Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 15, 2003; 9(9): 2054-2059
Published online Sep 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.2054
Published online Sep 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.2054
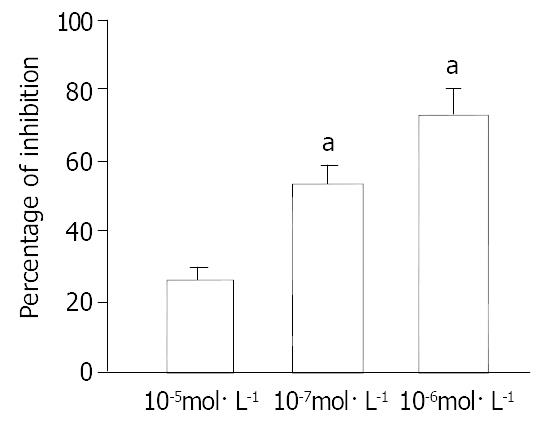
Figure 1 Effect of CNP on spontaneous contraction of gastric circular smooth muscle in a dose-dependent manner in guinea pigs.
aP < 0.01 vs 10-8 mol·L-1 group.
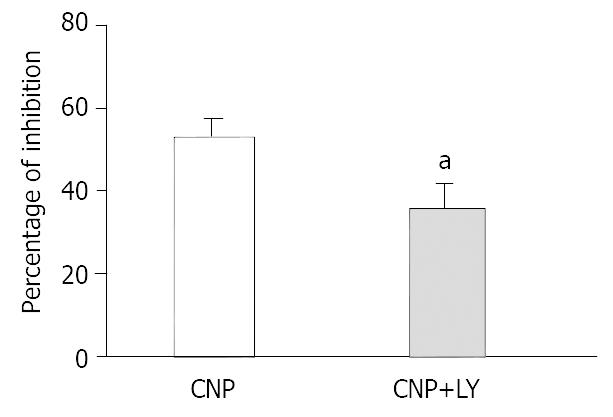
Figure 2 Effect of Ly83583 on CNP-induced inhibition in gastric circular smooth muscle of guinea pigs.
aP < 0.05 vs CNP group.
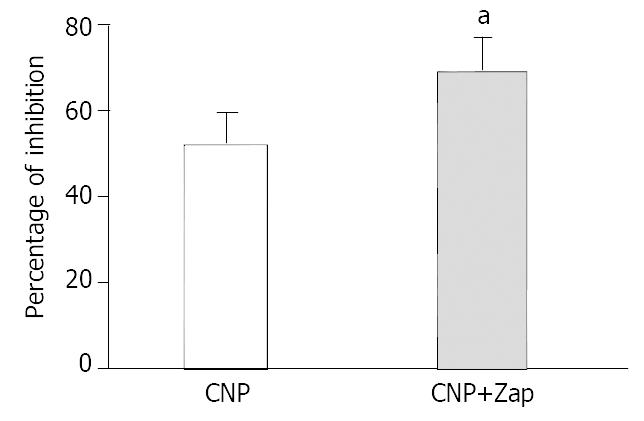
Figure 3 Effect of Zaparinast on CNP-induced inhibition in gastric circular smooth muscle of guinea pigs.
aP < 0.05 vs CNP group.
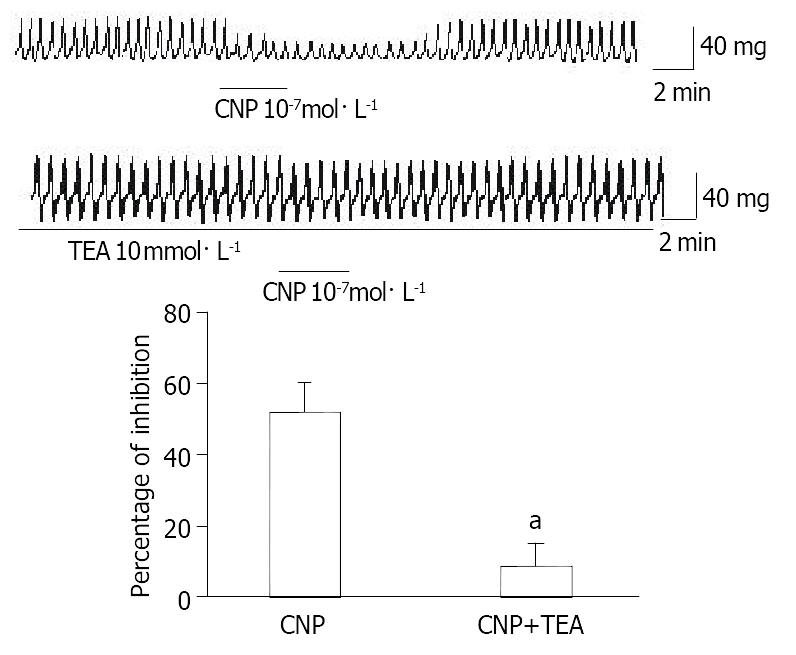
Figure 4 Effect of TEA on CNP-induced inhibition in gastric circular smooth muscle of guinea pigs.
aP < 0.01 vs CNP group.
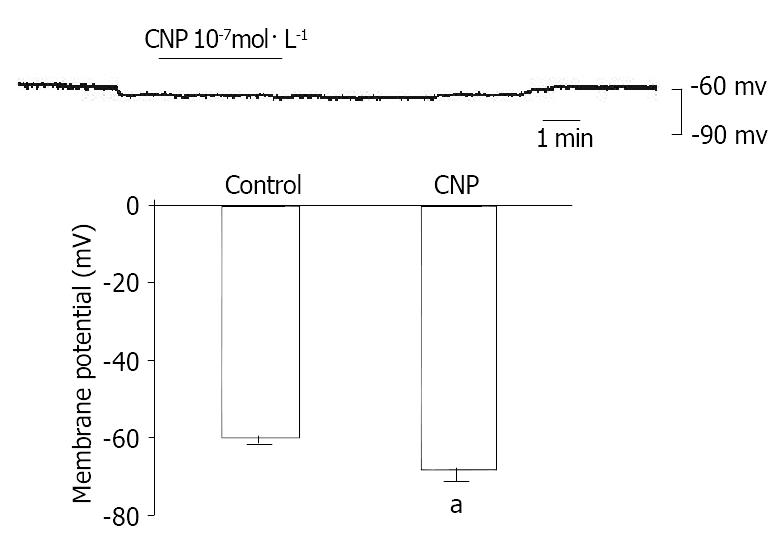
Figure 5 Effect of CNP on membrane potential of gastric circular myocytes in guinea pigs.
aP < 0.05 vs Control group.
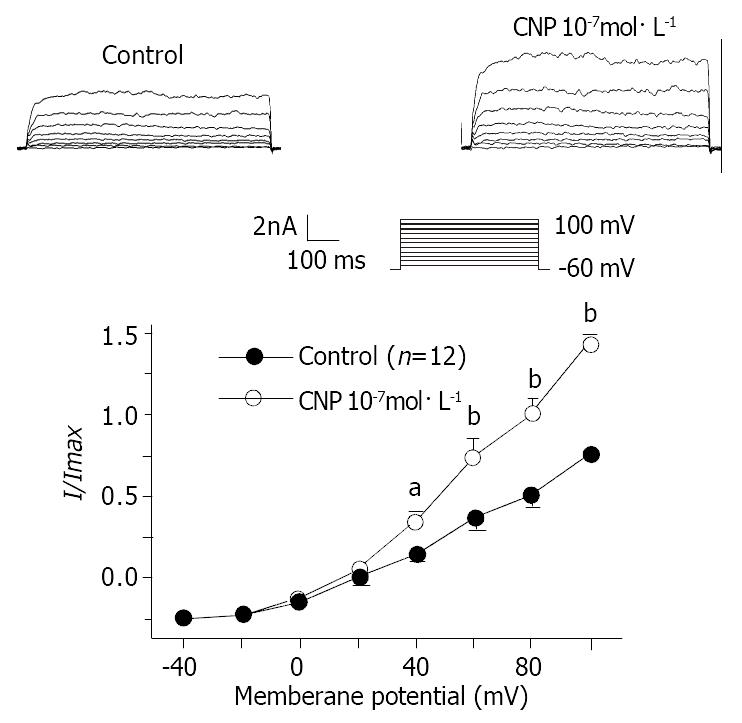
Figure 6 Effect of CNP on Ik(ca) in gastric circular smooth muscle of guinea pigs.
aP < 0.05 vs Control group; bP < 0.01 vs Control group.
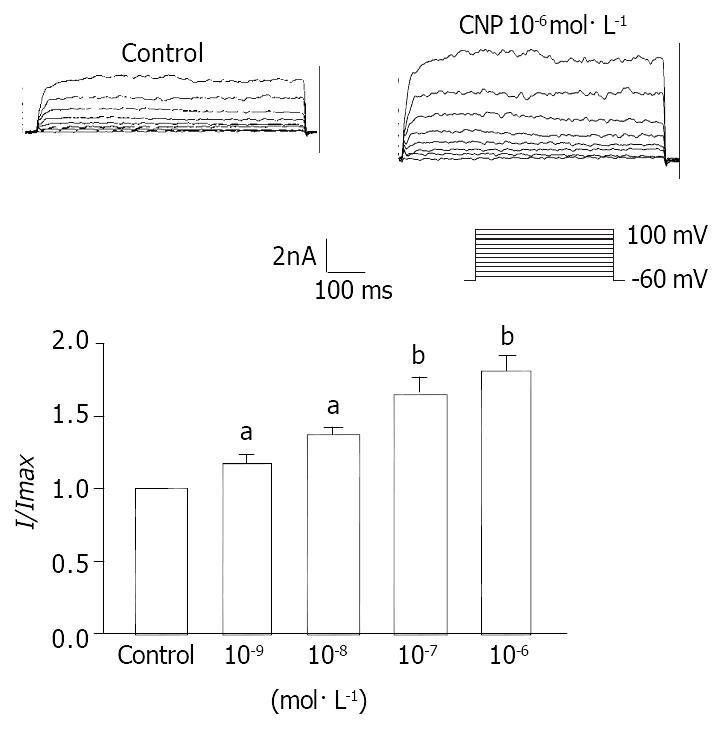
Figure 7 Dose-dependent manner of CNP calcium-activated potassium currents in gastric circular smooth muscle of guinea pigs.
aP < 0.05 vs Control group, bP < 0.01 vs Control group.
Figure 8 Effect of CNPon STOCs in gastric circular smooth muscle of guinea pigs.
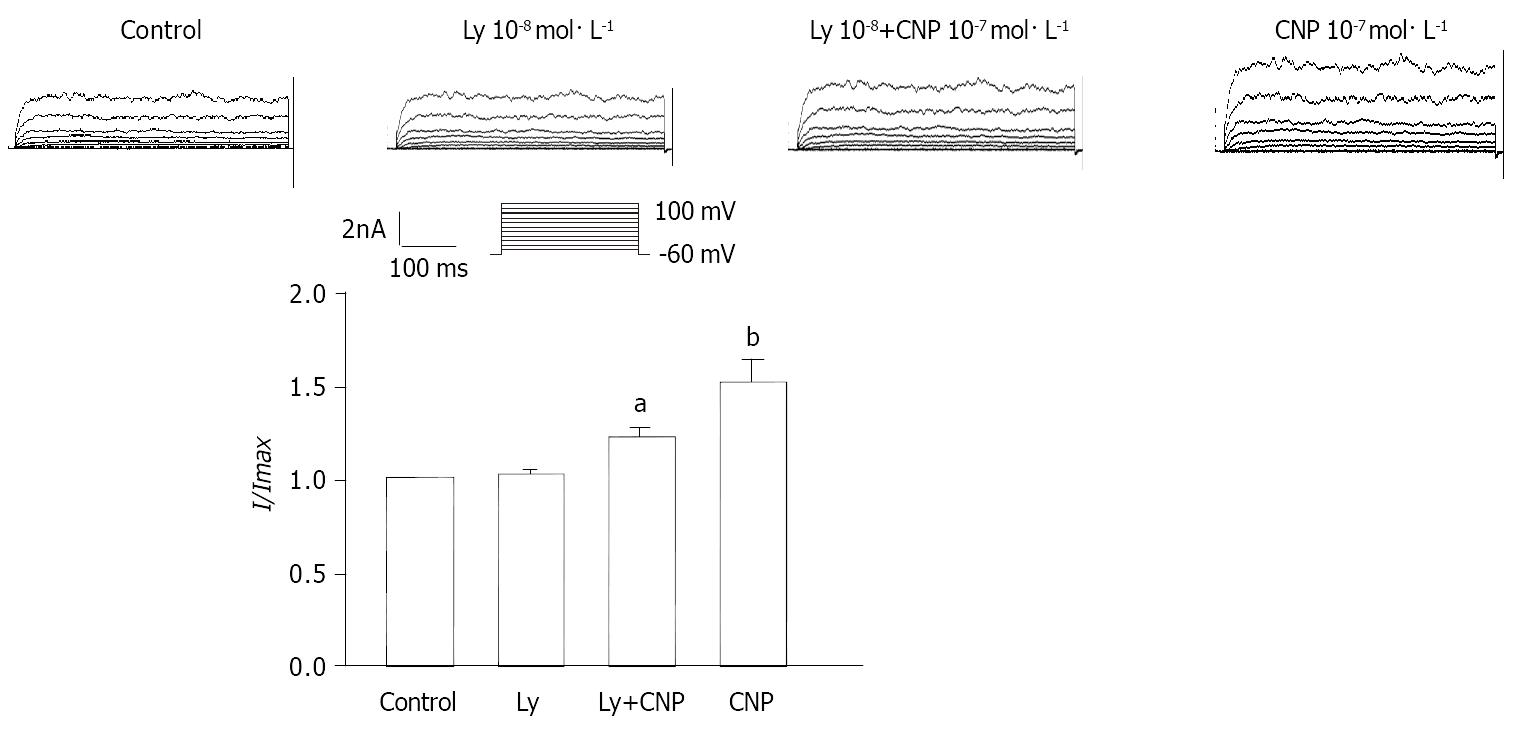
Figure 9 Effect of Ly83583 on CNP-induced increase of calcium-activated potassium currents in gastric circular smooth muscle of guinea pigs.
aP < 0.05 vs Ly group, bP < 0.01 vs Ly + CNP group.
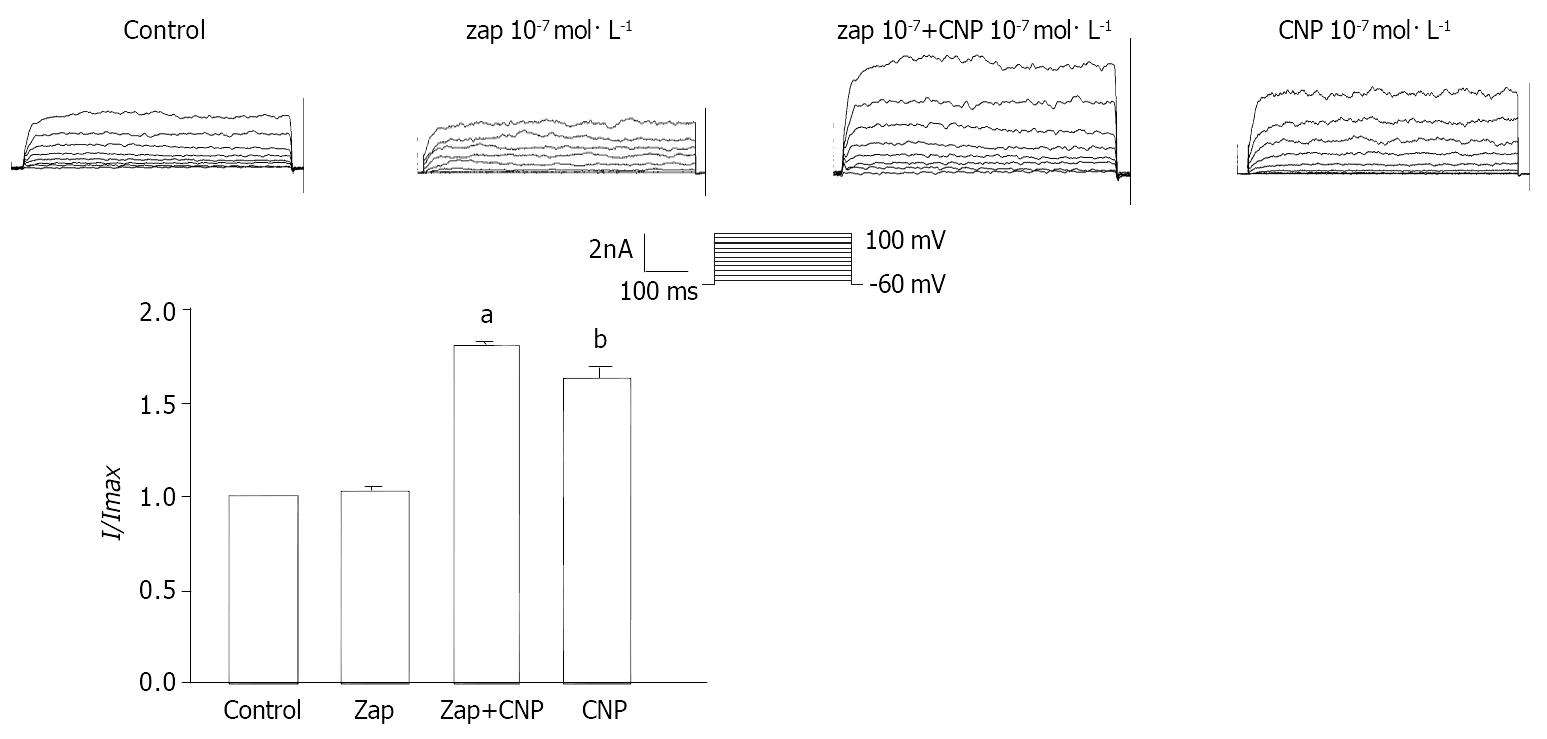
Figure 10 Effect of Zaparinast on CNP-induced increase of calcium-activated potassium currents in gastric circular smooth muscle of guinea pigs.
aP < 0.01 vs Zap group, bP < 0.01 vs Zap + CNP group.
- Citation: Guo HS, Cai ZX, Zheng HF, Li XL, Cui YF, Wang ZY, Xu WX, Lee SJ, Kim YC. Role of calcium-activated potassium currents in CNP-induced relaxation of gastric antral circular smooth muscle in guinea pigs. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(9): 2054-2059
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i9/2054.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.2054