Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 15, 2003; 9(8): 1799-1803
Published online Aug 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i8.1799
Published online Aug 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i8.1799
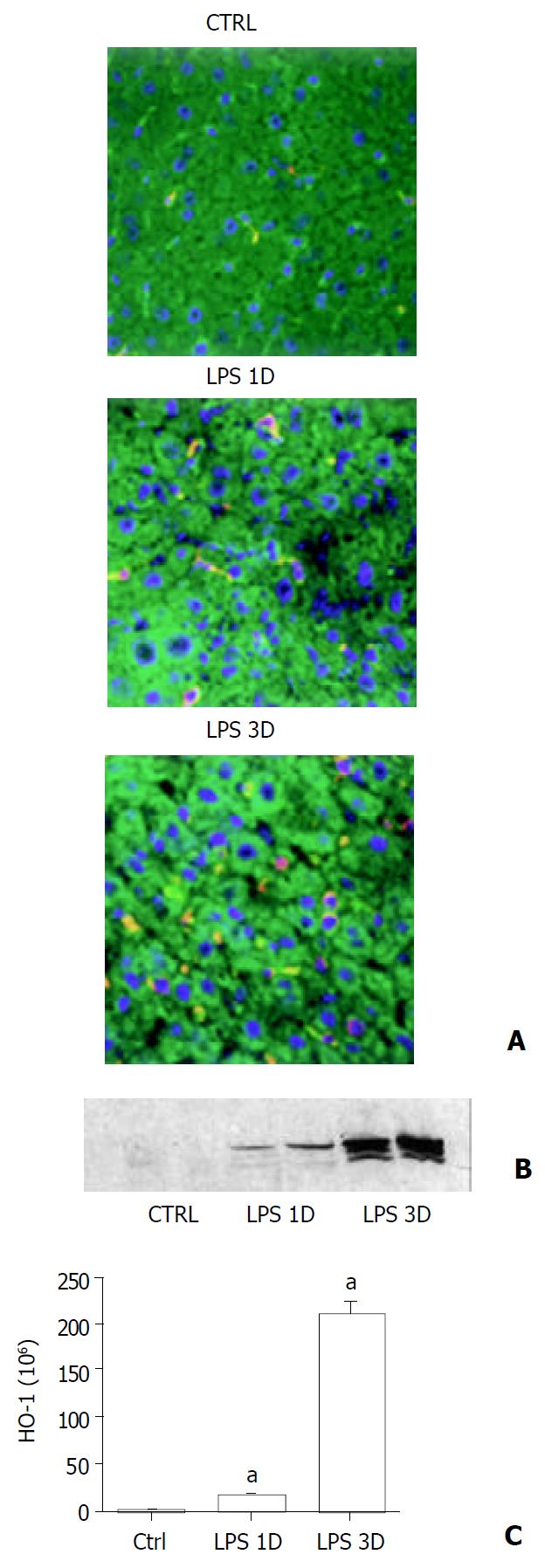
Figure 1 Liver HO-1 expression in wild type mice.
A: Immun-ofluorescent detection of HO-1 in liver. After different doses of LPS or sham treatment, liver HO-1 expression of wild type (C57) mice were visualized by immunofluorescent staining with a specific rabbit polyclonal antibody against HO-1 fol-lowed by indocarbocyanine (Cy3)-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG (red). The cell surface was counterstained with fluorescein-con-jugated wheat germ agglutinin (green), and the nucleus was counterstained with bis-benzimide (blue). HO-1 was present in liver of sham-treated animals (Ctrl). A single dose of LPS treatment increased liver HO-1 expression (LPS 1D). Furthermore, HO-1 expression was enhanced by three doses of LPS treatment (LPS 3D, magnification ×400). B: Immunoblotting detection of HO-1 in liver. C57 mice were treated with vehicle (Ctrl), single dose of LPS (LPS 1D) and three doses of LPS (LPS 3D). Liver tissue was homogenized, and immunoblotting analysis was performed. HO-1 protein was detected by immunoblotting with polyclonal rabbit antibody against HO-1. Data were representative of at least 2 experiments. C: Im-munofluorescent staining to quantitate HO-1 expression. Liver HO-1 expression was determined by immunofluorescent staining. Integrated intensity of HO-1 positive signal was masked and quantified by using Slidebook software (I. I. I. Inc., Denver, CO). aP < 0.05 vs. sham.
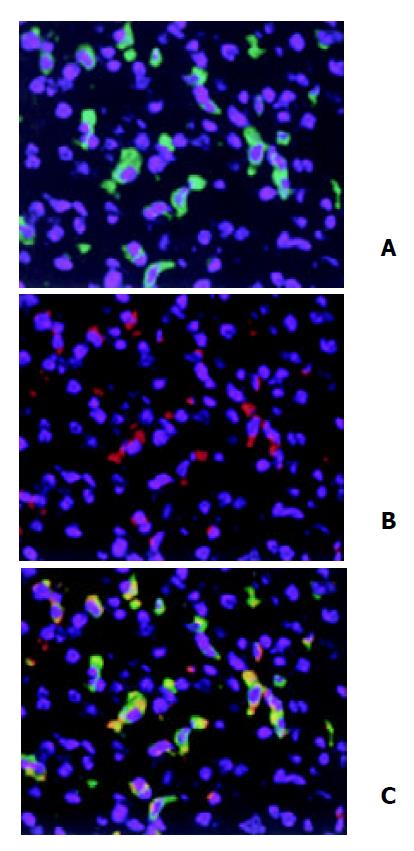
Figure 2 Double immunofluorescent staining of HO-1 local-ization in liver.
After three doses of LPS treatment, HO-1 and CD68 in liver tissue were detected by double immunofluores-cent staining with polyclonal rabbit antibody against HO-1 followed by FITC-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG (green) and mono-clonal rat antibody against mouse CD68 followed by Cy3-con-jugated anti-rat IgG (red). Cell nuclei were counterstained with bis-benzimide (blue). A: HO-1; B: Macrophages (Kupffer cells); C: HO-1 + Macrophages. magnification × 400.
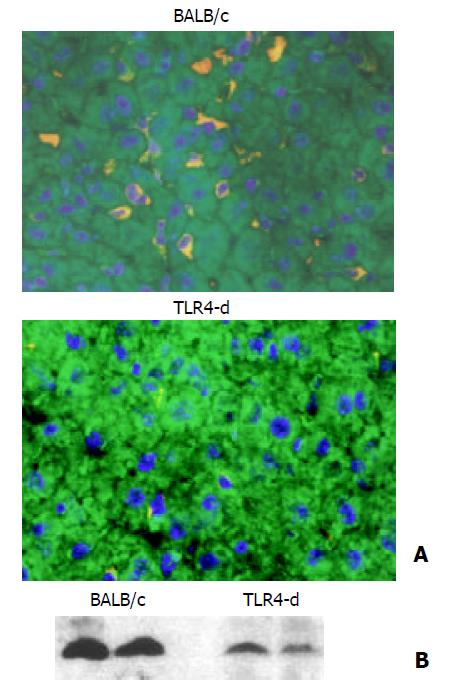
Figure 3 Effect of TLR4 mutation on liver HO-1 expression.
A: Immunofluorescent detection of HO-1 in liver. After three doses of LPS treatment, liver HO-1 expression was visualized by immunofluorescent staining with a specific rabbit polyclonal antibody against HO-1, followed by indocarbocyanine (Cy3)-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG (red). The cell surface was counter-stained with fluorescein-conjugated wheat germ agglutinin (green), and the nucleus was counterstained with bis-benzimide (blue). Liver HO-1 expression was abrogated in TLR4 mutated mice following LPS, but neither was influenced in BALB/c (control) mice (magnification ×400). B: Immunoblotting detection of HO-1 in liver. BALB/c and TLR4 mutated mice were treated with three doses of LPS. Liver tissue was homogenized, and immunoblotting analysis was performed. HO-1 protein was detected by immunoblotting with polyclonal rabbit antibody against HO-1. Data were repre-sentative of at least 2 experiments.
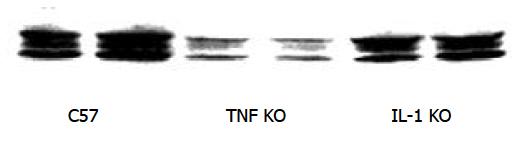
Figure 4 Effect of TNF KO and IL-1 KO on liver HO-1 expression.
Immunoblotting detection of HO-1 in liver. C57, TNF KO and IL-1 KO mice were treated with three doses of LPS. Liver tissue was homogenized, and immunoblotting analysis was performed. HO-1 protein was detected by immunoblotting with polyclonal rabbit antibody against HO-1. Data were representative of at least 2 experiments.
- Citation: Song Y, Shi Y, Ao LH, Harken AH, Meng XZ. TLR4 mediates LPS-induced HO-1 expression in mouse liver: Role of TNF-α and IL-1β. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(8): 1799-1803
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i8/1799.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i8.1799