a thrombophlebitis and subsequent spread of abscesses. Our patient did not have Lemiere’s, and is the first case described of fusobacterium pyogenic liver abscess in a young immunocompetent male with good oral hygiene. This case was complicated by sepsis, empyema, and subsequent abscesses located outside the liver. These abscesses’ have the propensity to flare abruptly and can be fatal. This case not only illustrates fusobacterium as a rare entity for pyogenic liver abscess, but also the need for urgent diagnosis and treatment. It is incumbent on physicians to diagnose and drain any suspicious hepatic lesions. While uncommon, such infections may develop without any overt source and can progress rapidly. Prompt drainage with antibiotic therapy remains the cornerstone of therapy.
Core tip: Pyogenic liver abscesses have the propensity to cause devastating effects; immediate drainage and antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment. Herein we report the first case of a pyogenic liver abscess from fusobacterium in a young, otherwise healthy immunocompetent individual.
-
Citation: Ahmed Z, Bansal SK, Dhillon S. Pyogenic liver abscess caused by
Fusobacterium in a 21-year-old immunocompetent male. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(12): 3731-3735 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i12/3731.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i12.3731
Pyogenic liver abscesses (PLA) are uncommon entities which require urgent diagnosis and treatment. If untreated they carry a high mortality. Hepatic abscess due to fusobacterium (gram negative anaerobic bacteria) is rare, but when reported they are associated with Lemierre’s disease, an infectious thrombophlebitis of the internal jugular vein. Such infections are typically seen in the setting of instrumentation, dental work, and incidental oral flora translocation. Herein, we present the first case of de novo hepatic abscesses due to fusobacterium in an otherwise healthy 20-year-old Caucasian male with no identifiable source of infection. His course was further complicated by development of multiple intra-abdominal abscesses with subsequent direct seeding into the right pleural cavity causing empyema.
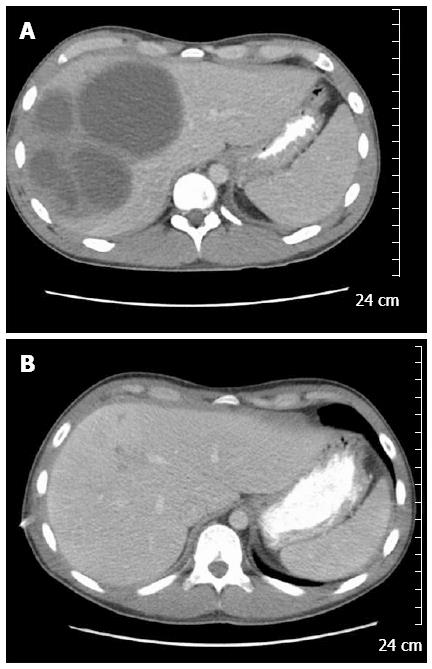
A 20-year-old Caucasian male was admitted with two weeks of progressive right upper quadrant abdominal pain, approximately 10 pound weight loss, fevers/chills, fatigue, and diarrhea. His social history was not significant for any IVDA, high risk sexual behavior, recent travel, exposure to contaminated water, or pet exposure. He was a college student and played baseball on the school team. On presentation his vital signs were stable and was afebrile. Examination revealed mild RUQ tenderness, but was otherwise unremarkable. His laboratory work revealed: leukocytosis with wbc count of 16.3 k/uL and anemia with Hgb of 7.6 gm/dL. Liver function tests revealed normal: AST (29 U/L)/ALT (44 U/L), total bilirubin (0.7 mg/dL); and mild elevation of alkaline phosphatase (158 U/L). Serologic workup was negative for human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus. Computed tomography (CT) imaging of abdomen/pelvis revealed multiple hepatic abscesses, the largest in the right lobe measuring 8.9 cm × 9.4 cm × 9.5 cm (Figure 1A). Aerobic and anaerobic blood cultures were collected and empiric antibiotic treatment was initiated with Vancomycin and Piperacillin/Tazobactam. Two percutaneous drains were placed in the largest hepatic abscesses. The hepatic abscesses’ anaerobic culture grew heavy Fusobacterium nucleatum (F. nucleatum). The patient denied any neck pain or recent dental infection, but did report recent routine dental cleaning. Neck imaging revealed patent jugular veins without tenderness or palpable cords. An ERCP was done to rule out a biliary source, and revealed normal hepatic, biliary, and pancreatic ducts.
One week after initiating treatment the patient developed respiratory distress and was found to have a large right sided multiloculated pleural effusion for which a chest tube was placed and pleural fluid analysis revealed empyema, likely due to direct extension of the pyogenic liver abscesses. The chest tube did not resolve the pleural effusion and the patient subsequently developed a trapped lung. He underwent evacuation of the pleural fluid and partial decortication with a VATS procedure. He developed 2 more abdominal abscesses, and one pelvic abscess, all required percutaneous drain drainage with resolution. A 2D trans-thoracic echocardiogram was unremarkable, apart from a mild pericardial effusion. The patient was placed on IV Ertapenem for 8 wk and discharged home in stable condition. Repeat imaging during out-patient follow-up showed complete resolution of his abscesses after 9 wk of treatment (Figure 1B).
The two most common types of liver abscesses are: PLA and amebic abscess. PLA is defined as an encapsulated mass containing purulent material[1-3]. Incidence varies with geographical location; PLA are more common in developed countries whereas amebic abscess are more common in developing countries. For PLA the reported incidence in the United States is 3.6 out of 100000 people[4,5]. The right hepatic lobe is the most common site of involvement, due to its larger size and having greater blood supply when compared to the left and caudate hepatic lobes[6]. PLA are more commonly polymicrobial rather than monomicrobial. Meddings et al[5], evaluated close to 18000 patients with PLA in the United States; and found the most commonly recorded bacterial infections were: Streptococcus species (29.5%) and Escherichia coli (18.1%). Of note, Taiwan had the highest reported incidence at 17.6 out to 100000 people, with Klebsiella being the most prominent bacterial organism being found. Anaerobic species are also not uncommon in such patients, with Bacteroides being most commonly isolated. Anaerobes are probably under-reported because of difficulty associated with culturing them. There are only a few case reports, which report fusobacterium as the causative organism. Of the two large PLA studies done by Meddings et al[5] and Chuang et al[7], none of them were reported to have been caused by Fusobacterium.
Liver abscess can occur from three mechanisms: (1) dissemination via the portal venous system is most common cause of pyogenic liver abscess. Intra-abdominal infections in portal bed region organes, result in septic thrombophlebitis causing micro-abscess formation in the liver. These micro-abscesses later coalesce to form larger single or multiple abscesses; (2) biliary tract disease such as biliary duct stone, stricture or malignancy, results in direct extension of infection through biliary channels to liver; and (3) hematogenous spread from systemic bacteremia can result from endocarditis, septic thrombophlebitis (Lemierre’s syndrome) or periodontal infections[8].
Notable risk factors for PLA include: diabetes mellitus, liver transplantation, intra-abdominal malignancy, biliary tract procedures, and immune system suppression[9]. Several recent studies from Taiwan mention an association between Klebsiella pneumoniae and colorectal cancer. Their studies show patients diagnosed with PLA had a fourfold increase in gastrointestinal malignancy, of which colorectal cancer was the most common[10-15].
Treatment of PLA includes prompt initiation of intravenous antibiotics and drainage of purulent material. The preferred method is via percutaneous drainage, with needle aspiration being an inferior choice due to requirement of repeated aspirations. Surgical intervention is recommended for: abscesses > 5 cm, gas forming organism, or biliary fistulization. Empiric broad spectrum intravenous antibiotics should include one of the following: ampicillin/sulbactam, ceftriaxone plus metronidazole, or meropenem. Definitive therapy is based on speciation of isolated organism. Recommended duration of antibiotics varies, usually ranging from 2-6 wk; depending on clinical improvement and resolution of abscess seen on CT imaging[3].
The genus Fusobacterium currently includes 13 species and belongs to family bacteroidaceae[16,17]. Most common species of Fusobacterium responsible for human infections are Fusobacterium necrophorum (F. necrophorum) and F. nucleatum. Fusobacterium is a nonsporeforming, nonmotile, gram negative small spindle-shaped rod[17,18]. F. nucleatum is part of normal oral flora[18,19]. Fusobacterium species possesses outer membrane proteins like other gram-negative bacteria[17]. The Lipopolysaccharides in the outer membrane proteins can act as endotoxins and provide other antigenic properties such as adhesion and co-aggregation which helps in invasion of the tissue and contribute towards virulence[17].
In 1936, Dr. Lemierre was the first to describe a periodontal source leading to septicemia from Fusobacterium. F. necrophorum is associated with younger healthy population while nucleatum is mostly associated with older patients with chronic medical conditions[20]. F. nucleatum had been associated with infections such as tropical skin ulcers, peritonsillar abscesses, pyomyositis, septic arthritis, bacteremia, intrauterine infections, bacterial vaginosis, urinary tract infections, pericarditis, endocarditis, myocarditis, and pulmonary infections[17,21]. F. Nucleatum has also recently been implicated as causative agent in chorioamnionitis and idiopathic preterm labor[16]. Association of F. Nucleatum infections with GI tract malignancies is attributed to the breach in mucosal lining resulting in invasive infections[18].
Annual incidence of Fusobacterium infections is between 0.6-3.5 cases per 1000000 people[20]. Su et al[22] pointed out that most Fusobacterium blood stream infections were from nucleatum species. Community acquired F. nucleatum infections tend to be more polymicrobial as compared to nosocomial which are almost always monomicrobial[23,24]. Risk factors for poor prognosis were presence of comorbid conditions such as diabetes mellitus, renal failure, dialysis and malignancy[18,20]. Nosocomial bacteremia was a significant mortality predictor with rates as high as 84% in one study[18]. F. nucleatum bacteremia without identifiable source is not uncommon. In such cases, a GI tract malignancy is often found[18].
The fusobacteria species are broadly susceptible to commonly used antibiotics, but reports of increasing resistance to: vancomycin, neomycin, erythromycin, amoxicillin, ampicillin, and phenoxymethylpenicillin; have emerged[17]. Recently some resistant patterns to quinolones had been identified with fusobacteria isolated from oral flora of dogs and cats[16]. An accurate identification of fusobacterium species is critical not only for taxonomic reasons but also for appropriate treatment of infection, since the susceptibility of different Fusobacterium species to antibiotics varies widely[17]. Only 13 cases have been reported of liver abscesses caused by F. nucleatum, 12 of which were in immunosuppressed individuals, and 1 mentioned by Kajiya et al[25] was an elderly immunocompetent individual[26-29]. Apart from our case, no other case has been reported in an otherwise young and healthy immunocompetent patient.
Pyogenic liver abscess from fusobacterium is a rare diagnosis and behaves clinically like any other anaerobic body cavity infections. It presents with fever, chills and weight loss in most cases. Surprisingly, jaundice and RUQ pain are inconsistent findings[8]. Course is indolent which could be used as a clinical clue on initial presentation. Necrosis of the tissue with putrid discharge and abscess formation are seen in later stages of the disease. Anemia and weight loss are indicators of long standing chronic infection. The spectrum of infections that can occur with Fusobacterium species is broad and carry a high mortality if untreated. Suspicion for anaerobic infections such as Fusobacterium should be kept high when a host with risk factors presents with indolent disease course. Also it should be kept in mind that while often seen in immunocompromised individuals, it can present, as in our case, in otherwise healthy individuals. It is postulated the patient got this invasive strain from possible plaques and/or minor oral cavity manipulation during routine dental cleaning. Prompt drainage along with empiric anaerobic coverage is recommended initially. The sequelae of this condition are fatal, prompt diagnosis and treatment with source control being the focus are crucial in preventing mortality.
A 21-year-old immunocompetent male with pyogenic liver abscess from Fusobacterium.
Right upper quadrant pain, fevers/chills, and weight loss in an otherwise healthy patient.
Hepatitis, hepatic cancer, biliary obstruction.
WBC count of 16.3 k/uL; Hgb of 7.6 gm/dL; liver function tests relatively within normal limits; liver serology negative.
Computed tomography imaging of abdomen/pelvis revealed multiple hepatic abscesses, the largest in the right lobe measuring 8.9 cm x 9.4 cm x 9.5 cm.
Culture of aspirates showing: gram negative anaerobe-Fusobacterium nucleatum (F. nucleatum), otherwise pathology negative.
Aspiration and drainage, along with IV antibiotics: Ertapenem.
Pyogenic liver abscesses’ in otherwise healthy individuals is not very common, case reports describe: invasive oral cavity manipulation, biliary translocation, and gastrointestinal migration as causes; none of which were present in this case.
PLA is used to denote pyogenic liver abscess.
This case report illustrates importance of recognizing pyogenic liver abscess as a possible entity in otherwise healthy individuals with no predilection, and urgent treatment with: Drainage and antibiotics.
The author presented a young, immunocompetent patient had liver abscesses caused by F. nucleatum, a nonsporeforming, nonmotile, gram negative small spindle-shaped rod. F. nucleatum is a rare cause of pyogenic liver abscess and high morbidity and mortality will happen if delayed diagnosis and treatment. It is interesting to readers to keep in mind if same scenario happened.
P- Reviewer: Boscá L, Ferenci P, Hashimoto N, Hsieh CC, La Mura V S- Editor: Ma YJ L- Editor: A E- Editor: Wang CH
| 1. | Haque R, Huston CD, Hughes M, Houpt E, Petri WA. Amebiasis. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1565-1573. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 640] [Cited by in RCA: 562] [Article Influence: 25.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 2. | Pang TC, Fung T, Samra J, Hugh TJ, Smith RC. Pyogenic liver abscess: an audit of 10 years’ experience. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:1622-1630. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 123] [Cited by in RCA: 106] [Article Influence: 7.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (3)] |
| 3. | Reid-Lombardo KM, Khan S, Sclabas G. Hepatic cysts and liver abscess. Surg Clin North Am. 2010;90:679-697. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Kurland JE, Brann OS. Pyogenic and amebic liver abscesses. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2004;6:273-279. [PubMed] |
| 5. | Meddings L, Myers RP, Hubbard J, Shaheen AA, Laupland KB, Dixon E, Coffin C, Kaplan GG. A population-based study of pyogenic liver abscesses in the United States: incidence, mortality, and temporal trends. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:117-124. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 187] [Cited by in RCA: 210] [Article Influence: 14.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Kasper DL, Zaleznik DF. Intra-abdominal infections and abscesses. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 16th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill 2005; 749. |
| 7. | Chuang HC, Chen TL, Chiang DH, Lee YT, Huang LJ, Wang FD, Fung CP, Liu CY. Clinical and bacteriological characteristics of pyogenic liver abscess in non-diabetic patients. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2009;42:385-392. [PubMed] |
| 8. | Wong WM, Wong BC, Hui CK, Ng M, Lai KC, Tso WK, Lam SK, Lai CL. Pyogenic liver abscess: retrospective analysis of 80 cases over a 10-year period. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;17:1001-1007. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 116] [Cited by in RCA: 109] [Article Influence: 4.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Thomsen RW, Jepsen P, Sørensen HT. Diabetes mellitus and pyogenic liver abscess: risk and prognosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:1194-1201. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 105] [Cited by in RCA: 101] [Article Influence: 5.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Kao WY, Hwang CY, Chang YT, Su CW, Hou MC, Lin HC, Lee FY, Lee SD, Wu JC. Cancer risk in patients with pyogenic liver abscess: a nationwide cohort study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012;36:467-476. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Koo HC, Kim YS, Kim SG, Tae JW, Ko BM, Lee TI, Jeong SW, Jang JY, Kim HS, Lee SH. Should colonoscopy be performed in patients with cryptogenic liver abscess? Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2013;37:86-92. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Jeong SW, Jang JY, Lee TH, Kim HG, Hong SW, Park SH, Kim SG, Cheon YK, Kim YS, Cho YD. Cryptogenic pyogenic liver abscess as the herald of colon cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27:248-255. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 49] [Cited by in RCA: 51] [Article Influence: 3.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Qu K, Liu C, Wang ZX, Tian F, Wei JC, Tai MH, Zhou L, Meng FD, Wang RT, Xu XS. Pyogenic liver abscesses associated with nonmetastatic colorectal cancers: an increasing problem in Eastern Asia. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:2948-2955. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 50] [Cited by in RCA: 46] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Huang WK, Chang JW, See LC, Tu HT, Chen JS, Liaw CC, Lin YC, Yang TS. Higher rate of colorectal cancer among patients with pyogenic liver abscess with Klebsiella pneumoniae than those without: an 11-year follow-up study. Colorectal Dis. 2012;14:e794-e801. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 3.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Lai HC, Lin CC, Cheng KS, Kao JT, Chou JW, Peng CY, Lai SW, Chen PC, Sung FC. Increased incidence of gastrointestinal cancers among patients with pyogenic liver abscess: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology. 2014;146:129-37.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 68] [Cited by in RCA: 62] [Article Influence: 5.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Citron DM. Update on the taxonomy and clinical aspects of the genus fusobacterium. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;35:S22-S27. [PubMed] |
| 17. | Bolstad AI, Jensen HB, Bakken V. Taxonomy, biology, and periodontal aspects of Fusobacterium nucleatum. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1996;9:55-71. [PubMed] |
| 18. | Yang CC, Ye JJ, Hsu PC, Chang HJ, Cheng CW, Leu HS, Chiang PC, Lee MH. Characteristics and outcomes of Fusobacterium nucleatum bacteremia--a 6-year experience at a tertiary care hospital in northern Taiwan. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011;70:167-174. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Könönen E, Kanervo A, Salminen K, Jousimies-Somer H. beta-lactamase production and antimicrobial susceptibility of oral heterogeneous Fusobacterium nucleatum populations in young children. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999;43:1270-1273. [PubMed] |
| 20. | Afra K, Laupland K, Leal J, Lloyd T, Gregson D. Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of Fusobacterium species bacteremia. BMC Infect Dis. 2013;13:264. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Storm JC, Ford BA, Streit JA. Myocardial infection due to Fusobacterium nucleatum. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013;77:373-375. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Su CP, Huang PY, Yang CC, Lee MH. Fusobacterium bacteremia: clinical significance and outcomes. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2009;42:336-342. [PubMed] |
| 23. | Brook I. Fusobacterial infections in children. J Infect. 1994;28:155-165. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 59] [Cited by in RCA: 55] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Hwang JJ, Lau YJ, Hu BS, Shi ZY, Lin YH. Haemophilus parainfluenzae and Fusobacterium necrophorum liver abscess: a case report. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2002;35:65-67. [PubMed] |
| 25. | Kajiya T, Uemura T, Kajiya M, Kaname H, Hirano R, Uemura N, Tei C. Pyogenic liver abscess related to dental disease in an immunocompetent host. Intern Med. 2008;47:675-678. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 33] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Scoular A, Corcoran GD, Malin A, Evans BA, Davies A, Miller RF. Fusobacterium nucleatum bacteraemia with multiple liver abscesses in an HIV-I antibody positive man with IgG2 deficiency. J Infect. 1992;24:321-325. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Crippin JS, Wang KK. An unrecognized etiology for pyogenic hepatic abscesses in normal hosts: dental disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992;87:1740-1743. [PubMed] |
| 28. | Tweedy CR, White WB. Multiple Fusobacterium nucleatum liver abscesses. Association with a persistent abnormality in humoral immune function. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1987;9:194-197. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Kim YH, Yoon HJ, Park CW, Kim JH, Lee MK, Kim KB, Na DJ, Kim JM. [A case of liver abscess caused by Fusobacterium nucleatum in a patient with recurrent periodontal diseases]. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011;57:42-46. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |