Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 15, 2003; 9(7): 1629-1632
Published online Jul 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i7.1629
Published online Jul 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i7.1629
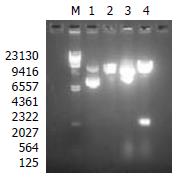
Figure 1 Restriction endonuclease enzyme analysis for recombinant bacmid.
Lane M. (/HindIII standard DNA molecular weight marker, Lane 1. pFastBacHTc plasmid, Lane 2. pFastBacHTc plasmid digested with HindIII and EcoRI, Lane 3. pFBCNS3N plasmid, Lane 4. pFBCNS3N plasmid digested with HindIII and EcoRI.
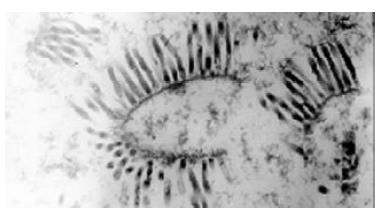
Figure 2 Recombinant bacoluvirus in insect cells under transmission electron microscope (× 36000).
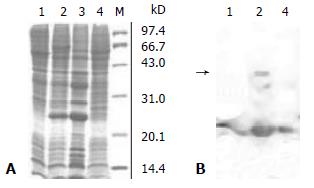
Figure 3 SDS-PAGE analysis (3A) and Western blotting analysis (3B) for the recombinant HCV serine proteinase expressed in insect cells.
3A. lane 1. untransfected Sf9 cells, lane 2. Sf9 cells transfected with rvBacNS3N, lane 3. the pellet of the cell lysate transfected with rvBacNS3N, lane 4. the supernatant of the cell lysate transfected with rvBacNS3N, Lane M. low molecular weight markers. 3B lanes 1, 2, 4 corresponded to Figure 3A.
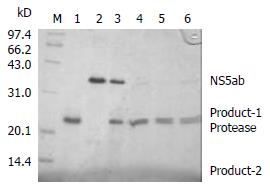
Figure 4 In vitro trans-cleavage at the NS5A/5B site of the recombinant HCV serine proteinase.
Lane M. low molecular weight markers, lane 1. the purified HCV serine proteinase, lane 2. the substrate HCV NS5ab protetin, lanes 3-6. cleavage reaction after 0, 10, 20 and 30 min.
-
Citation: Hou LH, Du GX, Guan RB, Tong YG, Wang HT.
In vitro assay for HCV serine proteinase expressed in insect cells. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(7): 1629-1632 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i7/1629.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i7.1629