Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 15, 2003; 9(9): 1900-1903
Published online Sep 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.1900
Published online Sep 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.1900
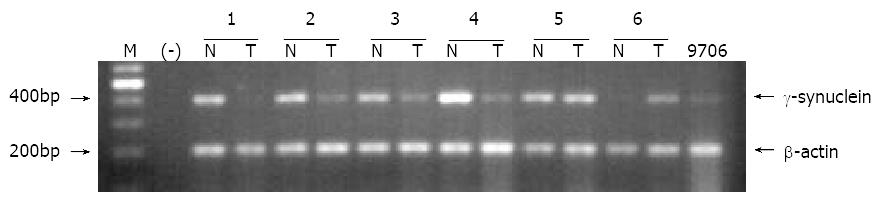
Figure 1 Simi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of human γ-synuclein mRNA in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
The γ-synuclein fragment (384 bp) was amplified by 20 cycles PCR using the paired primers as indicated in Material and Methods. Five micrograms of total RNA isolated from human ESCC tissues and corresponding normal tissues were used as templates for cDNA synthesis respectively. β-actin was used as an internal control. T: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissue, N: corresponding normal tissue, 9706: human ESCC 9706 cell line, (-): negative control, M: 100 bp DNA marker.
Figure 2 Identification of exogenous γ-synuclein expression in 9706/γ-syn stable cell line.
Exogenous HA tagged γ-synuclein was detected by Western blot using anti-HA antibody in 9706/γ-syn cells. β-actin was used as internal control.
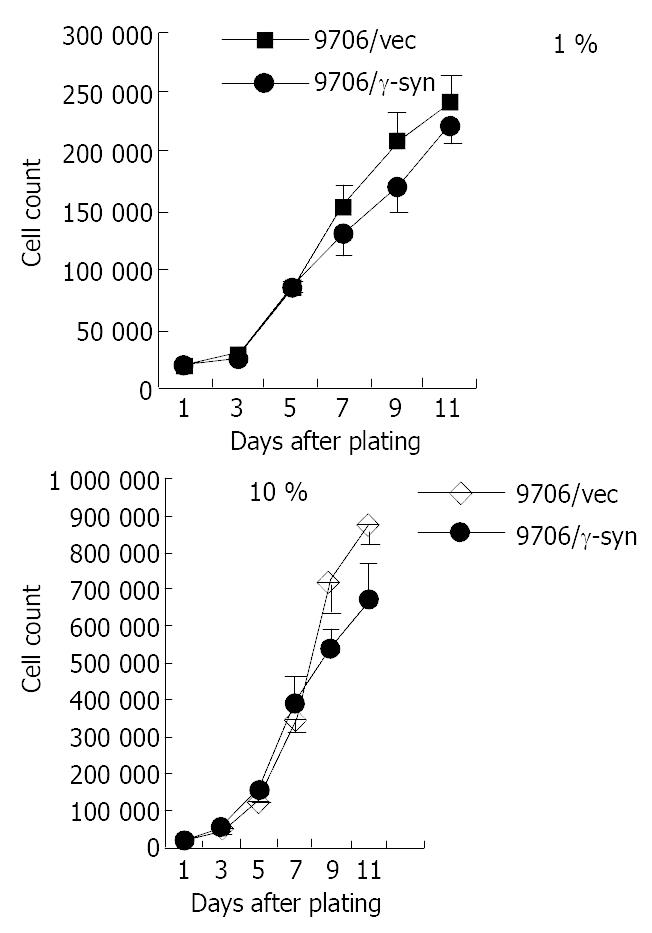
Figure 3 Effect of γ-synuclein over-expression on cell growth of 9706 cells with 1% and 10% FBS respectively.
ESCC 9706/γ-syn and 9706/vec were seeded in triplicate of 24-well plate in DMEM plus 1% FBS and 10% FBS. The growth curve showed that 9706/γ-syn cells grew more slowly than that of control cells, both in low and high serum medium in dishes.
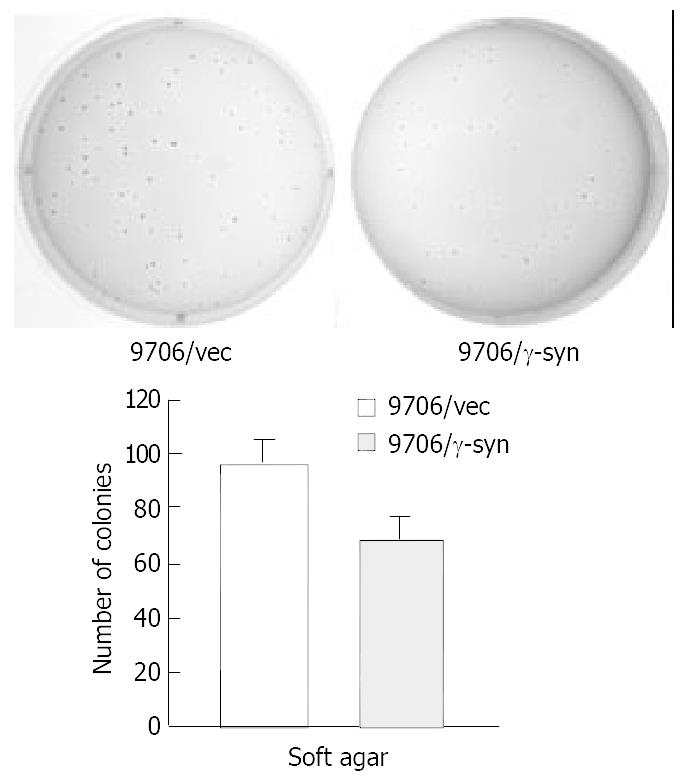
Figure 4 Colony formation of ESCC 9706 cells transfected with vector and γ-synuclein.
200 cells from each of the cell pools were plated in six-well plates. After 14 days, the colonies were stained with 0.2% p-iodonitroterazolium violet and photographed. The number of colonies per well was quantified. Experiments were repeated three times with consistent and reproducible results.
- Citation: Zhou CQ, Liu S, Xue LY, Wang YH, Zhu HX, Lu N, Xu NZ. Down-regulation of γ-synuclein in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(9): 1900-1903
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i9/1900.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.1900