Published online Mar 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i12.1887
Revised: January 9, 2006
Accepted: January 31, 2007
Published online: March 28, 2007
- Citation: Tekin A, Küçükkartallar T, Kartal A. A dıfferent approach for sterılızatıon of lıver hydatid cysts. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(12): 1887-1887
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i12/1887.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i12.1887
Many different methods have been used in surgical treatment of liver hydatid cysts[1]. However, two methods have been frequently used recently: one is used to radically remove the cyst and the other is used to shrink the cyst cavity after treated with scolocidal agents. One of the most important principles for the treatment of hydatid cyst is to avoid the contact of fluid in the cavity with the adjacent tissues during cyst cavity contacts with scolek killers at certain time.
If the cysts are easily accessible, sterilization of the cavity is not a problem. However, it is difficult to give a desirable amount of scolek killer agents to the cavity in some cases because the cyst is located in posterior lung segments. For this reason, we present an easy but effective method.
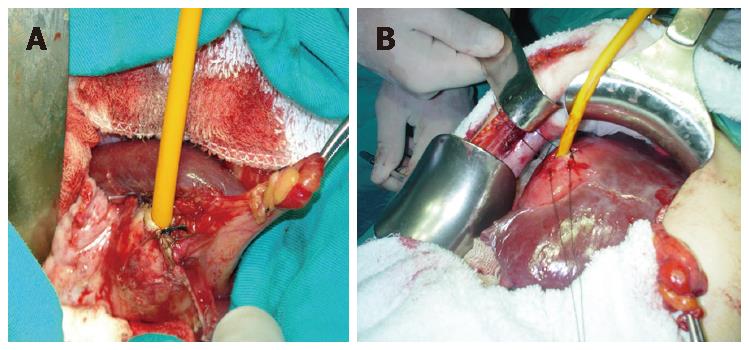
The cyst can be accessed by performing a suitable incision. The surrounding of the cyst is isolated with cloth absorbing saline solution. The cyst ingredients are evacuated with a trochar aspirator. When there is no bile in the content, a thick foley catheter is placed into the cyst and its balloon is blown (the balloon should be blown to the level not to be taken out when pulled tightly from the orifice) (Figure 1A and B). The cavity is filled with scolek killers and clamped. A balooned catheter is fixed tightly through a retractor. After a certain period of time, the solution given to the cyst through the balloon catheter kept in tension is taken out and the cyst becomes smaller and smaller.
Two different techniques have been used in the treatment of hydatid cyst: one is used radically remove the cyst and the other is used to evacuate the content in the cyst and to make the cyst cavity smaller. The second technique is used more often than the first, and the biggest disadvantage of these two techniques is that there is a risk of developing peritonea disease if the fluid leaks into the abdomen during operation. Many different techniques have been used to avoid this[1-3]. Here the most important thing is to prevent fluid leaking into the abdomen and keeping the scolosid killer agents in the cyst for a certain period of time in order to kill the live scoleks. It is easy to do this with the lung cysts on the frontal surface of the lungs. However, it is quite difficult to perform this for the cysts on diaphragmatic surface. In our clinic, the technique has been used in 45 patients between 2002 and 2005. No recurrence of liver hydratid crysts was found in any patients, suggesting that this technique which provides adequate contact with scoleks in the cyst and prevents liquid leaking into peritonea can be used in the treatment of lung cyst disease.
S- Editor Wang J L- Editor Wang XL E- Editor Chin GJ
| 1. | Langer B. Hepatic echinococcosis. Current surgical therapy. 5th ed. St. Louis: Mosby-Year Book 1992; 271-273. |
| 2. | Kayaalp C. Evacuation of hydatid liver cysts using laparoscopic trocar. World J Surg. 2002;26:1324-1327. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Morris DL. Surgical management of hepatic hydatid cyst. Hydatid disease current medical & surgical management. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann Ltd 1992; 60-61. |