Published online Sep 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i36.6026
Revised: March 13, 2013
Accepted: March 21, 2013
Published online: September 28, 2013
AIM: To examine whether rendezvous endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is associated with less pancreatic damage, measured as leakage of proenzymes, than conventional ERCP.
METHODS: Patients (n = 122) with symptomatic gallstone disease, intact papilla and no ongoing inflammation, were prospectively enrolled in this case-control designed study. Eighty-one patients were subjected to laparoscopic cholecystectomy and if intraoperative cholangiography suggested common bile duct stones (CBDS), rendezvous ERCP was performed intraoperatively (n = 40). Patients with a negative cholangiogram constituted the control group (n = 41). Another 41 patients with CBDS, not subjected to surgery, underwent conventional ERCP. Pancreatic proenzymes, procarboxypeptidase B and trypsinogen-2 levels in plasma, were analysed at 0, 4, 8 and 24 h. The proenzymes were determined in-house with a double-antibody enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Pancreatic amylase was measured by an enzymatic colourimetric modular analyser with the manufacturer’s reagents. All samples were blinded at analysis.
RESULTS: Post ERCP pancreatitis (PEP) occurred in 3/41 (7%) of the patients cannulated with conventional ERCP and none in the rendezvous group. Increased serum levels indicating pancreatic leakage were significantly higher in the conventional ERCP group compared with the rendezvous ERCP group regarding pancreatic amylase levels in the 4- and 8-h samples (P = 0.0015; P = 0.03), procarboxypeptidase B in the 4- and 8-h samples (P < 0.0001; P < 0.0001) and trypsinogen-2 in the 24-hour samples (P = 0.03). No differences in these markers were observed in patients treated with rendezvous cannulation technique compared with patients that underwent cholecystectomy alone (control group). Post procedural concentrations of pancreatic amylase and procarboxypeptidase B were significantly correlated with pancreatic duct cannulation and opacification.
CONCLUSION: Rendezvous ERCP reduces pancreatic enzyme leakage compared with conventional ERCP cannulation technique. Thus, laparo-endoscopic technique can be recommended with the ambition to minimise the risk for post ERCP pancreatitis.
Core tip: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) with sphincterotomy and stone extraction is a standard procedure in the management of common bile duct stones. Rendezvous ERCP reduces pancreatic enzyme leakage compared with conventional ERCP cannulation technique. Thus laparo-endoscopic technique can be recommended to prevent post ERCP pancreatitis.
- Citation: Swahn F, Regnér S, Enochsson L, Lundell L, Permert J, Nilsson M, Thorlacius H, Arnelo U. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography with rendezvous cannulation reduces pancreatic injury. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(36): 6026-6034
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i36/6026.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i36.6026
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) with endoscopic sphincterotomy and stone extraction is considered a standard procedure in the management of common bile duct stones (CBDS). Currently ERCP is often performed before the cholecystectomy (preoperative ERCP) or after it (postoperative ERCP). An alternative and increasingly appealing strategy is to carry out ERCP during the cholecystectomy (intraoperative ERCP) as a one-step procedure.
Many authors caution against using ERCP to aid surgical intervention in the management of CBDS owing to the risks of procedure-induced pancreatitis and postoperative failure to cannulate the bile duct. Despite more than three decades of efforts to reduce complication rates, post-ERCP pancreatitis (PEP) remains the most frequent, feared and unpredictable complication with an overall incidence ranging from 3% to 15%[1-5] whereas failure to achieve deep biliary cannulation varies between 1.5% and 20%[6,7]. The most serious of the several known procedure-related risk factors of PEP are closely associated with prolonged and repeated attempts at cannulation and inadvertent contrast filling of the pancreatic duct[2,8].
Rendezvous cannulation involves a combined laparo-endoscopic approach and can be used in conjunction with intraoperative ERCP. The concept was described for the first time in 1993[9]. Approaches for and definitions of rendezvous cannulation have varied over the years, but the basic principle remains an antegrade biliary cannulation over the papilla of Vater. If conducted correctly, the rendezvous procedure offers immediate biliary cannulation and avoids inadvertent cannulation of the pancreatic duct[10].
The question underlying our study is whether combining rendezvous cannulation with ERCP might reduce the incidence of PEP. Considering the incidence of PEP, large study groups are needed to investigate the impact of different ERCP techniques. On the other hand, pancreatic enzyme leakage is a sensitive marker of pancreatic damage related to development of acute pancreatitis and has been used as such in numerous previous studies[11]. In the clinical laboratory, pancreatic amylase is the most frequently used early sign of acute pancreatitis[12-15]. Procarboxypeptidase B (proCAPB) has been suggested as an even more sensitive marker for acute pancreatitis, while the proenzyme trypsinogen-2 may be a useful indicator for acute pancreatitis as well as revealing the severity of pancreatitis[16-19].
The aim of our prospective case-control study was to investigate whether use of rendezvous cannulation technique could prevent post-ERCP pancreatic damage in patients treated for gallbladder and common bile duct stones. The primary end point was estimated as leakage of pancreatic pro-enzymes (pancreatic amylase, proCAPB and trypsinogen-2) after ERCP.
Between April 2005 and November 2010 patients who fulfilled the inclusion criteria (Table 1) were recruited as they presented at the Department of Surgical Gastroenterology, Karolinska University Hospital. All patients had a physical examination, were screened for baseline serum markers and were examined with abdominal ultrasonography, CT-scan or MRCP to confirm cholecysto- and/or choledocholithiasis and to rule out ongoing pancreatitis and/or cholecystitis. Among these patients we identified three study groups. Regardless of suspicion of CBDS, patients with cholecystolithiasis who were fit for surgery, were prepared for a standard laparoscopic cholecystectomy. According to the results of the intraoperative cholangiography, patients were allocated to one of two groups: rendezvous ERCP group (positive finding of CBDS) or laparoscopic cholecystectomy only (negative finding of CBDS). The third group, which received conventional ERCP, included patients with high suspicion of choledocholithiasis who had already had a cholecystectomy and patients with cholecystolithiasis and CBDS who were unsuitable for surgery. All patients were hospitalised for a minimum of 24 h, had a clinical examination at 4, 8 and 24 h postoperatively, and had a 30-d follow-up interview by telephone. Post ERCP pancreatitis was defined as post-procedural onset of upper abdominal pain lasting more than 24 h and combined with pancreatic amylase concentration in serum of at least three times the upper reference limit[20].
| Inclusion criteria |
| Clinical and radiological findings fulfilling indication for cholecystectomy due to gallstone |
| Clinical and radiological findings fulfilling indication for ERCP due to CBDS |
| Adult, ≥ 18 yr |
| Informed consent |
| Exclusion criteria |
| Acute or chronic pancreatitis |
| Acute cholangitis |
| Acute cholecystitis |
| Antiinflammatory medication |
| Failure to perform cholangiography |
| Pancreatic or biliary cancer |
| Prior ERCP with sphincterotomy |
| Conversion from laparoscopic to open cholecystectomy |
Demographic and procedure-related data were collected prospectively before and after the procedure and follow-up data were noted at 4, 8 and 24 h postoperatively and at 30 d follow-up. All patients gave oral and written informed consent before they entered the study, which was approved by the Regional Research Ethics Committee of Stockholm.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy was performed according to standard laparoscopic technique with pneumoperitoneum, introduction of four troachars and isolation of the cystic duct. All procedures included intraoperative cholangiography through a small incision of the cystic duct to check for CBDS and to delineate bile duct anatomy.
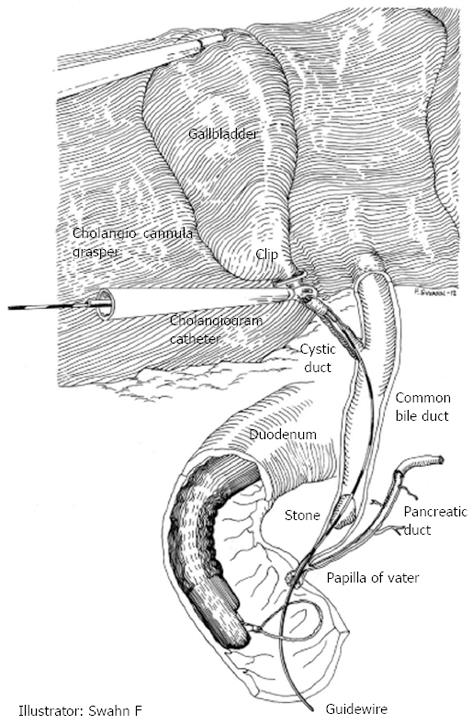
When cholangiography during laparoscopic cholecystectomy reveals CBDS, the endoscopist is called to the operating room. While waiting for the endoscopist to arrive, the surgeon inserts a transcystic guide wire (Jagwire™ 450 cm × 0.0635 cm or 450 cm × 0.0889 cm, Boston Scientific Corporation, Natick, MA, United States) through the existing cholangiography catheter and advances the guide wire through the choledochus, papilla of Vater into the duodenum. The pneumoperitoneum is deflated to facilitate transoral introduction and positioning of the duodenoscope. For rendezvous cannulation, the guide wire is captured with a polypectomy snare and pulled gently through the working channel of the duodenoscope (Figure 1). When the guide wire is in place, a sphincterotome is introduced over it and the rendezvous cannulation can be completed when the sphincterotome enters the common bile duct. After sphincterotomy, any stones are extracted with retrieval balloons or baskets. The first sweeping is done in choledochus along the transcystic guide wire. Then the guide wire is extracted (with the balloon catheter positioned in choledochus) and repositioned in the intrahepatic ducts to allow clearance of possible remaining supracholedochal stones. If there is any suspicion that stone clearance may be incomplete, a biliary stent is inserted.
Conventional ERCP was performed with Olympus TJF-160R or TJF-160VR (Olympus Optical, Tokyo, Japan) and wire-guided cannulation (WGC) technique through a sphincterotome (Autotome™ RX 44 Cannulating Sphincterotome, Boston Scientific Corporation, Natick, MA, United States). The complexity of cannulation was rated subjectively by the endoscopist, based particularly on the difficulty of cannulation, the number of inadvertent pancreatic duct cannulations and contrast injections with pancreatic duct filling. If the cannulation required more than six attempts or precut technique, it was considered a difficult cannulation.
All procedures were performed by one of three senior endoscopists with 7-15 years’ experience of ERCP and with a present procedure rate of approximately 150-300 ERCP investigations per year. All patients were investigated under general anesthesia. Prophylactic antibiotics were administrated as a single intravenous dose of 4 g piperacillin and 0.5 g tazobactam (Tazocin®, Wyeth AB, Solna, Sweden) prior to all procedures. Cholangiography was performed by using Iohexol (Omnipaque®, GE Healthcare, Stockholm, Sweden) monomeric non-ionic contrast medium. Sphincterotomy was carried out with pulsating cutting and coagulation diathermy system (ERBE, Elektromedizin, Tübingen, Germany).
Blood samples were collected in ice-cold EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) tubes immediately prior to surgery or endoscopy (0-sample) and sampling repeated at 4 ± 1 h, 8 ± 2 h and 24 ± 4 h after laparoscopic cholecystectomy or ERCP. Plasma was obtained after centrifugation at 2200 r/min for 10 min and then frozen and stored at -70 °C until further analysis.
ProCAPB B and trypsinogen-2 levels in plasma were determined in-house with a double-antibody enzyme linked immunosorbent assay developed at the Department of Surgery, Clinical Sciences, Skåne University Hospital, Malmö[17,19]. Pancreatic amylase was measured by an enzymatic colourimetric modular analyser with the manufacturer’s reagents (Roche, Diagnostics Gmbh, Mannheim, Germany) at the Department of Clinical Chemistry at Karolinska University Hospital in Huddinge, accredited by the Swedish Board for Accreditation and Conformity Assessment. All samples were blinded at analysis.
This study was conducted with the approval of the Regional Research Ethics Committee of Stockholm, Sweden.
Power calculations assumed a pancreatic enzyme reaction rate of 14% with the use of the conventional ERCP cannulation technique. Assuming a reduction in pancreatic reaction rate to 1% in the rendezvous group and 1% in the control group, 40 patients in each study arm were required to determine this difference with a 95% probability and with a 75% power (χ2 test of equal proportions). The variables pancreatic amylase, proCAPB and trypsinogen-2 were analysed using a mixed linear model with one between-group factor i.e., conventional ERCP, rendezvous ERCP and control group and one within-group factor, time (0, 4, 8 and 24 h) and the subsequent interaction between the factors. In case of significant interactions, simple main effect tests were performed, i.e., effects of one factor when the level of the other factor was fixed. Results are presented as mean, SD and 95% CIs. The distribution of some variables (e.g., proCAPB, trypsinogen-2, pancreatic amylase) was positively skewed and in these cases the variables were log-transformed before the formal analyses. The binomial response was subsequently analysed by fitting a generalised estimating equations model with the Genmod procedure in SAS® System 9.1, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, United States. These latter parameters are presented as OR and 95%CI. P-values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
A total of 139 patients (41 men and 98 women) with a median age of 54 years were enrolled into the study. During the inclusion period 17 patients were excluded due to: acute pancreatitis immediately prior to ERCP (n = 3), conversion of the operation from laparoscopic to open cholecystectomy (n = 6), tumour (n=4), and retraction of informed consent (n = 4), leaving 122 participants for further analyses. Relevant preoperative demographic characteristics (Table 2) did not differ between the three study groups in terms of gender, BMI, physical status according to ASA-classification, baseline laboratory values for CRP, pancreatic amylase, proCAPB and trypsinogen-2. However, there was a difference in age, with the conventional ERCP group being somewhat older. In addition, there was an expected difference between the control group and the other two groups regarding bile duct width, alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin levels but no significant difference between the rendezvous and conventional ERCP group.
| Group | CV ERCP (n = 41) | RV ERCP (n = 40) | LC control2 (n = 41) | P value |
| Female | 24 (59) | 31 (77) | 33 (80) | 0.06 |
| Age, (yr) | 64 ± 14 | 47 ± 16 | 50 ± 15 | 0.003 |
| Body mass index | 29 ± 8.1 | 27 ± 5.9 | 27 ± 4.9 | 0.21 |
| Physical status, ASA-score | 0.33 | |||
| Grade 1 | 12 (29) | 20 (50) | 20 (49) | |
| Grade 2 | 23 (56) | 16 (40) | 16 (39) | |
| Grade 3 | 6 (15) | 4 (10) | 5 (12) | |
| Laboratory values, median (25th-75th) | ||||
| Bilirubin, < 26 mmol/L | 28.0 (9.0-97.5) | 29.0 (10.0-81.0) | 9.0 (7.0-16.0) | 1.001 |
| Alkaline phosphatase, < 1.9 μcat/L | 3.9 (2.2-5.8) | 2.4 (1.6-4.4) | 1.8 (1.1-2.8) | 0.601 |
| C-reactive protein, < 10 mg/L | 5.0 (5.0-14.0) | 5.0 (5.0-5.0) | 5.0 (5.0-5.0) | 0.541 |
| Pancreatic amylase, 0.15-1.10 μcat/L | 0.4 (0.3-0.7) | 0.4 (0.3-0.5) | 0.4 (0.3-0.6) | 0.561 |
| Procarboxypeptidase B, nmol/L | 7.9 (5.4-16.3) | 5.4 (3.5-7.4) | 5.3 (3.0-9.5) | 0.871 |
| Trypsinogen-2, 30-110 μg/L | 126.0 (83.0-208.4) | 118.0 (86.3-132.6) | 88.5 (68.6-142.3) | 0.391 |
PEP emerged in three (7%) of the 41 patients cannulated with conventional ERCP, vs none of those cannulated by use of rendezvous technique (P = 0.24) (Table 3). According to the Cotton criteria[20], one of these cases was classified as moderate and two as mild. Cannulation of the biliary duct was scored as difficult in nine (22%) cases where conventional ERCP was used, and precut sphincterotomy was performed in six of these (15%). There were three (7%) cases of unsuccessful cannulation and these failures were not associated with juxtapapillary diverticula or other duodenal abnormalities. Contrast medium was inadvertently infused into the main pancreatic duct in 11 (27%) of the patients in the conventional ERCP group. In the rendezvous ERCP group, transcystic antegrade biliary rendezvous cannulation was successful in all 40 cases and no unintentional cannulation or opacification of the pancreatic duct occurred.
| Group | CV ERCP (n = 41) | RV ERCP (n = 40) | LC control1 (n = 41) | P-value |
| Difficult cannulation, > 6 attempts | 9 (22) | 0 (0) | NA | 0.002a |
| Precut techniques | 6 (15) | 0 (0) | NA | 0.03a |
| Cannulation failure | 3 (7) | 0 (0) | NA | 0.24 |
| Pancreatic cannulation | 13 (32) | 0 (0) | NA | < 0.001a |
| Pancreatic duct opacification | 11 (27) | 0 (0) | NA | 0.001a |
| Stone clearance at index procedure | 33 (81) | 38 (95) | NA | 0.01a |
| Stone size | 6.4 ± 5.1 | 5.5 ± 3.2 | NA | 0.40 |
| Median endoscopic procedure time, minutes (range) | 36 (10-80) | 28 (17-55) | NA | 0.11 |
| Post ERCP pancreatitis | 3 (7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.24 |
| Hyperamylasemia, > 3 fold rise above upper reference value, with or without post ERCP pancreatitis | 6 (15) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.03a |
| Pancreatic amylase (μcat/L), 4 h | 2.0 ± 4.2 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 0.0015a |
| Pancreatic amylase (μcat/L), 8 h | 3.5 ± 9.0 | 0.6 ± 0.3 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 0.03a |
| Pancreatic amylase (μcat/L), 24 h | 2.4 ± 6.0 | 0.6 ± 0.3 | 0.4 ± 0.2 | 0.056 |
| Procarboxypeptidase B (nmol/L), 4 h | 90.7 ± 237.7 | 7.2 ± 8.1 | 6.5 ± 9.3 | < 0.0001a |
| Procarboxypeptidase B (nmol/L), 8 h | 111.7 ± 287.3 | 7.9 ± 7.9 | 8.0 ± 18.4 | < 0.0001a |
| Procarboxypeptidase B (nmol/L), 24 h | 47.4 ± 131.7 | 8.5 ± 7.9 | 8.2 ± 9.2 | < 0.0001a |
| Trypsinogen-2 (μg/L) 24 h | 317.8 ± 547.1 | 145.6 ± 67.2 | 134.0 ± 80.2 | 0.03a |
Complete CBDS clearance at the index procedure was achieved in 38 (95%) of the rendezvous ERCP procedures vs 29 (71%) patients in the conventional ERCP group (P = 0.01), even though there was no significant difference in stone size (P = 0.40) or procedure time (P = 0.11) between the two study groups. After an additional ERCP, all patients, including the three whose initial cannulation failed, had their bile ducts cleared of stones.
In the 41 control patients, no case of pancreatic duct opacification during cholangiography was noted, nor was acute pancreatitis or hyperamylasemia observed. Two major postoperative complications were recorded: one patient had postoperative intra-abdominal bleeding which did not need surgical intervention and one had postoperative bile leakage from the cystic duct, which was successfully treated by endoscopic placement of a temporary stent.
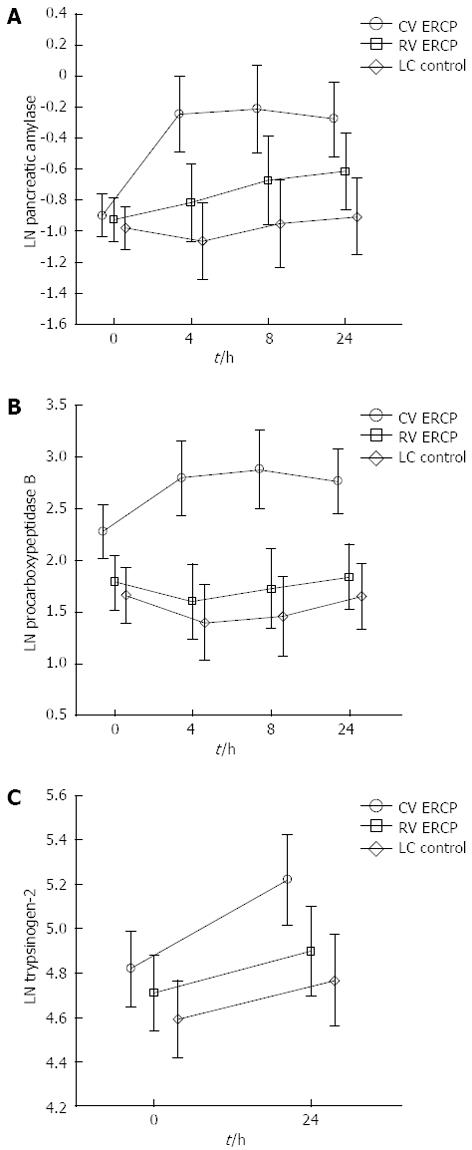
The post-procedural time course of pancreatic amylase showed no difference between the controls and the rendezvous ERCP group (Figure 2A). In those subjected to a conventional ERCP, amylase levels had already increased significantly at 4 h and remained elevated throughout the 24-h monitoring time. Virtually the same picture emerged concerning the plasma levels of proCAPB (Figure 2B). Plasma concentrations of trypsinogen-2 were also significantly increased at 24 h in patients subjected to a conventional ERCP (Figure 2C). CRP values rose as expected in the groups subjected to surgery (rendezvous and control group) at 24 h after the completion of the procedure.
We explored other possible confounders but were unable to demonstrate any relationship between these laboratory variables and procedure time, the number of cannulation attempts, age, gender, comorbidity, degree of CBD dilatation, number or size of CBDS or the need for precut cannulation techniques. However, if side branches of the pancreatic duct side had been filled with contrast medium, this was significantly associated with the plasma level of proCAPB (P = 0.009) and most likely pancreatic amylase (P = 0.051).
This study shows that transcystic guide wire assisted rendezvous cannulation at ERCP can be done in conjunction with bile duct stone clearance without increasing post-procedural leakage of pancreatic enzymes. This observation supports the hypothesis that rendezvous cannulation can prevent the risk of PEP. In fact, inadvertent contrast injection into the pancreatic duct during conventional ERCP was the factor most clearly associated with leakage of pancreatic enzymes into the systemic circulation, which we interpret as indicating risk of developing PEP.
The correlation between ERCP and PEP can be difficult to study, owing to the large number of patients required to ensure sufficient statistical power. In order to overcome these methodological difficulties, we utilised two biochemical markers, proCAPB and trypsinogen-2, as surrogate variables of pancreatic inflammatory response. These have both been shown to be superior to lipase and pancreatic amylase as diagnostic markers of acute pancreatitis, especially if the objective is to distinguish mild from severe pancreatitis[21,22]. ProCAPB and trypsinogen-2 have also been shown to discriminate pancreatitis from non-pancreatic disorders with an accuracy of 95% to 99%[19,21]. This distinction is essential, since two of our three study groups were subjected to additional surgical trauma in the form of laparoscopic cholecystectomy, which might increase unspecific inflammatory responses.
A potential weakness of the study is the lack of randomisation. Indeed, our original intention was to perform a randomised controlled trial. However, based on the promising results of our previous attempts with rendezvous ERCP[23], we considered it ethically indefensible to perform conventional ERCP intraoperatively. First, the operating theatre during ongoing surgery is poorly suited for conventional ERCP and endoscopy under suboptimal circumstances would expose the patient to an unnecessary risk of pancreatic injury. Second, a study design where patients are randomised to postoperative ERCP could increase the risk of cannulation failures that would necessitate additional surgical exploration of the common bile duct. Therefore we considered this alternative study design more appropriate to address our research question. The present case-control design opens for selection bias, e.g., in that patients selected for laparoscopic cholecystectomy with or without rendezvous ERCP were younger than those selected for conventional ERCP, of whom most had already their gallbladder removed, in some cases years earlier. However, this is to some degree counterbalanced by the fact that young age has repeatedly been found to be an independent risk factor for PEP[3,4,24,25] whereas older patients may be protected, e.g., by age-related pancreatic atrophy[26]. These factors would be more likely to underestimate than overestimate the associations we found.
We observed only three cases of the clinically relevant outcome, PEP, all in the group subjected to conventional ERCP group and none in the rendezvous group. This difference did not reach statistical significance, most likely due to low statistical power. Previous trials have proposed a relationship between rendezvous cannulation and a decreased risk of PEP but to date these studies have been either too small or not adequately designed to address this pertinent question. A recent systematic review by La Greca et al[10] concluded that intraoperative ERCP and bile duct clearance during laparoscopic cholecystectomy was associated with low risk of PEP and could be recommended. Scrutiny of the cited papers reveals that in cases involving complete transcystic bile duct cannulation, where the guide wire was brought into the duodenal lumen, the incidence of PEP was even lower, ranging from 1.7% to 2.2%[27,28]. This contrasts to studies in which cannulation was not complete, where the corresponding incidence of PEP ranged from 3% to 7.6%[29-32]. Our data confirm to these previous findings and highlight the relevance of completing the rendezvous guide wire based cannulation to minimise PEP.
In most conventional ERCP procedures, biliary cannulation is easy, completely uneventful and antegrade cannulation can be regarded as redundant. Our definition of difficult cannulation is arbitrary and subjective; however, even the most experienced endoscopist cannot predict whether a cannulation is going to be difficult or not until an attempt has been made, and each attempt at cannulation is potentially harmful. This is one of several arguments in favour of making rendezvous cannulation routine during laparoscopic cholecystectomy: regardless of the appearance of the papilla, the success rate of single-pass biliary cannulation approaches 100%. Repeat interventions, use of precut incision and so on should be kept to a minimum to diminish the risk of a variety of procedure-related complications.
Opacification of the pancreatic duct is another significant sign associated with difficult cannulation and the development of pancreatitis[3,8,24,25,33]. In our series, we found a significant correlation between elevated levels of amylase (P < 0.001) or proCAPB (P = 0.002) and inadvertent cannulation and injection of contrast material into the pancreatic duct. Moreover, all three of our patients who developed PEP had had contrast medium injected into the pancreatic duct. Clearly, many of the risks associated with difficult cannulation, inadvertent pancreatic duct cannulation and contrast injection can be circumvented with rendezvous cannulation.
Current clinical evidence suggests that the risk of pancreatitis can be reduced, at least among high-risk patients, by temporary placement of a pancreatic stent that dislodges spontaneously[34,35]. At the time we began our study there was no routine of using prophylactic pancreatic stents at our institution and we have therefore not offered this option during the study. Such stenting could clearly have affected the outcome for patients who were allocated to the conventional ERCP group and had a guidewire or minimal contrast injection into the pancreatic duct. Nonetheless, we firmly believe that it is preferable to use a technique that completely avoids cannulation of the pancreatic duct.
Transient asymptomatic hyperamylasemia has very little clinical significance and is usually not recognised as a complication. In the present study the levels of amylase after conventional ERCP were increased at 4, 8 and 24 h compared with levels in the rendezvous and the control group. These results are in line with other reports[36], where a majority of the ERCP procedures involving cannulations that were characterised as difficult were associated with hyperamylasemia and PEP.
A few prospective studies[16,18,37] demonstrate that patients affected by PEP have significantly elevated concentrations of trypsinogen-2 in urine six and 24 h after the index procedure, even in if the pancreatitis is mild. Our study confirms these findings: we found higher concentrations of trypsinogen-2 in plasma at 24 h in the conventional ERCP group than in the rendezvous and control groups. Taken together the surrogate markers we have used to detect early signs of PEP appear to be of high clinical relevance.
An additional advantage of the rendezvous approach, one of utmost clinical relevance, appeared when we analysed the CBDS clearance rate. Even though all stones were eventually cleared in both study groups, there was a significant advantage for the rendezvous technique during the index procedure. This finding is in line with the compilation of 21 reports by La Greca et al[10] which demonstrated an overall success rate of 92.3% for rendezvous ERCP.
In conclusion, combined laparo-endoscopic transcystic guidewire rendezvous cannulation of the CBD minimizes the risk of unintentional pancreatic duct engagement and subsequent inflammatory damage to the gland. In addition, more complete CBDS removal can be offered. Thus, intraoperative ERCP with rendezvous cannulation technique shall be recommended to manage CBDS in conjunction with cholecystectomy.
The authors wish to express their gratitude to deceased professor Anders Borgström for taking part of the initial planning of the study and Mrs. Anne-Marie Rohrstock for skilful laboratory technical assistance, both at the Department of Surgery, Malmö University Hospital. We also thank Mrs. Elisabeth Berg, LIME Karolinska Institutet, for the statistical analysis and to professor Margery K Herrington for linguistic support. Preliminary data has been presented in abstract form during poster session at the 19th United European Gastroenterology Week meeting (Endoscopy Suppl I, 2011; 43: P1140).
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) with sphincterotomy and stone extraction is a standard procedure in the management of common bile duct stones (CBDS). The method is, however, marred by complications like pancreatitis, bleeding and perforation. Intraoperative rendezvous ERCP during cholecystectomy with cannulation over a guidewire represents an alternative method to remove CBDS that theoretically may, due to a significantly reduced risk to cannulate the pancreatic duct, decrease the risk of procedural induced pancreatitis.
The concept of rendezvous cannulation involving a combined laparo-endoscopic approach and used in conjunction with intraoperative ERCP has been described previously. The question whether intraoperative rendezvous ERCP reduces the risk of post ERCP pancreatitis (PEP) rate or not is, however, not known mainly due to the fact that the incidence of PEP is rather low and large study groups are therefore needed in order to reach enough statistical power to investigate the impact of different ERCP techniques.
To overcome the methodological difficulties in studying the effects of intraoperative rendezvous ERCP on PEP the authors utilised two highly sensitive and specific biochemical markers, procarboxypeptidase B and trypsinogen-2, as surrogate variables of pancreatic inflammatory response. These have both been shown to be superior to lipase and pancreatic amylase as diagnostic markers of acute pancreatitis, especially if the objective is to distinguish mild from severe pancreatitis.
The study results have helped to obtain an increased knowledge of the beneficial effects that intraoperative rendezvous ERCP may have in reducing PEP. The proposed mechanism for this is that, due to cannulation over the guidewire, the risk of cannulating the pancreatic duct and thus injecting contrast in the duct is minimal.
ERCP: An endoscopic method to examine the bile- and pancreatic ducts as well as to, by intervention, remove, common bile duct stones or relieve bile duct obstruction. Pancreatic amylase, procarboxypeptidase B and trypsinogen-2: Biochemical markers that serve as surrogate variables of pancreatic inflammatory response.
The authors of this paper report that intraoperative rendezvous ERCP reduces the release of the pancreatic markers (pancreatic amylase, procarboxypeptidase B and trypsinogen-2) compared with conventional ERCP. As only a few papers have been published in this topic, this paper can provide additional data for the accumulation of the knowledge in this field. The case control design of the study, however, opens for selection bias which weakens the power of the conclusion.
P- Reviewers Al Mofleh IA, Li YY S- Editor Gou SX L- Editor A E- Editor Zhang DN
| 1. | Andriulli A, Loperfido S, Napolitano G, Niro G, Valvano MR, Spirito F, Pilotto A, Forlano R. Incidence rates of post-ERCP complications: a systematic survey of prospective studies. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:1781-1788. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 669] [Cited by in RCA: 772] [Article Influence: 42.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Bailey AA, Bourke MJ, Williams SJ, Walsh PR, Murray MA, Lee EY, Kwan V, Lynch PM. A prospective randomized trial of cannulation technique in ERCP: effects on technical success and post-ERCP pancreatitis. Endoscopy. 2008;40:296-301. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 153] [Cited by in RCA: 164] [Article Influence: 9.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Cheng CL, Sherman S, Watkins JL, Barnett J, Freeman M, Geenen J, Ryan M, Parker H, Frakes JT, Fogel EL. Risk factors for post-ERCP pancreatitis: a prospective multicenter study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:139-147. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 414] [Cited by in RCA: 434] [Article Influence: 22.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Christensen M, Matzen P, Schulze S, Rosenberg J. Complications of ERCP: a prospective study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;60:721-731. [PubMed] |
| 5. | Freeman ML, Nelson DB, Sherman S, Haber GB, Herman ME, Dorsher PJ, Moore JP, Fennerty MB, Ryan ME, Shaw MJ. Complications of endoscopic biliary sphincterotomy. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:909-918. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1716] [Cited by in RCA: 1689] [Article Influence: 58.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 6. | Cennamo V, Fuccio L, Zagari RM, Eusebi LH, Ceroni L, Laterza L, Fabbri C, Bazzoli F. Can a wire-guided cannulation technique increase bile duct cannulation rate and prevent post-ERCP pancreatitis?: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:2343-2350. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 110] [Cited by in RCA: 109] [Article Influence: 6.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Williams EJ, Taylor S, Fairclough P, Hamlyn A, Logan RF, Martin D, Riley SA, Veitch P, Wilkinson M, Williamson PJ. Are we meeting the standards set for endoscopy? Results of a large-scale prospective survey of endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatograph practice. Gut. 2007;56:821-829. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 160] [Cited by in RCA: 178] [Article Influence: 9.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Cheon YK, Cho KB, Watkins JL, McHenry L, Fogel EL, Sherman S, Lehman GA. Frequency and severity of post-ERCP pancreatitis correlated with extent of pancreatic ductal opacification. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;65:385-393. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 102] [Cited by in RCA: 100] [Article Influence: 5.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Deslandres E, Gagner M, Pomp A, Rheault M, Leduc R, Clermont R, Gratton J, Bernard EJ. Intraoperative endoscopic sphincterotomy for common bile duct stones during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1993;39:54-58. [PubMed] |
| 10. | La Greca G, Barbagallo F, Sofia M, Latteri S, Russello D. Simultaneous laparoendoscopic rendezvous for the treatment of cholecystocholedocholithiasis. Surg Endosc. 2010;24:769-780. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 34] [Cited by in RCA: 42] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Skude G, Wehlin L, Maruyama T, Ariyama J. Hyperamylasaemia after duodenoscopy and retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Gut. 1976;17:127-132. [PubMed] |
| 12. | Gottlieb K, Sherman S, Pezzi J, Esber E, Lehman GA. Early recognition of post-ERCP pancreatitis by clinical assessment and serum pancreatic enzymes. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996;91:1553-1557. [PubMed] |
| 13. | LaFerla G, Gordon S, Archibald M, Murray WR. Hyperamylasaemia and acute pancreatitis following endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Pancreas. 1986;1:160-163. [PubMed] |
| 14. | Testoni PA, Bagnolo F. Pain at 24 hours associated with amylase levels greater than 5 times the upper normal limit as the most reliable indicator of post-ERCP pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;53:33-39. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Testoni PA, Bagnolo F, Caporuscio S, Lella F. Serum amylase measured four hours after endoscopic sphincterotomy is a reliable predictor of postprocedure pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94:1235-1241. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 34] [Cited by in RCA: 37] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Kemppainen E, Hedström J, Puolakkainen P, Halttunen J, Sainio V, Haapiainen R, Stenman UH. Urinary trypsinogen-2 test strip in detecting ERCP-induced pancreatitis. Endoscopy. 1997;29:247-251. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Kimland M, Russick C, Marks WH, Borgström A. Immunoreactive anionic and cationic trypsin in human serum. Clin Chim Acta. 1989;184:31-46. [PubMed] |
| 18. | Kobayashi K, Sasaki T, Serikawa M, Inoue M, Itsuki H, Chayama K. Assessment of trypsinogen-2 levels as an early diagnostic for post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2011;40:1206-1210. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Müller CA, Appelros S, Uhl W, Büchler MW, Borgström A. Serum levels of procarboxypeptidase B and its activation peptide in patients with acute pancreatitis and non-pancreatic diseases. Gut. 2002;51:229-235. [PubMed] |
| 20. | Cotton PB, Lehman G, Vennes J, Geenen JE, Russell RC, Meyers WC, Liguory C, Nickl N. Endoscopic sphincterotomy complications and their management: an attempt at consensus. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991;37:383-393. [PubMed] |
| 21. | Hedström J, Kemppainen E, Andersén J, Jokela H, Puolakkainen P, Stenman UH. A comparison of serum trypsinogen-2 and trypsin-2-alpha1-antitrypsin complex with lipase and amylase in the diagnosis and assessment of severity in the early phase of acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:424-430. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Kylänpää-Bäck ML, Repo H, Kemppainen E. New laboratory tests in acute pancreatitis. Addict Biol. 2002;7:181-190. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Enochsson L, Lindberg B, Swahn F, Arnelo U. Intraoperative endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) to remove common bile duct stones during routine laparoscopic cholecystectomy does not prolong hospitalization: a 2-year experience. Surg Endosc. 2004;18:367-371. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 76] [Cited by in RCA: 72] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Freeman ML, DiSario JA, Nelson DB, Fennerty MB, Lee JG, Bjorkman DJ, Overby CS, Aas J, Ryan ME, Bochna GS. Risk factors for post-ERCP pancreatitis: a prospective, multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;54:425-434. [PubMed] |
| 25. | Loperfido S, Angelini G, Benedetti G, Chilovi F, Costan F, De Berardinis F, De Bernardin M, Ederle A, Fina P, Fratton A. Major early complications from diagnostic and therapeutic ERCP: a prospective multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998;48:1-10. [PubMed] |
| 26. | Laugier R, Bernard JP, Berthezene P, Dupuy P. Changes in pancreatic exocrine secretion with age: pancreatic exocrine secretion does decrease in the elderly. Digestion. 1991;50:202-211. [PubMed] |
| 27. | Morino M, Baracchi F, Miglietta C, Furlan N, Ragona R, Garbarini A. Preoperative endoscopic sphincterotomy versus laparoendoscopic rendezvous in patients with gallbladder and bile duct stones. Ann Surg. 2006;244:889-893; discussion 893-896. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 109] [Cited by in RCA: 119] [Article Influence: 6.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Rábago LR, Vicente C, Soler F, Delgado M, Moral I, Guerra I, Castro JL, Quintanilla E, Romeo J, Llorente R. Two-stage treatment with preoperative endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) compared with single-stage treatment with intraoperative ERCP for patients with symptomatic cholelithiasis with possible choledocholithiasis. Endoscopy. 2006;38:779-786. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 90] [Cited by in RCA: 88] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Cemachovic I, Letard JC, Begin GF, Rousseau D, Nivet JM. Intraoperative endoscopic sphincterotomy is a reasonable option for complete single-stage minimally invasive biliary stones treatment: short-term experience with 57 patients. Endoscopy. 2000;32:956-962. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Hong DF, Xin Y, Chen DW. Comparison of laparoscopic cholecystectomy combined with intraoperative endoscopic sphincterotomy and laparoscopic exploration of the common bile duct for cholecystocholedocholithiasis. Surg Endosc. 2006;20:424-427. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 67] [Cited by in RCA: 69] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Meyer C, Le JV, Rohr S, Duclos B, Reimund JM, Baumann R. Management of common bile duct stones in a single operation combining laparoscopic cholecystectomy and peroperative endoscopic sphincterotomy. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2002;9:196-200. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Wei Q, Wang JG, Li LB, Li JD. Management of choledocholithiasis: comparison between laparoscopic common bile duct exploration and intraoperative endoscopic sphincterotomy. World J Gastroenterol. 2003;9:2856-2858. [PubMed] |
| 33. | Cotton PB, Garrow DA, Gallagher J, Romagnuolo J. Risk factors for complications after ERCP: a multivariate analysis of 11,497 procedures over 12 years. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;70:80-88. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 449] [Cited by in RCA: 468] [Article Influence: 29.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Choudhary A, Bechtold ML, Arif M, Szary NM, Puli SR, Othman MO, Pais WP, Antillon MR, Roy PK. Pancreatic stents for prophylaxis against post-ERCP pancreatitis: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73:275-282. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 212] [Cited by in RCA: 183] [Article Influence: 13.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 35. | Sofuni A, Maguchi H, Mukai T, Kawakami H, Irisawa A, Kubota K, Okaniwa S, Kikuyama M, Kutsumi H, Hanada K. Endoscopic pancreatic duct stents reduce the incidence of post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis in high-risk patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;9:851-858; quiz e110. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 104] [Cited by in RCA: 113] [Article Influence: 8.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | La Greca G, Barbagallo F, Di Blasi M, Chisari A, Lombardo R, Bonaccorso R, Latteri S, Di Stefano A, Russello D. Laparo-endoscopic “Rendezvous” to treat cholecysto-choledocolithiasis: Effective, safe and simplifies the endoscopist’s work. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:2844-2850. [PubMed] |