Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 15, 2003; 9(12): 2805-2808
Published online Dec 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i12.2805
Published online Dec 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i12.2805
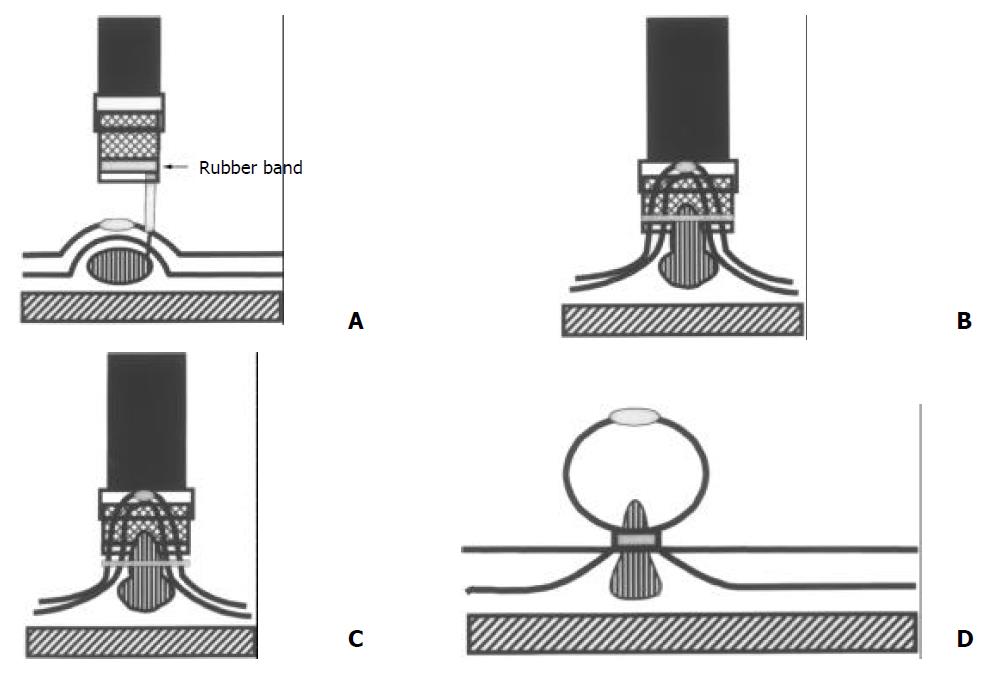
Figure 1 A: One to 4 ml of distilled water was injected locally into the submucosa adjacent to the polyp to lift the lesion from the muscle layer.
B: The raised lesion was aspirated into the hood. C: The polyp was ligated by a rubber band after the air was pumped through the air feeding tube. D: The pneumoactivated EVL device set was removed.
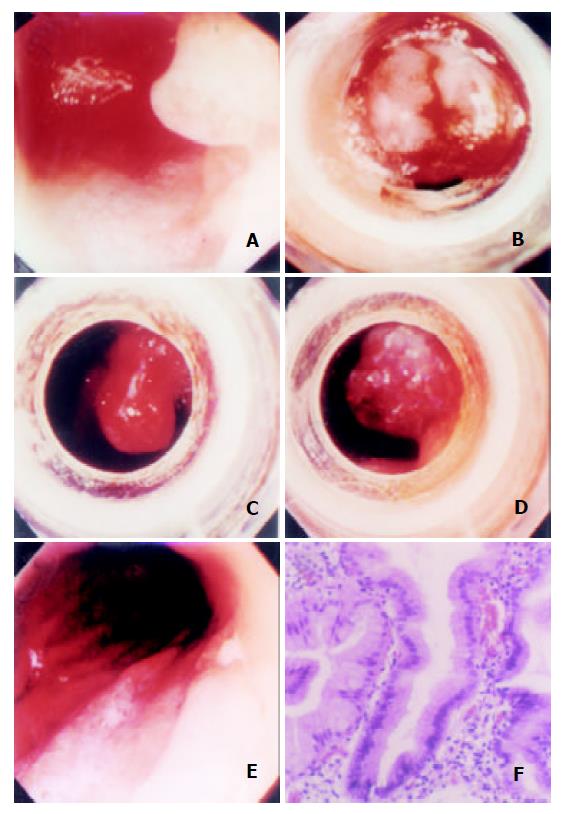
Figure 2 EBL for a hyperplastic polyp.
A: A polyp over the posterior wall of corpus. B: The polyp was aspirated into the hood and ligated with a rubber band after local injection of distilled water into the submucosa. C: The polyp congested immediately after ligation. D: The polyp developed cyanotic change about 4 minutes later. E: An artificial ulcer presented at the previous ligation site. F: Pathological examination of the strangulated polyp revealed both foveolar hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa and severe venous congestion in the lamina propria.
- Citation: Lo CC, Hsu PI, Lo GH, Tseng HH, Chen HC, Hsu PN, Lin CK, Chan HH, Tsai WL, Chen WC, Wang EM, Lai KH. Endoscopic banding ligation can effectively resect hyperplastic polyps of the stomach. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(12): 2805-2808
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i12/2805.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i12.2805