INTRODUCTION
Limb ischemia-reperfusion (LIR) injury has been observed in atherosclerosis, thrombosis or injury to the great vessels in the extremities, severe crushing injury and surgery[1-3]. It can lead to limb edema, skeletal muscle dysfunction, and necrosis, and may further result in the dysfunction and structural damage to other organs such as the heart, lungs, brain, small intestines, and so on[4,5]. Therefore, protection against ischemia-reperfusion injury has become an important focus of research in clinical work.
In recent years, many narcotics have been used to reduce the damage caused by ischemia-reperfusion[6-8]. The new anti-cholinergic drug penehyclidine hydrochloride (PHC), reported to have protective effects against organ injury[9-11], was developed by the Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology in China (Academy of Military Medical Sciences) to minimise side effects harmful to the cardiovascular system[12,13]. To date, no reports on the protective effects of PHC against LIR in the small intestines have been published. In this study, the serum and small intestinal tissue diamine oxidase (DAO), plasma endotoxin (reflecting the barrier function of the small intestinal mucosa), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity of the small intestinal tissue, as well as serum tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin (IL)-10 levels (reflecting damage to the small intestine) were examined in rats.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Experimental animals
One hundred and eight healthy 6-mo-old male Wistar rats weighing 220-250 g were provided by the Medical Experimental Animal Center of the Gansu College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China. The rats were randomly divided into 3 groups: the sham-operation group (group S), limb ischemia-reperfusion group (group LIR), and penehyclidine hydrochloride post-conditioning group (group PHC). Each group was divided into subgroups (n = 6 in each group) according to ischemic-reperfusion time, i.e. immediately (T1), 1 h (T2), 3 h (T3), 6 h (T4), 12 h (T5), and 24 h (T6).
Animal model
The LIR model was established as follows: the rats were fasted 12 h preoperatively with unlimited drinking water; and exposed to 2% isoflurane until the loss of righting reflex, and fixed onto a sit-board on the operating table. The posterior limbs of the rats were ligated with elastic rubber bands above the greater trochanter to completely block the blood flow. Group S was anesthetized, but did not undergo ligation. Group LIR was ligated until complete ischemia of the lower limbs, and released after 3 h to restore blood flow to the posterior limbs; reperfusion was conducted for 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 h. In group PHC, the rubber band was released after 3 h of ischemia, and then 0.15 mg/kg PHC was injected into the tail veins, followed by reperfusion for 1, 3, 6, 12 and 24 h. After the reperfusion at pre-set time points (T1-T6), the rats were sacrificed under deep isoflurane anaesthesia. All experiments were conducted according to the protocols approved by the Lanzhou University Animal Care and Use Committee. About 5 mL of blood was drawn from the inferior vena cava of the rats. The blood was centrifuged at 3000 r/min for 15 min to separate the serum, which was stored at -20°C for further target detection. The small intestines of the rats were quickly removed up to 5 cm from the ileocecal valve and washed three times with normal saline. Then, 0.5 g of the small intestines were ground into tissue homogenate in a glass homogeniser; after centrifugation at 3500 r/min for 20 min, the resultant supernatant was diluted into a 10% solution with normal saline and stored at -20°C for further target detection. The remaining small intestines were fixed in 10% formalin, embedded in paraffin, stained with hematoxylin and eosin, sectioned, and observed for pathological changes under optical microscope.
Evaluation of changes in the barrier function of the small intestinal mucosa
The rat small intestinal tissue and serum DAO were detected using a spectrophotometer with an automatic biochemical analyser (OLYMPUS-AU5400; kit provided by the Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, China). Plasma endotoxin was measured using a quantitative chromogenic substrate assay (Xiamen TAL Experimental Plant Co., Ltd.).
Evaluation of damage mechanism in the small intestine
SOD and MPO activities in the rat small intestinal tissue were measured by colorimetry (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute). Serum TNF-α and IL-10 were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Wuhan Boster Biological Technology, Ltd., China).
Statistical analysis
All data were reported as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined by one-way analysis of variance using SPSS version 17.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
RESULTS
Rat small intestinal pathological changes
The small intestinal microstructure of the group S rats were normal: the villi were lined with normal epithelial cells, the interstitium was congestion-free, and gland morphology was normal. The small intestinal tissue of the group LIR rats had obvious pathological changes: the villi were malpositioned, atrophied, and shorter and thicker; loose interstitial edema with lymphocytic infiltration was observed, and lymph node follicles and submucosal lymphatic vessels were filled with lymphocytes. The small intestinal microstructure of the group PHC had certain pathologic changes that were less pronounced than in the group LIR.
Changes in the barrier function of the small intestinal mucosa
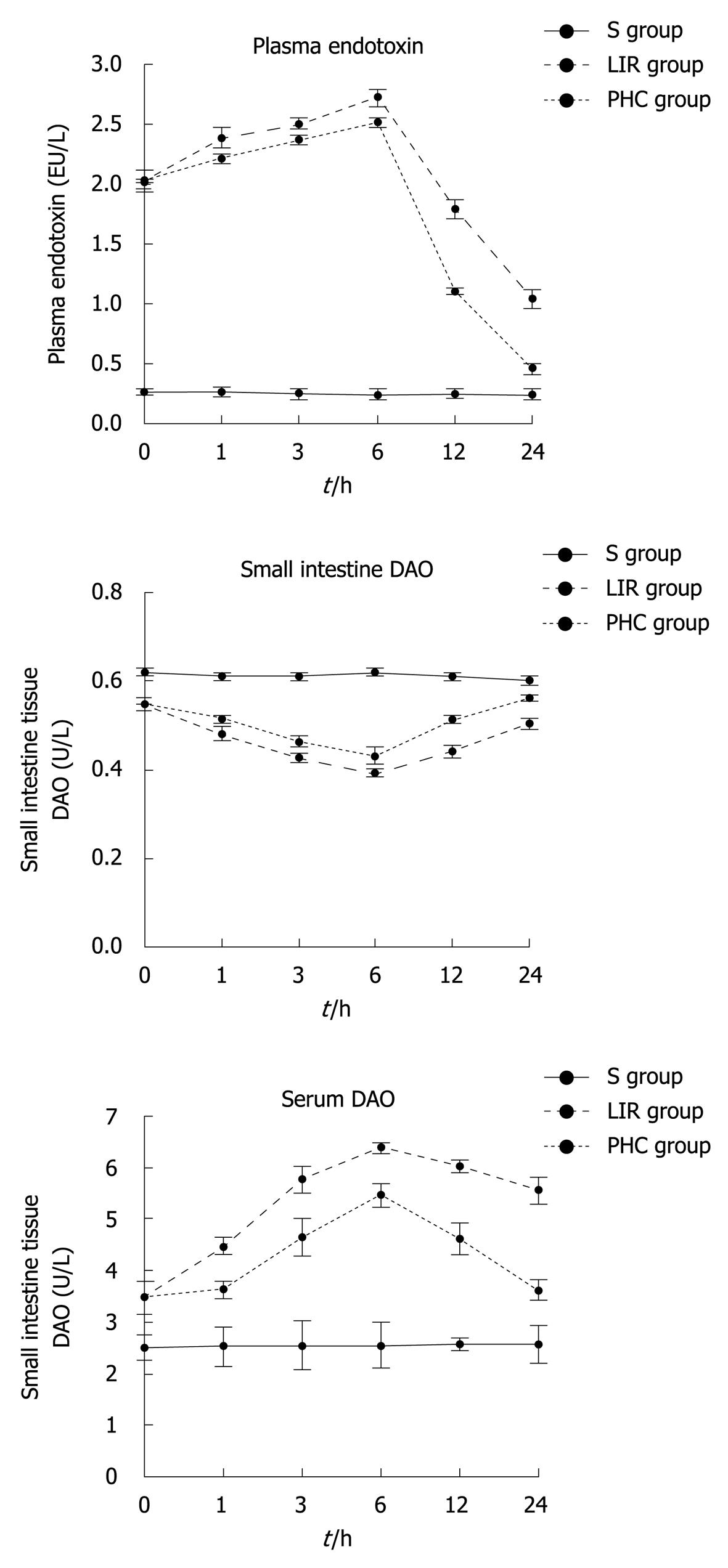
DAO is an enzyme synthesised primarily in gastrointestinal mucosal cells. The intestinal tissue and serum levels of DAO have been used as an indicator of the integrity and functional mass of the intestinal mucosa[14,15]. When intestinal mucosal integrity was disrupted during shock, burns, abdominal aortic surgery, liver disease, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and so on, an increase in intestinal permeability and translocation of bacteria endotoxin, and plasma endotoxin as well, was observed[16,17]. In the groups LIR and PHC, serum DAO and plasma endotoxin levels at all preset time-points of reperfusion (T1-T6) increased compared with the group S (P < 0.05), whereas the tissue DAO content decreased (P < 0.05). Compared with the T2-T6 of group LIR, the tissue DAO activity of group PHC increased (P < 0.05), whereas the serum DAO activity and plasma endotoxin concentration were decreased (P < 0.05). The tissue and serum DAO activity and plasma endotoxin concentration reached its peak (P < 0.05) (Figure 1) compared with other preset time-points of reperfusion at T4 in the groups LIR and PHC.
Figure 1 Changes of intestinal tissue diamine oxidase, serum diamine oxidase and plasma endotoxin in rats.
S group: Sham-operation group; LIR group: Lower limb ischemia-reperfusion group; PHC group: Penehyclidine hydrochloride post-conditioning group. DAO: Diamine oxidase.
Changes of certain factors in damage mechanism in the small intestine
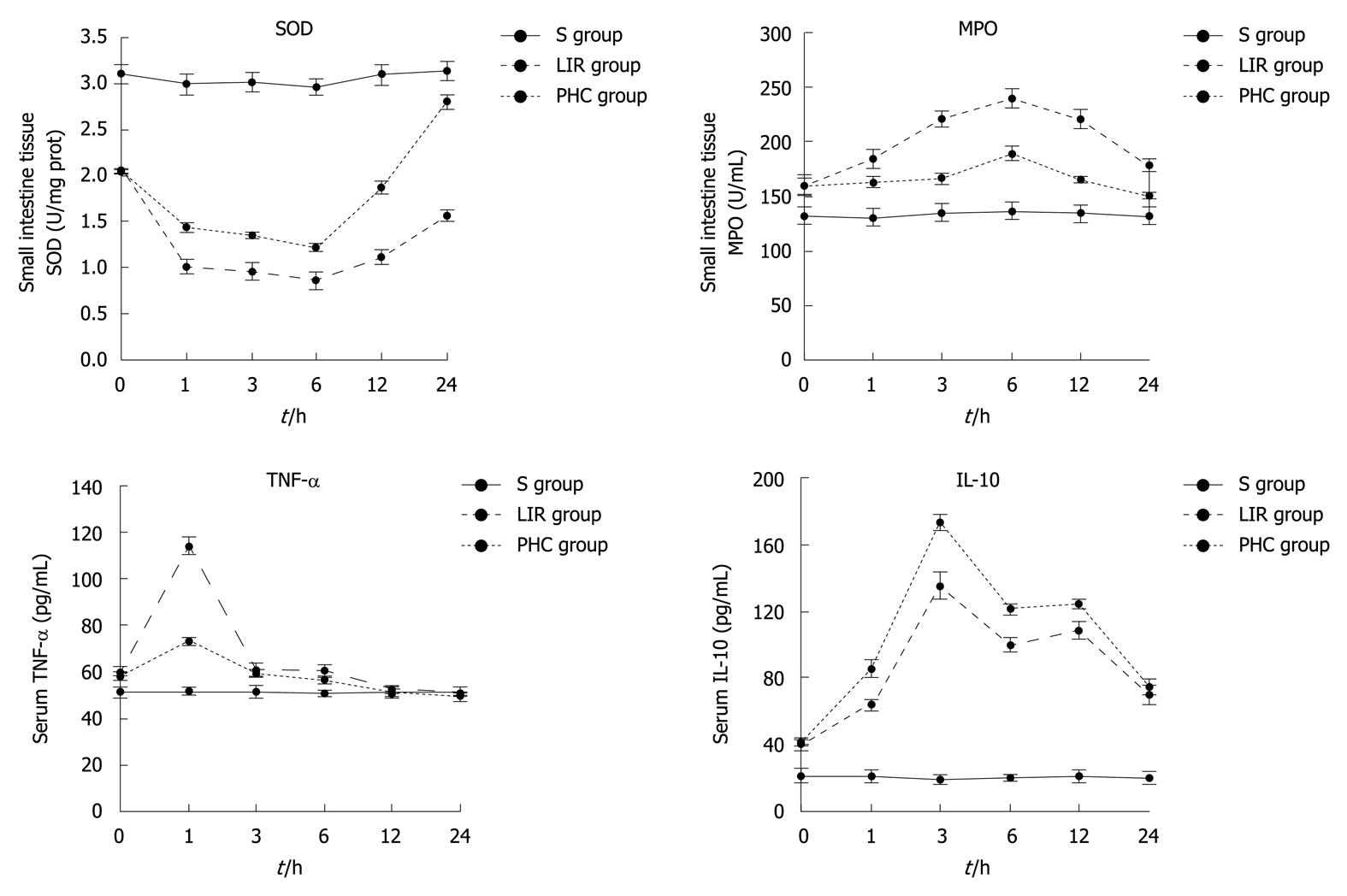
In the groups LIR and PHC, the MPO activity of the small intestinal tissue and serum IL-10 at T1-T6, and serum TNF-α at T1-T4 were higher than those in the group S (P < 0.05), whereas the tissue SOD activity at T1-T6 was lower (P < 0.05). In group PHC, the tissue SOD activity at T2-T6 and serum IL-10 at T2-T5 were significantly higher than those in group LIR (P < 0.05); however, the tissue MPO activity at T2-T6 and serum TNF-α at T2 and T4 decreased (P < 0.05). In the groups LIR and PHC, the tissue SOD and MPO activities reached their peak at T4 (P < 0.05) while TNF-α reached its peak at T2 (P < 0.05). Thereafter, TNF-α gradually decreased, and even decreased at T5 and T6 in group S (P≥ 0.05); IL-10 at T3 exhibited the highest concentration (P < 0.05) even at T4-T5, and the serum IL-10 also maintained a relatively high concentration (Figure 2).
Figure 2 Changes of intestinal tissue superoxide dismutase, intestinal tissue myeloperoxidase, serum tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-10 in rats.
S group: Sham-operation group; LIR group: Lower limb ischemia-reperfusion group; PHC group: Penehyclidine hydrochloride post-conditioning group. SOD: Superoxide dismutase; MPO: Myeloperoxidase; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-10: Interleukin-10.
DISCUSSION
The gastrointestinal tract in ischemia-reperfusion injury is of interest, not only because its functions are damaged, but also it is a potential factor of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) associated with reperfusion injury[18,19]. When the intestinal barrier is injured, the gut endotoxins may enter into the extraintestinal tissues and produce free radicals and cytokines that potentiate the development of MODS[20-22]. In the group LIR, at different reperfusion time points, the small intestinal mucosa had varying degrees of injury, including neutrophil and lymphocyte infiltration, as well as small intestinal epithelial cell degeneration, necrosis, or even sloughing off. This result shows that LIR injury induces injury to the small intestinal mucosa. Meanwhile, the small intestinal tissue DAO activity in the group LIR was lower than in the group S; however, the activity of serum DAO and the plasma endotoxin were significantly higher than in the group S, indicating that the mucous membrane barrier of the rat small intestines was destroyed and gut permeability changed, leading to the absorption of gut cavity endotoxin and small intestinal tissue DAO into the blood stream.
LIR injury leading to permeability changes in intestinal mucosal reperfusion injury may be closely related to the production of excessive oxygen free radicals and inflammatory cytokines[19,20,23,24]. Oxygenated free radicals appear to play a prominent role in mediating the damage associated with gastrointestinal diseases. The production of reactive oxygen metabolites in ischemia-reperfusion involves oxidases found in resident phagocytic cells, as well as microvascular and mucosal epithelial cells[25]. SOD is a key enzyme that eliminates free radicals by converting superoxide anions into hydrogen peroxide, which is then removed by glutathione peroxidase and catalase. A high amount of oxygen free radicals is generated during ischemia followed by reperfusion, which leads to excessive consumption of SOD[26]. MPO, on the other hand, is released upon activation to catalyse the formation of oxidants, which can lead to tissue damage during chronic inflammation, and serves as a major enzymatic catalyst of lipid peroxidation at inflammation sites[27]. In this paper, the small intestinal tissue SOD activity of the group LIR during reperfusion was lower than that of the group S, but higher than that of MPO. This shows that an increase in oxygen free radicals and lipid peroxidation occurs, resulting in changes in the pathophysiology of the small intestinal mucosa, causing mucosal epithelial damage, edema, and activation of inflammatory immune cells.
Ischemia and reperfusion injury are associated with the coordinated activation of a series of cytokines and adhesion molecules[27-29]. When the intestinal damage releases a large amount of inflammatory cytokines, including rapidly produced TNF-α, inflammatory cells accumulate and intestinal inflammatory damage occurs. IL-10 modulates pro-inflammatory cytokine production and tissue injury following ischemia-reperfusion injury[30]. A study showed that the exogenous administration of IL-10 reduced the systemic inflammatory response in a rodent model of intestinal reperfusion injury, an effect associated with the inhibition of cytokine production and neutrophil accumulation[31]. Being anti-inflammatory, the release of IL-10 can modulate pro-inflammatory cytokine production and reperfusion-associated tissue injuries[32]. This experiment also suggested that IL-10 may inhibit the role of TNF-α.
PHC mainly blocks muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, which shows a wide range of biological activities, including antioxidation, cytoprotective activity, and so on. PHC can inhibit lung vascular leak, inflammation and p38MAPK activation, signalling a potential role in lipopolysaccharide and alleviation of lung injuries by inhibiting apoptosis in lung tissue cells[9]. Wang et al[10] found that PHC attenuated the acute lung injury induced by endotoxin involving the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathway. The inhibition of NF-κB activation in intestinal epithelial cells prevented the increase in systemic TNF-α concentrations after intestinal ischemia and reperfusion[33]. In this study, PHC post-conditioning significantly reduced the pathological damage to the small intestine with lower limb ischemia-reperfusion injury. Although this damage was inevitable, the small intestinal injury in the group PHC was less severe than that in the group LIR. PHC post-conditioning increased SOD activity and reduced MPO activity, thereby reducing oxygen free radicals to diminish tissue damage. PHC post-conditioning can effectively lower the blood levels of DAO, endotoxin and TNF-α, which disrupt the effects of the organisation. PHC post-conditioning can also promote the production of anti-inflammatory factor IL-10, which inhibits TNF-α and reduces inflammatory cell accumulation in the local organization.
In conclusion, PHC post-conditioning can improve small intestinal mucosal injury induced by lower limb ischemia-reperfusion. It increases SOD activity to scavenge oxygen free radicals, reduces the production of inflammatory cytokine TNF-α, and increases the production of anti-inflammatory factor IL-10. The protective action of PHC post-conditioning on ischemia-reperfusion injury may be controlled by various mechanisms, which should be explored by further investigations.
COMMENTS
Background
Limb ischemia-reperfusion (LIR) injury can not only lead to damage of limb itself and other organs such as the heart, lungs, brain, small intestines and so on, but also may further trigger a systemic inflammatory response and multiple organ dysfunction mainly induced by dysfunction and structural damage of intestines. Penehyclidine hydrochloride (PHC) is a new anticholinergic drug with antimuscarinic, antinicotinic activities, retained potent central and peripheral anticholinergic activities. Although PHC has protective effects against septic shock and organ injury, the effects of PHC post-conditioning against LIR in the damage of the small intestines remains unknown.
Research frontiers
Damage of the gastrointestinal tract in ischaemia-reperfusion injury is of interest because it functions not only as a target organ but also as a potential effecter of the multiple organ dysfunction associated with reperfusion injury. The authors used PHC post-conditioning to protect the damage to the barrier function of the small intestinal mucosa caused by LIR injury, because PHC post-conditioning can significantly inhibit the production of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), suppress excessive expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase, counteract lipid peroxidation and increase superoxide dismutase (SOD) level.
Innovations and breakthroughs
The authors aimed to investigate the protective effect of PHC post-conditioning in the damage to the barrier dysfunction of the small intestine caused by LIR injury. The results indicate that PHC post-conditioning may reduce the permeability of the small intestines after LIR. Its protection mechanisms may be related to inhibiting oxygen free radicals and inflammatory cytokines for organ damage.
Applications
Although additional studies are necessary to confirm this effect in humans, the authors found the protective effect of PHC in the clinical management of patients with limb ischemia-reperfusion. PHC used in surgical operation might reduce the damage of small intestine from limb ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Terminology
PHC is a new anti-cholinergic drug, selectively blocking M1, M3 receptors and N receptor. Compared with other anticholinergics, the notable advantage of PHC is that it does not accelerate heart rate, and it can improve microcirculation, inhibit lipid peroxidation, attenuate the release of lysome, and depress microvascular permeability.
Peer review
This manuscript demonstrated that PHC post-conditioning can improve small intestinal mucosal injury induced by lower limb ischemia-reperfusion. It increases SOD activity to scavenge oxygen free radicals, reduces the production of inflammatory cytokine TNF-α, and increases the production of anti-inflammatory factor interleukin-10.