Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 15, 2003; 9(12): 2720-2725
Published online Dec 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i12.2720
Published online Dec 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i12.2720
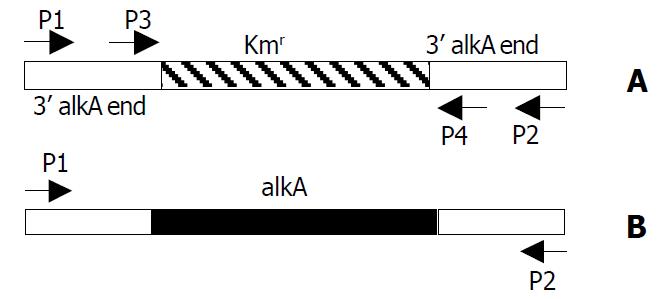
Figure 1 Location of primers P1, P2, P3 and P4 in PCR prod-ucts of alkA and 028pKm.
A: 028pKm (about 1.4 kb); B: alkA (about 1.7 kb).
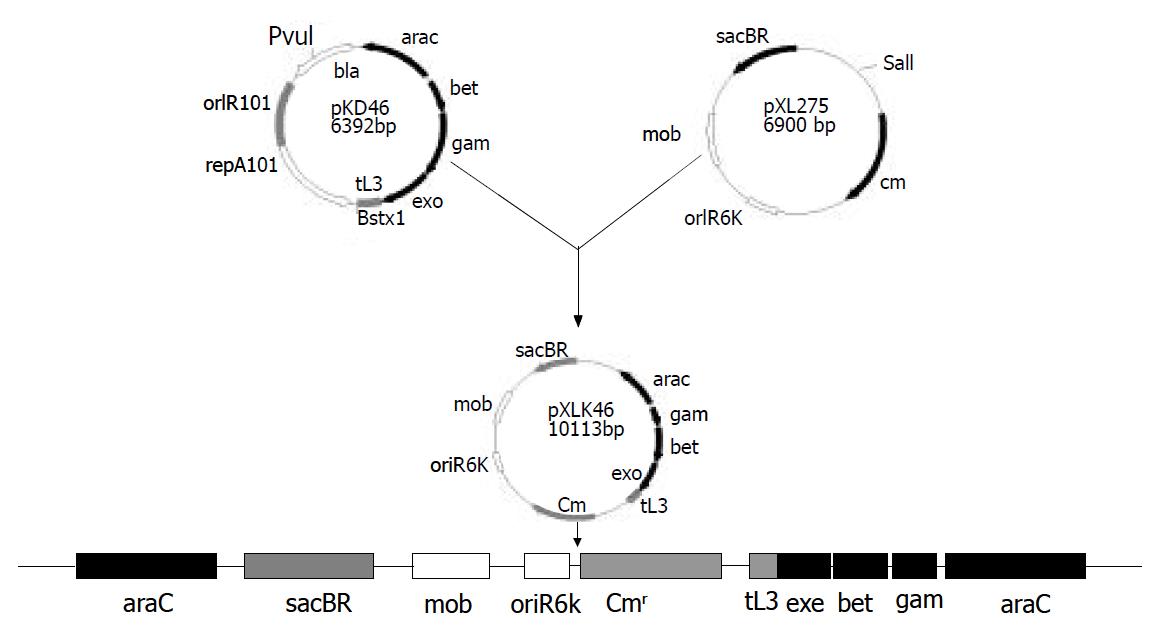
Figure 2 Construction and chromosomal integration of pXLkd46 plasmid.
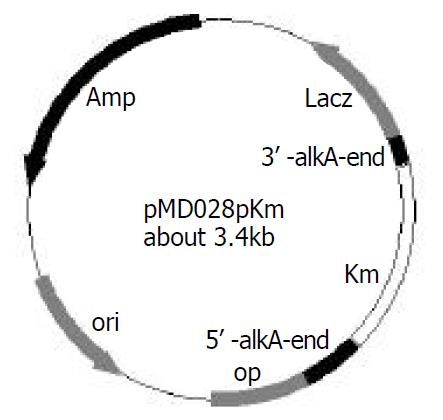
Figure 3 Construction of recombinant plasmid pMD028pkm.
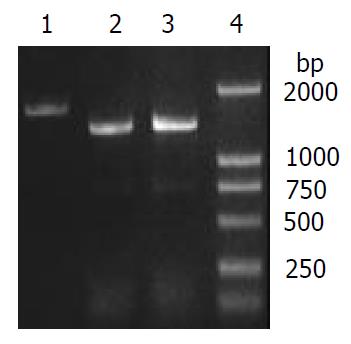
Figure 4 Verification of alkA gene deletion of 2457T028D mutant by PCR.
1: alkA PCR product (amplified from 2457T05), 2: 028pKm PCR product (amplified from 2457T028D), 3: 028Kkm PCR product (amplified from pMD028pKm), 4: DL2000 Marker.
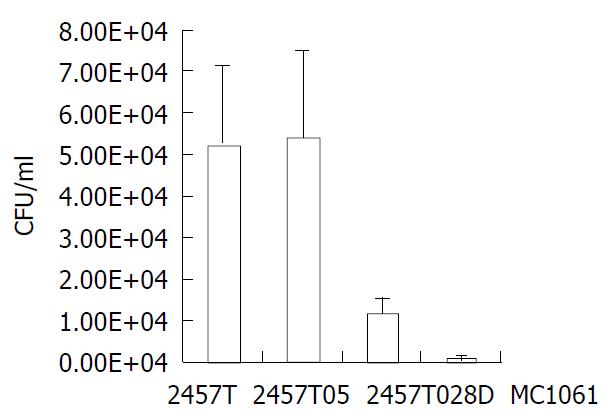
Figure 5 Comparison of HeLa cells infected by 2457T, 2457T05, 2457T028D and MC1061.
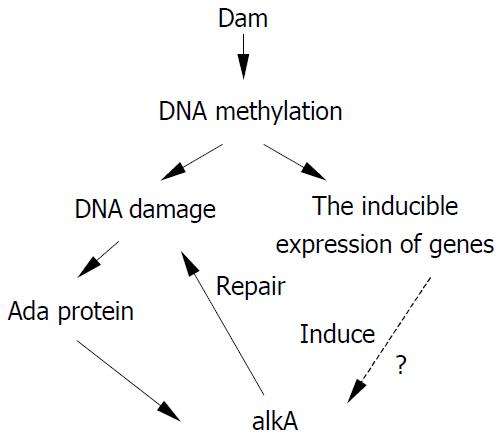
Figure 6 Hypothesis illustrating the relationship between alkA and damage of DNA methylation.
-
Citation: Shi ZX, Wang HL, Hu K, Feng EL, Yao X, Su GF, Huang PT, Huang LY. Identification of
alkA gene related to virulence ofShigella flexneri 2a by mutational analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(12): 2720-2725 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i12/2720.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i12.2720