Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2010; 16(23): 2851-2866
Published online Jun 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i23.2851
Published online Jun 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i23.2851
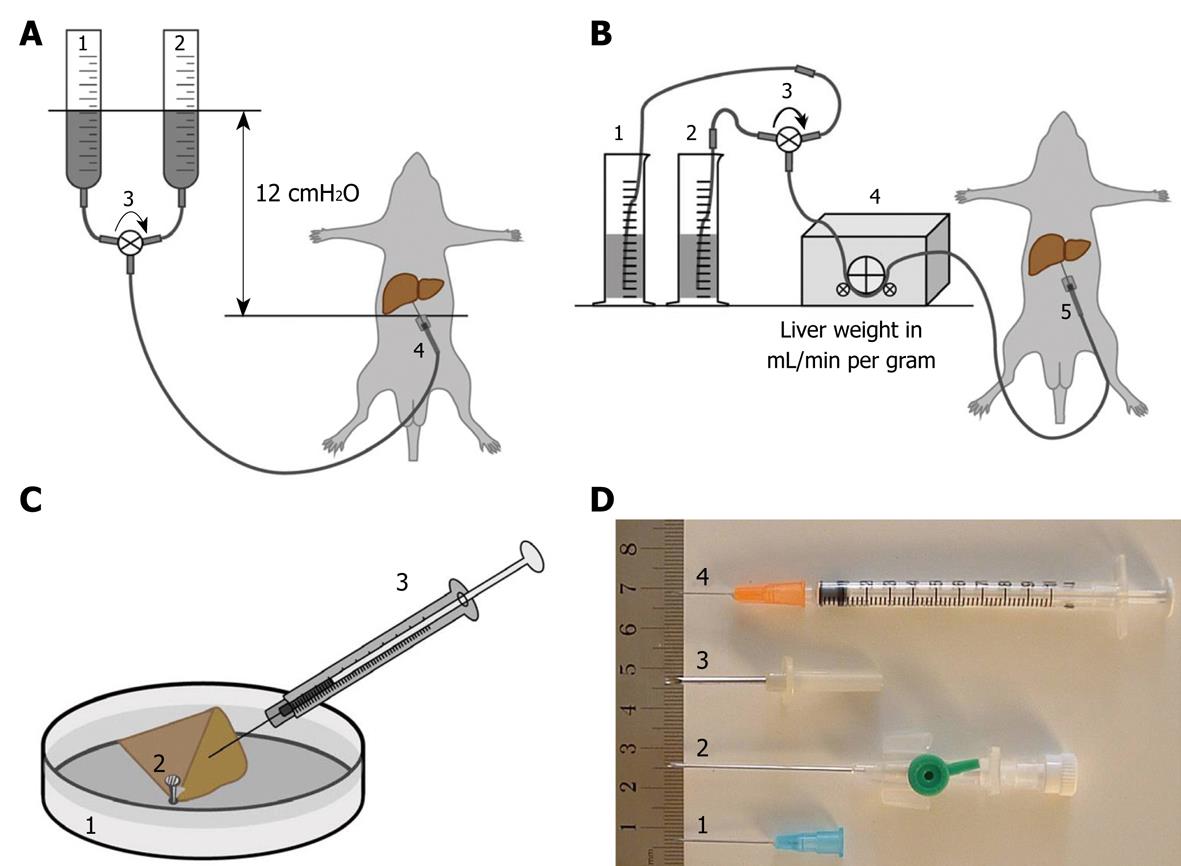
Figure 1 Diagram schematically depicting the different and most frequently used perfusion-fixation methods, including perfusion-fixation needles, to fix hepatic tissue.
A: Gravity-mediated perfusion fixation using 12 cm water pressure: (1) pre-perfusion buffer; (2) fixative solution; (3) tri-valve system (e.g. Discofix® C, B. Braun, Switzerland) that facilitates the change-over between both solutions; and (4) cannulation of the portal vein; B: Roller pump-mediated perfusion fixation at a flow of 1 mL/g liver tissue: (1) pre-perfusion buffer; (2) fixative solution; (3) tri-valve system; (4) low-flow peristaltic pump; and (5) cannulation of the portal vein; C: Injection or puncture perfusion fixation, using a needle to inject fixative into a wedge biopsy of about 1 cm × 1 cm × 1 cm dimensions. Injection to approach a rate of 1 mL/min: (1) Petri dish filled with 37°C physiological saline solution; (2) liver tissue wedge fixed by the tip of a forceps; and (3) syringe containing fixative solution; D: Different types of needles and their variants commonly used for portal vein insertion: (1) 18-23 G needle typically used for gravity-mediated perfusion for rat and mouse livers; (2) 18 G needle catheters are recommended for peristaltic-pump-mediated perfusion; (3) 12-13 G needles are typically used for larger animals such as rabbits; and (4) 25 G syringes are ideal for the injection of fixative solution in hepatic tissue. In case of accidental failure of procedure A or B, method C (injection perfusion) can be used to save the preparation.
- Citation: Wisse E, Braet F, Duimel H, Vreuls C, Koek G, Olde Damink SW, van den Broek MA, De Geest B, Dejong CH, Tateno C, Frederik P. Fixation methods for electron microscopy of human and other liver. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(23): 2851-2866
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i23/2851.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i23.2851