Published online Jun 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i21.3453
Revised: December 28, 2005
Accepted: January 14, 2006
Published online: June 7, 2006
Anorectal melanoma is a very rare tumor with poor prognosis. Rectal bleeding is the most frequent symptom and surgical treatment ranges from local excision to radical abdominoperineal resection. We report a case of a 75-years-old male patient who presented with a history of recurrent rectal bleeding, and whose histopathological diagnosis was melanoma. Macroscopically, we found two distinct tumors in anorectal region, 0.5 cm and 1.5 cm from dentate line. The first one was pedunculated, on a thin stalk, measuring 1 cm in greatest diameter, and the second one was sessile and nodular measuring up to 2.8 cm in largest diameter. Microscopic examination and immunohistochemical analysis of both tumors confirmed the diagnosis of melanoma. This case represents multiple synchronous primary melanoma of the anorectal region, with a possibility that one of the lesions is primary melanoma and the second one is a satellite lesion.
- Citation: Balicevic D, Tomic K, Bekavac-Beslin M, Kovacevic I, Mijic A, Belicza M, Kruslin B. Synchronous anorectal melanoma. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(21): 3453-3455
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i21/3453.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i21.3453
Anorectal melanoma is a rare condition accounting for 0.2%-3% of all melanoma cases, and 0.1%-4.6% of all malignant tumors of the rectum and anus[1,2,3]. Melanoma is defined as “rectal” when it occurs in the rectum above the anorectal junction[4], while anal canal is below anorectal line. Rectal bleeding was the most common reported symptom, and sometimes the importance of the bleeding is underestimated as it was assumed to be a sign of hemorrhoid disease causing a delay in making the correct diagnosis and starting treatment[4,5]. Surgical treatment of this tumor ranges from the radical abdominoperineal resection with bilateral inguinal lymphadenectomy, to the conservative local excision alone[4]. Long-term survival is very low; approximately 6.7% to 12% of patients were reported to be free of disease five years after their operations[6,7]. Most recent studies did not find correlation between tumor necrosis and blood vessel invasion and survival rate, while correlation of survival and tumor thickness is controversial. In the most studies, tumors evaluated by flow cytometry that showed aneuploidy correlated with poorer prognosis. S-phase fraction higher than 15% also correlated with a worse prognosis[4,5].
A 75-year-old male patient presented with a history of recurrent rectal bleeding which had become more frequent and severe during the previous year. Colonoscopy revealed only one polipoid and fragile mass in the rectum, and punch biopsy showed pigmented melanoma. Computed tomography (CT) scan and ultrasound did not find enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
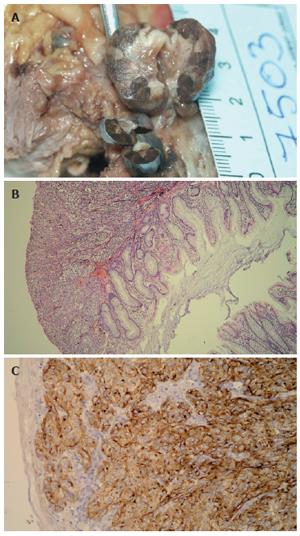
Pathologic examination of the received specimen revealed two distinct tumorous masses; the first one that was pedunculated, on a thin stalk, 0.5 cm above dentate line, measuring 1 cm in greatest diameter. The second one was sessile and nodular, 1.5 cm above dentate line, measuring up to 2.8 cm. Both tumors were bluish brown on cut sections (Figure 1A).
After surgery, all specimens were formalin fixed, paraffin embedded, cut at 5 µm and routinely stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Deparaffinisation and immunohistochemical staining was performed following Microwave Streptavidin ImmunoPeroxidase (MSIP) protocol on DAKO TechMate™ Horizon automated immunostainer. We used primary antibodies to HMB-45 and S-100 (purchased from DAKO, Copenhagen, Denmark). Microscopically, both tumors were composed of atypical spindle cells with prominent nucleoli and highly pigmented. First tumor, the smaller one, was covered with squamous epithelium, partially ulcerated, infiltrating mucosa and submucosa but without extension to the muscle layer. Mitotic rate was 10/10 HPF. The larger tumor was covered with partially ulcerated columnar epithelial cells, without muscle layer infiltration (Figure 1B). Mitotic rate was 13/10 HPF. Tumor thickness, measured by computer program, was 5.75 mm for the smaller tumor, and 9.11 mm for the larger one. Both tumors showed immunohistochemically positive reaction for HMB-45 and S-100 (Figure 1C).
Paraffin embedded specimens were processed for the flow cytometry. Cellular DNA content and proliferative activity were analyzed on a FACSCalibur flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson, San Jose, CA) using excitation wave-length at A488 nm and 15-mW argon ion laser. DNA histograms were generated on at least 20 000 nuclear events with a Mod-FitLT V2.0 (Verity Software House Inc.,Topshame, ME and Becton Dickinson).
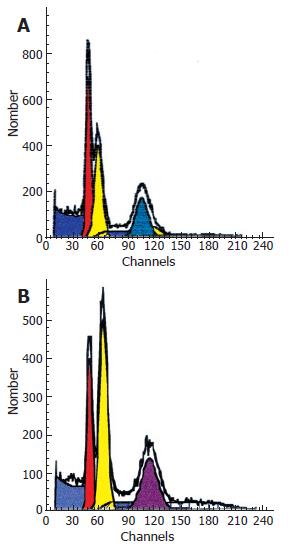
DNA flow cytometry analysis showed two aneuploid peaks (hypodiploid and hyperdiploid populations) in both tumors, but with different DNA indexes and S-phase fractions (Figure 2A, 2B). S-phase fraction for the polipoid tumor, covered with squamous epithelium was 11.84%, and for the nodular one, covered with columnar epithelium was 26.82%.
Anorectal melanoma is a very rare neoplasm, and in the reviewed literature we did not find any similar case of anorectal melanoma, either with satellite lesion or with multiple melanomas in anorectal region. We found only one reported case of metachronous melanoma in the upper digestive system, involving esophagus and stomach[8]. The case presented in this paper is specific by reporting two, synchronous melanomas, of which one of the tumors was found in anal canal, and it was partially covered by ulcerated squamous epithelium, while the other one was in rectum, covered with partially ulcerated columnar epithelium. Between described tumors there was an area of normal rectal mucosa without tumor involvement. For almost 30 years patient had recurrent bleeding because of hemorrhoid disease, which probably caused delay in making a correct diagnosis. Although some authors did not find difference in overall survival between patients treated with local excision and those with abdominoperineal resection[2,9], the study from the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center by Brady et al. suggested abdominoperineal resection as a better approach for patients without advanced disease, because patients treated with abdominoperineal resection were more commonly associated with better long-term survival than those treated with other procedures[4,6]. After physical, CT scan and ultrasound examination which did not find any signs of metastatic disease, patient was treated by radical abdominoperineal resection.
The most important doubt in this case is the nature of both lesions. Are they both primary anorectal melanoma or is one of the two tumor primary, and which one, and the second one is probably a satellite lesion
In skin melanomas, satellite lesions are defined as tumor nests or nodules within 2 cm of the primary tumor, while in-transit metastasis involves skin or subcutaneous tissue more than 2 cm from the primary tumor, but not beyond the regional lymph nodes. The significance of their presence is seen in survival studies, where lymph node metastasis is one of the most important predictor factors of survival in melanoma patients, and presence and number of involved lymph nodes is more important than actual gross dimension of the involved lymph node. In new melanoma staging system, patients with in-transit metastases or satellite lesions without lymph node disease have a similar prognosis to those with positive lymph node metastases. In the revised staging system, these patients are now upstaged as having N2c disease compared with the 1997 staging system in which these patients were considered as having T4 disease[10].
In this case, it is likely that one of the lesions is primary tumor and the second one is the satellite lesion. Concerning colonoscopy, which was performed few months before surgery, and which found only one polipoid tumor, it is possible that the smaller tumor is primary, and the second one is a satellite lesion. Hypothesis that one of the tumors is a satellite lesion is also supported with histological findings, because both tumors are composed of the same histological type. However, the surface of both tumors is ulcerated, making it very difficult to establish connection of the tumor cells with the surface, and concerning different S-fases on DNA flow cytometry there is still a possibility that this is the case of a multiple synchronous primary melanoma in anal canal and rectum.
Importance of distinguishing exact nature of the found lesions, if we could apply the same rules as for staging cutaneous melanoma, is better staging and predicting prognosis.
This case represents the multiple synchronous primary melanoma of the anorectal region, with a possibility that one of the lesions is primary melanoma and the second one is a satellite lession.
S- Editor Wang J L- Editor Ma JY E- Editor Ma WH
| 1. | Goldman S, Glimelius B, Påhlman L. Anorectal malignant melanoma in Sweden. Report of 49 patients. Dis Colon Rectum. 1990;33:874-877. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 119] [Cited by in RCA: 102] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Thibault C, Sagar P, Nivatvongs S, Ilstrup DM, Wolff BG. Anorectal melanoma--an incurable disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 1997;40:661-668. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 155] [Cited by in RCA: 136] [Article Influence: 4.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Weinstock MA. Epidemiology and prognosis of anorectal melanoma. Gastroenterology. 1993;104:174-178. [PubMed] |
| 4. | Pantalone D, Taruffi F, Paolucci R, Liguori P, Rastrelli M, Andreoli F. Malignant melanoma of the rectum. Eur J Surg. 2000;166:583-584. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Ben-Izhak O, Levy R, Weill S, Groisman G, Cohen H, Stajerman S, Misselevich I, Nitecky S, Eidelman S, Kerner H. Anorectal malignant melanoma. A clinicopathologic study, including immunohistochemistry and DNA flow cytometry. Cancer. 1997;79:18-25. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Brady MS, Kavolius JP, Quan SH. Anorectal melanoma. A 64-year experience at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center. Dis Colon Rectum. 1995;38:146-151. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 219] [Cited by in RCA: 181] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Cooper PH, Mills SE, Allen MS Jr. Malignant melanoma of the anus: report of 12 patients and analysis of 255 additional cases. Dis Colon Rectum. 1982;25:693-703. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 129] [Cited by in RCA: 105] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Dabrowski A, Zinkiewicz K, Szumilo J, Zgodzinski W, Cwik G, Skoczylas T, Wallner G. Unusual clinical course of metachronous melanomas of the upper digestive system. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:2197-2199. [PubMed] |
| 9. | Slingluff CL Jr, Vollmer RT, Seigler HF. Anorectal melanoma: clinical characteristics and results of surgical management in twenty-four patients. Surgery. 1990;107:1-9. [PubMed] |
| 10. | Kim CJ, Reintgen DS, Balch CM. The new melanoma staging system. Cancer Control. 2002;9:9-15. [PubMed] |