Published online Apr 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i15.1890
Revised: December 19, 2009
Accepted: December 26, 2009
Published online: April 21, 2010
AIM: To examine the coexistence of metachronous and synchronous cancer in branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas (IPMN).
METHODS: We reviewed the records of 145 patients with branch duct IPMN between January 1991 and April 2008 and assessed the relationship between IPMN and intra- or extra-pancreatic carcinoma and the outcome of IPMN.
RESULTS: The mean observation period was 55.9 ± 45.3 mo. Among the 145 patients, the frequency of extra-pancreatic cancer was 29.0%. The frequency of gastric cancer, colon cancer, breast cancer, and pancreatic cancer were 25.5%, 15.7%, 13.7%, and 9.8%, respectively. Twenty (13.8%) of the patients died. The cause of death was extra-pancreatic carcinoma in 40%, pancreatic cancer in 25%, IPMN per se in 20%, and benign disease in 15% of the patients.
CONCLUSION: The prognosis for IPMN depends not on the IPMN per se, but on the presence of intra- or extra-pancreatic cancer.
- Citation: Ikeuchi N, Itoi T, Sofuni A, Itokawa F, Tsuchiya T, Kurihara T, Ishii K, Tsuji S, Umeda J, Moriyasu F, Tsuchida A, Kasuya K. Prognosis of cancer with branch duct type IPMN of the pancreas. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(15): 1890-1895
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i15/1890.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i15.1890
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas (IPMN) shows a wide spectrum of histological presentations, ranging from adenoma with mild atypia to adenocarcinoma, and was first described by Ohashi et al[1] in 1980. IPMN is divided into two types, the main duct type and the branch duct type. In general, branch duct IPMN develops slowly and has a comparatively good prognosis. However, in several studies, it became evident that IPMN is a disease that very frequently coexists with cancer. Therefore, the prognosis of IPMN is more closely related to the coexisting disease than to IPMN per se[2-8]. In the present study, the prognostic significance of the coexistence of metachronous and synchronous cancer in branch duct IPMN was investigated.
The subjects were 145 patients with branch duct IPMN, including 33 resected and 112 non-resected cases, between January 1991 and April 2008, who had been periodically followed-up to date. The ratio of males to females was 79:66, the mean age was 66.3 ± 10.2 years (range: 29-89 years), and the mean observation period was 55.9 ± 45.3 mo (range: 1-217 mo). We classified IPMN into the main duct type without multi-locular dilatation of the branch duct, and the branch duct type. The Institutional Review Board of Tokyo Medical University reviewed and approved the entire study.
In our department, we consider that surgery for the branch type IPMN is indicated when the diameter of the cyst is 30 mm or more, the diameter of the mural nodule is 10 mm or more, and cytology findings of the pure pancreatic juice reveal suspected malignancy.
For regular follow-up, we performed hematological tests, including those for tumor markers (carbohydrate antigen 19-9, and carcinoembryonic antigen) and pancreatic enzymes (amylase, lipase, and elastase-1), and several types of imaging (ultrasonography, endoscopic ultrasonography, computed tomography, or magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography) every 6 to 12 mo.
We assessed the clinicopathological findings as outlined below. (1) The relationship between IPMN and intra- or extra-pancreatic cancer; and (2) Prognosis of IPMN.
Normally distributed data are presented as mean ± SD. Significance was analyzed by the χ2 test or Fisher’s exact probability test, and Aspin-Welch’s t-test. Statistically significant differences were denoted by P < 0.05. Statistical analysis was performed using Stat Mate III (ATMS Co Ltd, Tokyo, Japan).
The resected patients had significantly greater mean cyst diameter, diameter of the main pancreatic duct, and height of node protrusion compared to those of non-resected patients (P < 0.05, P < 0.01, and P < 0.01, respectively, Table 1).
| Total (n = 145) | Resection (n = 33) | Non-resection (n = 112) | |
| Age (mean ± SD) (yr) | 66.3 ± 10.2 | 63.9 ± 10.5 | 67.0 ± 10.1 |
| NS | |||
| Male:female | 79:66 | 20:13 | 59:53 |
| NS | |||
| Median diameter of cystic lesion (mm) | 20.1 ± 13.0 | 23.8 ± 11.5 | 19 ± 13.3 |
| P < 0.05 | |||
| Median diameter of MPD (mm) | 2.2 ± 2.3 | 3.6 ± 3.3 | 1.7 ± 1.8 |
| P < 0.01 | |||
| Median diameter of mural nodule (mm) | 1.6 ± 5.3 | 5.8 ± 9.8 | 0.3 ± 1.6 |
| P < 0.01 | |||
There was no statistically significant difference regarding the diameter of the cystic lesion, main pancreatic duct, and mural nodule between the branch type IPMN in patients with or without intra or extra-pancreatic cancer, regardless of whether the IPMN had been resected or not (Table 2).
| IPMN with intra- or extra-pancreatic cancer (resection/non-resection) | IPMN without intra- or extra-pancreatic cancer (resection/non-resection) | P value | |
| n | 47 (16/31) | 98 (19/79) | |
| Age | 68.4 (65.0/70.0) | 65.4 (63.2/66.4) | NS |
| Sex (male:female) | 22:25 (7:9/15:16) | 57:41 (13:6/44:35) | NS |
| Median diameter of cystic lesion (mm) | 20.8 ± 11.8 (23.3 ± 10.4/19.5 ± 12.4) | 19.7 ± 13.6 (23.0 ± 13.3/19.0 ± 13.7) | NS |
| Median diameter of MPD (mm) | 2.2 ± 2.4 (3.5 ± 3.6/1.6 ± 1.2) | 2.1 ± 2.3 (3.6 ± 2.9/1.7 ± 1.9) | NS |
| Median diameter of mural nodule (mm) | 2.1 ± 5.7 (5.3 ± 8.7/0.5 ± 1.9) | 1.3 ± 5.1 (5.6 ± 10.5/0.3 ± 1.5) | NS |
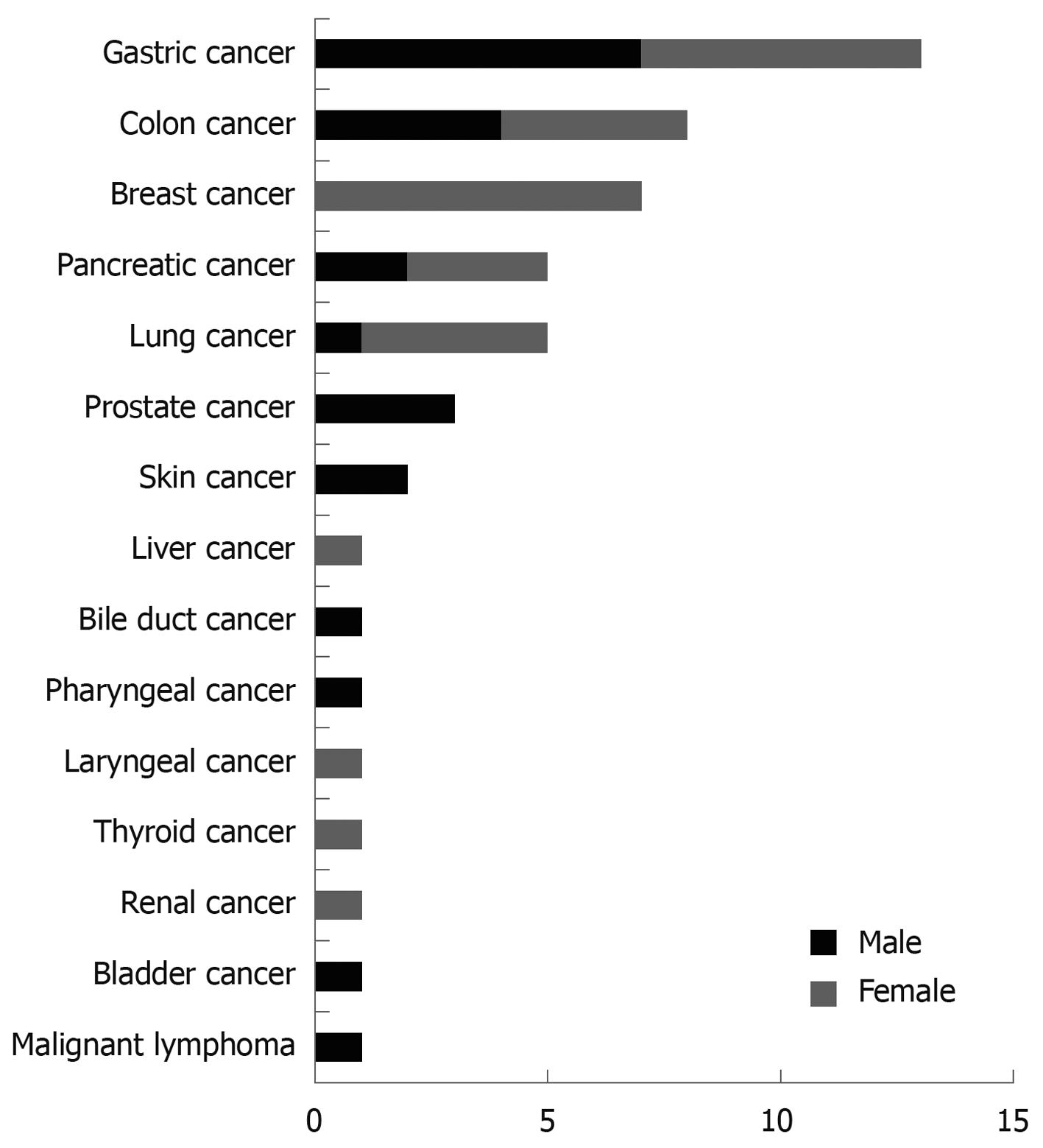
Details of intra- or extra-pancreatic cancer in patients with IPMN are shown in Figure 1. Four patients (one man, three women) had metachronous double cancer. Gastrointestinal cancer accounted for 41.2% (21/51).
Incidence of, and detection time for, intra- or extra-pancreatic cancer in patients with IPMN are shown in Table 3. Briefly, detection prior to IPMN was seen in 56.9% (29/51), simultaneous detection of cancer and IPMN was seen in 27.5% (14/51), five of which were pancreatic cancer, and cancer was detected in 15.7% (8/51) during follow-up for IPMN.
| Neoplasm | Consciousness detection prior IPMN | Simultaneous with detection of carcinoma and IPMN | During follow-up for IPMN | Total |
| Gastric cancer | 7 (1) | 3 (3) | 3 (0) | 13 (4) |
| Colon cancer | 4 (1) | 4 (0) | 0 | 8 (1) |
| Breast cancer | 5 (2) | 0 | 2 (0) | 7 (2) |
| Pancreatic cancer | 0 | 5 (4) | 0 | 5 (4) |
| Lung cancer | 3 (2) | 1 (1) | 1 (0) | 5 (3) |
| Prostate cancer | 2 (0) | 0 | 1 (1) | 3 (1) |
| Skin cancer | 2 (1) | 0 | 0 | 2 (1) |
| Liver cancer | 1 (0) | 0 | 0 | 1 (0) |
| Bile duct cancer | 0 | 0 | 1 (0) | 1 (0) |
| Pharyngeal cancer | 1 (0) | 0 | 0 | 1 (0) |
| Laryngeal cancer | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) |
| Thyroid cancer | 1 (0) | 0 | 0 | 1 (0) |
| Renal cancer | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) |
| Bladder cancer | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) |
| Malignant lymphoma | 1 (0) | 0 | 0 | 1 (0) |
| Total | 29 (9) | 14 (9) | 8 (1) | 51 (19) |
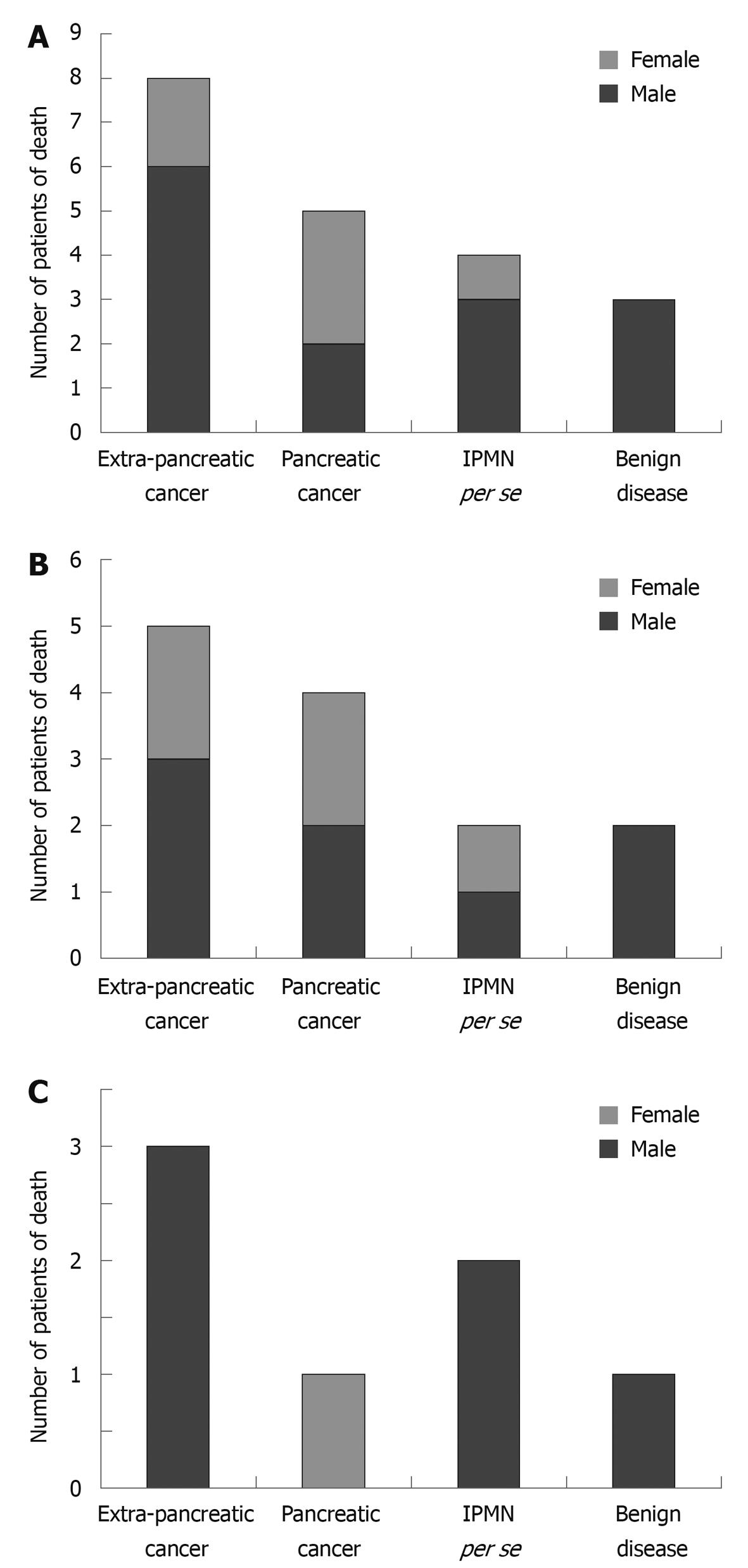
Of the 145 patients with IPMN, 13.8% (20/145) died. As shown in Figure 2, the cause of death was extra-pancreatic cancer in 40% (8/20), pancreatic cancer in 25% (5/20), IPMN per se in 20% (4/20), and benign disease in 15% (3/20) of the patients. In particular, the cause of death of resected and non-resected cases is shown in Figure 2B and C.
The clinicopathological findings in four fatal cases of IPMN are shown in Table 4. The ratio of men to women was 3:1, the mean age was 64.5 years, two patients underwent surgery immediately after detection, and both had invasive adenocarcinoma accompanying IPMN. In one of the resected patients, the cyst diameter was 35.0 mm and the height of node protrusion was 19 mm. However, lymph node metastasis was observed post-operatively and the patient died of cancer 14 mo later. The other patient was found to have a nodular lesion with a diameter of 26.6 mm and pancreatic cancer was diagnosed. The patient underwent surgery, but hepatic metastasis occurred post-operatively and she died of cancer eight mo later. Of the patients that died of cancer due to IPMN, two refused surgery and were therefore under observation only. They died at 37 and 112 mo, respectively, after detection. One non-resected patient initially had a 60 mm cyst and a 10 mm height mural nodule. When the patient died 37 mo later, the diameter of the cyst was 90 mm and the height of the mural nodule was 30 mm. The other non-resected patient initially had a cyst 20 mm in diameter with no mural nodule protrusion and when the patient died 112 mo later, the cyst had become a nodular lesion with a diameter of 64 mm.
| Sex | Age (yr) | Region | Change of cystic lesion (mm) | Change of MPD (mm) | Change of mural nodule (mm) | Resection | Histopathological result | Period from diagnosis (operation) to death (mo) | Cause of death | |
| Case 1 | Male | 89 | Head | 60→90 | 10→20 | 10→30 | (-) | Adenocarcinoma (ch+, du+) | 37 | Cancer of death |
| Case 2 | Male | 58 | Head | 20→64 | 3→10 | 0→64 | (-) | Adenocarcinoma (ch+, du+) | 112 | Cancer of death |
| Case 3 | Male | 53 | Tail | 35 | 1 | 19 | (+) | Invasive ductal carcinoma derived from IPMN (INFα, mpd+) | 15 (14) | Cancer of death |
| Case 4 | Female | 58 | Head | 0 | 1 | 26.6 | (+) | Invasive ductal carcinoma derived from IPMN (INFβ, V2, ne1, du+, rp+) | 9 (8) | Cancer of death |
We set out in determine the prognostic factors affecting cases of IPMN accompanied by cancer. In the present study, it became evident that cases complicated with metachronous and synchronous cancers in branch-type IPMN are quite common. Other studies that closely investigated such patients reported frequencies of extra-pancreatic cancer of 23.6%-46.8% and of a total of 864 IPMN patients, 32.9% (284/864) had extra-pancreatic cancer, which is almost the same as the subjects in the present study, where the frequency was 29.0% (42/145)[2-10] (Table 5). In addition, the most frequently occurring complications were gastric cancer and colon cancer, which was the same as in this study (Table 6).
| Author (yr) | Number of IPMN patients | Extra-pancreatic cancers with IPMN patients | Age (mean ± SD) | Male:female | Follow-up period (mo) |
| Zhong (1996) | 21 | 5 | NA | NA | NA |
| Sugiyama (1999) | 42 | 15 | NA | NA | NA |
| Adsay (2002) | 28 | 8 | NA | NA | NA |
| Osanai (2003) | 148 | 35 | 70.9 | 31:4 | NA |
| Kamisawa (2005) | 79 | 37 | NA | NA | NA |
| Eguchi (2006) | 69 | 32 | NA | NA | NA |
| Choi (2006) | 61 | 18 | 64.2 ± 8.4 | 13:5 | 65.8 ± 8.5 |
| Yoon (2008) | 210 | 77 | 65.3 ± 9.0 | 47:30 | 24.7 |
| Ishida (2008) | 61 | 151 | 67.0 ± 7.0 | 12:3 | 50.9 |
| Present study | 145 | 422 | 68.3 ± 9.0 | 20:26 | 49.8 ± 42.4 |
| Total | 864 | 2843 |
| Neoplasm | Zhong (1996) | Sugiyama (1999) | Adsay (2002) | Osanai (2003) | Kamisawa (2005) | Egichi (2006) | Choi (2006) | Yoon (2008) | Ishida (2008) | Present study | Total |
| Gastric cancer | 0 | 4 | 0 | 8 | 12 | 4 | 8 | 29 | 6 | 13 | 84 |
| Colon cancer | 3 | 5 | 0 | 11 | 7 | 8 | 4 | 16 | 4 | 8 | 66 |
| Lung cancer | 0 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 25 |
| Bile duct cancer | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 1 | NS | 2 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 18 |
| Prostate cancer | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 11 |
| Renal cancer | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 11 |
| Breast cancer | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | NS | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 10 |
| Esophageal cancer | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | NS | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 9 |
| Malignant lymphoma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | NS | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 9 |
| Bladder cancer | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 7 |
| Liver cancer | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | NS | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Thyroid cancer | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NS | 1 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 5 |
| Ampullary cancer | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | NS | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 5 |
| Skin cancer | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | NS | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 4 |
| Uterine cancer | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | NS | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Laryngeal cancer | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | NS | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Pharyngeal cancer | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | NS | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Ovarian cancer | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NS | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Duodenal cancer | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NS | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Other cancer or unknown | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 |
| Total | 5 | 15 | 8 | 35 | 37 | 32 | 18 | 77 | 17 | 46 | 290 |
On the other hand, other studies reported pancreatic cancer occurring in 3.8 to 9.2% of IPMN cases[6,11,12]. In our study it was 3.5% (5/145), which was slightly lower. In general, the etiology of second primary tumors is complex, involving multiple factors such as: (1) shared risk factors for the primary and secondary tumors, (2) host susceptibility to the development of specific tumors, (3) altered immunity as a result of the primary tumor and/or treatment, and (4) treatment with cytotoxic agents (radiotherapy and chemotherapy)[3]. In the present study, there was no clearly significant difference between cases complicated with other organ cancers and those without such complications in terms of cyst diameter, diameter of the main pancreatic duct, and presence or absence of mural nodules. This demonstrated that these data cannot be used as indices in the discovery of intra or extra-pancreatic cancer. Thus, further investigations, including follow-up studies, are necessary.
In the present study, most cases of IPMN were diagnosed after extra-pancreatic cancer was diagnosed. However, there are also reports stating that the time of IPMN diagnosis is unrelated to the onset of extra-pancreatic cancer[3,5].
The follow-up period and imaging modality for follow-up vary according to reports, and no consensus has been obtained. In this study, no case of pancreatic cancer occurred during follow-up. However, several researchers have reported pancreatic cancer after diagnosis of IPMN[6,11-15]. These findings demonstrate that periodic follow-up is necessary, even after IPMN is diagnosed.
The 5-year survival of patients with IPMN that undergo resection was reported to be for 36%-66%, even among those with invasive cancer. Thus, longer survival than that for pancreatic cancer can be expected[16-20]. According to our data, 25% of deaths were due to pancreatic cancer, while 40% were due to cancer of other organs. On the other hand, the follow-up periods of two patients who refused surgery and opted for conservative treatment, but who then died due to IPMN, were 37 and 112 m, which was relatively long. Our data demonstrated that to determine the prognosis for IPMN, intra- or extra-pancreatic cancer is the key factor, rather than the IPMN per se.
In conclusion, to decide on the prognosis for IPMN, the presence of intra- or extra-pancreatic cancer is the main prognostic factor, rather than IPMN per se. Therefore, there is no fixed algorithm regarding the follow-up period or methodology, but in all cases, close follow-up, especially for the development of cancer, is very important.
Several investigators have suggested that the prognosis of the intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas (IPMN) is more closely related to coexisting diseases than IPMN per se.
In reports on studies that closely investigated such patients, the frequency of extra-pancreatic cancer was 23.6%-46.8% in a total of 864 IPMN patients, and 32.9% (284/864) had extra-pancreatic cancer, which corresponds well with the data from the subjects in the present study, where the frequency was 29.0% (42/145). On the other hand, many studies reported pancreatic cancer to occur in 3.8% to 9.2% of IPMN cases.
It appears to be important to determine the presence of intra- or extra-pancreatic cancer when examining the patients with IPMN.
IPMN including branch duct type and main pancreatic duct type, have high risk for intra- or extra-pancreatic cancer, leading to death of patients.
This is an interesting paper.
Peer reviewer: Pascal Bucher, MD, Chef de Clinique (FMH), Service de Chirurgie Viscérale et Transplantation, University Hospital Geneva, 4, Rue Gabrielle Perret Gentile, Geneva, 1211, Switzerland
S- Editor Wang YR L- Editor Stewart GJ E- Editor Ma WH
| 1. | Ohashi K, Murakami Y, Maruyama M. Takekoshi T, Ohta H, Ohhashi I, Takagi K, Kato K. Four cases of mucous secreting pancreatic cancer (in Japanese with English abstract). Prog Dig Endosc. 1982;20:348-351. |
| 2. | Zhong LJ, Satou K, Moriizumi S, Shimosegawa T, Koizumi M, Toyota T. An analysis of the disease associated with “mucin-producing tumor of the pancreas” (in Japanese with English abstract). J Jpn Pancreas. 1996;11:289-292. |
| 3. | Sugiyama M, Atomi Y. Extrapancreatic neoplasms occur with unusual frequency in patients with intraductal papillary mucinous tumors of the pancreas. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94:470-473. |
| 4. | Adsay NV, Conlon KC, Zee SY, Brennan MF, Klimstra DS. Intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: an analysis of in situ and invasive carcinomas in 28 patients. Cancer. 2002;94:62-77. |
| 5. | Osanai M, Tanno S, Nakano Y, Koizumi K, Habiro A, Korgo Y. Extrapancreatic neoplasms in patients with intraductal papillary mucinous tumor of the pancreas: analysis in surgical and follow-up series (in Japanese with English abstract). J Jpn Pancreas Soc. 2003;18:565-569. |
| 6. | Kamisawa T, Tu Y, Egawa N, Nakajima H, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A. Malignancies associated with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:5688-5690. |
| 7. | Eguchi H, Ishikawa O, Ohigashi H, Tomimaru Y, Sasaki Y, Yamada T, Tsukuma H, Nakaizumi A, Imaoka S. Patients with pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms are at high risk of colorectal cancer development. Surgery. 2006;139:749-754. |
| 8. | Choi MG, Kim SW, Han SS, Jang JY, Park YH. High incidence of extrapancreatic neoplasms in patients with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Arch Surg. 2006;141:51-56; discussion 56. |
| 9. | Yoon WJ, Ryu JK, Lee JK, Woo SM, Lee SH, Park JK, Kim YT, Yoon YB. Extrapancreatic malignancies in patients with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas: prevalence, associated factors, and comparison with patients with other pancreatic cystic neoplasms. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15:3193-3198. |
| 10. | Ishida M, Egawa S, Kawaguchi K, Aoki T, Sakata N, Mikami Y, Motoi F, Abe T, Fukuyama S, Katayose Y. Synchronous and metachronous extrapancreatic malignant neoplasms in patients with intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Pancreatology. 2008;8:577-582. |
| 11. | Uehara H, Nakaizumi A, Ishikawa O, Iishi H, Tatsumi K, Takakura R, Ishida T, Takano Y, Tanaka S, Takenaka A. Development of ductal carcinoma of the pancreas during follow-up of branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Gut. 2008;57:1561-1565. |
| 12. | Yamaguchi K, Ohuchida J, Ohtsuka T, Nakano K, Tanaka M. Intraductal papillary-mucinous tumor of the pancreas concomitant with ductal carcinoma of the pancreas. Pancreatology. 2002;2:484-490. |
| 13. | Komori T, Ishikawa O, Ohigashi H, Yamada T, Sasaki Y, Imaoka S, Nakaizumi A, Uehara H, Tanaka S, Mano Y. Invasive ductal adenocarcinoma of the remnant pancreatic body 9 years after resection of an intraductal papillary-mucinous carcinoma of the pancreatic head: a case report and comparison of DNA sequence in K-ras gene mutation. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2002;32:146-151. |
| 14. | Rautou PE, Lévy P, Vullierme MP, O'Toole D, Couvelard A, Cazals-Hatem D, Palazzo L, Aubert A, Sauvanet A, Hammel P. Morphologic changes in branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: a midterm follow-up study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6:807-814. |
| 15. | Tada M, Kawabe T, Arizumi M, Togawa O, Matsubara S, Yamamoto N, Nakai Y, Sasahira N, Hirano K, Tsujino T. Pancreatic cancer in patients with pancreatic cystic lesions: a prospective study in 197 patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:1265-1270. |
| 16. | Kitagawa Y, Unger TA, Taylor S, Kozarek RA, Traverso LW. Mucus is a predictor of better prognosis and survival in patients with intraductal papillary mucinous tumor of the pancreas. J Gastrointest Surg. 2003;7:12-18; discussion 18-19. |
| 17. | Salvia R, Fernández-del Castillo C, Bassi C, Thayer SP, Falconi M, Mantovani W, Pederzoli P, Warshaw AL. Main-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: clinical predictors of malignancy and long-term survival following resection. Ann Surg. 2004;239:678-685; discussion 685-687. |
| 18. | Chari ST, Yadav D, Smyrk TC, DiMagno EP, Miller LJ, Raimondo M, Clain JE, Norton IA, Pearson RK, Petersen BT. Study of recurrence after surgical resection of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:1500-1507. |
| 19. | Yamao K, Ohashi K, Nakamura T, Suzuki T, Shimizu Y, Nakamura Y, Horibe Y, Yanagisawa A, Nakao A, Nimuara Y. The prognosis of intraductal papillary mucinous tumors of the pancreas. Hepatogastroenterology. 2000;47:1129-1134. |
| 20. | Wang SE, Shyr YM, Chen TH, Su CH, Hwang TL, Jeng KS, Chen JH, Wu CW, Lui WY. Comparison of resected and non-resected intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. World J Surg. 2005;29:1650-1657. |